- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Jan 20, 2022
BiodiverCities BY 2030: TRANSFORMING CITIES’ RELATIONSHIP WITH NATURE
Recently, a report titled ‘BiodiverCities by 2030: transforming cities relationships with nature’ was launched.
 Findings of the Report:
Findings of the Report:
 Indonesia is relocating its capital from Jakarta?
Indonesia is relocating its capital from Jakarta?
 Battle of Kohima:
Battle of Kohima:
 Open data
Open data
 Extension
Extension
 INS Ranvir
INS Ranvir
 What was the Devas-Antrix deal?
What was the Devas-Antrix deal?
- The report was released by the BiodiverCities by 2030 Initiative (WEF), in collaboration with the Alexander von Humboldt Institute and the government of Colombia.
 Findings of the Report:
Findings of the Report:
- Globally, cities contribute 80% to global GDP and 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Around 75% of the population on Earth will be living in cities by 2050 (currently 56%).
- Around 44% of global GDP in cities is estimated to be at risk of disruption from nature loss.
- During 1990-2015, the global urban population increased an average of 1.9 times.
- In the same period (19990-2015), the urban footprint increased an average of 2.5 times.
- Urbanization accounts for 11-16% of global biodiversity loss.
- Spatially (re)integrating nature in urban planning. (Elaborated in the diagram)
- Restoring nature as the backbone of cities’ development.
- land-sparing interventions.
- Nature-based solutions (NbS): Sustainable use of nature
- By shifting investment to nature-based solutions (NbS) for infrastructure, cities can build a climate-resilient environment, reducing biological impact.
- NbS are 50% more cost-effective than “grey” alternatives. But still, they received just 0.3% of overall spending on urban infrastructure in 2021.
- NbS investments could create more than 59 million jobs by 2030 and will also save the natural ecosystem.
- BiodiverCities by 2030 is a joint initiative of the World Economic Forum (WEF) and the Alexander von Humboldt Institute, supported by the Government of Colombia.
- It aims to support city governments, businesses and citizens, to enable cities to live in harmony with nature by 2030.
- BiodiverCities have five characteristics: guiding nature-positive actions on infrastructure, governance, economy, health and wellbeing.
 Indonesia is relocating its capital from Jakarta?
Indonesia is relocating its capital from Jakarta?
- Rising sea levels: Due to climate change, the water levels in the Java Sea are rising and weather events are becoming more extreme.
- It is being predicted that a third of the city could be underwater by 2050.
- Giant Garuda, a coastal development project was launched by the government, to protect the Jakarta city from floods.
- Severe congestion on densely populated Java Island has resulted in poor quality air and traffic gridlocks.
- Jakarta is the largest Indonesian city with a population of 1 crore people.
- Serious Infrastructure problems: Jakarta, being the centre for administration, governance, finance and trade, has inevitably led to relentless construction in the city.
- Infrastructures prevents water seepage, resulting in increased run-off water.
- The new capital is named Nusantara, an old Javanese term which means "archipelago".
- It is located in the North Penajam Paser and Kutai Kartanegara regions of the East Kalimantan province, on the lesser populated island of Borneo.
- East Kalimantan is located over 1,400 km from Jakarta and it does not have a history of natural disasters.
- East Kalimantan is an area with immense water resources and habitable terrain.
- The plans for new capital depict a utopian design aimed at creating an environmentally friendly "smart" city.
- The new capital will act as the centre of the government, whereas Jakarta will continue to be Indonesia’s business and financial centre.
- It could damage ecosystems in the region, and threaten rainforests that are home to Borneo's endangered species.
- The forests of the East Kalimantan region are home to orangutans, sun-bears and long-nosed monkeys.
- Malaysia moved its government to Putrajaya from Kuala Lumpur in 2003.
- Myanmar moved its capital to Naypyidaw from Rangoon in 2006.
 Battle of Kohima:
Battle of Kohima:
- The battle took place in Kohima, today the capital of Nagaland, in 1944.
- It was one of the fiercest battles of the Second World War.
- The battle is often referred to as the Stalingrad of the East.
- The British National Army Museum voted this battle as “Britain’s Greatest Battle”.
- On the height of the Second World War, the Japanese planned an incursion in India via Burma.
- The plan was codenamed Operation U Go.
- The Japanese forces wished to attack the garrison stationed at Kohima and take it after which they would take Assam and then march on to Delhi.
- The British Indian troops held on their strategic positions and troubled the Japanese with their artillery fire.
- The Japanese brought along with them about 5000 oxen to be slaughtered for food, but most of the animals died on the way.
- British reinforcements arrived in Dimapur to relieve the forces at Kohima.
- This caused the Japanese to fall back.
- The Japanese were also defeated during the in the subsequent Battle of Imphal.
- Defeat for the British Indian Army would have meant that the Japanese could strike further into India.
- Kohima was of key strategic importance, at the highest point of the pass through the jungle mountains to Dimapur, now Nagaland’s commercial hub adjoining Assam.
- The fall of Dimapur would have meant leaving the Allied defenders of Imphal at the mercy of the Japanese soldiers fighting alongside Subhash Chandra Bose’s Indian National Army.
- On April 3 1944, those who had fallen in the defence of Kohima were buried on the battlefield, which later became a permanent CWGC cemetery.
- It is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states.
- The members are Australia, Canada, United Kingdom, India, New Zealand and South Africa.
- The commission was founded by Sir Fabian Ware and constituted through Royal Charter in 1917 as the Imperial War Graves Commission.
- Function: To mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations military service members who died in the two World Wars.
 Open data
Open data
- Open Data is the idea that data should be freely available to everyone to use and republish as they wish, without restrictions from copyright, patents or other mechanisms of control.
- The goals of the open-source data movement are similar to those of other "open(-source)" movements such as open-source software, hardware, open content, open specifications, open education etc.
- Term "open data" itself is recent, gaining popularity with the rise of the Internet and World Wide Web and, especially, with the launch of open-data government initiatives such as Data.gov, Data.gov.uk and Data.gov.in.
- One of the most important forms of open data is open government data (OGD), which is a form of open data created by ruling government institutions.
- Availability and Access: The data must be available as a whole and at no more than a reasonable reproduction cost, preferably by downloading over the internet.
- Re-use and Redistribution: The data must be provided under terms that permit re-use and redistribution including the intermixing with other datasets.
- Universal Participation: Everyone must be able to use, re-use and redistribute - there should be no discrimination against fields of endeavour or against persons or groups.
- Urban resilience: Open data system can help to build resilience infrastructure in cities by mapping crowded and hazard zones in the city.
- Increases transparency and accountability: It will increase transparency about government spending on urban planning. Residents have the ability to see exactly what their government has achieved, and how much more needs to be done.
- Access to information: Information such as Real-time bus timetables, information on social housing, care initiatives, playgroups and public contracts can be easily accessible to citizens.
- Economic growth: Open data isn’t just helping citizens, organizations and businesses in smart cities – it is also helping to drive tourism and its associated economy.
- Making data available for a charge.
- Compilation in databases or websites to which only registered members or customers can have access.
- Use of a proprietary or closed technology or encryption which creates a barrier for access.
- Copyright statements claiming to forbid (or obfuscating) re-use of the data, including the use of "no derivatives" requirements.
- Patent forbidding re-use of the data.

- The new 5G technology could interfere with instruments such as altimeters, which measure how far above the ground an airplane is travelling.
- Altimeters operate in the 4.2-4.4 GHz range and the concern is that the auctioned frequencies sit too close to this range.
- No risk of unsafe interference has been identified in Europe.
 Extension
Extension
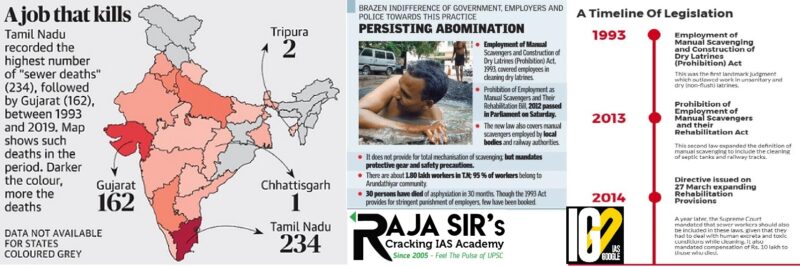
- The tenure of the present NCSK is ending in March 2022.
- The major beneficiaries of this extension would be the Safai Karamcharis and identified manual scavengers.
- As per a survey conducted in accordance with the Manual Scavengers Act, 2013 a total of 58,098 Manual Scavengers was identified on 31.12.2021.
- A person engaged or employed by an individual or a local authority or an agency or a contractor for manually cleaning, carrying, disposing off, or otherwise handling in any manner human excreta in an insanitary latrine or in an open drain or pit into which human excreta from the insanitary latrine is disposed of or on a railway track or in such other spaces or premises as the Central Government or State Government may notify before the excreta fully decomposes in such manner as may be prescribed and the expression ‘Manual Scavenging’ shall be construed accordingly.
- The National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK) Act, 1993established a body called National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK), for the next 4 years.
- But, the validity of the NCSK Act was extended twice in 1997 and 2002 respectively.
- The NCSK Act ended in 2004, thereafter the tenure of the NCSK has been extended as anon-statutory body, under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment from time to time through resolutions.
- It is a non-statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It does not enjoy the powers of civil court.
- Composition:
- A Chairman (in the rank and status of the union minister for States)
- Four members, including a lady member (in the rank and status of the Secretary to the Government of India)
- A Secretary (in the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India)
- Other supporting staff.
- Consultation, Reporting, and Recommending the Central and State Governments on any matter concerning Safai Karamcharis or welfare schemes related to the Safai Karamcharis.
- Monitoring proper implementation of the Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013.
- Take steps for:
- mitigating the hardships of Safai Karamcharis
- socio-economic upliftment of the Safai Karamcharis.
- Safai Karamchari Andolan & Others Vs. Union of India (2014): When a person engaged in cleaning of sewer/septic tank dies while cleaning the same, his family/ kin are entitled to Rs. 10 lakh compensation.
- REvil (an amalgam of “ransomware” and “evil”), is a Russia-based hacking organisation.
- REvil works by threatening to publish the encrypted information on their page Happy Blog unless the ransom was received.
- Mostly the ransom was received in the form of cryptocurrencies due to perceived anonymity and ease of online payment.
- They also offer ransomware as services (RaaS), by leasing the hacking technology to third-party hackers.
- A Ransomware is a file blocking virus that encrypts files after infection.
- It encrypts the victim's files, making them inaccessible, and demands a ransom payment to decrypt them.
- Examples: Trojan, WannaCry worm.
 INS Ranvir
INS Ranvir
- INS Ranvir, among the oldest warships in the Navy, is a Soviet-era destroyer and was commissioned in April 1986.
- It is the fourth of the five Rajput-class destroyers built for the Indian Navy.
- It is the first of the Ranvir class.
- The other Ranvir class destroyer is INS Ranvijay.
 What was the Devas-Antrix deal?
What was the Devas-Antrix deal?
- An agreement was signed between Antrix, government company and Devas Multimedia Pvt Ltd.
- Under the deal, ISRO would lease to Devas two communication satellites (GSAT-6 and 6A) for 12 years for Rs 167 crore.
- Devas would provide multimedia services to mobile platforms in India using S-band transponders on the satellites, with ISRO leasing 70 MHz of S-band spectrum.
- After six years the deal was annulled by the government following a Cabinet Committee on Security decision to terminate the agreement to use the S-band for security purposes.
- Devas approached various tribunals seeking compensation and was awarded compensation of $1.2 billion by an International Chamber of Commerce tribunal in 2015.
- Antrix filed a plea in the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) in January 2021 for liquidation of Devas in India, which it said was incorporated in a fraudulent manner.
- The NCLT ordered the liquidation, which was up held by the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal and by the Supreme Court.
- It is an Indian government-owned company under the administrative control of the Department of Space.
- It was incorporated in September 1992.
- It launched 239 satellites between 2016 and 2019.
- To commercially exploit space products of Indian Space Research Organization.
- To providing technical consultancy services and transferring technologies to industry.
- It is the arbitration between companies or individuals in different states, usually by including a provision for future disputes in a contract.
- It allows the parties to avoid local court procedures.
- India is a signatory to the Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Arbitral Awards, 1958, commonly known as the New York Convention.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies