- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
April 27, 2024 Current Affairs
World Trade Organization (WTO) is celebrating 30 years of the Marrakesh Agreement.
Marrakesh Agreement:
- The Marrakesh Agreement is the foundational treaty of the World Trade Organization (WTO), which was signed by 123 countries in Marrakesh, Morocco, in 1994.
- This agreement succeeded the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). It significantly changed how international trade rules and organizations were managed.
Objectives of Marrakesh Agreement:
- One key objective is to reduce trade barriers to boost economic growth.
- It aims to promote fair competition on an international scale.
- The agreement seeks to ensure full employment and increase effective demand across the globe.
- Another goal is to expand the production and trade of goods and services.
- It focuses on optimizing the use of world resources to foster sustainable growth.
Key Features of Marrakesh Agreement:
- The agreement established the World Trade Organization (WTO) as the global authority on trade rules.
- It expanded trade regulations to include not just goods but also services and intellectual property, under the General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) and the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- The Dispute Settlement Understanding (DSU) was instituted to resolve trade disputes legally.
- The Trade Policy Review Mechanism was introduced to enhance transparency and ensure compliance in trade policies.
- The WTO was structured with governance bodies like the Ministerial Conference and the General Council to oversee these regulations.
UNCTAD marks 60th anniversary with rebranded as UN Trade and Development.
UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development):
- The UNCTAD, short for United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, was established in 1964. It was set up as a permanent intergovernmental body by the United Nations General Assembly.
- Its main goal is to assist developing countries, especially those that are least developed or transitioning, to effectively integrate into the global economy.
Membership:
- UNCTAD has 195 member nations, including India.
Headquarters:
- The headquarters of UNCTAD are in Geneva, Switzerland.
Missions of UNCTAD:
- UNCTAD helps countries explore options to tackle large-scale development challenges.
- It supports efforts to diversify economies and reduce reliance on commodities.
- The organization aims to limit exposure to financial volatility.
- UNCTAD promotes a global partnership for development and seeks to improve coherence in global economic policymaking.
- It ensures that all countries reap the benefits of development gains linked to trade.
Objectives of UNCTAD:
- Diversify economic activities to minimize dependence on commodities.
- Promote global partnerships and coherence in economic policy-making.
- Ensure that all countries benefit from trade-related development gains.
Structure of UNCTAD:
- The highest policy-making body of UNCTAD is the Conference, which meets every four years to establish policies and create work programs.
Functions of UNCTAD:
- The Trade and Development Board acts as the executive body, managing operations when the Conference is not in session.
- The UNCTAD Secretariat, a part of the UN Secretariat, carries out policy analysis, monitors and implements decisions, and facilitates technical cooperation and information exchanges.
Key Activities of UNCTAD:
- UNCTAD conducts economic and trade analysis and facilitates consensus-building.
- It offers technical assistance to make use of trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
Reports of UNCTAD:
- The organization publishes important reports such as the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and the Least Developed Countries Report.
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) was granted ‘Navratna’ status by the Department of Public Enterprises.
- Comparing year-on-year figures, IREDA witnessed a 32% rise in net profit, while it remained consistent quarter-on-quarter at ₹337 crore.
Criteria for Classification of Navratna Status:
- To qualify for Navratna status, a company must first attain the Miniratna category-I designation and be included in Schedule A of Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs).
- For a company to achieve Navratna status, it must report a net profit of more than Rs 5,000 crore for three consecutive years, and maintain an average annual turnover of Rs 25,000 crore for three years, or have an annual average net worth of over Rs 15,000 crore for three years.
- CPSEs must have achieved an ‘excellent’ or ‘very good’ rating in the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) for three out of the last five years.
- Also, eligible CPSEs must attain a composite score of 60 or above in six selected performance indicators.
Benefits Avail:
- The Indian government granted Navratna status to premier public sector undertakings (PSUs), empowering them to execute significant investments of up to ₹1,000 crore without requiring approval from the central authority.
- These firms are permitted to allocate up to 30% of their net worth annually, provided it remains under ₹1,000 crore.
- They have the option to participate in joint ventures, forge partnerships, and set up overseas subsidiaries.
- The status gives the Board of Directors of these CPSEs the power to allow mergers and acquisitions in India and abroad.
- However, they need approval from the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) to make investments abroad.
Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA):
- Under the Aegis of: IREDA is a non-banking financial institution under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, established in 1987.
Evolution:
- 1987: It was established and later to be classified under the “Public Financial Institution” under section 4 ‘A’ of the Companies Act, 1956, and is officially registered as a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- 2015: The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) acknowledged IREDA’s contributions by conferring upon it the status of Mini Ratna (Category-I).
- 2023: The MNRE, has upgraded IREDA from Schedule B to Schedule A category Central Public Sector Enterprises. This paved the way for IREDA to attain Navratna status, granting it greater financial autonomy.
- 2024: The Department of Public Enterprises granted ‘Navratna’ status to IREDA.
- Mandate: IREDA is engaged in promoting, developing and extending financial assistance for setting up projects related to new and renewable sources of energy.
- It offers financial assistance to projects that produce electricity using fresh and sustainable sources. The government holds a 75% ownership stake in the company.
Some Remarkable Projects of IREDA:
- Green Rooftops Scheme, World’s First Floating Solar PV Project, Financing Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS).
Fiat to monitor use of liquid nitrogen in food items.
Liquid Nitrogen:
- It is an inert, colorless, odorless, noncorrosive, nonflammable, and extremely cold element.
- It is a cryogenic liquid (Cryogenic liquids are liquefied gases that have a normal boiling point below –130°F (–90°C).
- Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of –320°F (–196°C).
Health impacts:
- Liquid nitrogen can scorch the organ or part of the body it contacts, making it appear like frost bites.
- It can damage the lips, tongue, throat, lungs, and stomach. It may cause lesions or burn tissues.
- If it reaches the stomach, the organ could get perforated. In the lungs, it could produce CO2 and the person could become unconscious.
Applications:
- It is used to cool and freeze food rapidly.
- In food production and industrial processes, a cooling tray filled with liquid nitrogen is used to rapidly cool materials or equipment by immersing the product in nitrogen.
- In the wellness and sports industry, cryosaunas with liquid nitrogen vapor are used for cryotherapy.
- Liquid nitrogen test chambers are used in technology and material sciences to test the performance and durability of materials and devices at extremely low temperatures.
Cryosurgery:
Cryosurgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves the use of extreme cold to destroy or remove abnormal tissues, such as tumors or warts. The procedure involves applying a freezing agent, such as liquid nitrogen or argon gas, directly onto the targeted area.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently issued the draft regulatory framework for loan products aggregated by lending service providers to ensure transparency for borrowers.
Lending Service Providers (LSPs):
- LSPs are engaged by the Regulated Entities (REs) (banks or NBFCs) to carry out some functions of RE in connection with lenders’ functions on digital platforms.
- The LSPs generally, under an outsourcing arrangement, offer their services to REs for a fee or commission.
- RBI defines an LSP as an agent of an RE that carries out one or more functions of the lender, including customer acquisition, underwriting support, pricing support, disbursement, servicing, monitoring, collection, and loan recovery on behalf of the RE.
- In simple terms, LSPs are loan aggregators which provide loans from their partner REs.
- In some cases, a RE can also act as an LSP.
- They are technology-centric entities which have the client reach and are thus capable of offering a marketplace for both lenders and borrowers.
- LSPs entail aggregation of loan offers from multiple lenders on an electronic platform, which enables the borrowers to compare and choose the best available option to avail a loan from one of the available lenders.
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Defence Ministers’ meeting took place in Astana, Kazakhstan.
- Agreements and Declarations: During the meeting, a protocol was signed by the Defence Ministers of all SCO Member States.
- A Joint Communique was issued after the meeting, in which the SCO Defence Ministers agreed to develop the idea of ‘One Earth, One Family, One Future’, which is rooted in the ancient Indian philosophy of ‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’.
- India’s Commitment to Peace and Counterterrorism: The Defence Secretary of India reiterated India’s commitment towards maintaining peace, stability and security in the SCO region.
- He emphasized the need to adopt a zero-tolerance approach towards terrorism in all its forms for prosperity and development of the SCO Member States.
- He mentioned India’s long-standing proposal of Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the United Nations.
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO):
- The SCO is an eight-member multilateral organization, established on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai, China by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
- Origin: Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Shanghai Five (1996) emerged from a series of border demarcation and demilitarization talks which the four former Soviet republics held with China to ensure stability along the borders.
- Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organization in 2001, the Shanghai Five was renamed the SCO.
- Official Languages: Russian and Chinese
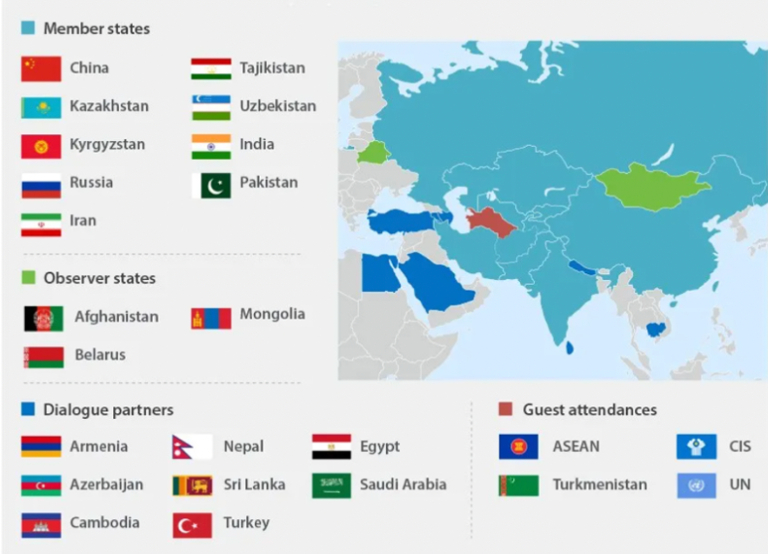
- Member states: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan and Iran.
- Observer States: Afghanistan, Belarus, Mongolia
- Coverage: The SCO’s geographic scope covers 60 percent of Eurasia and represents 40 percent of the world’s population, with a combined GDP accounting for 20 percent of the global economy.
- Chairmanship: The Chairmanship of SCO is by rotation for a year by Member States.
Objectives:
- To strengthen mutual trust, friendly relations and cooperation among young people of SCO member States.
- It seeks to counter western influence in Eurasia.
- India and SCO:
- India was granted Observer status at the July 2005 Astana Summit, and subsequently participated in all SCO forums open to Observers.
- India and Pakistan became members at the Astana Summit, in 2017.
Organizational Structure:
- Heads of State Council: The supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organizations, and considers international issues.
- Heads of Government Council: Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs: Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
- Secretariat: The Secretariat of the SCO serves to implement organizational decisions and decrees, documents (such as declarations and agendas).









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies