- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Feb 12, 2022
INDIA’S FIRST mRNA COVID-19 VACCINE LIKELY TO BE ROLLED OUT BY APRIL
Data from human trials of India’s first homegrown mRNA COVID-19 vaccine are likely to be presented to authorities for evaluation by the end of the month.
 What is PMMVY?
What is PMMVY?



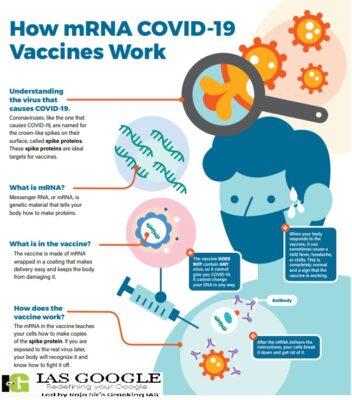
- The mRNA vaccine being developed by Pune-based Genova Biopharmaceuticals is currently in phase 2/3 trials to evaluate the safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of the candidate vaccine in healthy subjects. Around 4,000 volunteers have been recruited for the trial.
- India has so far approved at least six vaccines that can be manufactured locally but only two — Covishield and Covaxin —have been administered to over 99% Indians.
- The mRNA vaccine, can also purportedly be tweaked to be effective against newer variants, but so far, all the vaccines developed — including the prospective Gennova vaccine — have been customized to the original SARS-CoV-2.
- Messenger RNA is a type of RNA that is necessary for protein production. In cells, mRNA uses the information in genes to create a blueprint for making proteins.
- Once cells finish making a protein, they quickly break down the mRNA. mRNA from vaccines does not enter the nucleus and does not alter DNA.
- mRNA vaccines work by introducing a piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein, usually a small piece of a protein found on the virus’s outer membrane.

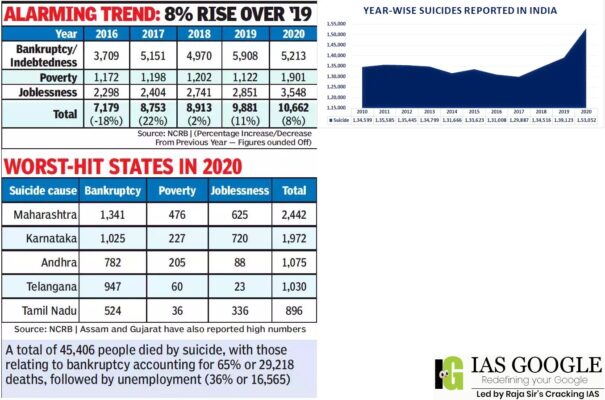
- As many as 9,140 people ended their lives due to unemployment, the highest number of such cases — 3,548 were reported in 2020, the year a lockdown was imposed in the country due to COVID-19.
- 5,213 people committed suicide due to bankruptcy or indebtedness in 2020, 5,908 in 2019 and 4,970 in 2018. A total of 3,548 people committed suicide due to unemployment in 2020, 2,851 in 2019 and 2,741 in 2018.
- The government had launched a number of programmes for employment and income generation for the citizens such as the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Rojgar Yojana (ABRY) to incentivise employers for creation of new jobs along with social security benefits and restoration of employment.
- The National Career Service (NCS) Project for job seekers and employers for job-matching in a dynamic, efficient and responsive manner has a repository of career content for job seekers.
- To address the burden of mental disorders, the government is implementing the National Mental Health Programme (NMHP) and is supporting the implementation of the District Mental Health Programme (DMHP) under NMHP in 692 districts of the country.
- The total number of beneficiaries enrolled during each of the last three financial years under the PMMVY is more than the indicative target.
 What is PMMVY?
What is PMMVY?
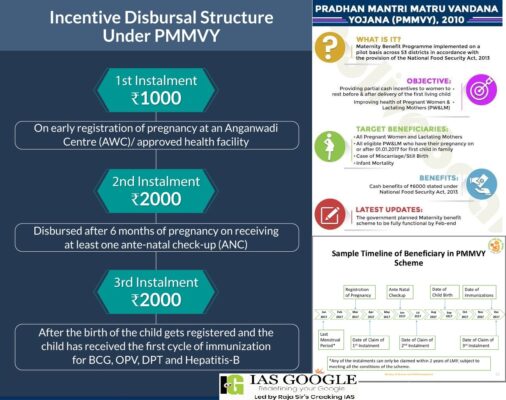
- The PMMVY scheme was announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in a televised address to the nation on December 31, 2016.
- It provides a benefit of 5,000 in three instalments to a woman for her first living child upon meeting certain conditions. This is meant as partial compensation for loss of wage during her pregnancy so that she can get proper nutrition.
- The scheme is only for those women who are not employed by the Central or State governments or a Public Sector Undertaking and don’t receive similar benefits under any law.
- It is clubbed with the Janani Suraksha Yojana scheme which provides nearly 1,000 for institutional births so that altogether mothers get 6,000 in maternity benefit.

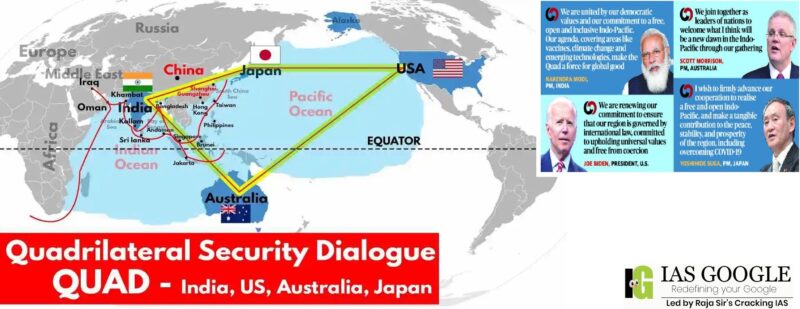
- One of the issues expected to figure prominently in the meeting is the Quad vaccine partnership, and expediting the roll out of one billion doses of Covid-19 vaccines across the Indo-Pacific.
- A vaccine experts’ group is working to align the plans of Quad members to support health security and the Covid-19 response across the Indo-Pacific.
- Military cooperation between the Quad members has increased in recent months and the navies of the four countries participated in the Malabar exercise for the second consecutive year in 2021.
- The Quad is an informal strategic forum comprising four nations, namely -- United States of America (USA), India, Australia and Japan.
- One of the primary objectives of Quad is to work for a free, open, prosperous and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- The group met for the first time in 2007 on the sidelines of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- It is considered an alliance of maritime democracies, and the forum is maintained by meetings, semi-regular summits, information exchanges and military drills of all the member countries.
- The motive behind the Quad is to keep the strategic sea routes in the Indo-Pacific free of any military or political influence.
- The core objective of the Quad is to secure a rules-based global order, freedom of navigation and a liberal trading system.

- The aim is to promote ‘Made in India’ drones but the ban will not apply to the import of drone parts.
- The government has taken a series of steps to boost domestic manufacturing of drones and drone components including announcing a Rs 120-crore Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and liberalising drone operation rules.
- Import policy for drones in CBU (Completely Built Up) /CKD (Completely Knocked Down)/SKD (Semi Knocked Down) form, is prohibited with exceptions provided for R&D, defence and security purposes.
- The new Drone Rules, 2021 reduced compliances and fees required to be paid to operate drones.
- The Civil Aviation Ministry also launched an airspace map of India, demarcating areas where drones can be used without permission and areas in which drones cannot be operated without obtaining prior permission from authorities.

- The petition sought a ban on the movement of motorboats in the eco-sensitive area and declared the Mangaljodi bird sanctuary a silent zone.
- The PIL stated that illegal motorboats are operating for fishing purposes on the Mangaljodi wetland part of Chilika lagoon which was declared an Important Bird Area (IBA).
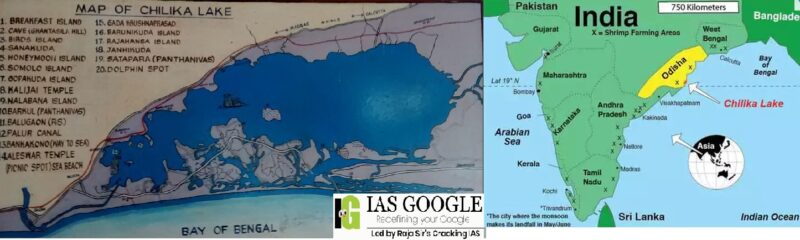
- Chilika Lake is a brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda and Ganjam in the state of Odisha in eastern India.
- It is connected to the Bay of Bengal by a 32 km long and 1.5 km wide channel that mostly runs parallel to the Bay separated by a narrow spit whose width varies between 100 m to several kilometers.
- A number of islands are present in the lagoon, prominent among which are Krushnaprasad, Nalaban, Kalijai, Somolo and Birds Islands.
- Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lake with estuarine character that sprawls along the east coast of India.
- It is considered to be the largest lagoon in India and counted amongst the largest lagoons in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory waterfowl found anywhere on the Indian sub-continent.
- It is one of the hotspots of biodiversity in the country, and some rare, vulnerable and endangered species listed in the IUCN Red List of threatened Animals inhabit the Lake area for atleast part of their life cycle.
- Chilika lake was designated as a "Ramsar Site", i.e. a wetland of International Importance. The Nalaban Island within the lake is notified as a Bird Sanctuary under Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Earlier, the Tamil Nadu government had taken exception to Governor R N Ravi’s Republic Day speech articulating the benefits of NEET, the medical entrance exam.
- Although envisaged as an apolitical head who must act on the advice of the council of ministers, the Governor enjoys certain powers granted under the Constitution, which includes:
- giving or withholding assent to a Bill passed by the state legislature, or
- determining the time needed for a party to prove its majority, or
- that which party must be called first do so, generally after a hung verdict in an election.
- No provisions laid down for the manner in which the Governor and the state must engage publicly when there is a difference of opinion.
- From the Administrative Reforms Commission of 1968 to Sarkaria Commission of 1988, several panels have recommended reforms, such as selection of the Governor through a panel comprising the PM, Home Minister, Lok Sabha Speaker and the CM, apart from fixing his tenure for five years.
- The recommendations have also been made for a provision to impeach the Governor by the Assembly.

- The satellites were designed to burn up on reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere, and did not create debris in space.
- Solar storms are magnetic plasma ejected at great speed from the solar surface.
- They occur during the release of magnetic energy associated with sunspots (‘dark’ regions on the Sun that are cooler than the surrounding photosphere), and can last for a few minutes or hours.
- Not all solar flares reach Earth, but solar flares/storms, solar energetic particles (SEPs), high-speed solar winds, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) that come close can impact space weather in near-Earth space and the upper atmosphere.
- Solar storms can hit operations of space-dependent services like global positioning systems (GPS), radio, and satellite communications.
- Geomagnetic storms interfere with high-frequency radio communications and GPS navigation systems.
- Aircraft flights, power grids, and space exploration programmes are vulnerable.
- CMEs, with ejectiles loaded with matter travelling at millions of miles an hour, can potentially create disturbances in the magnetosphere, the protective shield surrounding the Earth.
- Astronauts on spacewalks face health risks from possible exposure to solar radiation outside the Earth’s protective atmosphere.

- World Book of Records UK is an organisation that catalogues and verifies extraordinary records across the world with authentic certification.
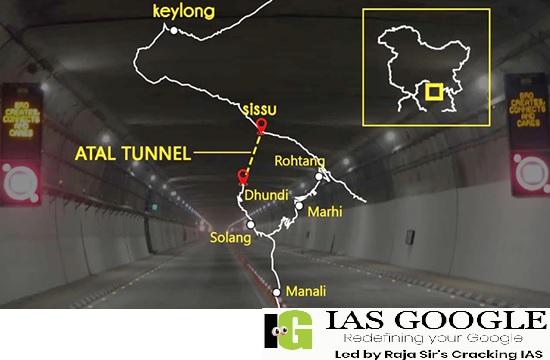
- The Atal Tunnel was dedicated to the nation by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on October 3, 2020.
- The 9.02 km long, strategically significant, Atal Tunnel, that runs under the 'Rohtang Pass' was constructed on the Manali - Leh Highway under the challenging conditions of freezing temperatures in extremely difficult terrain.
- Construction of this tunnel has reduced the distance on Manali - Sarchu road by 46 km and travel time by four to five hours, providing all-weather connectivity on the Manali - Leh axis.

- Global geolocation technology specialist TomTom released the 11th annual Traffic Index.
- The report has complied with the detailed traffic trends in 404 cities in 58 countries throughout 2021.
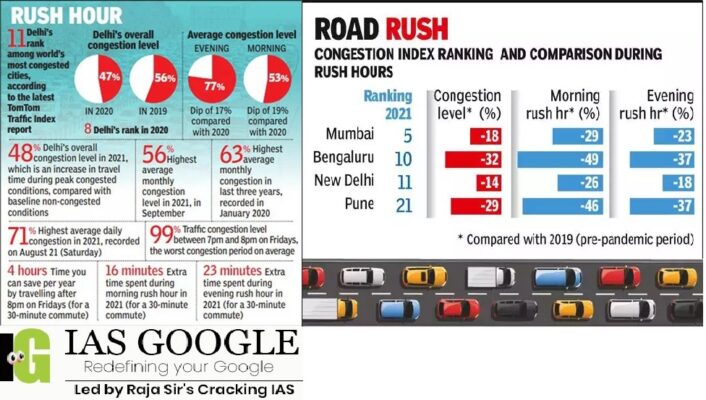
- According to the report, Delhi had a congestion level of 48% in 2021 compared with 47% in 2020 and 56% in 2019.
- A 48% congestion means that on average, travel times were 48% longer than during baseline non-congestion conditions. A 30minute trip in free-flow condition would take 14 minutes longer on average with a 48% congestion. The average congestion level in 2021, according to the report, ranged between 77% during evening peak hours and 53% during the morning rush hour.
- The highest average daily congestion in 2021, 71%, was on Saturday, August 21 last year, when the city recorded 139 mm of rainfall. Overall, September saw the highest average monthly congestion level of 56%, followed by October (54%) and December (53%).
- The lowest congestion levels were logged in April and May with 38% and 15%, respectively, when the deadly second Covid wave kept the capital immobile.
- In 2021, the data suggests the average travel time will increase by 1 minute per day.
- According to the report, an average Delhiite will spend 152 hours, or six days and eight hours, of extra time when driving in the rush hours in 2021.
- This ranges from 23 minutes extra driving in rush hour per 30 minutes of a trip during the evening rush hour and an extra 16 minutes during the morning rush for a 30-minute trip.
- In 2019, an average Delhiite spent 28 minutes extra for a 30-minute trip during the evening peak and 22 minutes extra during the morning rush.
- The average time lost by a Delhiite in rush hour traffic over 2019 was seven days and 22 hours.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies