- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Explain the formation of the polar vortex. Why is Polar vortex shifting southward?. Examine the implications of such an increased frequency of shift in Asia.
A polar vortex refers to an expanse of cold air that generally circles the Arctic region but occasionally shifts south from the North Pole. It is held in place by the Earth’s rotation and temperature differences between the Arctic and mid-latitudes.
In the Northern Hemisphere, it tends to be much farther north than the jet stream, a strong river of wind that separates Arctic air to the north and much warmer air to the south. While the jet stream is present year-round, the polar vortex only occurs in winter. The polar vortex usually does not have much impact on weather beyond the poles, but occasionally the polar vortex becomes disrupted: when the jet stream moves south, cold air from the polar vortex can plunge farther south as well.
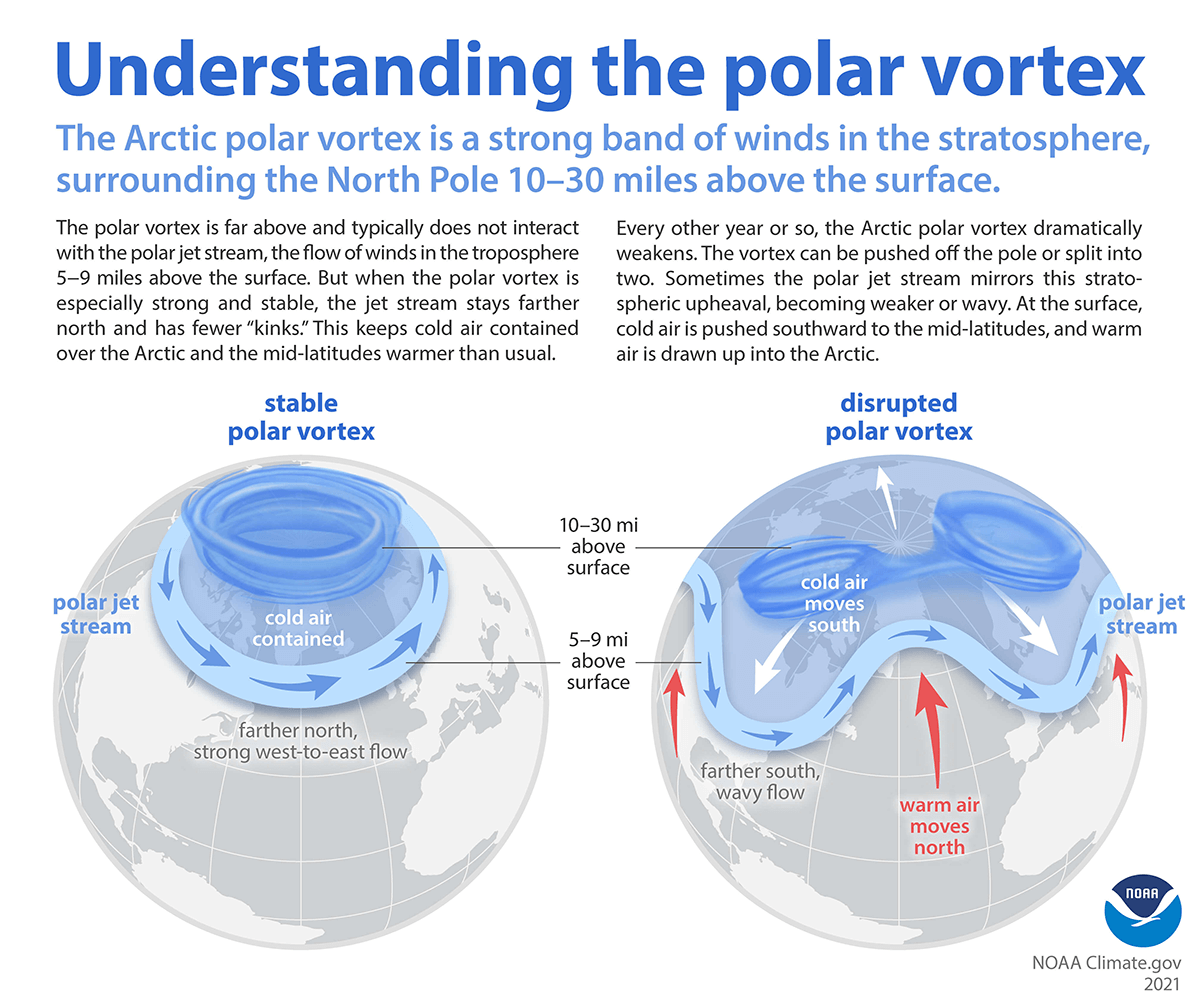
This shift happens naturally but now is expected to increase due to climate change:
- When variations in temperatures grow between arctic and mid-latitudes, the polar vortex can shift south. This is expected to increase as temperatures are turning erratic.
- In long term, the weakening of the polar jet stream is expected to lead to this shift: warming of the Earth has led to the loss of Arctic sea ice, transforming a highly reflective icy surface to a dark absorptive surface. It is warming higher latitudes and reducing the temperature difference between the warmer mid-latitude and polar regions. This weakens and destabilizes the polar jet stream, causing it to dip into lower latitudes, bringing polar air farther south.
However, there is still a lack of uncertainty about the exact impact of climate change on the intensity and severity of these changes.
A polar vortex this year in Asia has led to extreme winters. Thus such a shift can substantially impact Asia:
- Human impacts. Hundreds of millions of people across East Asia have suffered from the cold temperatures, with cold wave conditions in many states of India in mid-January.
- These effects are aggravated by other conditions such as droughts. Evidence came up suggesting that recent droughts in Asia have made the region more susceptible to temperature extremes with more than 150 people dying due to cold in Afghanistan in the last twenty days.
- Such cold conditions cause material loss also for example delayed flights, damage to buildings, affect water supply lines, etc.
- Damage to crops has the potential to impact agricultural supplies and food security causing hunger to rise.
- Increased extremes such as high cold and high heat waves have the potential to impact vulnerable sections more such as those who cannot afford heating and cooling appliances, increasing mortalities and morbidities. It can impact people’s health and productivity.
There is a need for more research on these phenomena and how global warming and climate change are about to impact their geographical spread, intensity, etc. This would lead to better climate adaptation strategies, particularly for the vulnerable sections of the global south. Such impacts should further be brought into global debates at the Conference of Parties to bring urgency for the shift towards better climate cooperation among all.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies