- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 24, 2022 Current Affairs
Railway Budget 2022-23: What is Kavach? Know about Indian Railways plans to enhance safety with this world-class tech
- Indian Railways has indigenously developed an automatic train protection system rechristened as ‘Kavach’ (Train Collision Avoidance System), to prevent accidents due to human error resulting in Signal Passing at danger and over-speeding.
- It is a set of electronic devices and Radio Frequency Identification devices installed in locomotives, in the signalling system as well the tracks, that talk to each other using ultra high radio frequencies to control the brakes of trains and also alert drivers, all based on the logic programmed into them.
- One of its features is that by continuously refreshing the movement information of a train, it is able to send out triggers when a loco pilot jumps signal, called Signal Passed at Danger (SPAD), a grave offence in railway operations with respect to safety, and the key to accidents like collision.
- The devices also continuously relay the signals ahead to the locomotive, making it useful for loco pilots in low visibility, especially during dense fog.
- Other benefits of ‘Kavach’ include controlling speed of trains by automatic application of brakes on approach of turnouts, repeating of signal aspects in cab, which is useful for higher speeds & foggy weathers, and auto whistling at level crossing gates.
Google approaches NCLAT against CCI’s order on Android devices
- Google, was slapped with a fine of Rs 1,338 crore by CCI after being found guilty of anti-competitive behaviour in the Android mobile application ecosystem
Anticompetitive practices
- It refers to a wide range of business practices in which a firm or group of firms may engage to restrict inter-firm competition to maintain or increase their relative market position and profits without necessarily providing goods and services at a lower cost or of higher quality.
CCI
- The Competition Commission of India (CCI) was established in March 2009 by the Government of India under the Competition Act, 2002 for the administration, implementation, and enforcement of the Act.
- Composition of the CCI
- The Commission consists of one Chairperson and six Memberswho shall be appointed by the Central Government.
- It is a quasi-judicial body which gives opinions to statutory authorities and also deals with other cases.
- The Chairperson and other Members shall be whole-time Members
- Objectives:
- It will eliminate practices having adverse effects on competition.
- To Promote and sustain competition.
- It helps in protecting the interests of consumers.
- Ensuring freedom of trade in the markets of India.
- It will Establish a robust competitive environment through:
NCLAT
- It was constituted under Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013 for hearing appeals against the orders of the National Company Law Tribunal(s) (NCLT), with effect from 1st June 2016.
- Functions:
- Hearing appeals against the orders passed by NCLT(s) under Section 61 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC).
- To hear and dispose of appeals against any direction issued or decision made or order passed by the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- It also hears and disposes of appeals against the orders of the National Financial Reporting Authority.
656 Startups Supported by Approved Incubators under Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS)
- Aim: provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market-entry, and commercialization.
- Nodal Department: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- An Experts Advisory Committee (EAC) has been created by DPIIT to execute and monitor the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme.
- It is implemented with effect from 1st April 2021 with a corpus of Rs.945 crores.
- Eligibility conditions for startups:
- A startup, recognized by DPIIT, incorporated not more than 2 years ago at the time of application.
- Startups should not have received more than Rs.10 lakh of monetary support under any other Central or State Government scheme.
- Individual entrepreneurs are not eligible to apply for support under the scheme. Only DPIIT-recognized startups can apply for this scheme.
- Shareholding by Indian promoters in the startup should be at least 51% at the time of application to the incubator for the scheme.
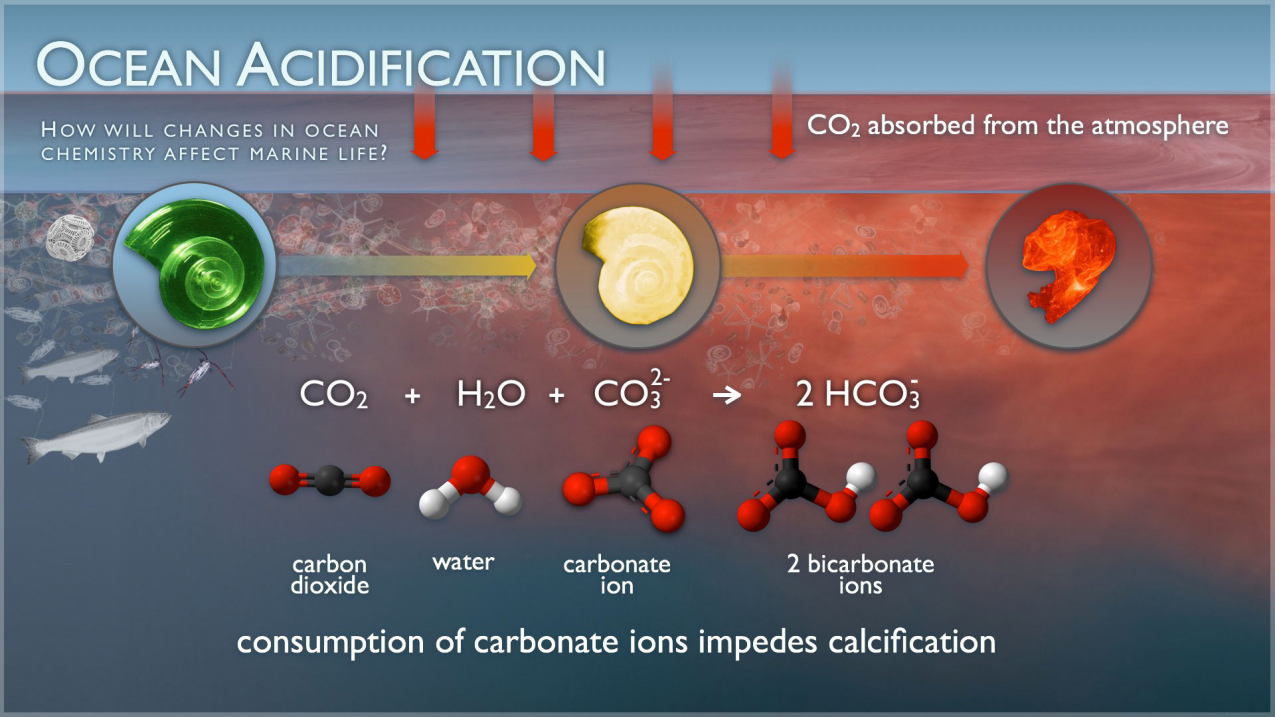
Acidification Of Great Lakes :By NOAA
- Recently, a study by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Ocean, Coastal, and Great Lakes Acidification Research Plan said, by 2100 even the Great Lakes of North America might approach acidity at the same rate as the oceans.
- The increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide has caused the world’s oceans to turn more acidic, but the new finding that the freshwater bodies are also turning acidic is a shock.
- Scientists are building a sensor network to measure the carbon dioxide and pH levels of the Lakes, starting with developing a system to detect the water chemistry trends of Lake Huron, one of the five Great Lakes.
Acidification
- It is a phenomenon resulting from the release of protons from certain substances into the ecosystem. These emissions increase the acidity (decrease in pH) of water and soils.
- Acidification of oceans or freshwater bodies takes place when excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere gets rapidly absorbed into them. The absorption of carbon dioxide leads to a lowering of the pH, which makes the water bodies more acidic.
- Consequences of acidification
- It will decrease native biodiversity,
- It will create physiological challenges for organisms,
- There are possibilities of permanently altering the structure of the ecosystem.
Great Lakes
- The Great Lakes of North America, or simply the Great Lakes, are five interconnected bodies of water straddling the US-Canada border. They are the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world.
- The Great Lakes are Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. The US-Canada border passes through Lakes Superior, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. Lake Michigan lies entirely in the US.
- They drain into the Gulf of St Lawrence in the North Atlantic through the St Lawrence River.
- Formation: The Great Lakes are believed to be formed some 20,000 years ago when the Earth started to warm and water from melting glaciers filled the basins on its surface, according to NOAA.
- Significance :
- Today, the Great Lakes contain a fifth of the world’s total freshwater and are a crucial source of irrigation and transportation.
- The Great Lakes also serve as the habitat for more than 3,500 species of plants and animals.
Bureau of Indian Standards published 21,890 standards for products, process specification, service sectors, code of practice and methods of test terminology
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the National Standards Body of India established under the BIS Act 2016.
- Objective: Harmonious development of the activities of standardisation, and quality assurance of goods and articles.
- It works under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution.
- BIS represents India in International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO
- It is an independent, non-governmental international organization with a membership of 167 national standard bodies.
- Through its members, it brings together experts to share knowledge and develop voluntary, consensus-based, market-relevant International Standards that support innovation and provide solutions to global challenges.
IEC
- The IEC is a global, not-for-profit membership organization, whose work underpins quality infrastructure and international trade in electrical and electronic goods.
- The IEC brings together more than 170 countries and provides a global, neutral and independent standardization platform to 20 000 experts globally.
- It administers 4 Conformity assessment systems whose members certify that devices, systems, installations, services and people work as required.
15 Start-ups selected in first cohort of NIRMAN accelerator will work towards solutions in healthcare and agriculture
- This is the first cohort of the NIRMAN Accelerator Program launched by Start-ups Incubation and Innovation Centre (SIIC) IIT Kanpur.
- The accelerator program is supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) under the Ministry of Science & Technology through its NIDHI scheme.
National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI) scheme
- It is an umbrella programme conceived and developed by the Innovation & Entrepreneurship division, Department of Science & Technology.
- Aim: To nurture start-ups through scouting, supporting and scaling innovations.
- Key stakeholders: Various departments and ministries of the central government, state governments, academic and R & D institutions, mentors, financial institutions, angel investors, venture capitalists and private sectors.
- Funding: By the National Science & Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board (NSTEDB).
- NIDHI Accelerator: An accelerator is typically a 3-6 months fast track structured program helping ideas get accelerated to the next orbit.
Objectives of NIDHI-Accelerators
- To fast-track the growth of potential start-ups through rigorous mentoring and networking support in a short span through existing TBIs.
- To attract subject matter experts, mentors, and angel investors to get associated with technology Business Incubators through structured accelerator programs.
- To build a vibrant start-up ecosystem, by establishing a network between academia, financial institutions, industries and other institutions.
- To act as a hub for several incubators in the region, so that high-potential start-ups can be fast-tracked for increased exposure and validation.
Characteristics of NIDHI -Accelerator Programs
It is envisaged that 2 broad types of Accelerator Programs will be supported by NSTEDB under this scheme
- Sectoral Programs: These are accelerator programs focused specifically on start-ups focused on a certain sector or theme. For example Smart Cities or healthcare.
- **Non-Sectoral Programs:**Non-sectoral accelerator programs are most relevant for locations where a critical mass of ventures within a specific sector may not exist.
Rashtriya Gokul Mission envisages development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds
- The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying is implementing RGM for development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- The scheme is important for enhancing milk production and productivity of bovines to meet the growing demand of milk and making dairying more remunerative for the rural farmers of the country.
- Objectives
- To enhance productivity of bovines and increasing milk production in a sustainable manner using advance technologies.
- To propagate use of high genetic merit bulls for breeding purposes.
- To enhance Artificial insemination coverage through strengthening breeding network and delivery of Artificial insemination services at farmers doorstep.
- To promote indigenous cattle & buffalo rearing and conservation in a scientific and holistic manner.
- Funding Pattern: All the components of Scheme will be implemented on 100% grant-in-aid basis except the components of:
- accelerated breed improvement programme under the component subsidy of Rs 5000 per IVF pregnancy will be made available to participating farmers as GoI share;
- promoting sex sorted semen under the component subsidy upto 50% of the cost of sex sorted semen will be made available to participating farmers and
- establishment of breed multiplication farm under the component subsidy upto 50% of the capital cost maximum upto Rs.2.00 crore of the project will be made available to entrepreneur.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana envisages insurance coverage to fishers
- PMMSY was launched in September 2020 with an aim to double the income of fish farmers and fishers in the country. It focuses on sustainable development of India’s fisheries sector and is a part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat scheme.
- The scheme focuses on activities with potential to generate employment such as seaweed and ornamental fish cultivation. It also emphasises on the breeding technique for quality brood, seed & feed and species diversification.
Implementation
- It is an umbrella scheme with two separate Components namely (a) Central Sector Scheme (CS) and (b) Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS).
- The CSS Component is further segregated into Non-beneficiary oriented and beneficiary orientated subcomponents/activities under the following three broad heads:
- Enhancement of Production and Productivity
- Infrastructure and Post-harvest Management
- Fisheries Management and Regulatory Framework
- PMMSY will be implemented in all the States and Union Territories for a period of 5 (five) years from FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
Key Initiatives and Progress
- PMMSY includes key activities such as fishing vessel insurance, support for new/upgrade of fishing vessels, aquaculture in saline/alkaline areas, Sagar Mitras, nucleus breeding centres, fisheries and aquaculture start-ups, incubators, and integrated aqua parks.
- PMMSY inter-alia provides insurance coverage to fishers which includes fish workers, fish farmers and any other categories of persons directly involved in fishing and fisheries related allied activities. The insurance coverage provided under the PMMSY includes
- 5,00,000/- against accidental death or permanent total disability
- 2,50,000/- for permanent partial disability
- Hospitalization expenses in the event of accident for a sum of Rs. 25,000/-.
Funding Plan:
- Central Sector Scheme – The entire scheme cost will be borne by the central govt. Also, in cases of direct beneficiary-oriented activities undertaken by central government entities such as the NFDB, central assistance will be up to 40% of the project cost for the general category and 60% for the SC/ST/women category.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) – In case of CSS components and subcomponents implemented by the states/UTs, the entire project cost will be shared between the centre and state.
Facial Recognition Technology
- Facial recognition refers to the technology capable of identifying or verifying a subject through an image, video, or any audiovisual element of the face. Generally, this identification is used to access an application, system, or service and it works like a face scanner.
- It is a method of biometric identification that uses that body measures, in this case, face and head, to verify the identity of a person through its facial biometric pattern and data.
- The technology collects a set of unique biometric data of each person associated with their face and facial expression to identify, verify and/or authenticate a person.
Biometric Facial Recognition Uses Cases
- Face identity recognition uses focus on verification or authentication. This technology is used, for example, in situations such as:
- Second authentication factor, to add extra security in any log-in process.
- Access to mobile applications without a password.
- Access to previously contracted online services (login on online platforms, for example).
- Access to buildings (offices, events, facilities of any kind.
- Payment method, both in physical and online stores.
- Access to a locked device.
- Check-in in tourist services (airports, hotels…).
Benefits of Facial Recognition?
- A fastest process: facial recognition allows for fast and smooth remote identity verification.
- User experience: facial recognition systems offer a unique, smooth, and fast user experience, avoiding the need for time-consuming office visits or video conferences and wait times.
- Security: Like fingerprints or voice, each face is unique and has inimitable characteristics. Facial recognition systems, programs, or software compare through facial biometrics and facial recognition algorithms.
- Compliance: Facial recognition through video identification is the only method recognised as a standard for remote identity verification for high-risk operations (opening bank accounts, signing contracts, etc.).
Intranasal vaccine gets clearance as booster option in Covid fight
- In nasal approach, the vaccine dose is given via nose, rather than orally or through the arm.
- As the target is to deliver a dose which goes right into the respiratory pathways, the vaccine is either injected through a specific nasal spray or through aerosol delivery.
- As the virus normally enters the body through the nose, the nasal vaccine causes immune system to make proteins in the blood and in the nose that help you fight the virus.
- A doctor will spray the vaccine into nostrils with a small syringe that has no needle. It usually takes about two weeks for it to start to work.
- Given the potency and rapid spread of the coronavirus, it makes sense to develop vaccines for the airway as well as the more standard jabs.
Benefits of nasal vaccine
- An effective nasal dose not only protects against Covid- 19, but it also prevents the spread of the disease by offering another kind of immunity that occurs primarily in the cells that line the nose and throat.
- The nasal vaccine targets immune cells present in the mucosal membrane and tissue- which provides systematic as well as mucosal immunity present in other sites such as lungs and the intestines. Hence, a nasal vaccine may be more capable of inoculating crowds against the deadly infection and prevent even mild symptoms from developing.
- An intranasal vaccine will not only be simple to administer but reduce the use of medical consumables such as needles, syringes, etc., significantly impacting the overall cost of a vaccination drive.
- The ability to accomplish effective immunization with a single nasal dose is a major advantage, offering broader reach and easier administration.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies