- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
August 03, 2024 Current affairs
Uttar Pradesh Nazul Properties (Management and Utilization for Public Purposes) Bill
- The Uttar Pradesh Nazul Property Bill, 2024, aims to regulate Nazul land by preventing its conversion into private ownership.
- Under this Bill, court proceedings or applications for transferring Nazul land to private individuals or institutions will be cancelled and rejected, ensuring these lands remain under government control.
- If payments were made anticipating ownership changes, the Bill mandates refunds with interest calculated at the State Bank of India’s Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR) from the deposit date.
- Additionally, the Bill allows the government to extend lease for current leaseholders in good standing, who regularly pay rent and comply with lease terms. This ensures compliant leaseholders can continue using the land while maintaining it as government property.
- The Bill aims to streamline Nazul land management and prevent unauthorised privatisation.
Nazul Land
- Nazul land is owned by the government but is most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, generally between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it, taking back Nazul land.
- In almost all major cities in India, Nazul land has been allotted to different entities for a variety of different purposes.
Governance of Nazul Land
- For Adjudication: While several states have brought in government orders for the purpose of framing rules for Nazul land, The Nazul Lands (Transfer) Rules, 1956 is the law mostly used for Nazul land adjudication.
- Lease Renewal:By submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority. The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazul land.
Eco sensitive areas in Western Ghats
Centre reissues draft notification on Eco sensitive areas in Western Ghats.
Main highlights
- The draft notification proposes to declare 9,993.7 sq. km in Kerala, including 13 villages in two talukas of the landslide-hit district, ecologically sensitive.
- Overall, the notification includes 449 sq. km in Gujarat, 17,340 sq. km in Maharashtra, 1,461 sq. km in Goa, 20,668 sq. km in Karnataka, 6,914 sq. km in Tamil Nadu, and 9,993.7 sq. km in Kerala in the proposed ESA.
- The draft notification suggests a complete ban on mining, quarrying, and sand mining, with existing mines to be phased out within five years “from the date of issue of the final notification or on the expiry of the existing mining lease, whichever is earlier”.
- It also prohibits new thermal power projects. Existing projects can continue to operate, but expansion is not allowed.
- Large-scale construction projects and townships are also prohibited, except for repairing and renovating existing buildings.
Eco-Sensitive Areas (ESAs)
- Eco-Sensitive Areas (ESAs) are regions that require special protection because of their ecological significance.
- The purpose of designating these areas is to conserve biodiversity, protect environmental values, and regulate activities to prevent ecological damage.
- Western Ghats: Spanning six states in India: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, is an important example of ESA, due to its rich biodiversity, unique ecosystems, and the presence of numerous endemic species.
Related committees
Gadgil Committee (Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel - WGEEP)
- Established: March 2010
Key Recommendations:
- Division of the Western Ghats into Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ1, ESZ2, ESZ3) with varying levels of restrictions.
Prohibited Activities: No mining, thermal power plants, or large-scale industrial activities in ESZ1.
Kasturirangan Committee (High-Level Working Group on Western Ghats)
- Established: August 2012
Key Recommendations:
- Identification of 37% of the Western Ghats as Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA), divided into natural and cultural landscapes.
Prohibited Activities: Ban on mining, quarrying, and sand mining in the ESA.
- Emphasis on balancing ecological conservation with sustainable development.
Axiom-4 mission
India selects 2 crew members for Axiom-4 mission to ISS.
Axiom-4 Mission:
- Axiom Mission 4 (or Ax-4) is a private spaceflight to the International Space Station.
- It is operated by Axiom Space and uses a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft.
- The flight is in collaboration with NASAand will be the fourth flight of Axiom Space after Axiom Mission 1, Axiom Mission 2 and Axiom Mission 3.
- Scheduled to launch in 2024, Axiom-4 will continue the company''s pioneering efforts to establish a sustainable human presence in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Key Features
Spacecraft and Crew:
- The mission will use a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, launched atop a Falcon 9 rocket.
- The crew will consist of professional astronauts and private individuals, including researchers and potentially tourists, who have undergone rigorous training for the mission.
Duration and Activities:
- Axiom-4 is expected to be a short-duration mission, lasting approximately 14 days.
- During their time aboard the International Space Station (ISS), the crew will conduct scientific experiments, perform technology demonstrations, and engage in educational outreach.
Commercial Space Station Development:
- Axiom Space''s long-term vision includes building the world''s first commercial space station.
- The Axiom-4 mission is part of the company''s broader plan to eventually transition from the ISS to their own independent orbital outpost.
The Significance of Axiom-4
- The Axiom-4 mission is not just a technical achievement; it represents a broader vision of international cooperation and the democratization of space access.
- By participating in this mission, India is positioning itself as a significant player in the global space community. The experience and knowledge gained from this mission will be invaluable for future space endeavors and collaborations.
International Space Station (ISS)
|
Asiatic lions
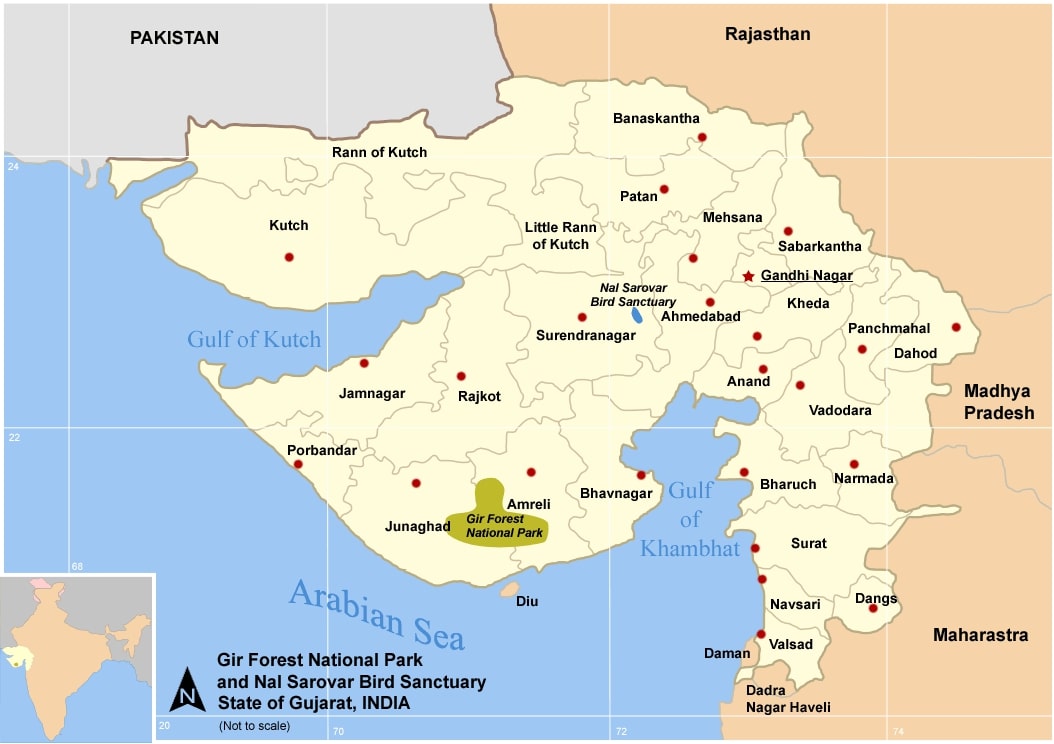
- Asiatic lion (Panthera Leo persica) is a sub-species of lion that is found only in the Gir Forest National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary in Gujarat, India.
- The Asiatic lion is one of the most endangered big cats in the world, with a population of less than 700 individuals in the wild.
- The Asiatic lion is found only in the Gir Forest National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary, which is a protected area covering an area of about 1412 sq. km in Gujarat.
- The Asiatic lion is slightly smaller than its African counterpart, with a distinctive fold of skin on its belly and a shorter, less bushy mane.
- Food Habits:Asiatic Lions are mainly dependent on Chital, Nilgai, Sambhar, Buffaloes and Goats for food. Sometimes they hunt smaller animals and if the need arises they kill the livestock or camel found in the neighbouring areas of Gir National Park.
Threats:
- Poaching
- Habitat fragmentation
- Lions die by falling into the unguarded wells around the Gir Protected Area.
- The threat of genetic inbreeding arises from a single population in one place.
Conservation Initiatives
- WWF supported barricading of 180 wells with local partners and Gujarat Forest Department.
- This initiative led to doubling the subsidy by the Gujarat government, and many farmers barricaded the wells with government support.
- To strengthen the efforts of Gir Protected Area towards managing conflict and poaching, WWF provided need-based support.
- WWF-India conducted a study to assess habitat change over a period of 20 years.
Gir National Park
- Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Junagadh districtof Gujarat.
- It was declared as a sanctuary in 1965 and a national park in 1975.
- The Gir Forests is the largest compact track of dry deciduous forests in the semi-arid western part of India.
- Gir is often linked with"Maldharis" (a traditional pastoral people) who have survived through the ages by having a symbiotic relationship with the lion.
Ransomware Attack
The attack has likely impacted 150-200 cooperative banks and RRBs.
Concept
- Ransomware is a type of malicious software (malware) that threatens to publish or blocks access to data or a computer system, usually by encrypting it, until the victim pays a ransom fee to the attacker.
- In many cases, the ransom demand comes with a deadline. If the victim doesn’t pay in time, the data is gone forever or the ransom increases.
- Users are shown instructions for how to pay a fee to get the decryption key. The costs can range from a few hundred dollars to thousands, payable to cybercriminals in Bitcoin.
Types of Ransomware:
- Encrypting Ransomware (Crypto Ransomware): Encrypts the victim''s data, demanding a ransom for the decryption key.
- Non-encrypting Ransomware (Screen-locking Ransomware): Locks the victim''s entire device, displaying a ransom demand on the screen.
Subcategories of Ransomware Include:
- Leakware or Doxware:Steals and threatens to publish sensitive data.
- Mobile Ransomware:Affects mobile devices, often using screen-lockers.
- Wipers:Threaten to destroy data, sometimes even if the ransom is paid.
- Scareware:Uses fear tactics to coerce payment, sometimes posing as legitimate alerts.
How to prevent ransomware
- Keep your operating system patched and up-to-date to ensure you have fewer vulnerabilities to exploit.
- Don’t install software or give it administrative privileges unless you know exactly what it is and what it does.
- Install antivirus software, which detects malicious programs like ransomware as they arrive, and whitelisting software, which prevents unauthorized applications from executing in the first place.
- And, of course, back up your files, frequently and automatically! That won’t stop a malware attack, but it can make the damage caused by one much less significant.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies