- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Jan 12, 2022
DEMENTIA CASES IN INDIA TO DOUBLE BY 2050, LANCET STUDY SHOWS
Dementia Cases in India is Expected to almost double by 2050
 Highlights:
Highlights:
 First Advance Estimates (FAE) of Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
First Advance Estimates (FAE) of Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
 Quarterly Economic Survey (QES):
Quarterly Economic Survey (QES):
 Highlights:
Highlights:
 Red Sanders
Red Sanders
 Who are the developing countries in the WTO?
Who are the developing countries in the WTO?
 Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
 Lal Bahadur Shastri (1904-66):
Lal Bahadur Shastri (1904-66):
 Digital Embossing Technology
Digital Embossing Technology
 Highlights:
Highlights:
- The number of dementia cases in India is expected to almost double by 2050
- The tally will increase to 11,422,692 from 3,843,118 in 2019.
- Neighbouring countries Bangladesh, Bhutan, Pakistan, and Nepal are likely to record an increase of 254 percent, 351 percent, 261 percent, and 210 percent, respectively.
- The Global tally of cases will increase almost triple to 153 million in 2050.
- The highest increase in cases is projected for North Africa, the Middle East, and Eastern Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Dementia is used to describe a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities severely enough to interfere with your daily life.
- Dementia results from a variety of diseases and injuries that primarily or secondarily affect the brain.
- Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and may contribute to 60-70% of cases.
- Symptoms: Memory loss, Difficulty communicating or finding words, Visual and spatial abilities, such as getting lost while driving, Reasoning or problem-solving, Handling complex tasks, Confusion, and
- Cure: Currently no cure available.
- Dementia is currently 7thleading cause of death among all diseases and one of the major causes of disability and dependency among older people globally.
- Currently, more than 55 million people live with dementia worldwide, and there are nearly 10 million new cases every year.
- Dementia mainly affects older people.

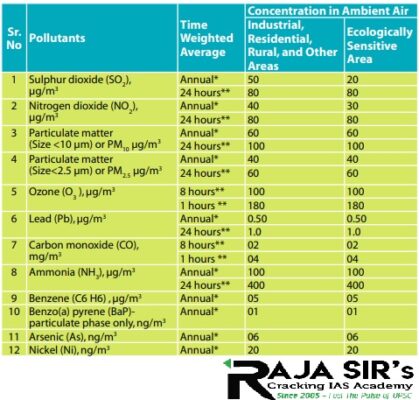
- NCAP Tracker is a joint project by news portal Carbon Copy and a Maharashtra-based start-up 'Respirer Living Sciences', designed to track air pollution.
- Cities are declared non-attainment if they consistently fail to meet the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) over a five-year period.
- Ghaziabad ranked as the most polluted city out of 132 non-attainment cities with highest levels of PM 2.5 and PM 10.
- Delhi was the second most polluted city with the highest PM 2.5 level and fourth in cities with the highest PM 10 level.
- PM 2.5 level continues to be more than 2.5 times the Central Pollution Control Board(CPCB)s safe limit of 40 ug/m3.
- It is 20 times the WHO’s safe limit of 5 ug/m3.
- Delhi reduced its PM levels only marginally.
- NAAQs are the standards for ambient air quality notified by the CPCB under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- To indicate necessary air quality levels required to ensure the protection of vegetation, health, and property.
- To provide a uniform yardstick for the assessment of air quality at the national level.
- To indicate the extent and need of the monitoring programme.
- NCAP was implemented across India in 2019.
- Aim: To meet the prescribed annual average ambient air quality standards at all locations in the country.
- Stringent implementation of mitigation measures for prevention, control and abatement of air pollution
- Augment public awareness and capacity building measures.
- Augment and strengthen air quality monitoring network across the country.
- Collaborative, multi-scale and cross-sectoral coordination between relevant Central Ministries, State Government and local bodies.
- Focus on measures, participatory and disciplined approach.
- Use the smart cities framework to launch the NCAP in the smart cities under the non-attainment cities.
- Integrating the existing policies and programmes of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and other initiatives of Government of India in reference to climate changes.
 First Advance Estimates (FAE) of Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
First Advance Estimates (FAE) of Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
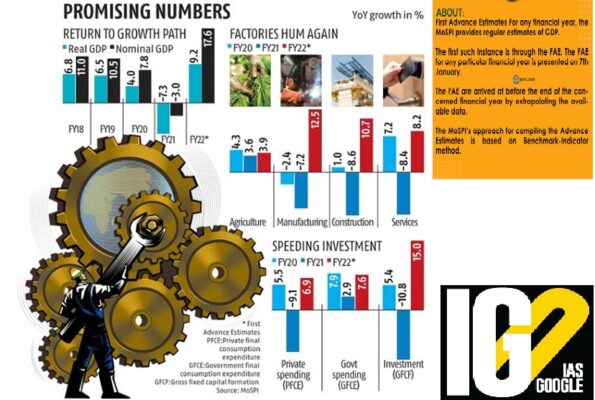
- The FAE were first introduced in 2016-17.
- It is published at the end of the first week of January, soon after the end of the third quarter (October, November, December).
- They are the “first” official estimates of how GDP is expected to grow in that financial year.
- They are also the “advance” estimates because they are published long before the financial year (April to March) is over.
- FAE do not include the formal third quarter GDP data, which is published at the end of February as part of the Second Advance Estimates (SAE).
- Significance: They are the GDP estimates that the Union Finance Ministry uses to decide the next financial year’s budget allocations.
- The FAE are derived by extrapolating the available data.
- The approach for compiling the Advance Estimates is based on Benchmark-Indicator method.
- The estimates available for the previous year (2020-21 in this case) are extrapolated using relevant indicators reflecting the performance of sectors.
- Gross value added (GVA) is defined as the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption.
- It is used to measure the output or contribution of a particular sector.
- When such GVAs from all sectors are added together and adding taxes (product) and reducing subsidies (product), we can get the GDP at market price.
- GVA thus shows the production contribution of a particular sector.
 Quarterly Economic Survey (QES):
Quarterly Economic Survey (QES):
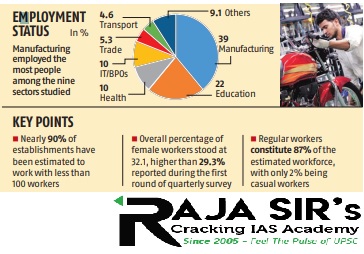
- The QES gives a consolidated view of employment from demand side at regular intervals.
- This data will help the government make evidence-based policy.
- A total of nine sectors were included for assessment which included:
- Manufacturing, education, health and the IT/BPO, transport, trade, construction, accommodation and restaurant, health and financial services.
- The report estimates the gross domestic product of India for the year 2021-22 at 2 per cent.
- These nine sectors account for about 85% of total employment in establishments with 10 or more workers.
- Number of establishments with less than 100workers were more than establishments with more than 100 workers.
- The overall percentage of female workers stood at 1%, higher than 29.3% reported during the first round of QES.
- Regular workers constitute 87% of the estimated workforce in the nine selected sectors, with only 2% being casual workers.
- However, in the construction sector, 20%of the workers were contractual and 6.4% were casual workers.
 Highlights:
Highlights:
- Diversion of very dense forests in the Eco-class 1 will now cost ₹15.95 per ha compared to ₹10.43 lakh earlier.
- Diversion of the open category of forests will now cost ₹11.16 lakh per ha compared to ₹7.44 lakh earlier.
- This will act as a deterrent to industries and projects on the extent of forest land they seek to divert.
- It is a monetary approximation of the value that is lost when a piece of forest land has been razed.
- As per the Supreme Court, it must be paid by those who use forest land for non-forestry purposes and only limited exemptions are permitted.
- The payments are received by the Compensatory Afforestation Fund(CAF).
- CAF use them for afforestation and reforestation purpose.
- CAF is managed by the Compensatory Afforestation Management and Planning Authority(CAMPA).
- It is calculated on the basis of the services and ecological value.
- There are prescribed formulae for calculating the amount which depends on the location and nature of the forest and the type of industrial enterprise that will replace a particular area of forest.

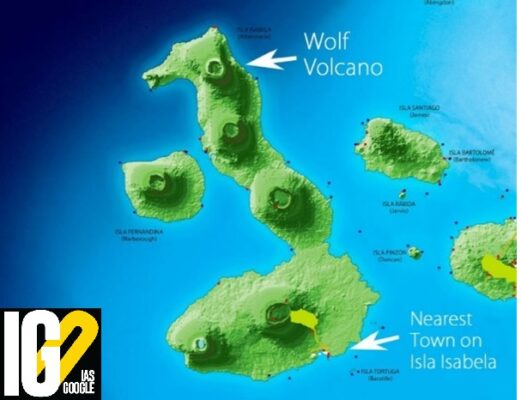
- Wolf volcano, also known as Mount Whiton is the highest volcano of the Galápagos archipelago.
- Location: It lies on the equator on the northern end of Isabela Island.
 Red Sanders
Red Sanders
- It is a species of sandalwood (Pterocarpus).
- It is endemic to the southern Eastern Ghats Mountain range of South India.
- This tree is valued for the rich red colour of its wood.
- The tree is not to be confused with the aromatic Santalum sandalwood trees that grow natively in South India.
- It is listed under Appendix II of CITES and is banned from international trade.
- This plant occurs as an endemic species in the hills of Cuddapah, Kurnool, Chittoor, Nellore and Prakasam districts of Andhra Pradesh and sporadically occurring in some pockets of adjoining states of Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- It is known for their rich medicinal and therapeutic properties.
- They are high in demand across Asia, particularly in China and Japan, for use in cosmetics and medicinal products as well as for making furniture, woodcraft and musical instruments.
- It is grown in the northern plains of Karnataka especially in the Vijayapura district since 1900.
- However, the ones cultivated in India are known for their unique texture and high acidic value.
- The ascorbic acid content is the highest in these varieties.

- Coal plants emit pollutants like Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
- Coal is formed beneath the earth, due to the suppression of biological materials, over millions of years.
- Depending on the degrees of compression, Coal is found in a variety of forms.
- In India, the coal is found in 2 rock sequences, namely Gondwana Deposits and Tertiary Deposits.
- Around 80% of Indian coal deposits contain bituminous type, which is non-coking grade.
- Gondwana coals occur in Damodar Valley (Jharkhand-Bengal coal belt).
- Jharia (Jharkhand) is the largest Indian coalfield.
- Tertiary coals occur in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya and Nagaland.
- Apart from it, brown coal or lignite occur in the coastal areas of Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Gujarat and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Gondwana coals occur in Damodar Valley (Jharkhand-Bengal coal belt).
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2) gas is emitted by the burning of fossil fuels, including coal, gas and oil.
- Mostly, the thermal power plants(coal plants) dominate SO2 emissions.
- SO2 is also a natural by-product of volcanic eruptions.
- It can create secondary pollutants like sulfate aerosols, particulate matter, and acid rains.
- It affects the heart and lungs, making breathing more difficult.
- Can lead to formation of haze and smog, impacting visibility.
- SO2 converts to sulfuric acid aerosols that block incoming solar radiation and contribute to ozone destruction.
- Mission Parvarish aims to combat malnourishment among children aged six months to five years.
- Given by: SKOCH Group (a think tank)
- The SKOCH Award covers the best of efforts in digital, financial and social inclusion.
- The domains for receiving the awards are:
- Citizen service delivery
- Capacity building and empowerment
- Corporate governance
- Change management
- Inclusive growth
- Excellence in technology and application
 Who are the developing countries in the WTO?
Who are the developing countries in the WTO?
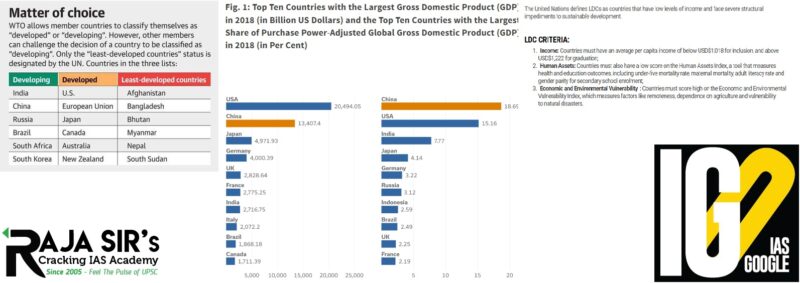
- Developing countries comprise a majority of the WTO membership.
- The WTO has not defined ‘developed’ and ‘developing’ countries.
- The member countries are free to announce whether they are ‘developed’ or ‘developing’.
- However, other members can challenge the decision of a member to make use of provisions available to developing countries.
- The developing country status owes its origin to the U.S. Trade Act of 1974.
- It authorised the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) to help poor countries develop faster.
- Special and differential treatment’ (S&DT) provisions: It includes the following:
- Longer time periods for implementing Agreements and commitments
- Measures to increase trading opportunities
- Provisions requiring all WTO members to safeguard the trade interests of developing countries
- preferential treatment for state enterprises
- China is the second largest economy in the world.
- It is the largest when calculated by purchasing power parity.
- The World Bank categorizes China as an “upper-middle-income” country.
- China is a major source of foreign direct investment in all corners of the world and provides billions of dollars in overseas development assistance.
- 12 of the 100 largest companies in the world by total market capitalization are Chinese.
- The WTO recognizes as least-developed countries (LDCs) those countries which have been designated as such by the United Nations.
- There are currently 46 least-developed countries on the UN list.
- The WTO recognises LDCs relying on a classification by the UN based on a criterion that is reviewed every three years.
- LDCs are often exempted from certain provisions of WTO pacts.
- Have preferential market access for goods and services;
- Receive technical assistance and capacity building.
- Receive financial and technical assistance provided by multilateral partners, such as special programmes and budget allocations at the UN, including the Technology Bank for LDCs
- Receive support to participate in international forums, such as caps and discounts on contributions to the budget of the United Nations and financial support for representatives of LDCs to travel to General Assembly.
- Investment Support Programme (ISP) for LDCs provides on-demand legal and professional technical advice to LDCs on investment-related negotiations and dispute settlement.
- ISP for LDCs was jointly designed by the International Law Organization (IDLO) and UN-OHRLLS (United Nations Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries).
 Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
- Established: 2016.
- Headquartered: Beijing.
- It is an international development bank that provides financing for infrastructure projects in Asia.
- Aim: To improve social and economic outcomes in its region, Asia, and beyond.
- The bank currently has 104 members, including 17 prospective members from around the world.
- China is the largest shareholder with 26.61% voting shares in the bank. India has 7.6% voting shares.
- The bank is headed by a Board of Governors composed of one Governor and one Alternate Governor appointed by each of the 86 member countries.
- A non-resident Board of Directors is responsible for the direction and management of the Bank.
- The bank staff is headed by a President who is elected by AIIB shareholders for a five-year term and is eligible for re-election once.
- It promotes sustainable Infrastructure and to support countries that are striving to meet environmental and development goals.
- The bank funds projects linking countries in the region and cross-border infrastructure projects for Roads, rail, ports, energy pipelines and telecoms across Central Asia, South East and South Asia and the Middle East.
- It also includes private capital mobilization and encouraging partnerships that stimulate private capital investment.
 Lal Bahadur Shastri (1904-66):
Lal Bahadur Shastri (1904-66):
- He was a follower of Mahatma Gandhi and participated in the Non-cooperation movement(the 1920s), Salt Satyagraha(1930), supported Individual Satyagraha(1940), and Quit India movement(1940s).
- He had recommended using “water-jets” instead of lathis to disperse the mob.
- He also served as the Minister for Railways and Minister for Home under the Union Cabinet, headed by PM Nehru(1950-60s).
- After the passing away of Nehru Ji in 1964, he became India’s 2nd Prime Minister.
- He was the first person to be posthumously awarded Bharat Ratna in 1966.
- He was instrumental in appointing the Committee on Prevention of Corruption under the Chairmanship of K. Santhanam.
- He translated autobiography of Marie Curie into Hindi language.
- During his time, due to rigorous Madras anti-Hindi agitations(1965), He assured that English will continue to be used as the official language.
- In response to food insecurity and international pressure, he appealed to Indians to skip a meal a week, called “Shastri Vrat”.
- He promoted the White Revolution and the Green Revolution(1965).
- Institutions established during his prime minister ship include the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and the Food Corporation of India (FCI).
- In 1964, he signed an agreement with Sri Lankan PM for more than 3 lakh Indian Tamils.
- In 1965 he visited Burma and re-established cordial relations with the military government of Burma.
- During the 1965 India-Pakistan war, he gave the slogan of ‘Jai Jawan Jai Kisan’.
- In 1965 with a United Nations-mandated ceasefire, the Indo-Pak war ended.
- In 1965, he and Ayub Khan(Pakistani PM) signed the Tashkent Declaration for peace and the end of the war.
 Digital Embossing Technology
Digital Embossing Technology
- Digital embossing is a technology that eliminates the need for printing plates, molds, chemicals, and solvents, emitting no pollutants or waste and reducing overall energy usage.
- It eliminates the need for printing plates, moulds, chemicals, and solvents, emitting no pollutants or waste and reduces overall energy usage.
- This innovative technology has been introduced, designed and implemented first time in India by National Atlas & Thematic Mapping Organisation (NATMO).
- The maps produced using this technology is not only useful for high-speed production of the maps but can also produce Braille Maps that can be used by more people for years together.
- Braille language is a tactile code enabling blind and visually impaired people to read and write by touch.
- It has various combinations of raised dots representing the alphabet, words, punctuation and numbers.
- It was developed by Louis Braille in the 1820s.
- Braille characters are formed using a combination of six raised dots arranged in a 3 x 2 matrix, called the braille cell.
- Braille language was started as a military code called night writing.
- NATMO is a premier National Organization in the field of thematic maps and atlas making, under the ministry of science and technology.
- Compilation of the National Atlas of India
- Preparation of the National Atlas maps in regional languages
- Preparation of thematic maps based on research studies on environmental and associated aspects and their impact on social and economic development.
- Installation of automated Mapping System for increasing speed and efficiency in mapping.
- Promote the use of geospatial information and technology in cartography.
- Geographical Researches
- Remote Sensing and Digital Image processing.
- Division on Cartography for the Visually Impaired.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies