- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Daily Current Affairs | 1st June 2020
PM Modi wishes Kashmiri Pandits on Jyeshtha Ashtami
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has extended wishes to the Kashmiri Pandit community on the occasion of Jyeshtha Ashtami.
What is Jyeshtha Ashtami?
- Jyeshtha or Jyēṣṭha is a month of the Hindu calendar. In India’s national civil calendar, Jyestha is the third month of the year.
- Jyeshtha Ashtami is an auspicious day which is the eighth day of the bright half of Jyeshtha (May–June) month.
- Every year, the date varies depending upon the Hindu calendar.
- According to belief, the Goddess changes the colour of the spring’s waters.
- Devotees flock the Mata Kheer Bhawani Temple or Tulmula Mandir in Kashmir in huge numbers.
- On this auspicious day, a grand feast and fest is held every year at Mata Kheer Bhawani Temple in Kashmir (especially by Kashmiri Pandit community), also known as Tulmula. It is celebrated with full gusto and vigour, as it marks the pradurbhava of the Goddess Ragnya (Kheer Bhavani or Ragnya Bhavani Mata).
- There are separate shran or snan kunds for ladies and gents, wherein people take a bath or sprinkle the water over their face, hands and feet before paying homage to the residing Ragnya Bhawani Mata. It is considered to be auspicious, and many believe that by doing so the goddess takes away all their worries.
- Ritually no specific procedure is prescribed for the Puja at Kheer Bhavani. The Bhringish Samhita simply says that the Devi, whose mantra is of fifteen syllables, accepts offerings of milk, sugar candy and ghee only.
- This portal has been jointly developed by the Ministry of Electronics and IT and IT Industry. National e-Governance Division of Ministry of Electronics and IT and NASSCOM from the IT industry will jointly run this portal.
- This portal shall work as a one stop digital platform for AI related developments in India, sharing of resources such as articles, startups, investment funds in AI, resources, companies and educational institutions related to AI in India.
- The portal will also share documents, case studies, research reports etc. It has section about learning and new job roles related to AI.
- The National Programme is open to students of classes 8 – 12 from Central and State government-run schools (including KVS, NVS, JNV) from across the country – all 28 States and 8 Union Territories and aims to bring about a change in the thought process and create a bridge for the digital divide.
- The Program will be implemented in a phase-wise manner and in its first phase, each of the State Education Department will nominate 10 teachers as per the eligibility criteria. Teachers may also self nominate themselves by fulfilling the eligibility criteria.
- These teachers will be provided orientation sessions aimed to help them understand the premise and identify 25-50 potential students for the Program.
- The identified students will attend online training sessions on AI and understand how to identify social impact ideas/projects that may be created using AI and submit their ideas through a 60 seconds video explaining a proposed AI enabled solution.
- There are many benefits of the hub and spoke model, and it’s perhaps easiest to understand these by comparing the hub and spoke model to the model it was intended to replace: the point-to-point model. The exact opposite of the hub and spoke model, the point-to-point model has goods and services go directly from Point A to Point B without going to a centralised distribution hub.
- In the point-to-point model, transportation costs can actually be higher than in a hub and spoke model. This happens because more routes are created in a point-to-point model, whereas products can be grouped and efficiently shipped following set routes in a hub and spoke model.
- A hub and spoke model also makes it possible for transport drivers to travel shorter distances and stay in a more centralised area. That’s because drivers can switch at the hub. In a point-to-point system, there’s no company space for drivers to easily meet and switch.
- Madhya Pradesh has become the first state to devise such a work plan.
- The state plans to survey skilled workers who were employed at industries elsewhere, but have now returned.
- The attempt is to provide work to the maximum number of returned skilled workers.
- After such workers requiring employment are identified, the government will contact factory, workshop owners and contractors overseeing infrastructure projects such as road and bridge construction.
- Rozgar Setu will be a platform to connect them with those needing these skilled workers. The State government will act as a [bridge] between workers and employers so that both are benefited.
- This would fulfil the manpower requirement of industries as well as provide employment to workers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- A so-called “D10″ club of democratic partners, including G7 countries – UK, US, Italy, Germany, France, Japan and Canada – plus Australia, South Korea and India will aim to create alternative suppliers of 5G equipment and other technologies to avoid relying on China.
- It proposes that one of the options involves channelling investment into existing telecommunication within the 10 member countries.
- The regulator said adequate availability of numbering resources is threatened because of an increase in the range of services and massive growth in the number of connections, especially in the mobile segment.
- The ongoing plan implemented in 2003, was developed keeping in mind the projections till the year 2033. The total number of telephone subscribers in India stands at 1,177.02 million with a tele-density of 87.45% at the end of January 2020.
- As a result, we find ourselves in a situation where we need to review the utilisation of the numbering resources and make some policy decisions to ensure that adequate resources are available for sustainable growth of the telecommunication services.
- It is the independent regulator of the telecommunications business in India.
- It was established in 1997 by an Act of Parliament to regulate telecom services and tariffs in India.
- In January 2000, TRAI was amended to establish the Telecom Disputes Settlement Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) to take over the adjudicatory functions of the TRAI.
- The TDSAT was set up to resolve any dispute between a licensor and a licensee, between two or more service providers, between a service provider and a group of consumers. In addition, any direction, TRAI orders or decisions can be challenged by appealing to TDSAT.
- President Trump announced last month that he was going to halt US funding for the WHO unless it undertook “substantive improvements” within 30 days.
- The WHO’s Director-General, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, had promised a review of its response to the pandemic and defended its independence.
- Founded in 1948 and based in Geneva, Switzerland, it is the UN agency responsible for global public health.
- Has 194 member states, and aims to “promote health, keep the world safe and serve the vulnerable.
- Involved in vaccination campaigns, health emergencies and supporting countries in primary care.
- Funded by a combination of members’ fees based on wealth and population and voluntary contributions.
- These are the dues countries pay in order to be a member of the Organization.
- The amount each Member State must pay is calculated relative to the country’s wealth and population.
- These contributions have declined, and now account for less than one-fourth of its funding.
- These come from Member States (in addition to their assessed contribution) or from other partners (organisations & individuals)
- They can range from flexible to highly earmarked.
- Top funders include Bill and Melinda Gates (USD 367.7 million), GAVI Vaccine Alliance, World Bank, Rotary International and the European Commission.
- The researchers have explained that the antibody binds to a domain that is conserved in both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, explaining its ability to neutralise both viruses.
- This antibody can help develop antigen detection tests and serological assays.
- This antibody — either alone or in combination — offers the potential to prevent and/or treat COVID-19, and possibly also other future emerging diseases in humans caused by viruses from the Sarbecovirus subgenus.
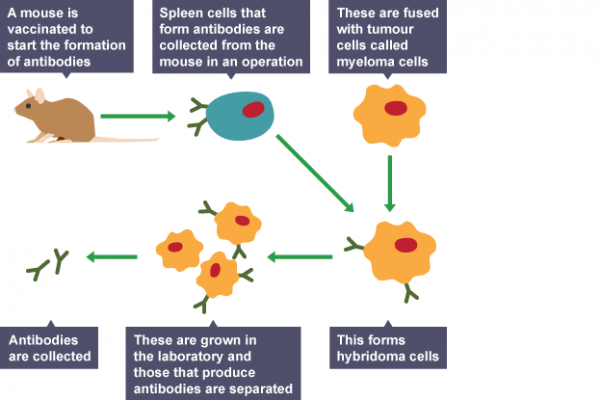
- An antigen is injected into a mouse
- The mouse naturally produces lymphocytes, which produce antibodies specific to the antigen
- Spleen cells which produce the lymphocytes are removed during a small operation
- The spleen cells are fused with human cancerous white blood cells called myeloma cellsto form hybridoma cells which divide indefinitely
- These hybridoma cells divide and produce millions of monoclonal antibodies specific to the original antigen
A mouse is injected with a vaccine containing an antigen to start the formation of antibodies
Uses of monoclonal antibodies Pregnancy test kits Pregnancy test kits use monoclonal antibodies. These have been designed to bind with a hormone called HCG which is found only in the urine of pregnant women. Monoclonal antibodies are attached to the end of a pregnancy test stick onto which a woman urinates. If she is pregnant, HCG will be present in her urine and will bind to the monoclonal antibodies on the test stick. This will cause a change in colour or pattern which will indicate pregnancy. These specific monoclonal antibodies in the pregnancy test will only bind with HCG. Pregnancy test sticks use monoclonal antibodies to tell if a woman is pregnant. Cancer diagnosis and treatment Cancerous cells have antigens. Monoclonal antibodies can be designed to bind specifically with these antigens. When injected into a person's body, the monoclonal antibodies will bind with these cancer cells and clump them together. This makes it easier to identify a cancerous tumour, which can then be treated or removed. Monoclonal antibodies have also been designed to treat cancer by:- carrying drugs that have been attached to them, to the tumour
- encouraging your immune systemto attack the cancer cells directly
- testing for pregnancy by detecting HCG hormones in urine
- testing for diseases such herpes and chlamydia, and HIV which can lead to the development of AIDS
- to treat conditions like cancer by carrying drugs directly to the tumour cells, and helping the immune system attack them
- monoclonal antibodies can be produced quickly despite the fact that it can be time consuming when they are made for the first time









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies