- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
July 07, Current affairs 2023
Climate change unveils new methane source: Groundwater springs of Norway
- Climate change has exposed a new source of methane in the Arctic: groundwater springs. As global warming drives glaciers to retreat, methane-rich groundwater springs are punching through the surface in the Arctic, the study published
- Methane, a greenhouse gas, is 84 times more potent than carbon dioxide on a 20-year timescale.
- In Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic, groundwater springs could be emitting more than 2,000 tonnes of methane annually.
- These springs are not part of the global methane budget. The global methane budget estimates the amount of methane released through sources and captured through sinks.
- The water in all but one site had high levels of dissolved methane, which escapes into the atmosphere. Further, these springs emit this greenhouse gas year-round, the researchers noted.
- The rocks are most likely regulating the springs’ emissions. For example, areas where groundwater emerged from shale rocks were found to be methane hotspots.
- High methane concentrations near shale rocks suggested a geologic or thermogenic (heat) source of gas, which moves upwards through fractures in the rocks and gathers under the glacier. A lot more methane gas could be trapped under glaciers, waiting to escape, the researchers explained.
Govt launches 3rd edition of National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment
NeSDA portal
- NeSDA framework, launched in August 2018 was conceptualized with an overall objective to measure the depth and effectiveness of existing e-Governance service delivery mechanisms.
- The Department has successfully released 2 editions of NeSDA study, viz., NeSDA 2019 and NeSDA 2021.
- This framework is based on the Online Service Index (OSI) of UN eGovernment Survey.
- The framework covers six sectors, Finance, Labour & Employment, Education, Local Government & Utilities, Social Welfare (including Agriculture & Health) and Environment (including Fire) sectors.
- Improvement in the country’s e-Governance landscape due to last 2 editions of NESDA study may be summarized in the following key take aways:
- Increase in e-Service Delivery
- Rise in use of Integrated / Centralized Portals for delivery of e-Services
- Improvement across assessment parameter scores
- The department undertakes NeSDA study biennially.
- This study assesses States, Union Territories (UTs), and focus Central Ministries on the effectiveness of e-Governance service delivery.
- NeSDA helps the respective governments improve their delivery of citizen centric services and shares best practices across the country for all States, UTs and Central Ministries to emulate.
Scientist discover extremely rare “leopard-print'' frog
- Scientific Name: Leptodactylus laticeps
- It is an extremely rare species found only in South American countries namely Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay.
- Threat: The frog is under threat as its habitat the Dry Chaco is cut down.
- Conservation status
- IUCN: Near Threatened
Grana Chaco
- It is lowland alluvial plainin interior south-central South America.
- It is bounded on the west by the Andes mountain ranges and on the east by the Paraguay and Paraná rivers.
- Physiography: It is a vast geosyncline basin formed by subsidence (or down warping) of the area between the Andean cordilleras on the west and the Brazilian Highlands on the east as it filled with alluvial debris from these two features.
- Climate: It is subject to climates that vary from tropical in the north to warm-temperate in the south.
- The Grana Chaco is a large expanse of forest and dusty plains straddling parts of Bolivia, Argentina, and Paraguay.
IN - US n salvage and explosive ordnance disposal exercise
EXERCISE – SALVEX
- Indian Navy – US Navy have been participating in joint Salvage and EOD exercises since 2005.
- It is the Seventh edition of SALVEX.
- The exercise saw participation from both the navies which included the ships – INS Nireekshak and USNS Salvor in addition to Specialist Diving and EOD teams.
- It also saw conduct of joint training exercises towards enhancing interoperability, cohesiveness and gaining from best practices mutually in Maritime Salvage and EOD operations.
- The constructive engagements on operational terms enhanced the skill-sets of the Diving teams in a number of diverse disciplines such as mine detection and neutralisation, wreck location and salvage.
Other exercises conducted between India and US
- Malabar Exercise: It is a quadrilateral naval exercise of India, USA, Japan and Australia
- Exercise Tiger Triumph: It is a humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief exercise.
- Yudh Abhyas: It is a joint military exercise
What is a ‘Gravity Hole’? Can Indian Ocean''s ‘Gravity Hole’ open doors to secrets of Earth''s origin?
Gravity hole
- The gravity hole is a region of the ocean where the effects of gravity are less than usual.
- It occurs at the bottom of the ocean where there are gravitational anomalies.
- Why it occurs? These anomalies are caused by variations in the gravitational pull of the Earth due to differences in the density of the materials that make up the Earth’s crust.
- The Indian Ocean is home to one of the most profound gravitational anomalies on Earth known as the Indian Ocean Geoid Low (IOGL).
- It was discovered in 1948 during a ship-based gravity survey by Dutch geophysicist Felix Andries Vening Meinesz.
- It is found in a large section of over three million sq. km in the Indian Ocean seafloor, located around 1,200 km southwest of India’s southern tip.
- It is estimated to have formed approximately 20 million years ago.
- Researchers said that the IOGL comprises slabs from the Tethys Ocean, a long-lost sea that plunged into the depths of the planet millions of years ago.
- The Tethys Ocean, which once separated the supercontinents of Gondwana and Laurasia is believed to have perturbed the African Large Low Shear Velocity province
Solar shooting stars: Scientists left stunned by ''rain of fireballs'' on Sun
Solar shooting stars
- These are massive clumps of plasma that plummet to the Sun''s surface at incredible speeds.
- These looks like a massive rain of fireballs that play a key role in heating up the corona which is the outermost part of the Sun''s atmosphere.
- The researchers observed these solar shooting stars using the Solar Orbiter spacecraft of the European Space Agency.
- This is the first time such impacts have been spotted.
- These observations were made from a close distance of just 30 million miles from the sun.
coronal rains formed on Sun
- The Coronal rain which is plasma firework displays consisting of gas with temperatures exceeding two million degrees Fahrenheit.
- Instead of water, coronal rains form when localised temperature drops, causing solar plasma to condense into dense lumps.
- These lumps then fall to the cooler surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere, as fiery rain at speeds of up to 220,000 miles per hour.
Significance of this observation
- This could help solve the mystery of why the corona, the outermost part of the Sun''s atmosphere, is hotter than the layers beneath it.
GST Council to discuss scope of budgetary support for units in hilly states
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
- It is an indirect tax (not directly paid by customers to the government), that came into effect from 1 July 2017 through the implementation of the 101st Amendment to the Constitution of India by the Indian government.
- It has actually replaced various indirect taxes such as - service taxes, VAT, excise and others in the country.
- It is levied on the manufacturer or seller of goods and the providers of services.
- Types of GST: State Goods and Services Tax (SGST), Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) and the Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST, on exports and imports).
GST Council
- Article 279A of the Indian Constitution gives power to the President of India to constitute a joint forum of the Centre and States called the GST Council, consisting of the -
- Union Finance Minister - Chairperson
- The Union Minister of State, in-charge of Revenue of finance - Member
- The Minister in-charge of finance or taxation or any other Minister nominated by each State Government - Members
- The GST Council is an apex committee to modify, reconcile or to make recommendations to the Union and the States on GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST laws, etc.
- Decisions in the GST Council are taken by a majority of not less than three-fourth of weighted votes cast.
- Centre has one-third weightage of the total votes cast and all the states taken together have two-third of weightage of the total votes cast.
- All decisions taken by the GST Council have been arrived at through consensus.
Iceland is the world’s most peaceful country; check where India stands
Global Peace Index
- It is released annually by the Institute for Economics and Peace (IEP).
- 2023 Global Peace Index (GPI) ranked 163 independent states and territories according to their level of peacefulness.
- It measures the state of peace across three domains:
- Societal safety and security;
- Ongoing domestic and international conflict;
- Militarization;
- Highlights of Global Peace Index 2023:
- The average level of global peacefulness deteriorated by 0.42 per cent.
- Iceland is the most peaceful country in the world – a title it has held since 2008. It is accompanied at the top by Denmark, Ireland, New Zealand, and Austria.
- Conversely, Afghanistan is the least peaceful country in the world for the eighth consecutive year. It is followed by Yemen, Syria, South Sudan, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- India has occupied the 126th spot in the rankings, two higher than its previous position.
- The report stated that India experienced an improvement of 3.5 per cent in overall peacefulness over the past year, owing to improvements in violent crime, neighbouring countries’ relations, and political instability.
- Among other countries, Nepal, China, Sri Lanka, United States of America, and Pakistan, and have been ranked 79, 80, 107, 131, 146, respectively.
Peru Declares Emergency as Ubinas Volcano Spews Ash
Ubinas Volcano
- Ubinas is a stratovolcano located in the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes.
- It is one of the most active volcanoes in Peru, with more than 26 eruptive episodes recorded in the last 500 years.
- The Ubinas volcano is part of a group of seven volcanoes in southern Peru located within a volcanic zone that extends from southern Peru to northern Chile.
- The affected area is situated within the "Ring of Fire," a region encompassing the edges of the Pacific Ocean that is renowned for its volcanic activity and seismic events, such as earthquakes.
- The upper portion of the volcano is made from lava flows from the Pleistocene.
- The depression (caldera) at the summit contains a cone of volcanic ash sporting a vent shaped like a funnel.
Stratovolcano
- The stratovolcano is a tall, steep, and cone-shaped type of volcano.
- Unlike flat shield volcanoes like in Hawaii, they have higher peaks. At the peak, stratovolcanoes usually have a small crater.
- Stratovolcanoes build up on height by layering lava, ash and tephra. By definition, they have alternating layers of pyroclastic and lava.
- When ash falls or lava flows, it solidifies and makes a narrower cone.
- Strato Volcanoes comprise the largest percentage (~60%) of the Earth''s individual volcanoes.
- Strato volcanoes are usually about half-half lava and pyroclastic material, and the layering of these products gives them their other common name of composite volcanoes.
After BPCL, IOC Announces Rights Issue
Rights Issue
- A rights issue is an invitation to existing shareholders to purchase additional new shares in the company.
- This type of issue gives existing shareholders securities called rights.
- With the rights, the shareholder can purchase new shares at a discount to the market price on a stated future date.
- The company is giving shareholders a chance to increase their exposure to the stock at a discount price.
- Until the date at which the new shares can be purchased, shareholders may trade the rights on the market the same way that they would trade ordinary shares.
- The rights issued to a shareholder have value, thus compensating current shareholders for the future dilution of their existing shares'' value.
- Dilution occurs because a right offering spreads a company’s net profit over a larger number of shares. Thus, the company’s earnings per share, or EPS, decreases as the allocated earnings result in share dilution.
- Rights Offering
- Companies most commonly issue a right offering to raise additional capital.
- A company may need extra capital to meet its current financial obligations.
- Troubled companies typically use rights issues to pay down debt, especially when they are unable to borrow more money.
OpenKylin
- It is China''s first open-source desktop operating system (OS).
- It is a Linux-based operating system built by a community of about 4,000 developers.
- OpenKylin users have access to the software’s lines of code and can modify them as they wish, unlike Microsoft and Apple, which keep the workings of Windows and MacOS systems secret.
Open-source operating system (OS)
- An Open-source OS is the OS in which source code is visible publicly and editable.
- The generally known Operating Systems like Microsoft’s Windows, Apple’s iOS and Mac OS, are closed OS.
- Closed Operating Systems are built with numerous codes and complex programming and that is called source code. This source code is kept secret by the respective companies (owners) and inaccessible to third parties. In the case of an Open-Source Operating system, everyone can access and edit the source code.
Pros and Cons of Open-Source Operating Systems:
- Pros:
- Cost-efficient – Most of the Open-Source OS is free. And some of them are available at a very cheap rate than the commercial closed products.
- Reliable and efficient – Most of them are monitored by thousands of eyes since the source code is public. So, if there is any vulnerability or bugs, they are fixed by the best developers around the world.
- FlexibilityThe greatest advantage is you can customize it as per your need and there is creative freedom.
- Cons:
- Security risk – Though the bugs are identified, there is a risk of attacks as the source code is available to the attackers.
- Complicated – It is not user-friendly as the closed ones. You need to have the minimum technical knowledge to use this software.
- Lack of support – If you meet with the problem, then there is no customer support to help you out.
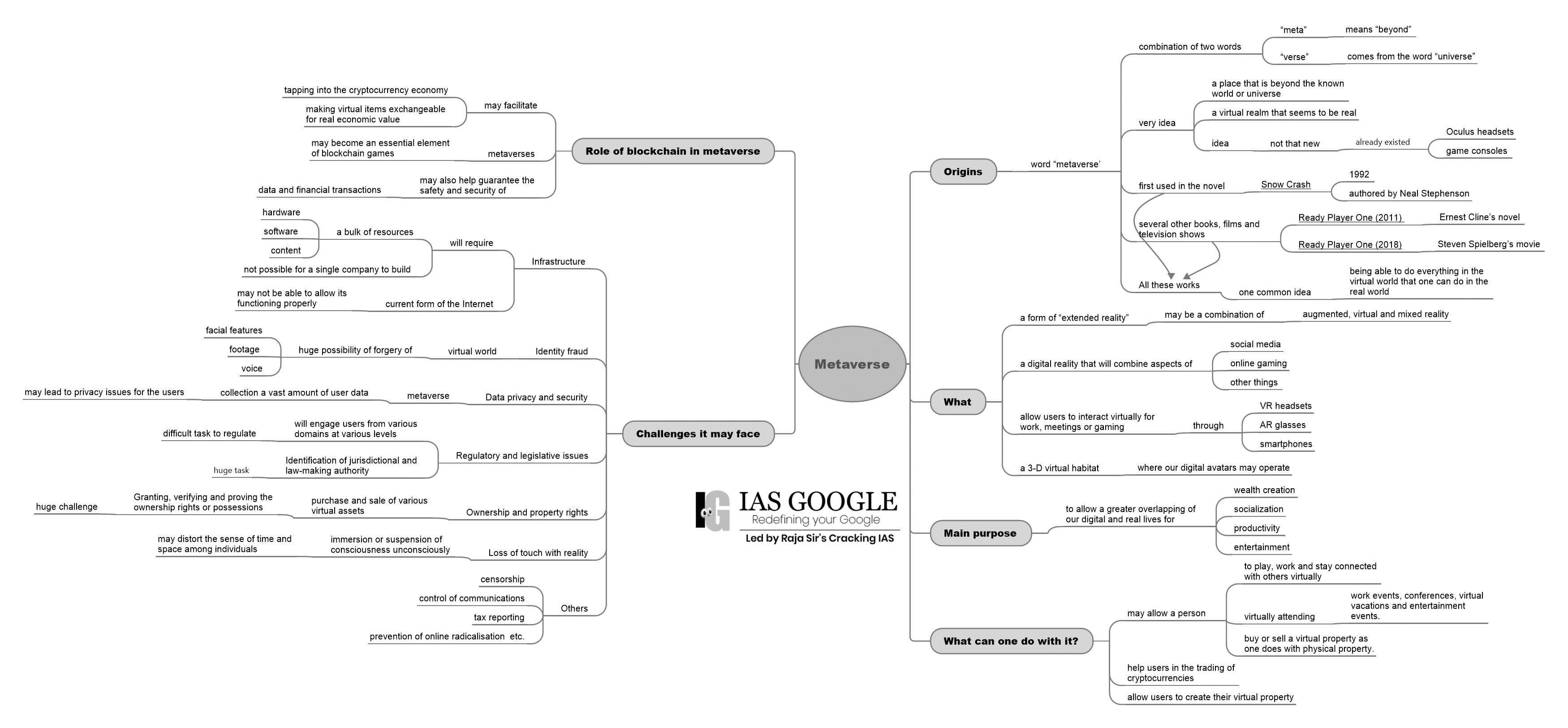
Metaverse and NFTs (non-fungible tokens)
Metaverse
- It is extension of real world into the digital realm.
- It gives a multi-user experience for anyone using it around the globe.
- Accessing this virtual world requires the Internet and digital devices.
- The technology behind this is called Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
- The growth of Digital India is accelerated by India’s large young population which is deeply acquainted with digital interactions and recreations.
Future Challenges and Opportunities of Meta-AI
While the technical, demographic and policy foundations for the metaverse appear to be present in India, there remains the operational challenge of building the metaverse.
- In 2023, this intelligence will be seen coming into more products that we use every day, for example, Gmail that will not just auto-suggest but also write next mail to the boss.
- The big disruptor could be an affordable device that logs users into the Metaverse easily, maybe it will just be a smartphone. The challenge will be with the hardware that lets people access these virtual worlds without making people bankrupt in the real world.
- The ChatGPT can answer “follow-up questions”, and can also “admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.” but most such AI elements are now in standalone products, which is more play than work.
- Twitter and Facebook are struggling to remain relevant amid an increasingly digital native audience. Meta, for instance, knows that it will have to think beyond its present social media platforms as users move to the Metaverse. But that might not be something that will shift soon.
- The Internet spreads is becoming more localized and multilingual, in countries like India. Hence, the tech challenge in more ways than one, as there need to test out new technologies that can convert the content of the internet for these new users without much human intervention.
 Significance of Metaverse
Significance of Metaverse
- As hybrid workforces become the norm and with travel still not as easy as earlier, extended reality (XR) could become the answer to collaborate and communicate virtually.
[XR is umbrella term for all the new technologies, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) plus those that are still to be created.]
- All immersive technologies extend the reality we experience by either blending the virtual and “real” worlds or by creating a fully immersive experience.
- A few more commercial versions of the Metaverse are expected to be accessible to regular users during the year.
Ethical Concerns related to AI
- Yet, the study in Nature also finds that AI can actively hamper 59 or 35% of SDG targets.
- AI requires massive computational capacity, which means more power-hungry data centres and a big carbon footprint.
- AI could multiply digital exclusion.
- Many desk jobs will be framed out by AI, such as accountants, financial traders and middle managers.
- Without clear policies on reskilling workers, the promise of new opportunities will in fact create serious new inequalities.
- Investment is likely to shift to countries where AI-related work is already established widening gaps among and within countries.
- AI also presents serious data privacy concerns.
- We shape the algorithms and it is our data AI operate on.
- In 2016, it took less than a day for Microsoft’s Twitter chatbot, “Tay”, to start emitting racist content, based on the material it encountered.
Principles of a Responsible AI
- Privacy and Security: Personal data of data subjects must be safe and secure, such that only authorised persons must access personal data for specified and necessary purposes, within a framework of sufficient safeguards to ensure this process.
- Safety and Reliability: AI systems must have built-in safeguards to ensure the safety of stakeholders.
- Equality: AI systems must ensure equality keeping in mind that similar people in similar circumstances are treated equally.
- Inclusivity and Non-Discrimination: AI systems must be developed to be inclusive of all stakeholders, and must not discriminate through bias between stakeholders on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth or residence in matters of education, etc.
- Principle of Transparency: The design and training of AI systems is key for its functioning. The system must be audited and be capable of external scrutiny to ensure transparency.
- Principle of Accountability: Since there are various actors in the process of developing, deploying and operationalizing an AI system, the accountability structures must be clearly set out in a publicly accessible and understandable manner.
- Protection and Reinforcement of Positive Human Values: It focuses on the possible harmful effects of AI systems through collection of personal data for profiling.
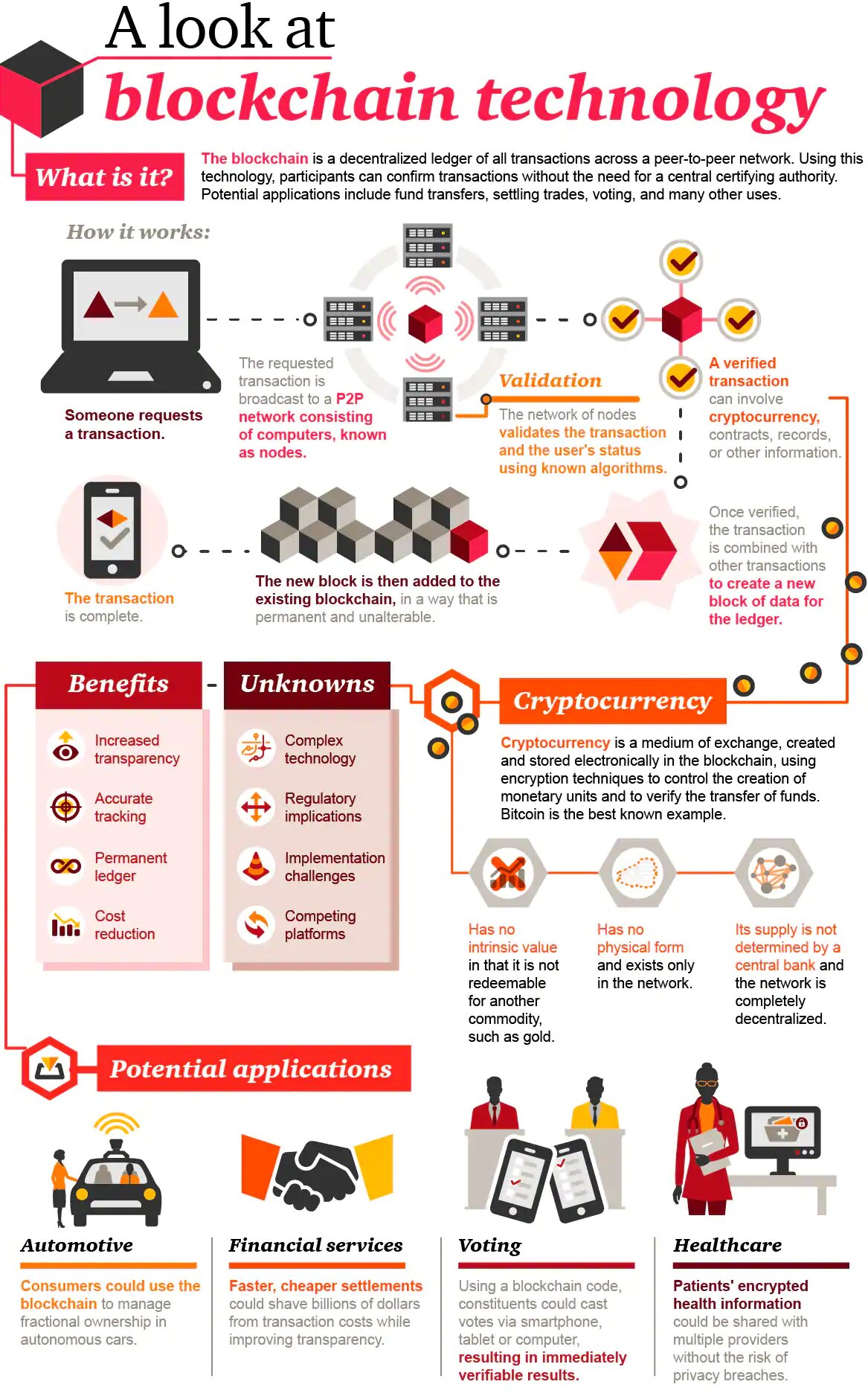
Non-Fungible Tokens
- Non-fungible tokens, often referred to as NFTs, are blockchain-based tokens that each represent a unique asset like a piece of art, digital content, or media.
- An NFT can be thought of as an irrevocable digital certificate of ownership and authenticity for a given asset, whether digital or physical. For example, Amitabh Bachchan NFT’s were on sale, Bachchan’s NFT collectable series included his father’s famous poem “Madhushala”, autographed vintage posters of himself, along with his other works.
- NFTs are created through a process called minting, in which the information of the NFT is recorded on a blockchain.
- They have become a popular way to buy and sell digital artwork.
- For Example: In 2020, the market capital of NFT bloomed, climbing 338 million from 41 million (2018)
|
Non-fungibility
|
Characteristics of a non-fungible tokens
- Uniqueness: Each NFT is unique and distinguishable from other tokens. It has its own specific characteristics, metadata, and ownership history.
- Indivisibility: NFTs cannot be divided or broken down into smaller units. They are treated as whole assets and cannot be exchanged on a like-for-like basis.
- Ownership and Authenticity: NFTs serve as proof of ownership and authenticity for a specific digital asset or item. They provide a verifiable record of the asset’s origin, ownership history, and attributes.
- Scarcity: NFTs can represent assets with limited availability or scarcity, adding to their value and collectibility. The scarcity may be predefined or determined by the creator or platform issuing the NFT.
|
NFT |
Cryptocurrency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Types of assets can non-fungible tokens be used for
- Non-fungible tokens can be created to represent virtually any asset, whether physical, digital or metaphysical.
- However, the most common NFT assets are digital art, digital collectible items, pieces of content like video or audio, and event tickets.
Benefits
- Disincentivize Plagiarism: They enable artists to create and sell unique and scarce digital works, without the risk of duplication or plagiarism.
- New Artistic Forms: They create a new form of artistic expression and innovation, where digital art can be interactive, dynamic, or collaborative, and where new genres and styles can emerge.
- Verifiability: The ownership of an NFT is recorded on a blockchain, which makes it easy to verify.
- Transferability: NFTs can be bought, sold, and traded on NFT marketplaces. This means that they can be used as a form of currency or investment.
- Authenticity: NFTs can be used to prove the authenticity of digital goods. This is because the ownership of an NFT is recorded on a blockchain, which makes it difficult to forge.
Challenges Associated with Non-Fungible Tokens
- Complexity: The technology and tooling behind non-fungible tokens and the decentralized applications that underpin them are still nascent.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: NFT has no recognized legal definition anywhere in the world. Different nations are forging forward with various classification schemes for NFT.
- High Consumption of Energy: They have a significant environmental impact, as they consume a lot of energy and generate a lot of emissions.
- Prone to Speculation: They are subject to market volatility and speculation, as the prices and demand of NFTs can fluctuate rapidly and unpredictably.
- Counterfeit and Fraudulent NFTs: There have been instances of fraudulent NFTs, which undermines trust in the NFT ecosystem and raises concerns about counterfeit NFTs circulating in the market.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies