- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
June 23,2024 Current Affairs
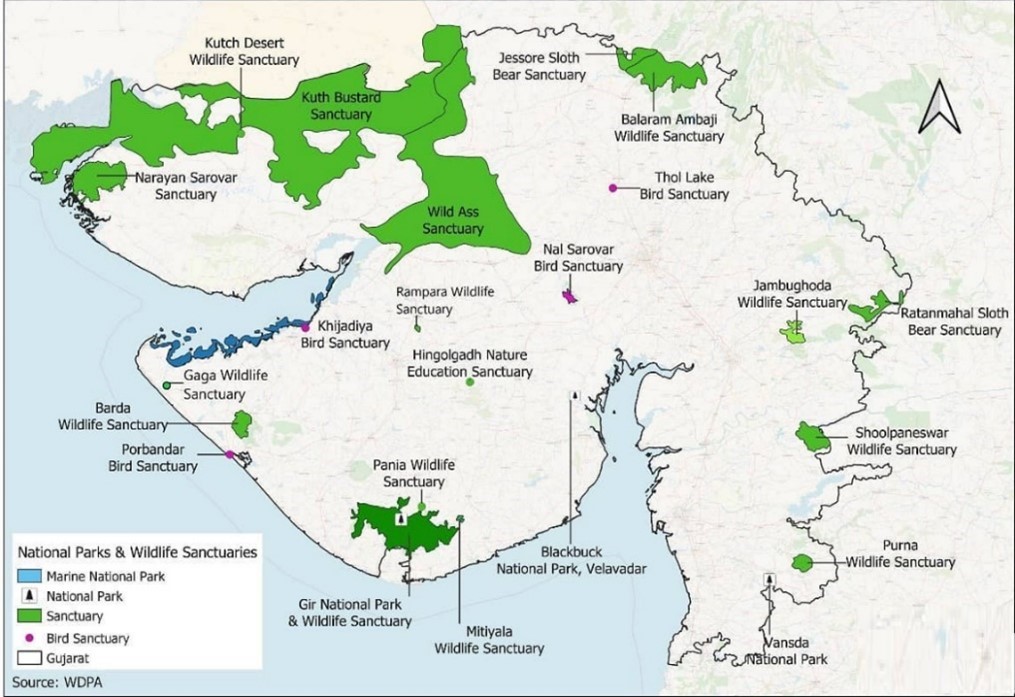
Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS)
- The Forest Department in Gujarat has initiated the translocation of spotted deer and sambars from Gir Forest to Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS), approximately 100 kilometers away.
- As lions make Barda sanctuary their second home
- Objective: This effort aims to enhance the prey population for Asiatic lions in BWS.
- This month, forest officials captured 23 spotted deer from Gir using the Boma technique and transported them to Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS) in Porbandar.
| Boma Technique: This method involves herding animals into an enclosure using funnel-like fencing. |
Reasons for Translocation-
- Supporting Lion Reintroduction: Lions return to Barda after a long absence, but the area lacks enough prey to sustain them.
- Translocating deer and sambars will provide a food source for these lions.
- Restoring the Ecosystem: Barda historically had lions, and reintroducing prey species helps restore the natural balance.
- Managing Gir Forest Population:Gir has a large spotted deer population (over 90,000).
- Translocating a small number helps manage Gir’s population while boosting Barda’s.
Barda Wildlife Sanctuary (BWS)
- Location: Gujarat, India.
- Proximity: About 15 kilometres from Porbandar and 100 kilometers west of Gir Forest National Park.
- Landscape: Hilly terrain covering 192.31 square kilometers.
- Rivers: Includes the Bileshvary River and the Joghri River.
- Dams: Two dams, Khambala and Fodara, are contained.
- Ethnic Communities: Inhabited by ethnic groups such as Maldharis, Bharvads, Rabaris, and Gadhvis.
- Development Project: The ‘Gir-Barda Project’ was initiated by the State Government in 1979 to establish Barda as a secondary habitat for the Asiatic lion.
Flora & Fauna
- Notable Plants: This sanctuary includes plants such as Rayan, Babul, Ber, Jamun, Amli, Gorad, Bamboo, Dhav, Dhudhlo, and others.
- Mammals: Leopard, hyena, wild boar, wolf, jackal, blue bull.
- Birds: Rare and endangered species like the spotted eagle and crested hawk eagle.
- Scientific Name: Panthera leo persica
- These are smaller than African lions.
- Breeding Season of Lions: Lions do not adhere to a particular breeding season, typically producing cubs approximately every two years.
- Gestation lasts an average of three to four months, with litter sizes typically ranging from one to four cubs.
- Reproductive Features: Lions are sexually mature by 2 years old, but males may not have the opportunity to mate until they are closer to 5 years old. They are polygamous, with the dominant male of the pride breeding with multiple females in the group.
Conservation Efforts
- Asiatic Lion Conservation Project: Initiated by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Duration: Approved for three financial years from 2018 to 2021.
- Objectives: Focuses on scientific management, community involvement, and coordination with multiple agencies for disease control and veterinary care to ensure the overall conservation of Asiatic lions.
- Habitat: West Bengal in the east to Rewa in Madhya Pradesh, central India.
- Current Habitat: Now restricted to Gir National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Distinct Feature: Notable for a longitudinal fold of skin along its belly.
Protection Status
- IUCN Red List: Classified as ‘Endangered’.
- CITES: Listed in ‘Appendix I’.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Included in ‘Schedule I’.
Threats
- Vulnerability: Susceptible to unpredictable events like plagues or natural disasters.
- Human Conflict: Poaching and retaliatory killings by locals near Gir National Park due to livestock attacks.
The World Health Organization (WHO) announced that Chad has successfully eradicated the gambiense form of human African trypanosomiasis (HAT).
- Chad eliminates human African trypanosomiasis as a public health problem
- Chad has become the first country of the year and the 51st worldwide to eliminate a neglected tropical disease (NTD).
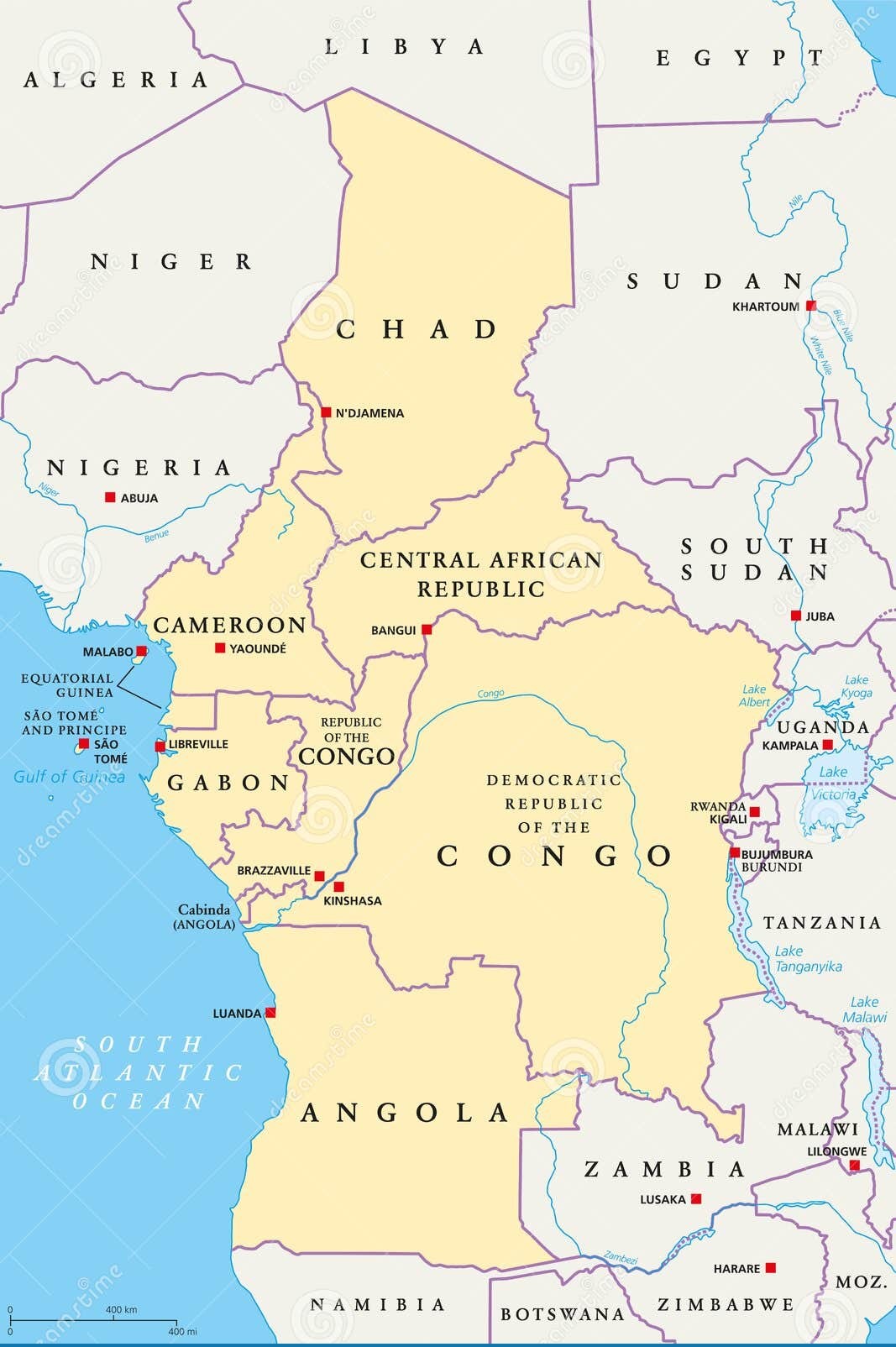
Chad
- It is a landlocked country in north-central Africa.
- It is largely a semi-desert country.
- Capital: N’Djamena
- Bordering Nations: Sudan, Niger, Libya and Central African Republic.
- Rivers: Chari and Logone
- Highest point: Mount Koussi
- WHO has validated the elimination of the gambiense form of HAT in seven countries:
- Togo (2020), Benin (2021), Ivory Coast (2021), Uganda (2022), Equatorial Guinea (2022)
- Ghana (2023), Chad (2024).
- Progress in the Fight Against NTDs: Chad has joined other countries that have eliminated sleeping sickness, contributing to the global target of eliminating 100 NTDs by 2030.
Human African Trypanosomiasis
- Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT) is commonly known as sleeping sickness.
- Disease Causing Agent: Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is caused by protozoan parasites.
- Transmission: Infected tsetse flies.
- Symptoms: The disease is typically fatal if untreated, causing symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and, in severe cases, coma.
Forms of HAT
- There are two forms of HAT based on the subspecies of the parasite:
- Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: Accounts for 92% of reported cases.
- Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense: Responsible for the remaining 8% of cases.
Government imposes stock limits on tur, chana dal to curb hoardings.
- Recently, the government imposed stock limits on tur (pigeon pea) and chana (chickpea) dal for all states and union territories until September this year.
- Stock-holding limit: A regulatory measure that imposes caps on the quantities of specific commodities, such as pulses, that retail shops and traders can store.
- Applicability: The Centre passed the Removal of Licensing Requirements, Stock Limits and Movement Restrictions on Specified Foodstuffs (Amendment) Order, 2024, specifying stock limits for wholesalers, retailers, supermarkets, millers and importers for the two commodities
Reason: The move is aimed to:
- Prevent hoarding.
- Curb unscrupulous speculation.
- Improve affordability of tur and chana for consumers.
- Curb Price Inflation.
Monitored by: The Department of Consumer Affairs has been closely monitoring Pulses stock position through the stock disclosure portal.
Government Initiatives to Stabilise Pulses Market and Ensure Affordability
- Enforcement of Mandatory Stock Disclosure: The department communicated with state governments to enforce mandatory stock disclosure by all stockholding entities.
- Follow-up visits to major pulses-producing states and trading hubs were conducted across the country.
- Stakeholder Meetings: Separate meetings were held with traders, stockists, dealers, importers, millers, and big-chain retailers to encourage truthful stock disclosure and maintain the affordability of pulses for consumers.
- Import Duty Reduction: To boost domestic production, the government reduced the import duty on desi chana by 66 per cent.
- The duty reduction has facilitated imports and prompted higher sowing of chana in major producing countries.
- Expected Increase in Kharif Pulses Sowing: The sowing of Kharif pulses like tur and urad is expected to rise significantly this season due to farmers’ high price realisation and the India Meteorological Department (IMD) prediction of above-normal monsoon rains.
- Imports of Tur from East Africa and Chana from Australia: Imports of the current year’s crop of tur from East African countries and Chana from Australia will help maintain the affordable availability of Chana to consumers.
Russia and North Korea recently signed the “Treaty on Comprehensive Strategic Partnership”.
- The pact between Russia and North Korea talks about cooperation on a wide range of issues, such as Nuclear energy, Space exploration, Food, and energy security, and mutual military support and unspecified technological assistance.
- A crucial part of the deal is the mutual defence provisions.
|
Historical Context
|
The Russia-North Korea Pact
- Mutual defence provisions: In case any one of the two sides is put in a state of war by an armed invasion from an individual state or several states, the other side shall provide military and other assistance with all means in its possession without delay in accordance with Article 51 of the UN Charter and the laws of the DPRK and the Russian Federation
- This provision echoes the 1961 agreement between the two nations.
|
Article 51 of the UN Charter It provides for the right of a member country to take individual or collective self-defence actions. |
Implications of the Pact on the Global World-
- Perceived Security Threat For Others: For South Korea and Japan, this treaty is likely to be perceived as a direct security threat.
- Both countries have long been concerned about North Korea’s nuclear program and military strength.
- Deterrence: This will likely push both countries to strengthen their defences and rethink their security policies.
- Japan: It has already abandoned its long-standing pacifist foreign policy and is building its military might.
- South Korea: It has convened an emergency meeting of its national security council in response and said it will now consider sending arms to Ukraine, something which it had thus far resisted.
- Increasing Dependence On USA: Both South Korea and Japan are likely going to cement their alliance with the United States further in order to strengthen their strength
- Strengthens The Anti-West Bulwark In Asia: Russia-North Korea pact could also encourage similar partnerships elsewhere, most notably with Iran
- China Is Likely To Be Conflicted About The Development: China would be wary of Russia’s growing military collaboration with North Korea, which could undermine its near-exclusive geopolitical influence over Pyongyang.
- It would also be concerned about a greater Western footprint in Asia as a result of this development.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies