- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
December 18, 2023 Current Affairs
India Deploys Counter UAV Systems At Military Installations Fearing Suicide Drone Attack
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has initiated plans to counter the increasing threat posed by unmanned aerial systems (UAS) by issuing Requests for Proposals (RFPs) for various counter-drone systems.
- These systems are designed to address different operational scenarios, particularly the challenge presented by multiple swarm drones.
Counter Unmanned Aircraft Systems (C-UAS)
- The C-UAS systems are intended to offer a comprehensive solution for detecting, tracking, identifying, designating, jamming, and neutralizing multiple threats simultaneously.
- Key features include:
- Multi-sensor Capability: Providing a comprehensive air situation picture using various sensors.
- Vehicle-Mounted System: Offering mobility for deployment in different operational areas.
- No-Fly Zone Enforcement: Intercepting identified threats and preventing unauthorized UAS intrusion.
- Recognition of Unknown UAS: Generating alerts based on user-defined parameters.
Micro Munitions Systems (MMS)
- These systems are designed to combat swarm drones attacking IAF bases from multiple directions.
- Key attributes of the MMS include:
- Guided Munition System: Capable of deploying multiple guided munitions laterally to counter swarms.
- Mobile Delivery Vehicle: Equipped with radar-controlled platforms launching 128 guided missiles per launch.
- Multi-Directional Engagement: Ability to launch missiles in various directions simultaneously.
Kamikaze Drone Systems (KDS)
- The KDS, also mounted on vehicles, aims to counter multiple swarm drones by utilizing satellite navigation-based flight and communication links.
- Notable features include:
- Satellite Navigation-Based System: Utilizing flight and communication links for drone control.
- Explosive-Laden Kamikaze Drones: Directing drones towards detected swarm drones to neutralize them by crashing into them.
- Comprehensive Air Situation Picture: Using radar and radio frequency detectors for detection, tracking, and neutralization.
Common Requirements for all Systems
- Integration with existing air defense and communication networks, anti-drone measures, and close-in weapon systems of the IAF.
- Deployment flexibility on rooftops or unprepared locations.
- All-weather capability and functionality at altitudes of up to 16,000 feet, ensuring nationwide deployment.
Swarm drones
- Swarm drones, also known as drone swarms or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarms, represent a groundbreaking approach to aerial operations.
- These systems consist of multiple drones working together in a coordinated manner to achieve various objectives.
Technology behind Swarm Drones:
Swarm Control and Communication:
- Swarm Algorithms: These are essential for controlling the behavior of individual drones within the swarm and ensuring coordination.
- Communication Protocols: Efficient communication is crucial. Drones can communicate directly or through a central system like a ground station or a leader drone.
- Decentralized Control: Swarm drones often use decentralized decision-making processes to enhance adaptability and resilience.
Sensing and Perception:
- Sensors: Drones are equipped with various sensors (e.g., cameras, LiDAR, GPS) for navigation, obstacle detection, and situational awareness.
- Computer Vision: Enables drones to recognize and track objects, people, or terrain features, aiding in navigation and mission execution.
- Machine Learning and AI: Algorithms enable drones to learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions based on incoming data.
Swarm Formation and Coordination:
- Formation Flying: Algorithms enable drones to maintain specific formations for different purposes, like maximizing coverage or minimizing vulnerability.
- Collaborative Tasks: Drones can collaborate to perform tasks collectively, such as mapping an area, delivering payloads, or conducting surveillance.
Applications of Swarm Drones:
Military and Defense:
- Surveillance and Reconnaissance: Swarm drones can cover vast areas, gather intelligence, and monitor enemy movements.
- Target Identification and Attack: They can identify and engage targets collectively, enhancing precision and efficiency.
- Electronic Warfare: Swarm drones can disrupt enemy communication systems or provide electronic support.
Civilian and Commercial:
- Search and Rescue: Swarm drones can cover large areas quickly, aiding in locating missing persons or disaster-stricken areas.
- Agriculture: They assist in crop monitoring, spraying pesticides, and assessing field conditions.
- Entertainment and Light Shows: Used for spectacular aerial displays during events and celebrations.
Infrastructure and Maintenance:
- Inspections: Swarm drones can inspect infrastructure like pipelines, power lines, and buildings more efficiently.
- Construction: They might assist in tasks like 3D mapping, material transport, and building maintenance.
Indian scenario:
- Several Indian startups and organizations have made notable strides in developing indigenous swarm drones capable of surveillance and performing attack missions.
Winners of Indian Air Force Swarm Drone Competition:
- NewSpace Research & Technologies Pvt Ltd: Led by former IAF officer Sameer Joshi, NewSpace won the ''swarm architecture'' award in the Indian Air Force''s competition. They secured a significant USD 15 million swarm drone order from the Indian Army. Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd. is supporting NewSpace in developing these drones.
- Flaire Unmanned Systems Pvt. Ltd. (Incubated by Delhi Technology University): This team partnered with Adani Defence and won the ''communication architecture'' award in the competition.
- Dhaksha Unmanned Systems: Awarded the ''drone architecture'' award in the competition, showcasing their expertise in designing advanced drone architectures.
DRDO''s Swarm Drone Technology Showcase:
- In November 2021, the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) showcased armed swarm technology designed for minimal human intervention.
- These drones are designed to operate in high-altitude regions, rough weather conditions, and boast a speed of 100 km/h.
- Notably, they possess the capability to strike multiple drones at a target, enhancing their effectiveness in combat scenarios.
Indian Air Force Initiatives:
- The Indian Air Force launched the Mehar Baba Swarm Drone Competition in 2018 to promote drone development.
- This three-year-long competition aimed to encourage different organizations to innovate and contribute to the advancement of swarm drone technology.
International Examples of Swarm Drone Deployment:
- The use of swarm drones has also been demonstrated on the international stage, notably by the Israeli Defence Forces.
- They utilized swarm drones to locate rocket launchers situated in Gaza, showcasing the effectiveness of these technologies in reconnaissance and target identification.
The development and acquisition of these systems underscore the IAF''s proactive approach in countering evolving threats from unmanned aerial systems, particularly swarm drones, and aim to bolster India''s defense capabilities against such threats in varied operational environments. These counter-drone systems represent a concerted effort to harness technology to safeguard against the growing challenges posed by drones in military and security contexts.
Karnataka HC asks authorities to remove encroachments of Bahmani Sultans'' fort in Kalaburagi
The Karnataka High Court directed the Kalaburagi district authorities to remove encroachments from the historical fort of Bahmani Sultans in the city.
- The Bahmani Sultanate, also known as the Bahmanid Empire, was a significant medieval Muslim state in the Deccan region of South India.
- It was established by Ala-ud-Din Hasan Bahman Shah in 1347 and lasted until 1527 when it fragmented into five smaller states.
Foundation and Expansion
- Establishment by Hasan Bahman Shah: The Bahmani Sultanate was founded by Hasan Bahman Shah, a governor appointed by the Delhi Sultanate. He declared independence and established his capital at Gulbarga.
- Territorial Expansion: Under subsequent rulers, especially during the reigns of Muhammad Shah I and Firuz Shah, the Bahmani Sultanate expanded its territories across the Deccan region, encompassing areas such as Gulbarga, Bidar, Bijapur, and Golconda (modern-day Hyderabad).
Administration and Governance
- Feudal System: The Sultanate was administratively divided into four provinces (Daulatabad, Bidar, Berar, and Gulbarga) with tarafdars or subedars governing each. The sultanate was governed through a decentralized feudal system. Provinces were ruled by governors known as walis or nayaks, who held considerable power in their respective regions.
- Central Administration: The sultanate had a centralized administrative structure with key departments handling revenue, justice, and military affairs.
Cultural and Socio-Economic Development
- Patronage of Arts and Culture: The Bahmani rulers were patrons of art, literature, and architecture. They encouraged the development of Deccani culture, which was a blend of Persian and Indian influences. Notable structures include Gulbarga''s Jama Masjid, Bidar''s Rangeen Mahal, and Bijapur''s Gol Gumbaz. Urdu, Persian, and Arabic literature flourished during this period.
- Promotion of Regional Languages: The Bahmani court supported the use of local languages like Dakhni (early form of Urdu) and Kannada, contributing to their literary growth.
- Economic Prosperity: Trade and commerce flourished in the Bahmani Sultanate due to its strategic location. The region was a center for international trade, particularly in horses, textiles, and spices.
Religious Policies
- Religious Tolerance: The sultans followed a policy of religious tolerance, allowing diverse religious communities like Hindus, Muslims, Jains, and Christians to coexist peacefully.
- Promotion of Syncretic Culture: The sultanate''s cultural milieu was marked by the syncretic blending of different religious traditions and practices.
Decline and Fragmentation
- Internal Strife and Dynastic Conflicts: As the Bahmani Sultanate expanded, internal conflicts and power struggles among the nobility weakened its unity.
- Rise of Five Successor States: In 1527, the sultanate disintegrated into five smaller states known as the Deccan Sultanates: Ahmadnagar, Bijapur, Golconda, Berar, and Bidar, each ruled by independent rulers.
Rulers
Founding Ruler:
- Ala-ud-Din Hasan Bahman Shah (1347-1358):
- Founder of the Bahmani Sultanate after declaring independence from the Delhi Sultanate.
- Established Gulbarga as the capital and began the Sultanate''s expansion in the Deccan region.
Early Rulers:
- Muhammad Shah I (1358-1375):
- Consolidated power and expanded Bahmani territories.
- Shifted the capital to Bidar.
- Promoted art, literature, and culture.
- Firuz Shah (1397-1422):
- Extended Bahmani rule further into the Deccan and introduced administrative reforms.
- Encouraged trade and commerce, contributing to economic prosperity.
Golden Age Rulers:
- Ahmad Shah I (1422-1436):
- Notable for his patronage of art and culture, fostering a thriving cultural scene.
- Facilitated the development of the Dakhni language (early form of Urdu).
- Alauddin Ahmad Shah II (1436-1458):
- Continued the cultural and literary advancements initiated by his predecessors.
- Faced internal revolts and external threats during his reign.
- Mahmud Gawan (1466 to 1481):
- Sultanate witnessed its zenith.
- Gawan''s military campaigns expanded the Sultanate''s territory, including the reconquest of Goa from Vijayanagar.
Later Rulers:
- Mahmud Shah I (1482-1518):
- Ruled during a period of internal turmoil and external invasions.
- Struggled to maintain unity among the nobility, leading to the weakening of the Sultanate.
- Kalim Allah (1518-1527):
- Last ruler of the unified Bahmani Sultanate.
- His reign witnessed escalating conflicts and a fragmented administration.
Fragmentation and Successor States:
- Krishnadeva Raya of the Vijayanagar Empire''s military campaigns fractured the Bahmani Sultanate into five smaller states known as the Deccan Sultanates:
- Ahmadnagar Sultanate: Founded by Ahmad Nizam Shah I.
- Bijapur Sultanate: Established by Yusuf Adil Shah.
- Golconda Sultanate: Founded by Quli Qutb Shah.
- Berar Sultanate: Ruled by Fathullah Imad-ul-Mulk.
- Bidar Sultanate: Established by Amir Barid.
- Each of these successor states operated independently, contributing to the cultural, artistic, and political landscape of the Deccan region.
- Battle of Talikota (1565): The conflict between the Deccan Sultanates and the Vijayanagar Empire culminated in the catastrophic Battle of Talikota, resulting in Vijayanagar''s downfall.
- Mughal Annexation: Subsequently, the Mughal Empire, notably under Akbar and later Aurangzeb, annexed the Deccan Sultanates into their dominion, marking the end of the Bahmani legacy.
- The Bahmani Sultanate, despite its fragmentation, left a lasting legacy in South India, influencing the region''s culture, architecture, and language, and shaping the course of history in the Deccan
The Bahmani Sultanate played a transformative role in South India''s history, establishing Islamic rule, contributing to the region''s cultural richness through architecture and literature, and shaping the political landscape. Its rise, conflicts with Vijayanagar, internal strife, and ultimate fragmentation into the Deccan Sultanates remain pivotal episodes in India''s historical tapestry, illustrating the complex interplay of power, culture, and regional dynamics during medieval times.
India receives two ''Romeo'' helicopters
Indian Navy has received the sixth MH-60R “Romeo” helicopter from Lockheed Martin.
- The company expects to complete the delivery of all the MH-60R choppers that India ordered by 2025.
Procurement and Specifications
- Acquisition and Cost: India signed a contract to acquire 24 MH-60R helicopters from the United States for $2.6 billion. The deal includes India-specific modifications and weaponry, such as Hellfire air-to-surface missiles and Mark 54 anti-submarine torpedoes.
- Operational Range and Capabilities:
- The MH-60R Seahawk is renowned for its multi-role capabilities, ranging from anti-submarine warfare (ASW) to maritime surveillance, anti-smuggling, anti-piracy, and search-and-rescue missions.
- Equipped with advanced sensors, systems, and weapons, the helicopter provides a comprehensive and versatile platform for various naval operations.
Deployment and Operational Significance
- Aircraft Carrier Operations:
- These helicopters are intended to be deployed on India''s aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya, significantly enhancing its aerial capabilities.
- Successful landings of MH-60R helicopters on indigenously built aircraft carrier INS Vikrant and destroyer INS Kolkata demonstrate their compatibility and readiness for carrier-based operations.
- Strategic Maritime Security:
- The induction of MH-60R helicopters enhances India''s maritime security posture by significantly boosting the Navy''s anti-submarine and anti-surface warfare capabilities.
- The helicopters play a pivotal role in patrolling critical maritime zones, safeguarding territorial waters, and countering maritime threats.
- Versatility and Operational Flexibility:
- The MH-60R''s adaptability for various missions ensures operational flexibility, making it an asset for combating diverse maritime challenges, including piracy, smuggling, and search-and-rescue operations.
Indigenous Integration and Future Plans
- India-Specific Modifications:
- The helicopters are undergoing India-specific modifications, likely tailored to suit the Indian Navy''s operational requirements and maritime environment.
- Strategic Partnership with the United States:
- The procurement underscores the strategic partnership between India and the United States in defense cooperation, providing India with access to advanced military technology and equipment.
- The MH-60R Seahawk helicopter, commonly known as the "Romeo," is a versatile and advanced maritime helicopter primarily operated by the United States Navy (USN).
- It serves as a multi-mission platform designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-surface warfare (ASuW), search and rescue (SAR), and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions.
Design and Capabilities:
- Variant of Sikorsky''s Seahawk Helicopter: The MH-60R is derived from the Sikorsky S-70B Seahawk and is built by Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation, now a part of Lockheed Martin.
- Advanced Sensors and Systems:
- The helicopter is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and systems, including the AN/APY-9 radar, sonobuoys, acoustic sensors, electronic support measures (ESM), and radar warning receiver (RWR), enabling comprehensive surveillance and threat detection capabilities.
- Weapons and Armament:
- It carries a range of advanced weapons, such as Hellfire missiles, Mark 54 torpedoes, and precision-guided rockets, making it effective in both anti-submarine and anti-surface warfare operations.
- Multi-Mission Capabilities:
- The MH-60R''s versatility allows it to conduct various missions, including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, search and rescue, medical evacuation, and maritime surveillance.
Operational Features:
- Enhanced Maritime Surveillance:
- Its advanced sensor suite allows for effective monitoring of surface vessels and submarines, detecting and tracking potential threats in maritime environments.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW):
- Equipped with sophisticated sonar systems, it can detect and engage submarines using torpedoes and depth charges.
- Anti-Surface Warfare (ASuW):
- Capable of engaging and neutralizing surface threats with precision-guided missiles and rockets.
- Search and Rescue (SAR):
- Its capacity for medical evacuation and SAR operations makes it an asset in saving lives during maritime emergencies.
International Deployment:
- International Operators:
- Apart from the US Navy, several other countries operate or have ordered the MH-60R for their naval fleets, including Australia, Denmark, Saudi Arabia, India, and others.
- Modernization and Upgrades:
- Continuous upgrades and modernization programs ensure that the MH-60R remains at the forefront of maritime helicopter technology, incorporating new sensors, weapons, and systems.
The induction of MH-60R Seahawk helicopters represents a significant leap in India''s maritime capabilities, particularly in anti-submarine warfare and multi-role naval operations. Their deployment on aircraft carriers and other naval assets reinforces India''s commitment to enhancing maritime security and signifies a vital step towards bolstering its naval force in the Indian Ocean Region.
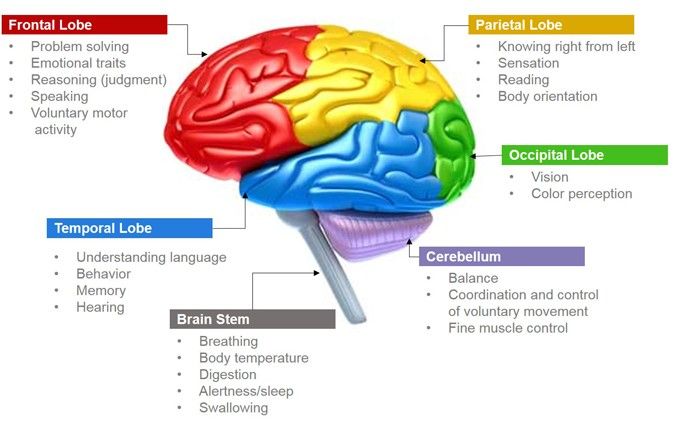
Cryo-EM reveals TAF15 as potential treatment target for frontotemporal dementia
An international team of researchers, which includes specialists from Indiana University School of Medicine, has discovered a protein that is present in the brains of patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD). This discovery reveals a new potential target for developing treatments for FTD.
- The research findings shed light on a significant discovery regarding frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and its association with a protein called TAF15. This protein has been identified to form amyloid filaments in nerve cells of the brain and spinal cord, contributing to neurodegenerative disorders.
Key Points
- Nature of FTD: FTD, a type of dementia, results from neuronal injury in the brain''s frontal and temporal lobes. It manifests with symptoms like unusual behaviours and emotional disturbances, often appearing in individuals aged 25 to 65.
- Role of TAF15: The study reveals that TAF15 protein forms amyloid filaments in brain and spinal cord cells in cases of FTD, potentially leading to the onset of this type of dementia.
- Research Methodology: The team, utilizing advanced cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) at atomic resolution, examined protein aggregates from the brains of individuals with FTD and motor weakness. Their analysis identified the presence of TAF15 amyloid filaments in multiple brain regions, including nerve cells of the motor system.
- Significance of Discovery: Neuropathologist highlights the importance of this breakthrough. Recognizing TAF15 as a potential target opens avenues for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to address this lesser-known form of frontotemporal lobar degeneration linked with FTD.
Implications
- Diagnostic Advancements: Understanding the role of TAF15 in FTD can aid in developing diagnostic tools for early detection of this form of dementia.
- Therapeutic Prospects: Identification of TAF15 as a potential target could lead to the development of therapeutic interventions to mitigate or prevent the progression of FTD associated with this protein.
- Research Direction: This discovery may pave the way for further investigations into TAF15-related mechanisms underlying FTD and related neurodegenerative disorders.
Frontotemporal dementia
- Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a term that covers a range of brain disorders that affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, which are responsible for personality, behaviour and language.
- FTD is different from Alzheimer''s disease, which mainly affects memory and cognition.
- It usually starts at a younger age, between 40 and 65 years old, and can cause dramatic changes in how a person thinks, acts and communicates.
- Some people with FTD may also develop movement problems, such as stiffness, tremors, muscle weakness or difficulty swallowing. These symptoms are similar to those seen in Parkinson''s disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
- In some cases, FTD may be linked to genetic mutations or inherited from a family member.
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis of FTD can be challenging, as it can be mistaken for other conditions, such as depression, bipolar disorder or schizophrenia.
- There is no specific test for FTD, but doctors may use brain scans, blood tests, neuropsychological tests and interviews to rule out other causes and identify the type of FTD.
- The progression of FTD varies from person to person, but it usually worsens over time and leads to severe disability and dependence.
Cure
- There is no cure for FTD, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life of people with FTD and their caregivers. These include medications, behavioural therapies, speech therapy, occupational therapy and physical therapy.
- Support groups, counselling and education can also help people cope with the emotional and social challenges of living with FTD.
|
Human Brain
●The human brain can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem. Each part has a different role and is made up of several subparts. Cerebrum ●The cerebrum is the largest and most visible part of the brain. It occupies the upper part of the skull and consists of two hemispheres (left and right) that are connected by a bundle of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum. ●It is covered by a thin layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex, which has many folds and grooves to increase its surface area. ●The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, language, creativity, and problem-solving. It also processes sensory information from the eyes, ears, nose, skin, and other organs. Cerebellum ●The cerebellum is located at the lower back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It is smaller than the cerebrum but has more neurons (nerve cells). ●It is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, posture, and fine motor skills. It also plays a role in learning and memory. Brainstem ●The brainstem is located at the base of the brain, where it connects to the spinal cord. It consists of three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. ●The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting. It also regulates sleep cycles and consciousness. |
Conclusion
- The research represents a significant step forward in unravelling the molecular mechanisms behind FTD, offering potential avenues for targeted treatments and an improved understanding of this complex neurological condition.
What is ketamine, the drug involved in Actor Matthew Perry’s death?
In recent years, ketamine has become a subject of widespread debate for its increased use in treating depression and serious mental health issues. While some experts and patients lauded it as lifesaving, others criticized it as addictive.
Ketamine
- Ketamine is a dissociative anaesthetic hallucinogen that has been used as an anaesthetic for animals since the 1960s and was later approved for human use by the US Food and Drug Administration.
- It is known for creating a feeling of detachment from pain and the environment. In recent years, ketamine has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects in treating depression and other serious mental health issues, especially in cases where traditional therapies have not been effective.
Methods of Consumption
- Patients with mental health issues typically take ketamine through an IV, nasal spray, or tablet once or twice a week for a specified treatment period.
- For recreational purposes, ketamine is often snorted as a white crystalline powder. It can also be injected or smoked.
Effects of Ketamine
- Some patients undergoing ketamine treatment report positive experiences, describing it as a "reset button for the brain." During treatment sessions, individuals may have pleasant visualizations and a sense of detachment, leading to a reduction in the perceived weight of daily problems.
- Ketamine affects brain receptors that traditional antidepressants do not target, leading to a psychedelic-like experience. This aspect is considered by many to be integral to the drug''s therapeutic effect.
Safety Considerations
- When used for medicinal purposes and in the right doses, some doctors argue that ketamine can be safe and effective in treating mental illnesses.
- There are concerns about potential addiction and health risks, especially when taken chronically in high doses. Chronic use may lead to severe bladder damage, and there are indications that abuse could result in cognitive impairment.
- There is limited research on prolonged ketamine treatment and its safety. Additionally, there is a lack of literature on addiction and abuse among medical users.
The safety and efficacy of ketamine, especially in non-medical settings, remain topics of ongoing research and debate. When used under medical supervision, ketamine can be a valuable tool for anaesthesia and potentially for certain mental health conditions, but its recreational use poses significant health risks.
Covid-19 JN.1 Highlights
The detection of the JN.1 sub-variant of COVID-19 in Kerala has triggered several responses and concerns.
- The JN.1 sub-variant, currently spreading in the US and China was identified in Kerala through routine surveillance by INSACOG (Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium).
- The case was discovered in Karakulam, Thiruvananthapuram, in a sample that tested positive on November 18. The patient experienced mild influenza-like illness (ILI) symptoms and has since recovered.
- The Union Health Ministry is actively coordinating with state health authorities and conducting mock drills across health facilities nationwide to assess their readiness and preparedness by December 18.
- JN.1 is closely related to the Pirola variant (BA.2.86) and carries one additional mutation in the spike protein compared to its relative.
Concerns and Observations
- An increasing trend of COVID-19 cases in Kerala, attributed partially to heightened testing of ILI cases, has been noted. Most cases are mild and recovering at home.
- Despite generally low global COVID-19 cases this year, a slight rise has been observed in early December, especially with the emergence of JN.1 in the US, China, and Singapore.
The detection of the JN.1 sub-variant of COVID-19 in Kerala prompts health authorities to initiate coordinated efforts. Despite its global prevalence, updated vaccines have shown efficacy against related variants, emphasizing the importance of ongoing preventive measures in managing the evolving landscape of COVID-19.
Surat Diamond Bourse: World''s Biggest Office Space
The inauguration of the Surat Diamond Burse by the Prime Minister marks a significant milestone in the diamond industry.
Surat Diamond Burse
World''s Largest Corporate Office
- Located in Khajod village near Surat, the Surat Diamond Bourse stands as the world''s largest corporate office hub.
- Built across 35.54 acres at a cost of Rs 3,400 crore, it surpasses the Pentagon, which held the title for the world''s largest office building for the past 80 years.
Boost to Diamond Industry
- Prime Minister emphasized the immense significance of this inauguration for the diamond industry.
- The facility includes a Customs Clearance House, Jewellery Mall, and International Banking and Safe Vaults, aiming to bolster the diamond trade.
Global Centre for Diamond Trading
- With the capacity to accommodate 4,200 traders from 175 countries, the Bourse is positioned to be a global hub for rough and polished diamonds.
- It offers a platform for diamond buyers worldwide to conduct trade activities in Surat.
Environmental Sustainability
- Despite its size, the Surat Diamond Bourse prioritizes minimizing environmental impact by following the principles of Panchtattva, aligning with nature''s five elements.
Innovative Energy Solutions
- The building showcases advanced rooftop solar energy projects implemented by URON Energy, promoting sustainability in its operations.
- It employs a radiant cooling system, highlighting innovative and eco-friendly technological features.
Symbol of Entrepreneurial Spirit
- PM hailed the significance of this structure, citing it as a testament to India''s entrepreneurial spirit and Surat''s historical contribution to the diamond trade.
- It is expected to function as a hub for trade, innovation, collaboration, and economic growth, generating employment opportunities.
|
Indian Diamond Industry ● India accounts for roughly 80% of the world''s polished diamonds by volume and 60% by value. ●Surat, India, is the undisputed diamond polishing capital, followed by Mumbai and Jaipur. ●India produces diamonds of all sizes and qualities, catering to diverse markets and budgets. ●The industry generates significant employment, contributing to India''s GDP and foreign exchange earnings. Over a million people are directly employed, with millions more indirectly benefiting. ●Concerns include rough diamond price fluctuations, dependence on imports, labour issues, and competition from other countries. |
- The Surat Diamond Bourse''s inauguration reflects a convergence of technological advancement, environmental consciousness, and economic aspirations, positioning itself as a pivotal centre for the global diamond trade while embracing sustainability.
Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
The Railway Minister clarified that the approximately 26,000 individuals who underwent training through the "Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana" until November 2023 would not be given priority for employment within the Indian Railways.
Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
- The Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana (RKVY) is a skill development initiative launched by the Ministry of Railways in collaboration with the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and the Sector Skill Councils (SSCs).
- RKVY is aligned with the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) and follows the standards and guidelines of the National Skill Development Agency (NSDA).
RKVY has three components
Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL)
- This component involves the assessment and certification of existing skills and competencies of railway employees based on their work experience and performance.
- RPL helps in validating and recognizing the skills acquired through informal or non-formal learning. RPL also helps in identifying the skill gaps and training needs of the employees.
Short Term Training (STT)
- This component involves the provision of short-term training courses to railway employees to bridge the skill gaps and upgrade their skills.
- STT courses are designed and delivered by NSDC-approved training partners in accordance with the National Occupational Standards (NOS) and Qualification Packs (QPs) developed by the SSCs. STT courses are conducted at railway premises or nearby locations for the convenience of the employees.
Train the Trainer (TTT)
- This component involves the training and certification of railway trainers and assessors who can conduct RPL and STT for other railway employees.
- TTT courses are conducted by NSDC-approved master trainers who have expertise in pedagogy, assessment and quality assurance. TTT courses are also aligned with the NOS and QPs of the respective trades and skills.
Key points about the Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana:
Objective
- The primary goal is skill enhancement. It aims to equip young individuals with technical skills that are in demand across different industries, thereby increasing their chances of employability or enabling them to start their businesses.
Training Focus
- The program provides entry-level skill training in diverse technical trades. Candidates undergo training in specific trades and receive certificates upon successful completion of the program.
Youth Empowerment
- The initiative is aimed at empowering unemployed youths by enhancing their skills, which can lead to better employment opportunities or encourage them to venture into entrepreneurship.
No Guarantee for Railway Jobs
- One crucial aspect highlighted by the Railway Minister is that completing this program does not assure candidates preferential treatment or job placements within the Indian Railways. The focus of the program is on skill development rather than guaranteeing employment within the railway sector.
Entrepreneurship Promotion
- Besides enhancing employability, the program encourages candidates to consider starting their own ventures or entrepreneurial initiatives. This could include using the acquired skills to create small businesses or startups.
Lack of State-wise Data
- The Indian Railways does not maintain state-wise data of candidates enrolled in the Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana. This indicates a broader approach aimed at skill development for youths across the country without focusing on specific regional statistics.
Overall Impact
- The initiative aims to contribute to the broader goal of skill development in India''s youth population. By enhancing skills and promoting entrepreneurship, it seeks to create a more capable and job-ready workforce.
- The Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana serves as a valuable initiative to empower young individuals by providing technical skills and certificates, its primary focus is on skill enhancement and fostering an entrepreneurial spirit rather than guaranteeing job placements within the Indian Railways. The aim is to equip the youth with skills that make them more employable across various industries or enable them to create their pathways in the job market.
Nyholm Prize
Professor Savita Ladage from the Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), has been awarded the prestigious Royal Society of Chemistry''s (RSC) Nyholm Prize for Education in recognition of her outstanding contributions to chemistry education.
- Professor Savita Ladage received the Royal Society of Chemistry’s Nyholm Prize for Education is a significant recognition of her exceptional contributions to chemistry education.
- Professor Ladage''s primary focus on advocating the significance of chemical education has been instrumental.
- Her efforts extend to mentoring chemistry educators and leading various programs benefiting teachers and students in advancing chemistry education across India.
- The Royal Society of Chemistry''s Nyholm Prize acknowledges her remarkable dedication to chemistry education. It places her among a group of esteemed individuals who have made significant contributions to the field.
- The award, comprising £5,000, a medal, and a certificate, reflects her outstanding commitment and influence in this domain.
The Nyholm Prize celebrates exceptional individuals contributing to various levels of education in the chemical sciences. This recognition extends to teachers, technicians, and others involved in shaping and advancing education in chemistry.
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra
The "Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra" is a nationwide campaign launched by the Government of India to promote the development and progress of the country.
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra
- It is a government initiative aimed at raising awareness about and monitoring the implementation of various flagship central schemes across India. These schemes include Ayushman Bharat, Ujjwala Yojana, PM Suraksha Bima, PM SVANidhi, and others.
- The program is a collaborative effort involving various Union ministries and state governments.
- It was flagged off by the Prime Minister on December 16, with the initial launch in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Telangana, and Mizoram—states where recent Assembly polls were held.
- The Yatra had started earlier in other states but was delayed in these five states due to the Model Code of Conduct being in place before the elections.
- The Yatra began on November 15 from Khunti, Jharkhand. In just one month, it reached over 2.50 crore citizens across 68,000 Gram Panchayats in the country.
The program has four primary objectives:
- Reaching out to the vulnerable: The Yatra aims to identify and connect with individuals who are eligible for various government schemes but have not yet availed of the benefits.
- Dissemination of information and generating awareness: The initiative focuses on spreading information about government schemes and creating awareness among the public.
- Interaction with beneficiaries through personal stories/experience sharing: The Yatra involves engaging with beneficiaries of government schemes, allowing them to share their personal stories and experiences with the implemented programs.
- Enrollment of potential beneficiaries: During the Yatra, efforts are made to enrol potential beneficiaries by collecting details and information from participants.
The "Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra" is a unique opportunity for the people of India to witness and celebrate the development and progress of their country. It serves as a platform for expressing aspirations and expectations for the future, reflecting the collective resolve and commitment of the people to make India a developed, empowered, and self-reliant nation.
SUVAS and SUPACE
The UK judiciary allows judges in England and Wales to use generative AI, for tasks such as text summarization, presentations, and emails.
- The "Guidance for Judicial Office Holders" issued in the UK emphasizes the need for cautious use of AI tools by judges, outlining potential risks and indications of AI-generated content in legal work.
- The document advises judges to be vigilant about signs suggesting the use of AI in legal arguments, such as unfamiliar case references, foreign citations, inconsistent legal submissions, American spellings, or persuasive yet erroneous content.
Potential Risks Associated with AI Use in Legal Practice
- Lack of Authoritative Information: Public AI chatbots may not retrieve answers from credible databases.
- Algorithmic Text Generation: AI tools produce text based on algorithms and training data, often predicting likely word combinations, potentially leading to inaccurate or biased output.
- Quality of Information: Information retrieved from AI tools might be incomplete, misleading, or biased, especially as current models are heavily influenced by US law.
- Privacy Concerns: Caution against entering private information into public AI chatbots due to data retention and sharing, suggesting the potential publication of inputted information.
- Mitigation Strategies: Suggestions include disabling chat history, limiting AI access to information, and reporting unintentional disclosures of private data.
Examples of Misuse in UK and US Cases
- Instances were cited where fabricated or fictitious legal arguments generated by AI were used in courts, leading to case rejections or sanctions against legal practitioners.
Indian Courts'' Engagement with AI:
- Punjab & Haryana HC''s ChatGPT Inquiry: Justice Anoop Chitkara sought ChatGPT''s response in a bail plea, emphasizing that any reference to ChatGPT aimed to illustrate bail jurisprudence but wasn''t considered conclusive.
- Supreme Court''s AI Tools: The Supreme Court of India developing tools like Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software (SUVAS) for language translation and the Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court’s Efficiency (SUPACE) for collecting and presenting relevant legal information to judges.
Supreme Court Vidhik Anuvaad Software (SUVAS)
- An AI-powered platform for translating judicial documents between English and nine vernacular languages: Hindi, Marathi, Kannada, Tamil, Telugu, Punjabi, Gujarati, Malayalam, and Bengali.
- Significance:
- Promotes access to justice by bridging the language barrier for non-English speaking litigants and legal professionals.
- Enhances understanding of legal proceedings and empowers individuals to participate effectively.
- Reduces reliance on human translators, saving time and resources.
- Contributes to the preservation and dissemination of legal knowledge in various languages.
Supreme Court Portal for Assistance in Court’s Efficiency (SUPACE)
- A comprehensive online platform providing judges with access to relevant legal information and tools to support their decision-making processes.
- Features:
- Case database with searchable judgments, orders, and precedents.
- Legal research tools for finding relevant statutes, rules, and commentary.
- Data analytics and visualization capabilities to identify trends and patterns in case law.
- Real-time case updates and notifications.
- Significance:
- Improves judicial efficiency by streamlining access to information and reducing time spent on research.
- Promotes consistency and predictability in judicial decisions by providing judges with a centralized repository of relevant precedents.
- Enhances transparency and accountability in the judicial process by making relevant information readily available to the public.
SUVAS and SUPACE aim to:
- Bridge the digital divide and promote inclusivity: Making legal information and processes accessible to a wider population regardless of language barriers or technological expertise.
- Improve the quality of justice: By providing judges with better tools for research and decision-making, these platforms can help ensure well-informed and consistent rulings.
- Increase efficiency and transparency: Streamlining processes and making information readily available can save time and resources, while also promoting public trust in the judiciary.
Challenges and Future Outlook
- Both initiatives face challenges like ensuring data accuracy, managing privacy concerns and adapting to technological advancements. However, their potential benefits are undeniable. With continued development and refinement, SUVAS and SUPACE can significantly contribute to a more efficient, accessible, and equitable Indian legal system.
- The guidance aims to ensure that while AI tools can be beneficial for certain tasks, they should be used judiciously, particularly in legal research and analysis, considering the potential implications on judicial decisions and the administration of justice.
UNIDROIT
India’s Uma Sekhar was elected to the governing council of the International Institute for the Unification of Private Law (UNIDROIT) in an election.
UNIDROIT
- UNIDROITis an intergovernmental organization whose objective is to harmonize private international law across countries through uniform rules, international conventions, and the production of model laws, sets of principles, guides and guidelines.
Origins
- Established in 1926 as part of the League of Nations, it was re-established in 1940 following the League''s dissolution through a multilateral agreement, the UNIDROIT Statute.
Members
- As of 2023 UNIDROIT has 65 member states.
UNIDROIT’s Convention
- UNIDROIT has prepared multiple conventions (treaties), but has also developed soft law An example are the UNIDROIT Principles of International Commercial Contracts.
- Distinctly different from the Convention on the International Sale of Goods (CISG)adopted by UNCITRAL, the UNIDROIT Principles do not apply as a matter of law, but only when chosen by the parties as their contractual regime.
Seat
- The seat of UNIDROIT is in Rome, Italy.
Membership
- Membership of UNIDROIT is restricted to States acceding to the UNIDROIT Statute.
- UNIDROIT’s 65 Member States are drawn from the five continents and represent a variety of different legal, economic and political systems as well as different cultural backgrounds.
Funding
- The Institute is financed by annual contributions from its Member States which are fixed by the General Assembly.
- Extra-budgetary contributions may be made to fund specific projects or activities
Structure
- UNIDROIT has an essentially three-tiered structure, made up of a Secretariat, a Governing Council and a General Assembly. The Secretariat is the executive organ of UNIDROIT responsible carrying out its Work Programme from day to day.
- It is headed by a Secretary-General appointed by the Governing Council on the nomination of the President of the Institute.
- The Secretary-General is assisted by a team of international civil servants and supporting staff.
Annual Reports on the activity of UNIDROIT
- The Governing Councilsupervises all policy aspects of the means by which the Institute’s statutory objectives are to be attained and in particular the way in which the Secretariat carries out the Work Programme drawn up by the Council. It is made up of one ex officio member, the President of the Institute, and 25 elected Members, mostly eminent judges, practitioners, academics and civil servants. The Governing Council is chaired by the President of the Institute who is a Member of the Council ex officio.
- The General Assembly is the ultimate decision-making organ of UNIDROIT: it votes the Institute’s Budget each year; it approves the Work Programme every three years; it elects the Governing Council every five years.
- It is made up of one representative from each member Government. The Presidency of the General Assembly is held, on a rotating basis and for one year, by the Ambassador of one of the Organisation’s member States.
Governing Council
- The Governing Council consists of 25 positions which are held by distinguished legal experts.
Languages
- The official languages of UNIDROIT are English, French, German, Italian and Spanish; its working languages are English and French.
Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB)
Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB), launched a programme in Saint Lucia on 14 December 2023.
Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB)
- Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) is a joint initiative of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) supporting countries in building tax audit capacity.
- TIWB Programmes complement the broader efforts of the international community to strengthen cooperation on tax matters and contribute to the domestic resource mobilisation efforts of developing countries.
- TIWB facilitates well-targeted, specialized tax audit assistance in developing countries around the world.
- Under TIWB tax audit experts work alongside local officials of developing country tax administrations on tax audit and tax audit-related issues.
- TIWB aims to transfer technical know-how and skills to developing countries'' tax auditors, as well as shared general audit practices.
Binsar Wildlife Sanctuary
- In a remarkable discovery, a tiger was spotted for the first time at Binsar Wildlife Sanctuary.
Binsar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Binsar Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the foothills of Himalayas in Almora district of Uttarakhand.
- The peak point known as Jhandi Dhar is at an elevation of 2412 meters.
- Apart from protecting wildlife, the sanctuary was established with an aim to conserve the broad leaf oak forests, mainly located in the Central Himalayan region.
- Binsar was the summer capital of the Chand Kings, who ruled Kumaon from the 11th to 18th centuries.
- The sanctuary has been declared an Important Bird Area by Bird Life International as there are more than 200 species of birds in the sanctuary, including Fork tail, Blackbirds, Laughing Thrush, Pheasant, Nuthatches, Parakeets and Monal.
European Bison
The ongoing war in Ukraine could affect the efforts to save European Bison.
European Wood Bison
- The European Wood Bison, also known as the wisent is a European species of bison.
- It is one of two extant species of bison, alongside the American bison.
- The European bison is the heaviest wild land animal in Europe, and individuals in the past may have been even larger than their modern-day descendants.
- During late antiquity and the Middle Ages, bison became extinct in much of Europe and Asia, surviving into the 20th century only in northern-central Europe and the northern Caucasus Mountains. During the early years of the 20th century, bison were hunted to extinction in the wild.
- The species – now numbering several thousand and returned to the wild by captive breeding programmes – is no longer in immediate danger of extinction, but remains absent from most of its historical range.
- The European bison is one of the national animals of Poland and Belarus.
- The European bison (Bison bonasus), Europe''s largest land mammal, has moved from Vulnerable to Near Threatened due to continued conservation efforts.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies