- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 28, 2021
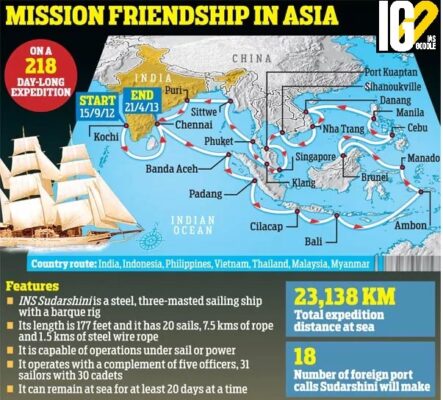
INS SUDARSHINI DEPLOYMENT TO GULF COUNTRIES TO ENHANCE FOREIGN TRAINING COOPERATION
Recently, the Ministry of Defence deployed Sail Training Ship (STS) INS Sudarshini to the Gulf.
 P.N.Panicker
P.N.Panicker
 State Health Index:
State Health Index:
 Highlights:
Highlights:
 Highlights:
Highlights:
 Highlights of the survey:
Highlights of the survey:
 Contributions of Edward O. Wilson:
Contributions of Edward O. Wilson:
 Highlights of course
Highlights of course
 What are the rogue planets?
What are the rogue planets?
 Highlights:
Highlights:

- Class and type: Three-masted barque
- It is indigenously built by Goa Shipyard Ltd.
- It was Commissioned in 2012.
- It is under Southern Naval command of Indian navy.
- The ship is a sister ship of INS Tarangini which was commissioned in 1997.
- Aim: To train, certify and place 10,000 Indian workers in the United Arab Emirates in one year in partnership with some of the leading employers in the region.
- Objective: To prepare a trained workforce in both the blue-collar and the white-collar job sectors, through skilling, up-skilling and re-skilling initiatives under TEJAS.
- The programme will converge with the existing skill development programmes and leverage training infrastructure of Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendra and Skill training institutes under the Central and state governments will ensure sourcing and supply of potential candidates.
- Work opportunities have been identified in sectors such as construction and facility management which includes electricians, plumbers and welders etc.
- The opportunity for India is estimated to be 3.6 million in the next five years, of which 2.6 million Indians can be potentially placed in the Gulf cooperation council countries, Europe, Australia, Canada, Russia and Malaysia.
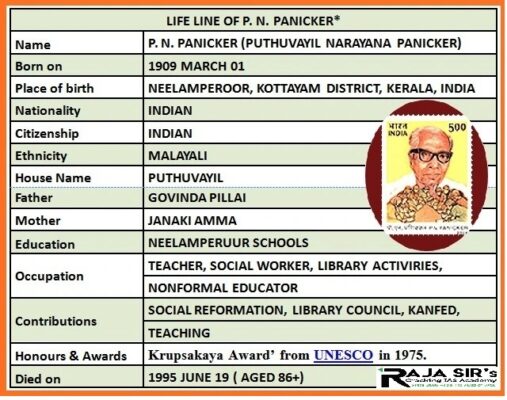
 P.N.Panicker
P.N.Panicker
- Panicker was born in a Nair family on 1909 March 1 at Neelampeeror.
- In 1926, he started the Sanadanadharmam Library as a teacher in his hometown.
- He led the formation of Thiruvithaamkoor Granthasala Sangham (Travancore Library Association) in 1945 with 47 rural libraries.
- Later, it became Kerala Granthasala Sangham (KGS).
- He spread an important message - "Vayichu Valaruka" which means "Read and Grow".
- Libraries created by the movement of Panicker later became a nerve centre of all social and cultural activities.
- He founded the Kerala Association for Non-Formal Education and Development (KANFED) in 1977.
- KANFED was instrumental in starting the Kerala State Literacy Mission, which led Kerala to its universal literacy movement.
- The report has been developed by NITI Aayog, with technical assistance from the World Bank, and in close consultation with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
 State Health Index:
State Health Index:
- It ranks states and Union Territories on their year-on-year incremental performance in health outcomes as well as their overall status.
- It is a weighted composite index based on 24 indicators grouped under the domains of:
- Health Outcomes
- Governance and Information
- Key Inputs/Processes
- Each domain has been assigned weights based on its importance with higher score for outcome indicators.
- To ensure comparison among similar entities, the ranking is categorized as:
- Larger States
- Smaller States
- Union Territories
- The index is being compiled and published since 2017.
- Among the larger states:
- Kerala has emerged as the best state in terms of overall health performance among larger states while Uttar Pradesh is the worst.
- Uttar Pradesh, Assam and Telangana are the top three ranking states in terms of annual incremental performance.
- Among smaller states:
- Mizoram emerged as the best performer in overall performance.
- Mizoram and Meghalaya registered the maximum annual incremental progress.
- Among UTs, Delhi, followed by Jammu and Kashmir, showed the best incremental performance.

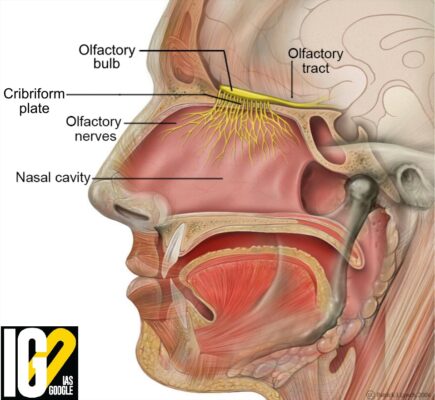
- The olfactory system is the sensory system used for smelling.
- It enables us to distinguish between many million different
- Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system and an accessory olfactory system
- A large proportion of these smells are associated with a threat to our health and survival, such as that of chemicals and rotten food.
- The olfactory organ takes up about 5% of the human brain.
- An olfactory bulb processes smells and in turn can transmits signals to parts of the brain that control movement and avoidance behaviour.
 Highlights:
Highlights:
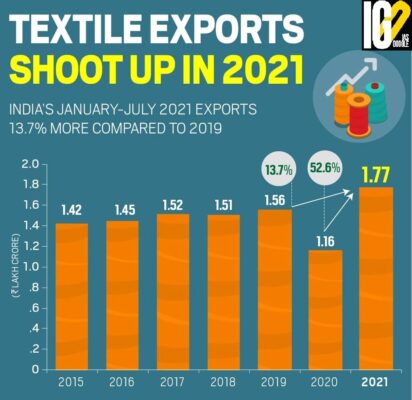
- China-plus-one policy has helped textile companies in achieving higher growth.
- China-plus-one policy is a business strategy to avoid investing only in China and diversify business into other countries.
- Textile Export was valued at $263 billion during the April-November period in 2021-22.
- The commodities included cotton yarn, fabrics, made-ups, handloom products, man-made yarn, jute, textiles and apparel
- The textile sector contributed 9 per cent of the total exports.
- Budget allotted- Rs. 3,514.79 crore in the 2020-21 budget.
- Aim-Make in India' and 'Zero Defect and Zero Effect' in manufacturing, the government provides credit linked capital investment subsidy.
- Schemes for the development of the Power loom Sector (Power-Tax):
- Aim-To improve the work efficiency and to enhance the competitiveness of power loom in the global market
- Aim- to provide infrastructure facilities for setting up textile units in potential growth areas matching with the international social and environmental standards.
- Aim-To generate employment opportunities through Apparel Manufacturing.
- Aim-to skill the youth for gainful and sustainable employment in the textile sector.
- Jute (ICARE- Improved Cultivation and Advanced Retting Exercise):
- Aim-to aware and train the jute farmers for efficient and effective utilization of the improved jute production technologies and increase the fibre productivity as well as quality on a larger scale.
- Aim- to facilitate the textile industry to become globally competitive using environmentally friendly processing standards and technology
- Aim- to scale up production by improving the quality and productivity and to empower downtrodden, poor & backward families through various activities of sericulture in the country.
- Aim-to serve weavers of the Block with all facilities of pre loom and post loom activities.
- Objectives-
- Promoting premium handicrafts products for the niche market.
- Expansion of production base for utility-based, life style and mass production handicrafts products.
- Preservation and protection of heritage/languishing crafts.
- Objectives-
- To increase the annual wool production in India
- To improve the quality of wool fibre and quality of processing the wool
- To establish service and research centres to improve the quantity and quality of import and export production
- To increase marketing and branding promotion for export production of wool.
- Aim- to promote textiles industry in the North East Region by providing infrastructure, capacity building and marketing support to the industry.
- Aim- to help exporters cut high logistics and other costs and enable them to compete globally
 Highlights:
Highlights:
- Naval ship INS Kesari entered Port of Maputo in Mozambique to ship meals.
- It is a COVID-19 relief mission followed by Mission Sagar II and Mission Sagar III.
- Launched-2020
- Aim- to deliver COVID-19 related assistance to the countries in the Indian Ocean Region.
- It is in line with ‘SAGAR — Security and Growth for All in the Region’.
- SAGAR- It is a blueprint for cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Launched- 2015
- Objective-to deepen economic and security cooperation with its maritime neighbors and assist in building their maritime security capabilities.
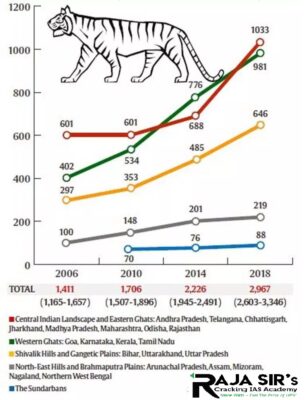
 Highlights of the survey:
Highlights of the survey:
- It is the first-time tiger counting will be carried in a Maoist-affected area.
- The connectivity between Tadoba Tiger Reserve and Indravati Tiger Reserve makes an important tiger habitat in central India.
- Location: Bijapur district of Chhattisgarh, India
- It is one of the three tiger reserve in the state along with Achanakmar Tiger reserve, Udanti- Sitanadi Tiger Reserve.
- The reserve was formerly known as Kutru National Park.
- The reserve had reserve had three tigers in 2018-19.
- Major river passing through the reserve- Indravati
- Legal Status:
- National Park- 1981
- Tiger Reserve- 1983
- Vegetation- Southern tropical moist mixed deciduous forests and Dry evergreen forests
- Flora-teak, lendia, salai, mahua, tendu, semal, haldu, ber and jamun.
- Fauna-tiger, leopard, striped hyena, wolf, wild buffalos, sloth bear, fox, hare, common langur, flying squirrel, chital, sambar, barking deer, nilgai, wild boar and gaur.
- Corridor: It has connectivity with several tiger reserves, viz. Kawal (Telangana), Tadoba (Maharashtra) and Kanha (Madhya Pradesh).
- The sanctuary is situated in the northern part of the Sundarbans delta in West Bengal, India.
- It was set up as a sanctuary in 1976.
- It is located at the confluence of the Matla and Gumdi rivers.
- Flora: Mangrove scrub, forest and swamp.
- Fauna: Water fowl, pelican, spotted deer, rhesus macaques, wild boar, tigers, water monitor lizards, fishing cats, olive ridley turtle, and migratory birds.
 Contributions of Edward O. Wilson:
Contributions of Edward O. Wilson:
- He was considered as the one of the world’s leading authorities on natural history and conservation.
- He was also as an entomologist (personae who studies insects).
- He also wrote a famous book, Sociobiology: The New Synthesis (1975).
- His Half-Earth Project calls for protecting land and sea to reverse the course of species extinction.
- The United Nations (UN) has urged countries for conserving 30 % of their land and ocean water by 2030. This target is known as “30 by 30”. This effort is from inspired in part by Wilson.
- Evolution studies large-scale biological changes occurred in an organism.
- It also explains how the evolution occurred in the past, and is still occurring now.
- Before 1850s many evolution theories were already in 1859, Charles Darvin in his book Origin of Species more logically explained the evolution. Till now, it is widely accepted evolution theory.
- It talks about evolution by way of natural selection.
- It says, organisms that were fit to adapt the changing environment structure, have only survived. In other words, it talks about survival of the fittest.
- All the species of living organisms have been gradually evolved from common ances
- Natural selection is not the only factor responsible for evolution, which Darwin didn’t focus on.
- Darwin didn’t mention any explanation about useful and useless modifications.
- There is no explanation for slow changes and abrupt changes.

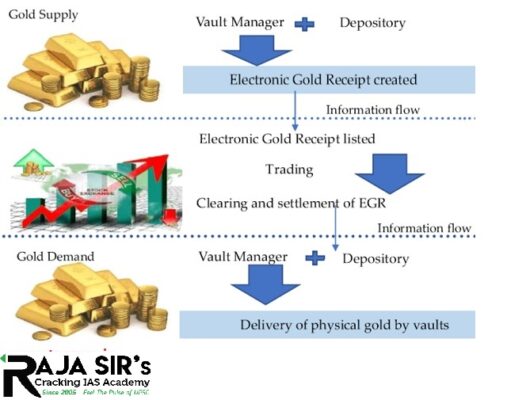
- EGR is an electronic receipt issued on the basis of deposit of underlying physical gold in accordance with the regulations made by SEBI.
- It will enable trading of EGR in existing exchanges under a separate segment.
- EGRs will be held in demat form and can be converted into physical gold when needed.
- EGR will have trading, clearing and settlement features akin to any other securities.
 Highlights of course
Highlights of course
- The certification program will create awareness on importance and benefits of energy audit and energy efficiency and conservation among students from engineering/diploma colleges.
- This will increase employability of youth in the domain of energy efficiency, climate change mitigation, and sustainability.
- It will create a pool of professionals to perform home energy audits based on the needs of the consumer (s).
- This will enable Domestic consumers to get Home Energy Audit carried out through respective SDA Certified Home Energy Auditor(s).
- A home energy audit is a process that helps to identify where home is losing energy and what steps can be taken to improve energy efficiency.
- It enables appropriate accounting, quantification, verification, monitoring, and analysis of energy use of various energy-consuming equipment and appliances in a house.
- It enables the submission of a technical report with recommendations for improving energy efficiency, with a cost-benefit analysis to reduce energy consumption.
- helps to understand where and how energy is used.
- can assess where home is losing the most energy and then proposes improvements to make to help save energy and reduce bills.
- reduces carbon footprint.
- improves the energy efficiency of home and increases control over home environment.
- The Government of India set up Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) in March 2002 under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Objective: Reducing energy intensity of the Indian economy.
- Mission: to assist in developing policies and strategies with a thrust on self-regulation and market principles, within the overall framework of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Energy Conservation Guidelines for MSME
- Roadmap of Sustainable and Holistic Approach to National Energy Efficiency (ROSHANEEE).
- Unlocking National Energy Efficiency Potential (UNNATEE).
- State Energy Efficiency Index
- National Carbon Market
 What are the rogue planets?
What are the rogue planets?
- Planetary bodies that do not revolve around the star and float freely in space, are called the Rogue planets.
- Instead of stars, they orbit the galaxy. They are gravitationally unbound to any stars. Due to this, their detection in space is very hard.
- Astronomers detect rogue planets using an astronomical phenomenon called gravitational microlensing.
- Gravitational microlensing was predicted by predicted in 1936 by Einstein using his General Theory of Relativity. It is process of brightening of a star by an object passing between the star and an observer.
 Highlights:
Highlights:
- Upward trend in disasters reflects the effects of man-made climate change.
- The most expensive disaster in 2021 was hurricane Ida, which lashed the eastern United States.
- Disasters costing several billion dollars include flooding in Canada, a late spring freeze in France that damaged vineyards, and a cyclone in India and Bangladesh.
- Cyclone Amphan was one of the strongest storms on record in the Bay of Bengal.
- It was also the costliest tropical cyclone of the year.
- Four of the ten costliest events occurred in Asia.
- The intensity of cyclones hitting the countries around the North Indian Ocean has been increasing over the last decades.
- Geographical situation and socio-economic conditions make the littoral states of the Bay of Bengal among the most vulnerable regions to climate change.
- Australia bushfires (Australia, $5 billion)
- Locust swarms (East Africa, $8.5 billion)
- Windstorms Ciara and Alex (Europe, $5.9 billion)
- Cyclone Amphan (India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, $13 billion)
- Atlantic Hurricane season (US, Central America, $40 billion)
- China floods (China, $32 billion)
- India floods (India, $10 billion)
- Kyushu floods (Japan, $5 billion)
- Pakistan floods (Pakistan, $1.5 billion)
- US West Coast fires (US, $20 billion)
- To prevent further disasters, countries must urgently cut greenhouse gas emissions.
- Richer countries need to provide more funding to support vulnerable communities living in poorer countries to help them adapt and build resilience to the impacts of climate change.
- All Governments must invest in the energy transition to renewables.
- Richer countries should support developing countries so they can leapfrog the fossil fueled development path taken by richer countries.
- A fund to address the loss and damage caused by climate change needs to be set up by the end of COP27.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies