- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 18, 2021
SC NOD TO BULLOCK CART RACES IN MAHARASHTRA
Recently, the Supreme Court allowed Maharashtra to resume bullock cart races in Maharashtra that were prohibited since 2017.

 Genesis of the issue:
Genesis of the issue:
 Right to be forgotten
Right to be forgotten
 Highlights of order
Highlights of order

 Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021:
Objectives:
Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021:
Objectives:
 Highlights of demands:
Highlights of demands:
 Recently, National Cadet Corps (NCC) and National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding to reuse plastic wastes collected by NCC Cadets during Puneet Sagar Abhiyan.
Recently, National Cadet Corps (NCC) and National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding to reuse plastic wastes collected by NCC Cadets during Puneet Sagar Abhiyan.
 Killer Robots:
Killer Robots:
 What is Parvovirus?
What is Parvovirus?
 Pegasus
Pegasus
 Recently, The Prime minister of India receives Bhutan’s highest civilian award.
Recently, The Prime minister of India receives Bhutan’s highest civilian award.
- It is on the basis of the amendments made by Maharashtra to the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act and the rules made under it.

 Genesis of the issue:
Genesis of the issue:
- The Supreme Court had banned various animal sports in 2014 as they violated provisions of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act (PCA).
- The sport included post-harvest Jallikattu or bullfights in Tamil Nadu and bullock-cart racing in Maharashtra, Punjab and other states.
- It struck down Tamil Nadu Regulation of Jallikattu Act, 2009.
- It stated that Bulls cannot be used as performing animals, either for the Jallikattu events or bullock-cart races in the state of Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and elsewhere in the country.
- The racing was banned due to a petition filed by People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA).
- Tamil Nadu passed an amendment to the PCA Act on 2017 exempting jallikattu.
- Karnataka Assembly followed the suit and passed a similar amendment exempting 'kambala' (traditional buffalo racing) and bullock cart racing sports from the ambit of PCA Act.
- Maharashtra Assembly also amended the PCA Act to permit the bullock cart race.
- The PETA petition contends that the new laws of 2017 violate the five internationally recognized freedoms:
- freedom from hunger, malnutrition and thirst;
- freedom from fear and distress;
- freedom from physical and thermal discomfort;
- freedom from pain, injury and disease;
- freedom to express normal patterns of behaviour.
- Activities such as jallikattu and bullock cart races form part of the cultural heritage of people in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Maharashtra under Article 29 (1) of the Constitution.
- Article 29 (1) mandates that “any section of the citizens residing in the territory of India or any part thereof having a distinct language, script or culture of its own shall have the right to conserve the same”.
- It is a traditional rural bull-racing sport in Maharashtra.
- It popularly known as 'chakkadi' and 'shankar path'.
- A breed called Khilar is mainly used in the race.
- It is associated with Ganpati festival celebrated in the state and is seen as a status symbol and an integral part of the state's culture.
- It is a bull-taming sport played in Tamil Nadu as part of the Pongal harvest festival.
- It is also known as 'eruthazhuvuthal'.
- Here, a bull is released into a crowd of people, where people try to control the bull at the same time.
- 'Bos Indicus' breed of bulls is used specifically for the sport.
- Kambala is a buffalo race performed in a slushy paddy field.
- It is a popular traditional sport in Coastal regions of Karnataka.
- Usually, the landlords compete against each other in this annual event.
- A cockfight is a blood sport between two roosters, specially bred for the matches.
- Often a blade or knife is tied to their limbs to inflict injury on the opponent.
- There is evidence that cockfighting was a pastime in the Indus Valley Civilization.
- It is most commonly a gambling game where bets are placed on the winning rooster.
- It is common in the state of Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- It is organised during Bihu (harvest festival) in the Hayagriva-Madhava Temple in Hajo near Guwahati, Assam.
- Often bulbuls are fed intoxicants to make them aggressive.
- It is held typically during the Pushkar Camel fair in Rajasthan.
- It is a blood sport that pits two dogs kept in cages without food for days, against one another for entertainment.
- It is held in the outskirts of Delhi and is often accompanied with illegal gambling/ betting.
- In this, a trainer makes the monkey dance to entertain the people, and earns money.
- It is banned in India.
- Fox Darshan is a ritual more than a sport.
- A village in Periyakrishnapuram had a tradition of a fox once a year during the Pongal Festival.
- Villagers find a fox, bring it to village and everyone dances and seek blessings.
- However, this ritual was banned some time ago.
- It is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted in 1960.
- Aim: To prevent the infliction of unnecessary pain or suffering on animals and to amend the laws relating to the prevention of cruelty to animals
- It extends to the whole of India except the State of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Prevents unnecessary pain or suffering on animals.
- Enshrines provisions for establishing the Animal Welfare Board of India, its powers, functions, constitution, and term of the office of members of the Board.
- Enshrines the guidelines regarding the experimentation on animals for scientific purposes and empowers a committee to make rules with regards to such experiments.
- Restricts the exhibition and training of performing animals.
- The PCA Act, 1960 provisions empower law enforcement agencies, animal welfare workers, and citizens who care for animals to take action against the culprits.
- Section 11of the PCA Act, 1960 deals with various forms of cruelties and atrocities perpetrated on both, domesticated and wild animals.
- It has 16 sub-sections dealing with the different forms of cruelty, under which a person is liable for a fine of ten rupees, which may extend to fifty rupees.
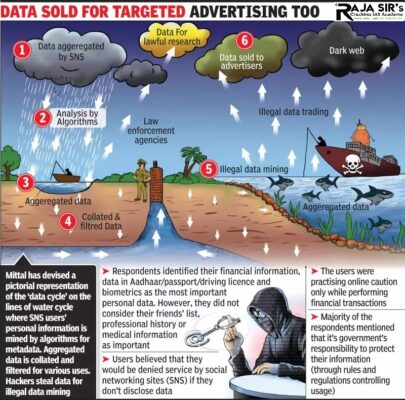
- Center said that Right to be forgotten is a new concept in India and its come under Right to privacy.
- Right to privacy is Fundamental right under article 21.

 Right to be forgotten
Right to be forgotten
- The right to be forgotten reflects the claim of an individual to have certain data deleted so that third persons can no longer trace them.
- Under the Right to be forgotten, users can de-link, limit, delete or correct the disclosure of their personal information held by data fiduciaries.
- The Right to be Forgotten falls under the purview of an individual’s right to privacy.
- In the landmark judgement of K.S. Puttaswamy vs union of India Supreme Court Stated that Right to privacy is a fundamental right under art 21.
- Privacy is, at its core, the right to be left alone.
- It is understood that society will not interfere in the choices made by the person so long as they do not cause harm to others.
- Right to privacy would mean that all persons have the right to be left alone by the state unless such intrusion is necessitated by a just, reasonable, and fair law.
- It may lead to violation of Art.19.
- Example: A person may want to de-link information about his criminal records and make it difficult for people to access certain journalistic reports when they google him.
- In the absence of specific legislation, RTBF emerges from the right to privacy under Article 21 and partly from the right to dignity under Article 14.
- Due to this its application is unclear because the RTBF will normally be claimed against a private party.
- This raises the question of whether fundamental rights which have traditionally only been enforceable vertically — against the State – can be enforced horizontally, that is, against private citizens.

 Highlights of order
Highlights of order
- A penalty of ₹200 crores on Amazon for failing to notify the details of its ‘combination’, as required in law.
- A separate penalty of ₹2 crores for suppressing the actual scope and purpose of the combination.
- Combination is a term used in competition law for acquisition, merger or amalgamation of two or more enterprises.
- In June 2019, the Competition Commission of India (CCI) accused Amazon of concealing facts and making false submissions when it sought approval for its investment to purchase a 49% stake in Future Group promoter firm Future Coupons Pvt Ltd.
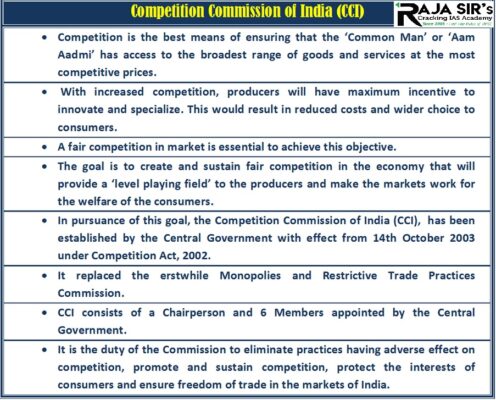
- It is the chief national competition regulator in India.
- It is a statutory body within the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- It was established in October 2003. It became fully functional in May 2009.
- It is responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002 in order to promote competition and prevent activities that have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in India.
- It looks into cases and investigate it if the same has negative impact on competition.
- CCI also approves combination under the act so that two merging entities do not overtake the market.

 Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021:
Objectives:
Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021:
Objectives:
- To fast-track research and patenting.
- To promote the cultivation of medicinal plants and ancient Indian medicine.
- Empower local communities to be able to utilise resources, particularly of medicinal value, such as seeds.
- Decriminalize certain provisions.
- Allow for foreign investment in research in biodiversity, including research, patent and commercial utilization, without compromising the national interest.
- Streamline the process of Patenting for Indian researchers to encourage patenting.
- The bill seeks to set up Regional Patenting centers be opened across the country.
- Exempt certain people from giving prior intimation to State Biodiversity Board for accessing biological resource from certain purposes. They Include:
- Registered AYUSH medical Practitioners
- People accessing codified traditional knowledge, cultivated medicinal plants and its products.
- People who are practicing indigenous medicine including Indian systems of medicine for sustenance and livelihood
- Exempting Indians cultivating medicinal plants and manufacturing products using codified traditional knowledge from payment of Access and benefit sharing.
- It prioritizes intellectual property and commercial trade at the expense of conserving biological resources.
- The Bill in the current form would pave the way for “bio piracy” and would mean AYUSH manufacturing companies would no longer need to take approvals.
- To provide for conservation of biological diversity, sustainable use of its components and fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the use of biological resources and knowledge.
- Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) is a 2010 supplementary agreement to the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- It is also known as ‘The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity’.
- Aim: Implementation of one of the three objectives of the CBD; i.e.,
- Fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources, thereby contributing to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
- It sets out obligations for its contracting parties to take measures in relation to access to genetic resources, benefit-sharing and compliance.
 Highlights of demands:
Highlights of demands:
- Ukraine and neighbouring nations should not be allowed to join NATO.
- It calls for no new military bases to be established in ex-Soviet countries.
- A ban on the deployment of U.S. and Russian warships and aircraft to areas from where they can strike each other's territory.
- NATO and Russia should work to “prevent incidents” in the Baltics and the Black Sea region.
- Telephone hotline should be established.
- It is an intergovernmental military alliance between European countries (28), North American countries (2), and Eurasian country.
- It is also called the North Atlantic Alliance.
- Formation- 1949
- Headquarters- Belgium
- Aim- to guarantee the freedom and security of its members through political and military means.
- Objective- To maintain the target defence spending of at least 2% of their GDP by 2024.
- It is a system of defence in which the member states agree to the mutual defence in response to an attack by a non-member external party.
- The Treaty of Dunkirk was signed by France and the United Kingdom as a Treaty of Alliance and Mutual Assistance in the attack by Germany or the Soviet Union in the aftermath of World War II.
- It is also referred as the Brussels Treaty Organization (BTO).
- It was created to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
- After the World War II, the relations between United States and USSR led to Cold War.
- USSR wanted to expand its territory with the help of communism and it led to the formation of NATO.
- As a result, North Atlantic Treaty was signed in 1949.
- It was a result of the talks for the military alliance.
- It included United States, Canada, Portugal, Italy, Norway, Denmark and Iceland.
- All agencies and organizations of NATO are integrated into the civilian administrative or military executive roles.
- The North Atlantic Council (NAC)
- It is the body which has effective governance authority and powers of decision in NATO.
- It consists of member states that are permanent representatives or representatives at higher level.
- The meetings are shared by the Security General.
- There is no voting or decision by majority.
- The Military Committee (MC)
- It is the body of NATO that is composed of member states' Chiefs of Defence (CHOD)
- It advises the North Atlantic Council (NAC) on military policy and strategy.
- The MC is led by chairman, who directs NATO's military operations.
- Allied Command Operations (ACO)
- It is the NATO command which is responsible for NATO operations
- Allied Command Transformation (ACT)
- It is responsible for transformation and training of NATO forces.
- India and Vietnam has historical roots in the common struggle for liberation from colonial rule and the national struggle for independence.
- First ever India-Vietnam Virtual Summit was co-chaired by Prime Minister of India and Prime Minister of Vietnam in December 2020.
- There are several bilateral mechanisms at different levels between India and Vietnam.
- The Joint Commission Meeting at the Foreign Ministers' level
- The Foreign Office Consultations
- Strategic Dialogue at Secretary-level
- During Financial Year (FY) April 2020 – March 2021.
- Bilateral trade between India and Vietnam reached US$ 11.12 billion
- With Indian exports to Vietnam amounting to US$ 4.99 billion
- Indian imports from Vietnam at US$ 6.12 billion.
- India has also been providing assistance to Vietnam within the ASEAN framework.
- Under the Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) framework, India has been taking up Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) in Vietnam for development of community infrastructure
- Both countries have facilitated simplified visa regime to promote bilateral tourism.
- Vietnam extended e-visa facilities to Indian citizens travelling to Vietnam.
- India has e-tourist visa arrangement for Vietnamese citizens since 2015.
- Vietnam has been a large recipient of training programmes under Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) programme.
- Indian Council of Cultural Relations has several annual scholarship programmes for Vietnam students.
- Indian Naval Ship INS Kiltan undertook a visit to Ho Chi Minh City to deliver flood relief materials for the people of Central Vietnam.
- In December 2020, the PASSEX Exercise was conducted with Vietnam People’s Navy and Indian navy.
 Recently, National Cadet Corps (NCC) and National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding to reuse plastic wastes collected by NCC Cadets during Puneet Sagar Abhiyan.
Recently, National Cadet Corps (NCC) and National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding to reuse plastic wastes collected by NCC Cadets during Puneet Sagar Abhiyan.
- Aim: To propagate the message of the Importance of clean seashores and beaches amongst the local population.
- Plastic wastes collected is planned to be handed over to NHAI which can use in road construction across the country.
 Killer Robots:
Killer Robots:
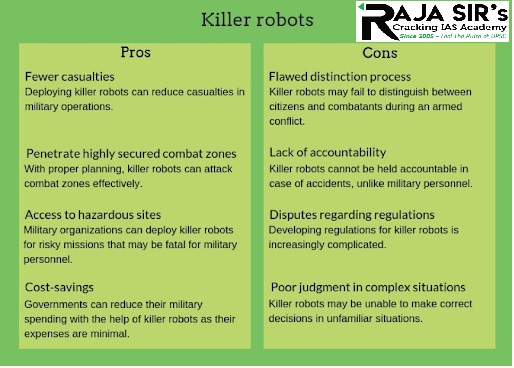
- They are widely considered to be weapons that make decisions with little or no human involvement.
- Rapid improvements in robotics, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and image recognition are making such armaments possible.
- It is a framework of rules that ban or restrict weapons considered to cause unnecessary, unjustifiable and indiscriminate suffering.
- It includes incendiary explosives, blinding lasers and booby traps that don’t distinguish between fighters and civilians.
- A total of50 States signed the Convention, which entered into force in
- The convention has no provisions for killer robots.
- Killer robots can fail in recognizing enemies.
- In this manner, they may violate the principle of distinction.
- The principle of distinction requires belligerents to distinguish between civilians and combatants during an armed conflict.
- If killer robots are deployed in areas where civilians are present, then the chances of civilians being attacked increase exponentially.
- Such incidents can be fatal for civilians and negatively affect reputation of the military.
- Killer robots cannot be held accountable in a manner similar to how military personnel can be held accountable.
- Also, it is increasingly difficult to determine whether a killer robot made a flawed decision due to bugs in the program or AI-based decision-making abilities.
- Deciding the most feasible approach for killer robot's regulations can be increasingly complicated.
- Training AI systems for scenarios without any historically documented data can be extremely complex.
- Robots may witness several new situations and make mistakes on-field, leading to dire consequences.
- Hence, killer robots may be unable to make correct decisions in unfamiliar situations.
- it is morally repugnant to assign lethal decision making to machines, regardless of technological sophistication.
- Such weapon systems raise ethical concerns for society about substituting human decisions about life and death with sensor, software and machine processes.
- A major advantage of deploying killer robots is that the number of casualties can be reduced significantly.
- Killer robots can help in dangerous missions, where there is a possibility of a high rate of casualties.
- Military organizations may also be able to get better results using killer robots as their attacks can be precise.
- The adoption of killer robots will enhance combat in highly secured zones.
- Military organizations can deploy killer robots in risky missions such as explosive ordnance disposal.
- They can be programmed to work efficiently in dangerous work sites.
- In radioactive areas, killer robots can be especially useful as they can work for longer hours compared to humans.
- Compared to the expenses of military personnel, the cost of killer robots can be lower.
- Killer robots would not require payroll and additional perks.
- The only expenses involved in killer robots would be their cost and maintenance charges.
- Hence, governments can significantly reduce their expenses and allocate saved funds to other domains such as education, social security, and housing.
 What is Parvovirus?
What is Parvovirus?
- It is a highly contagious viral disease that can be life-threatening in puppies and dogs.
- It affects the intestinal tract of canines with puppies being more susceptible.
- Symptoms: Diarrhoea, vomiting, drastic weight loss, dehydration and lethargy.
- The virus has reported a 90 percent mortality rate.
- How does the virus spread in dogs?
- Direct Transmission: The virus spreads through direct contact with an infected dog.
- Indirect Transmission: It occurs when a person has recently been exposed to an infected dog touches the puppy or when a puppy encounters a contaminated objectlike food collars and leashes.
 Pegasus
Pegasus
- Pegasus is spyware developed by the Israeli cyber arms firm NSO Group.
- It is a Trojan horse computer virus that can be sent “flying through the air” to infect cell phones.
- An investigation has found evidence of Pegasus being used by governments around the world for snooping on more than 50,000 phone numbers.
- The earliest version of Pegasus infected phones through what is called spear phishing text messages or emails that trick a target into clicking on a malicious link.
- In recent updates, Pegasus infections can be achieved through so-called “zero-click” attacks.
- It does not require any interaction from the phone’s owner to succeed.
- Once the spyware enters the device, it installs a module to track call logs, read messages, emails, calendars, internet history, and gather location to send the information to the attacker.
- The spyware hides intelligently using built-in self-destruct capabilities.
- If Pegasus fails to connect with its command-and-control server for more than 60 days, it self-destructs and removes all traces.
- If it detects that it was installed on the wrong device or sim card, it will again self-destruct.
- Malware is a code, typically delivered over a network, that infects, explores, steals, or conducts virtually any behavior an attacker wants.
- Types of Malwares: Adware, Botnets, Ransomware, Spyware, Trojans Malware.
- Provide remote control for an attacker to use an infected machine.
- Send spam from the infected machine to unsuspecting targets.
- Investigate the infected user’s local network.
- Steal sensitive data.
- Email attachments containing malicious code.
- Enabling file servers, such as those based on common Internet file systems (CIFS) and network file systems (NFS).
- File-sharing software can allow malware to replicate itself onto removable media and then onto computer systems and networks.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing can introduce malware by sharing files.
- It operates by inserting or attaching itself to a legitimate program or document that supports macros to execute its code.
- A virus has the potential to cause unexpected or damaging effects, such as harming the system software by corrupting or destroying data.
- Boot sector virus attack
- This type of virus attack can take control when the computer is started or booted. It can spread is by plugging an infected USB drive into your computer.
- Web scripting virus attack
- This attack exploits the code of web browsers and web pages. If users access such a web page, the virus can infect the user's computer.
- Browser hijacker
- This type of virus attack “hijacks” certain web browser functions, and a user may be automatically directed to an unintended website.
- Resident virus attack
- A resident virus attack can execute anytime when an operating system loads.
- Polymorphic virus attack.
- In this attack, the polymorphic virus changes its code each time an infected file is executed. It does this to evade antivirus programs.
 Recently, The Prime minister of India receives Bhutan’s highest civilian award.
Recently, The Prime minister of India receives Bhutan’s highest civilian award.
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo is also known as the order of the Dragon King.
- It is the highest decoration of the Kingdom of Bhutan.
- It is awarded in recognition of a lifetime of service to the people and the Kingdom of Bhutan.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies