- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
DECEMBER 03, 2025
Africa is gradually splitting into two plates
- A new study using resurrected 1960s magnetic data shows clear evidence of active seafloor spreading near the Afar triple junction, confirming that Africa is gradually splitting into two plates.
East African Rift Valley
- World’s largest active continental rift stretches ~3,500 km from the Red Sea to Mozambique, marked by elongate depressions and steep fault scarps produced by crustal extension.
Key Features
- Two distinct branches: the volcanic-rich Eastern Rift (Ethiopia–Kenya) and the seismically active Western Rift (Uganda–Malawi), each showing advanced stages of crustal thinning.
- Tectonic & volcanic zone: characterised by normal faults, fissures, active volcanoes like Erta Ale, and deep lakes such as Tanganyika formed by subsiding crust.
- Afar Triple Junction: a meeting point of the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden and East African rifts, making it one of Earth’s most dynamic tectonic regions.
- Divergent plate boundary: separates the Somali and Nubian plates, with measurable spreading of 5–16 mm/year in the north.
Formation of the Rift Valley
- Mantle plume upwelling increases heat flow and buoyancy, uplifting and thermally weakening the continental lithosphere beneath Ethiopia–Kenya.
- Tensional plate forces stretch the brittle crust, causing extensional stress that produces large, steep normal faults on both sides of the rift.
- Horst–graben structures form as blocks of crust drop down (grabens) while adjacent blocks rise (horsts), creating deep trough-like rift valleys.
- Magmatism & basaltic volcanism accompany crustal thinning, as fissure eruptions and flood basalts fill the widening rift floor over millions of years.
- Progressive divergence may eventually rupture the continental crust entirely, allowing seafloor spreading to create a new ocean basin.
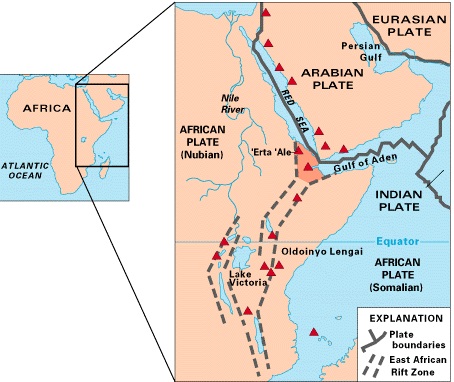
Factors Causing the African Rift
- Deep mantle superplume beneath East Africa pushes the lithosphere upward, generating uplift, stretching, and widespread magmatic weakening.
- Divergence between Somali & Nubian plates, moving 5–16 mm/year, progressively widens the rift and increases extensional strain on the crust.
- Afar triple-junction dynamics intensify crustal breakup as three spreading centres mechanically pull the region apart in different directions.
- High heat flow & magma intrusions reduce crustal strength, accelerating normal faulting and basin subsidence.
- Stress transfer from Red Sea & Gulf of Aden spreading centres propagates southward, reinforcing rifting from the northeast to Mozambique.
Implications of the Rift
- Geological Implications:
- Formation of a new ocean basin is likely once continental rupture completes, separating the Somali plate from the African mainland.
- Higher volcanic and seismic activity will persist along Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania as crustal thinning continues and magma pathways open.
- Creation of deep linear lakes & drainage shifts, altering hydrology and forming new basins such as expanded Lake Turkana or Malawi.
- Africa’s long-term geographic reconfiguration, producing two continents with newly emergent coastlines and submerged rift floors.
- Socio-Economic Implications:
- Frequent fissuring, fault scarps & earthquakes threaten roads, farms, schools, and settlements across Rift Valley nations.
- Damage to public infrastructure—as seen in Kenya and Ethiopia—will raise disaster-risk, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation.
- Future coastline emergence may give landlocked nations like Uganda and Zambia potential sea access, reshaping trade patterns.
Conclusion
- The East African Rift Valley represents one of Earth’s most active continental breakup zones, gradually reshaping Africa’s geography. Though unfolding over millions of years, its seismic and volcanic impacts are already visible today. Understanding this rifting is essential for managing future geological hazards and harnessing new resource opportunities.
DRDO Rocket-Sled Test
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully carried out a high-speed rocket-sled test of a fighter aircraft escape system.
- A rocket-sled test is a dynamic testing method that uses a rocket-propelled sled on a precisely aligned track to simulate real flight or impact conditions in a controlled environment.
- Objective: Assess the performance and reliability of a fighter aircraft escape system for aircrew recovery.
- Mechanism: The test employed a Light Combat Aircraft (LCA), accelerated to a precisely controlled velocity by solid propellant rocket motors.
- Location: It was conducted at the Rail Track Rocket Sled (RTRS) facility of the Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL) in Chandigarh.
- Collaboration: The test was carried out in partnership with Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Significance: It is a significant milestone for India’s indigenous defence capability, positioning India among an “elite club of nations” with in-house escape-system testing expertise.
Exercise EKUVERIN
- The 14th edition of the annual India-Maldives bilateral military exercise EKUVERIN is set to take place in Kerala from Dec 2nd to 15th.
EKUVERIN
- Exercise EKUVERIN (meaning ‘Friends’ in the Dhivehi language) is the annual bilateral military exercise between India and the Maldives, initiated in 2009.
- Conducted alternately in India & Maldives; 14th edition (2025) is being held in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, between the Indian Army and the Maldives National Defence Force.
- It focuses on enhancing interoperability for counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations across semi-urban, jungle and coastal terrain, with increasing integration of niche technologies.
- India also participates in Exercise Ekatha – an annual joint naval exercise with the Maldives and Exercise Dosti – a trilateral maritime exercise between the coast guards of India, the Maldives and Sri Lanka.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam 4.0
- Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan and Uttar Pradesh CM Yogi Adityanath inaugurated the fourth edition of Kashi Tamil Sangamam in Varanasi.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
- Inception: Launched in 2022 by the Ministry of Education to revive ancient civilizational and cultural ties between Varanasi (Kashi) and Tamil Nadu under the spirit of ‘Ek Bharat Shrestha Bharat.’
- Format: Month-long event in Varanasi featuring seminars, cultural performances, temple visits, cuisine exhibitions and academic exchanges.
- Fourth Edition: Begins 2 December 2025 under the theme “Learn Tamil – Tamil Karkalam”, with over 1,400 delegates from Tamil Nadu participating.
- Organisers: Coordinated by the Ministry of Education with IIT-Madras and Banaras Hindu University as knowledge partners, supported by the Uttar Pradesh government.
|
Historical Ties Between Kashi and Tamil Nadu
|
Swargadeo Chaolung Sukapha
- Every year, Assam Day (2 December) is celebrated to honour Chaolung Sukapha.
- Chaolung Sukapha was the founder of the Ahom Kingdom (1228 AD) and is known as the ‘Architect of Greater Assam’.
- Origin: He was a Tai prince of the Shan tribe, from Mong Mao (present-day Yunnan, China or the Upper Myanmar region).
- First Capital: He established his first principality at Charaideo in Upper Assam.
- Charaideo was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site (WHS) in July 2024.
Key contributions of Chaolung Sukapha
- Political Policy: He promoted reconciliation with indigenous groups like the Moran and Barahi tribes and supported intermarriage between the Ahoms and local communities.
- Administration: He divided the kingdom into khels or phoids, each led by an officer responsible for providing a fixed number of paiks; he created the high ministerial posts of Buragohain and Borgohain.
- Economic Contribution: He introduced wet-rice cultivation, turning the floodplains into productive farmland that became the backbone of the kingdom’s agrarian economy.
- Cultural Legacy: Interaction between the Tai-Ahom language, religion, and traditions formed a unique composite Assamese culture, later documented in the ‘buranjis’.
- Paiks were able-bodied adult males who provided compulsory labour or military service in exchange for rent-free, non-hereditary, non-transferable cultivable land called ga-mati.
- The buranjis (meaning “a storehouse of knowledge about the past”) were comprehensive historical chronicles, initially written in the Tai-Ahom language and later mainly in Assamese.
- Source (PIB)
Low Acceptance Rate of the PM Internship Scheme
- The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) told the Lok Sabha that only 20% of the 1.65 lakh internship offers under the Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme were accepted by candidates.
- Of the accepted offers, 20% of candidates quit their internships prematurely.
Factors Behind Lower Acceptance Rate
- Geographical Mismatch: Opportunities are concentrated in major industrial or urban centres located far from candidates’ hometowns.
- Longer Duration: The compulsory 12-month duration exceeds typical 3–6-month skill-building programmes that align with academic breaks or short transition periods.
- Role Mismatch: A mismatch between candidates’ aspirations and tasks assigned resulted in limited interest in the offered roles.
- Low Stipend: The ₹5,000 monthly stipend is insufficient to meet living costs, especially for candidates who need to relocate.
- Job Prospects: The scheme does not guarantee post-internship employment. Very few participants received full-time job offers during the pilot.
About PM Internship Scheme
- The Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme is a central-sector scheme that offers a 12-month paid internship to Indian youth in the top 500 Indian companies.
- Core Objective: The scheme aims to bridge the gap between academic learning and industry requirements through hands-on workplace exposure.
- Target: It plans to deliver one crore internships over a five-year implementation period (2024-29).
- Implementing Body: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) administers the scheme through a dedicated Prime Minister’s Internship Scheme (PMIS) Cell.
- Company Selection: The initial list of top 500 companies was chosen based on their average Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure.
- Duration: The internship spans 12 months, with at least six months spent in a real job environment.
- Financial Support: Interns receive a ₹5,000 monthly stipend, a ₹6,000 one-time joining grant, and insurance coverage under relevant government schemes.
Eligibility Conditions
- Eligibility Criteria: Applicants must be Indian citizens aged 21 to 24 with Class 10/12, ITI, polytechnic diploma, or bachelor’s degree qualifications.
- Work-Income Condition: Candidates must not be in full-time employment or formal education, and annual family income must be below ₹8 lakh.
- Ineligibility: Graduates from premier institutions (IITs, IIMs), higher qualifications (CA, MBBS, MBA), or with immediate family in government service, are not eligible.
National Strategy for Financial Inclusion 2025-2030
The Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released the new National Strategy for Financial Inclusion (NSFI) 2025-2030.
About NSFI
- It is a comprehensive plan to expand financial access and usage across India over the next five years.
- The NSFI is based on five strategic objectives, collectively known as ‘Panch-Jyoti’ (Five Lights).
- It has been developed under the Technical Group on Financial Inclusion and Financial Literacy (TGFIFL), in consultation with various stakeholders.
- Panch-Jyoti: A five-pillar strategy focusing on equitable financial services, women-led inclusion, finance–livelihood integration, financial education, and stronger customer protection.
Key Focus Areas
- Last‑Mile Delivery: Ensure every revenue centre has at least one banking outlet (branch, Digital Banking Unit, or fixed-point Business Correspondent).
- Business Correspondents: Provide fair pay for BCs and utilise their networks to distribute insurance, pensions, and mutual funds; a medium-term goal is achieving 30% women BCs.
- Digital Innovation: Explore programmable Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) for targeted credit flows and pilot its offline functionality in low-connectivity areas.
- Social Security: Integrate all banks and insurers onto the Jansuraksha portal for seamless enrolment and claims processing under PMJJBY and PMSBY.
- Product Development: Design bundled financial products, including combined life, health, accident, and property insurance for underserved users.
Alaknanda Galaxy Discovered in Early Universe
- Indian researchers at Pune have discovered a Milky Way–like spiral galaxy, Alaknanda, from the early universe ≈1.5 billion years after the Big Bang.
Spiral Galaxies
- Definition: Spiral galaxies are rotating systems of stars, gas, and dust shaped like a disk with spiral arms winding outward from a central bulge.
- Structure: They typically have three major components — a dense central bulge, a flat rotating disk with spiral arms, and an extended halo of stars and dark matter. E.g., Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, with a central bar-shaped bulge.
About Galaxy “Alaknanda”
- Location: A massive spiral galaxy with two well-defined spiral arms located ~12 billion light-years away, dating to when the universe was just 10% of its current age.
- Named by Researchers: Named “Alaknanda” after the Himalayan river; researchers saw it as a “sister” to Mandakini (another name for the Milky Way).
- Instrument: Discovered using James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), NASA’s most powerful space observatory launched in December 2021.
- Future Study Tools: Follow-up observations planned using Atacama Large Millimetre/submillimetre Array (ALMA) in Chile to study gas motion and galaxy kinematics.
- Significance of the Discovery: It challenges early models as Early-universe galaxies were expected to be chaotic, hot, clumpy and turbulent, not well-organised spirals.
Child Marriage Hotspot
- Child marriages in Madhya Pradesh have risen sharply by 47% since 2020, with Damoh district emerging as the worst hotspot in 2025.
- Parliamentary data shows 538 cases recorded this year, the highest in five years.
Child Marriage Hotspot:
- A persistent cluster of districts reporting disproportionately high child marriages, mainly in Bundelkhand, central MP, Gwalior–Chambal and tribal belts, indicating entrenched socio-economic vulnerabilities.
Trends
- Steady Statewide Rise: MP saw cases rise from 366 (2020) to 538 (2025) — a 47% increase despite awareness campaigns.
- District-Level Surge: Damoh alone accounts for 21% of all child marriages in 2025, jumping from 33 cases in 2024 to 115 in 2025.
- Regional Concentration: Bundelkhand, tribal and economically backward districts dominate the list, signalling poverty-linked, region-specific persistence.
Implications:
- Rising child marriages undermine girls’ education, health and economic participation, deepening intergenerational poverty.
- It increases risks of maternal mortality, early pregnancies and domestic violence.
- The trend signals weak enforcement of PCMA 2006, gaps in local governance, and failure of social protection schemes to reach the most vulnerable.
INS Aridaman
- India is set to commission INS Aridaman, its third indigenous nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), with Navy Chief Admiral Dinesh K.
INS Aridaman:
- INS Aridaman is India’s third indigenously built SSBN, part of the Arihant-class nuclear submarines under the Strategic Forces Command, designed to provide assured retaliatory capability under India’s no-first-use nuclear doctrine.
Built By: Constructed under the Advanced Technology Vessel (ATV)
Project, led by:
- Ship Building Centre, Visakhapatnam
- It integrates over 90% indigenous components, including its nuclear reactor.
- History of India’s Nuclear Submarine Programme:
- Initiated under the ATV programme in the late 1980s to achieve a credible underwater nuclear deterrent.
- INS Arihant (launched 2009, commissioned 2016) made India the 6th nation with operational SSBN capability.
- INS Arighat followed in 2024.
- INS Aridaman will be the third operational SSBN, marking the first time India will have a minimum rotation fleet for continuous at-sea deterrence.
Key Features of INS Aridaman:
- Displacement: ~6,000 tonnes (surface), ~7,000 tonnes (submerged)
- Reactor: 83 MW pressurised water reactor (BARC) enabling near-unlimited endurance
- Armament:
- Four vertical launch tubes
- Up to 24 K-15 Sagarika SLBMs (750 km range) or
- K-4 missiles with 3,500 km range
- Stealth Enhancements: Anechoic tiles, advanced sonar suite (bow, flank, towed array)
Significance:
- Strengthens Nuclear Triad: Provides survivable, assured second-strike capability essential under India’s no-first-use posture.
- Enhances Maritime Security: Expands Navy’s deterrence reach across the Indo-Pacific amid rising regional tensions.
- Boost to Aatmanirbhar Bharat: High indigenous content reflects mastery over complex nuclear naval propulsion.
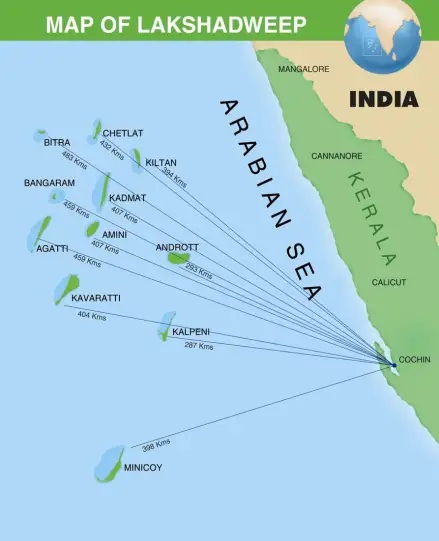
A new naval detachment on Bitra Island
- India is set to increase military presence in Lakshadweep, with a new naval detachment on Bitra Island becoming fully operational next year, alongside expanding Air Force facilities on Agatti and Minicoy.
Bitra Island
- Bitra is the smallest inhabited island of Lakshadweep, forming part of the Amindivi subgroup. It is a tiny coral atoll known for its ecological fragility, lagoon system, and cultural significance.
Location:
- Situated in the Arabian Sea, 483 km west of Kochi.
- Lies north of Perumal Par and southeast of Byramgore Reef within the Lakshadweep archipelago.
Formation:
- Bitra is a coral atoll, formed from the upward growth of coral reefs on submerged volcanic bases.
- Over time, biological accretion and reef-building created a ring-shaped lagoon system, with small sandy islands emerging on the reef surface.
Geological Features:
- Two islands: Main Bitra Island (≈0.177 sq km) + a small southern cay (≈0.009 sq km).
- Lagoon area: 45–54 sq km, protected by a surrounding coral reef.
- Reef barrier ensures calm lagoon waters even during monsoon storms.
Significance:
- Strategic: Now hosts a new Indian naval detachment, boosting surveillance across critical shipping lanes near the Arabian Sea.
- Cultural: Home to the shrine of Malik Mulla, an Arab saint, making it a pilgrimage site for islanders.
- Ecological: Historically a major seabird breeding ground; part of Lakshadweep’s fragile coral ecosystem.
- Human history: Permanently settled only in 1945, making it one of India’s newest inhabited regions.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies