- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
August 11th 2024, Current Affairs
Neelakurinji that blooms once in 12 years included in Red List of threatened species
Neelakurinji (Strobilanthes kunthiana), has been included on the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) official Red List of threatened species. This is the first ever Global Red List assessment for this flagship species of the montane grasslands of southwest India.
Neelakurinji Flowers
- In Neelakurinji, ‘Neela’ means blue, and ‘Kurinji’refers to the flowers.
- At maturity, the light blue colour of the flower’s changes to purple bluish.
- The flowers give the‘Nilgiri Mountain Range’ its name.
- The plant is named after the famous Kunthi River which flows through Kerala’s Silent Valley National Park, where the plant occurs abundantly
- It usually grows at an elevation of 1,300-2,400m.
The Habitats of Neelakurinji
- The Neelakurinji is not limited to the Western Ghats but can also be found in the Eastern Ghats'' Shevroys, the Annamalai hills of Idukki district, Agali hills of Palakkad in Kerala, and Sandur hills of Bellary district in Karnataka. In 2021, Neelakurinji flowers were found blooming in the Biligiri Ranganathaswamy Temple (BRT) Tiger Reserve in the Chamarajanagar District of Karnataka.
The Conservation Efforts for Kurinji
- The Kurinjimala Sanctuary in the Vallavada and Kottakamboor villages of the Idukki district is dedicated to preserving the Kurinji plant. The sanctuary spans 32 square kilometres and conducts various campaigns and events to promote ecosystem conservation.
- The Kurinji Andavar Temple situated in Kodaikanal, Tamil Nadu, dedicated to God Murugan, also plays a crucial role in the conservation of these plants.
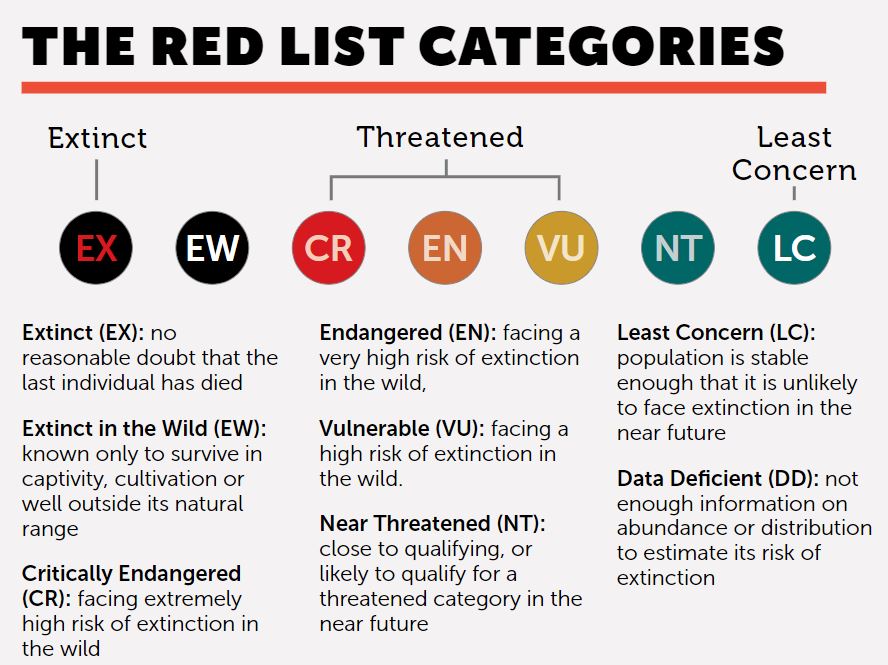
IUCN Red List
- The IUCN Red List is the foremost global resource for assessing the risk of extinction among animals, fungi, and plant species.
- Accessible to all, it serves as a crucial indicator of global biodiversity health, it offers comprehensive insights into species'' characteristics, threats, and conservation measures, playing a pivotal role in shaping informed conservation decisions and policies.
- The IUCN Red List Categories define the extinction risk of species assessed. Nine categories extend from NE (Not Evaluated) to EX (Extinct). Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) species are considered to be threatened with extinction.
PMAY-U 2.0 to give housing financiers more credit cushion
Key Highlights of PMAY-U 2.0:
- Increased Credit Risk Guarantee Fund: Corpus raised from ₹1,000 crore to ₹3,000 crore.
- Fund Management Transfer: Managed by National Credit Guarantee Company instead of National Housing Bank.
- Total Financial Assistance: ₹2.3 lakh crore subsidy over five years.
- Total Investment: ₹10 lakh crore.
- Target: Financial aid to 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families.
- Houses Sanctioned: 64 lakh houses approved so far.
- Construction Cost Sharing: Costs shared by Centre, State governments, UTs, urban local bodies, and beneficiaries.
- Technology and Innovation Sub-Mission (TISM): New initiative to be established under PMAY-U 2.0.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) falls under the Government’s mission - Housing for All by 2022 for urban housing being implemented by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- It makes home loans affordable for the urban poor by providing a subsidy on the Interest Rate of a home loan during repayment by way of EMI (Equated Monthly Instalments).
The Mission seeks to address the housing requirement of urban poor including slum dwellers through following programme verticals:
- Slum rehabilitation of Slum Dwellers with participation of private developers using land as a resource.
- Promotion of Affordable Housing for weaker section through credit linked subsidy.
- Affordable Housing in Partnership with Public & Private sectors.
- Subsidy for beneficiary-led individual house construction /enhancement.
Progress under PMAY-U Phase 1
- In the first phase of PMAY-U, 1.18 crore houses have been sanctioned, and more than 85.5 lakh houses have already been constructed and delivered to beneficiaries.
- The scheme has made significant strides in providing all-weather pucca houses to eligible candidates in urban areas.
PM Modi to release 109 climate resilient crop seeds
(Source: The Hindu)
Key Highlights:
- Release: PM Modi will release 109 new crop seed varieties developed by ICAR.
- Key Traits: High-yielding, climate-resilient, bio-fortified, and water-efficient.
- Crops: 34 field crops (e.g., cereals, millets, oilseeds) and 27 horticultural crops (e.g., fruits, vegetables, spices).
- Event: Takes place at India Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi.
- Objective: Direct benefits of agricultural research to farmers.
Climate Resilient Farming:
- It means the incorporation of adaptation, mitigation and other practices in agriculture which increases the capacity of the system to respond to various climate related disturbances by resisting damage and recovering quickly.
- It will essentially involve judicious and improved management of natural resources viz., land, water, soil and genetic resources through adoption of best practices.
Significance:
- Reduces hunger and poverty in the face of climate change for forthcoming generations.
- These practices can alter the current situation and sustain agricultural production from the local to the global level.

Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
- ICAR is an autonomous organisation under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Earlier Name: ICAR was formerly known as Imperial Council of Agricultural Research.
- Mandate:The ICAR has its headquarters in New Delhi. The Council is the apex body for coordinating, guiding and managing research and education in agriculture including horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences in the entire country.
The Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent returned to India after successfully participating in Exercise Udara Shakti 2024 in Malaysia’s Kuantan
- The joint air exercise was conducted in collaboration with the Royal Malaysian Air Force (RMAF) from 05 to 09 August 2024 at Kuantan, Malaysia.
About:
- The Indian Air Force participated in the air exercise with Su-30 MKI and C-17 aircraft while Malaysian Air Force will be flying Su 30 MKM aircraft.
- The four days of exercise witness the conduct of various aerial combat drills between the two Air Forces.
Background:
- The first bilateral Air Force exercise that staged frontline Sukhoi-30 combat aircraft was conducted in 2018.
- From 2008 to 2010, the Indian Air Force Training Team was deployed in Malaysia to give training to Malaysian pilots on the SU-30SKM aircraft.
Features of the Exercise Udara Shakti 2024
- The Exercise Udara Shakti 2024 was based on Training Exercisesand Subject Matter Expert Exchange concepts. The Training Exercises included air combat exercises involving the Su-30 planes of both countries.
- The Subject Matter Expert Exchange focused on sharing expertise, insights, and skills in aviation and engineering related to the Sukhoi-30 aircraft.
- Exercise Udara Shakti 2024 also featured the HOP Exercise, during which the pilots of both the Air Force flew and exchanged their Sukhoi fighter planes. The Indian pilot flew the Malaysian Su-30, while the Malaysian pilot flew the Indian SU-30MKI.
- The main goals of the HOP EX were to test fighter aircraft, exchange ideas and experiences regarding combat tactics, and explore differences in aircraft equipment functionality.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies