- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
May 08, 2024 Current Affairs
European Parliament and the European Council reached to provisional agreement to establish the first EU-level Carbon Removal Certification Framework.
- Aim: To enhance carbon removal technologies and carbon farming by setting quality criteria standards.
- Includes monitoring and reporting processes to prevent greenwashing.
Carbon Farming:
- Carbon farming involves implementing regenerative agricultural practices that aim to restore ecosystem health, improve agricultural productivity and soil health, and mitigate climate change.
- It integrates carbon sequestration into the management of agricultural landscapes and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- This practice is adaptable across various agro-climatic zones.
- Common Forms of Carbon Farming: It includes rotational grazing, agroforestry, conservation agriculture, integrated nutrient management, agro-ecology, livestock management, and land restoration.
- Optimal Conditions for Carbon Farming: Regions with long growing seasons, sufficient rainfall, and substantial irrigation provide the best conditions to sequester carbon, through vegetation growth.
- In regions with adequate rainfall and fertile soil, the potential for carbon sequestration through practices like agroforestry (integrating trees and shrubs with crops) and conservation agriculture (minimising soil disturbance) may be particularly high.
Advantages of Carbon Farming:
- Diversification of Farm Income: Agroforestry practices including silvopasture and alley cropping can diversify farm income by sequestering carbon in trees and shrubs.
- Enhancement of Soil Health: Conservation agriculture can help minimize soil disturbance and enhance organic content, particularly in places with other intense agricultural activities.
- Conservation agriculture techniques include zero tillage, crop rotation, cover cropping, and crop residue management (stubble retention and composting)
- Promoting Soil Fertility: Integrated nutrient management practices promote soil fertility and reduce emissions by using organic fertilizers and compost.
- Ecosystem Resilience: Agro-ecological approaches such as crop diversification and intercropping have benefits for ecosystem resilience.
- Reducing Methane Emissions: Livestock management strategies including rotational grazing, optimising feed quality, and managing animal waste can reduce methane emissions and increase the amount of carbon stored away in pasture lands.
Definitions:
- Silvopasture: It is the integration of trees and grazing livestock operations on the same land. These systems are intensively managed for both forest products and forage, providing both short- and long-term income sources.
- Alley cropping: It is defined as the planting of rows of trees and/or shrubs to create alleys within which agricultural or horticultural crops are produced.
- Intercropping: It is the practice of growing two or more crops in proximity.
- Organic Farming: In this type of farming, organic manure and natural pesticides are used instead of chemicals. No genetic modification is done to increase the yield of the crop.
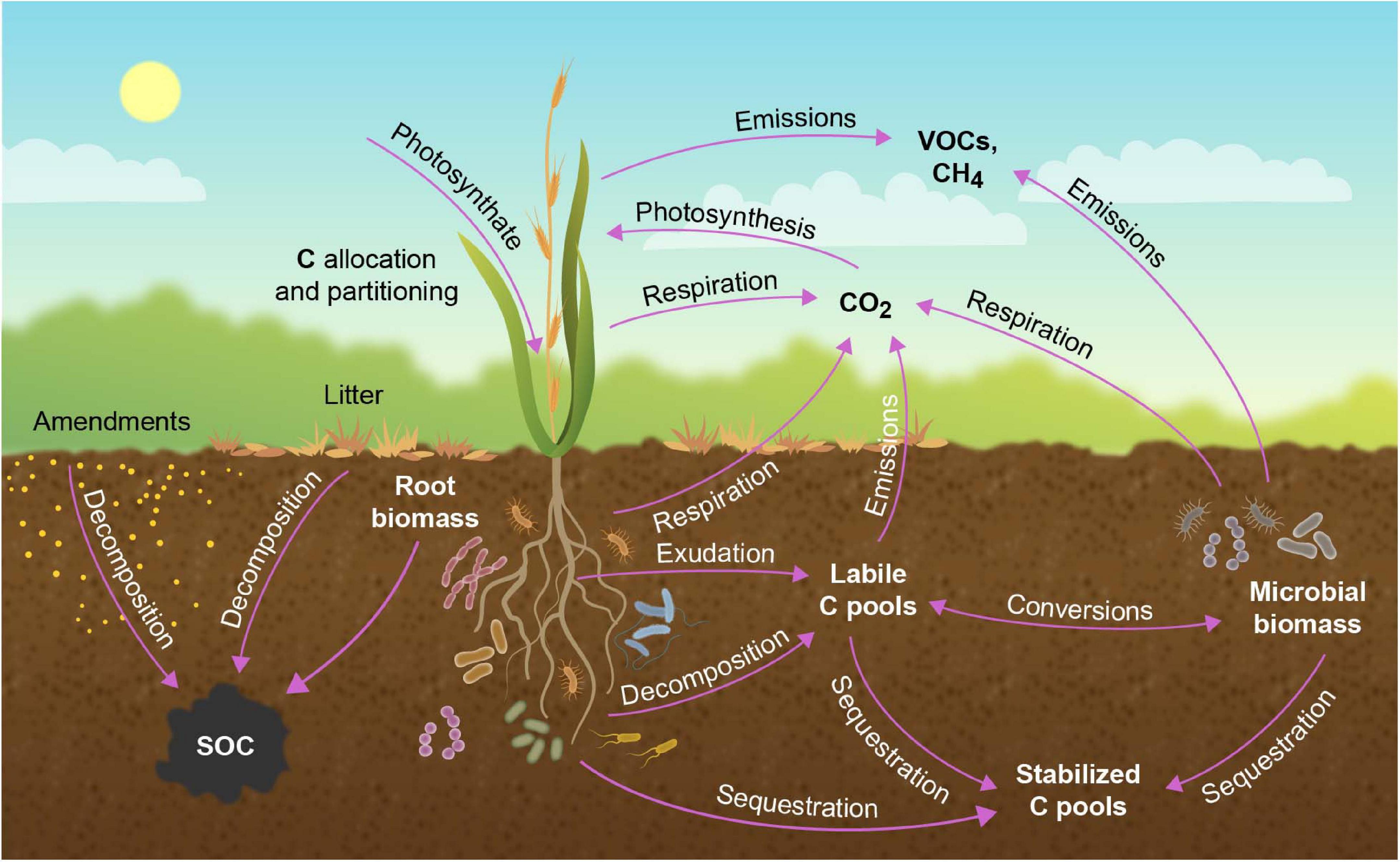
Challenges to Carbon Farming
- Limited water availability: It can hinder the growth of plants, thus restricting the potential for sequestration through photosynthesis.
- For example, practices like cover cropping, which require additional vegetation between main crop cycles, may not be viable due to the added water demand.
- Carbon farming can be challenging in hot and dry areas where the availability of water is limited, and prioritized for drinking and washing needs.
- Carbon Sequestration: It is a climate change mitigation technology where CO2 is captured from power plants and other industrial processes instead of being emitted to the atmosphere.
- The captured CO2 is then stored in the subsurface with the goal of keeping it out of the atmosphere indefinitely.
- Plant Selection for Carbon Sequestration: Selecting which plants to grow also becomes crucial because not all species trap and store carbon in the same amounts or in an equally effective manner.
- Financial Constraints: The adoption of carbon farming practices may require financial assistance for farmers to overcome the costs of implementing them.
- In India, small-scale farmers may lack the resources to invest in sustainable land management practices and environmental services.
India''s first high-performance System-On-Chip (SoC), developed by an IIT-Madras incubated startup.
- It will reduces dependency on imported chips, enhancing self-sufficiency in the semiconductor sector.
System-On-Chip (SoC):
- An SoC integrates multiple electronic components into a single chip, functioning like a mini-computer.
- Embedded into the printed circuit board (PCB) of various devices, enhancing their compactness and efficiency.
- Secure IoT runs at 700 MHz, positioning it as a high-performance microcontroller.
Key Features
- Cost-effective: Costs 30% less than other chips in the same category.
- Versatility and adaptability: Designed to be flexible for use in a wide range of applications.
- Security: Features top-notch security measures suitable for modern demands.
- High computing power: Capable of managing complex operations across various devices.
- Programmability: Allows for customization according to specific requirements of devices.
Applications
- Used in deep embedded applications like smart locks, fans, speakers, and wearables.
- Applicable to smart city devices, such as connected systems for electricity, water, and gas metering.
- Enhances features of automotive technologies, including EV battery management systems.
- Suitable for IoT devices across different sectors including vision technologies and home automation.
The Army and the Indian Air Force will likely have their MQ-9B Predator Drones in Gorakhpur and Sarsawa.
MQ-9B Predator drone:
- The MQ-9B Predator drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle, also known as "Predators."
- It includes two variants: SkyGuardian and SeaGuardian.
- SkyGuardian is a remotely piloted aircraft system (RPAS) that serves as the next generation of RPAS.
- SeaGuardian, used by the Indian Navy since 2020, is a maritime-focused version of the SkyGuardian.
- The MQ-9B series are High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) drones, capable of flying for over 40 hours in all types of weather, utilizing a satellite.
- Total of 31 MQ-9B Predator drones are distributed as follows:
- Indian Navy has 15 SeaGuardian drones.
- The Army and the Indian Air Force each have eight SkyGuardian drones.
- Equipped with advanced technologies such as Multi-mode Radar and an electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) sensor.
Capable of multiple roles, including:
- Offensive missions
- Surveillance
- Reconnaissance
- Intelligence operations
- Over-the-horizon targeting
- Airborne early warning
- Electronic warfare
Kerala''s health department recently reported West Nile fever cases in three districts.
West Nile Fever:
- It is a disease caused by the West Nile Virus (WNV).
- WNV is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
- Birds are the natural hosts of WNV.
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- It can cause a deadly neurological disease in humans.
- It is named after the West Nile district of Uganda, where it was first identified in 1937.
Transmission:
- It is most commonly spread to people by the bite of an infected mosquito. The mosquitoes get the virus when they bite an infected bird.
- There is no evidence that WNV can be spread directly from one person to another.
- But there have been a few cases where it has spread through organ transplants.
Symptoms:
- Most people infected by the virus are asymptomatic (no symptoms).
- Symptoms include fever, headache, tiredness, body aches, nausea, vomiting, occasional skin rash, and swollen lymph glands.
- The symptoms of severe disease (also called neuroinvasive disease, such as West Nile encephalitis or meningitis or West Nile poliomyelitis) include headache, high fever, neck stiffness, stupor (near-unconsciousness), disorientation, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness, and paralysis.
Treatment:
- There is no medicine or vaccine available against the WNV.
- Treatment is based on supportive care involving hospitalisation, intravenous fluids, respiratory support, and prevention of secondary infections.
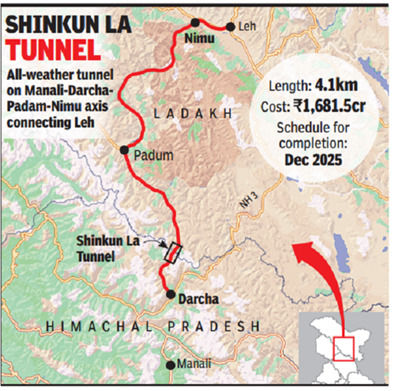
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is preparing to commence the construction of the Shinkun La Tunnel.
Shinkun La Tunnel:
- It is an upcoming motorable tunnelunder the 16,580 feet high Shinku-La pass between Himachal’s Lahaul valley and Ladakh’s Zanskar valley.
- It is located on the Nimu-Padam-Darcha Road link.
- The length of the tunnel will be 4.1 km.
- After completion, the Shinku-la tunnel will be the longest high altitude highway tunnel in the world.
- The Border Roads Organization (BRO) will construct the tunnel at a cost of Rs. 1,681.5 crores.
- It will provide all-weather road connectivity to Ladakh, and this will be the shortest route to the border areas of Ladakh.
- It is expected to streamline the transportationof heavy machinery to strategic locations such as Kargil, Siachen, and the Line of Control (LOC), reducing travel distances by approximately 100 km.
- The traffic movement in the tunnel will not be vulnerable to long-range artillery shelling or missile firings, either by China or Pakistan.
Border Roads Organisation (BRO):
- It is a road construction executive force in India that provides support to the Indian Armed Forces.
- Establishment: It was formed on 7 May, 1960, to secure India''s borders and develop infrastructure in remote areas of the north and north-east states of the country.
- It develops and maintains road networks in India''s border areas and friendly neighboring countries.
- This includes infrastructure operations in 19 states and three union territories (including Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan, and Sri Lanka.
- Officers and personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF) form the parent cadre of the BRO.
- It is also staffed by officers and troops drawn from the Indian Army''s Corps of Engineers on extra regimental employment (on deputation).
- BRO is also included in the Order of Battle of the Armed Forces, ensuring their support at any time.
- Motto of the organization: Shramena Sarvam Sadhyam (everything is achievable through hardwork).









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies