- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
News Information Bureau | 10th August 2020
From Satyagraha to Swachchgraha: PM Narendra Modi launches Rashtriya Swachhata Kendra
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has inaugurated the Rashtriya Swachhata Kendra – an interactive experience centre on the Swachh Bharat Mission.
A tribute to Mahatma Gandhi, the Rashtriya Swachhata Kendra (RSK) was first announced by the Prime Minister on 10th April 2017, on the occasion of the centenary celebrations of Gandhiji’s Champaran Satyagraha.
"Rashtriya Swachhata Kendra"
 Concern
Concern
 Global magnetic field of the solar corona measured for the first time
A significant advance has been made by an international team of solar physicists led by those from Peking University, China, and National Center for Atmospheric Research of the U.S. The group has measured the global magnetic field of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, for the very first time. This research has been published in the journal Science.
What does the research aim to study?
Global magnetic field of the solar corona measured for the first time
A significant advance has been made by an international team of solar physicists led by those from Peking University, China, and National Center for Atmospheric Research of the U.S. The group has measured the global magnetic field of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, for the very first time. This research has been published in the journal Science.
What does the research aim to study?


- The RSK has a balanced mix of digital and outdoor installations tracking India’s transformation from having over 50 crore people defecating in the open in 2014 to becoming open defecation free in 2019.
- The facility is a tribute to Gandhi’s efforts for a swachh (clean) India. It will mostly cater to tourists and schoolchildren, to educate them about the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- From portrayals showing Gandhi with students, to women or ‘ranimistris’ building toilets and PM Modi’s 2014 address from the ramparts of the Red Fort, outdoor art installations in the facility educate visitors about the mission’s journey.
- The Rashtriya Swachhta Kendra has been built in the last five months at a cost of around Rs 5 crore. It will be a part of schoolchildren’s guided tours to the Rajghat. Entry will be free for children.
- On this occasion, the Prime Minister launched ‘Gandagi Mukt Bharat’, a special week long campaign for swachhata in the run up to Independence Day, during which each day till 15th August will have special swachhata initiatives in urban and rural India to re-enforce the jan andolan for swachhata.
- Under the scheme, Rs. 1 Lakh Crore will be provided by banks and financial institutions as loans to Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Marketing Cooperative Societies, Farmer Producers Organisations (FPOs), Self Help Group (SHG), Farmers, Joint Liability Groups (JLG), Multipurpose Cooperative Societies, Agri-entrepreneurs, Startups, Aggregation Infrastructure Providers and Central/State agency or Local Body sponsored Public Private Partnership Project.
- Loans will be disbursed in four years starting with sanction of Rs. 10,000 crore in the current year and Rs. 30,000 crore each in next three financial years.
- All loans under this financing facility will have interest subvention of 3% per annum up to a limit of Rs. 2 crore. This subvention will be available for a maximum period of seven years.
- Further, credit guarantee coverage will be available for eligible borrowers from this financing facility under Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) scheme for a loan up to Rs. 2 crore. The fee for this coverage will be paid by the Government.
- In case of FPOs the credit guarantee may be availed from the facility created under FPO promotion scheme of Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare (DACFW).
- Moratorium for repayment under this financing facility may vary subject to minimum of 6 months and maximum of 2 years.
- The National, State and District level Monitoring Committees will be set up to ensure real-time monitoring and effective feed-back.
- The duration of the Scheme shall be from FY2020 to FY2029 (10 years).
- The Project by way of facilitating formal credit to farm and farm processing-based activities is expected to create numerous job opportunities in rural areas.
- Agri Infra fund will be managed and monitored through an online Management Information System (MIS) platform.
- It will enable all the qualified entities to apply for loan under the fund. The online platform will also provide benefits such as transparency of interest rates offered by multiple banks, scheme details including interest subvention and credit guarantee offered, minimum documentation, faster approval process as also integration with other scheme benefits.
- The scheme was started with a view to augment the income of the farmers by providing income support to all landholding farmers’ families across the country.
- Under the Scheme an amount of Rs.6000/- per year is transferred in three 4-monthly instalments of Rs. 2000/- directly into the bank accounts of the farmers, subject to certain exclusion criteria relating to higher income status.
- The Scheme was formally launched on 24th February, 2019 at Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh.
- The Common Service Centres (CSCs) have also been authorised to do registration of the farmers for the Scheme upon payment of fees.
- The PM-KISAN Scheme initially provided income support to all Small and Marginal Farmers’ families across the country, holding cultivable land upto 2 hectares.
- Its ambit was later expanded w.e.f. 01.06.2019 to cover all farmer families in the country irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- Affluent farmers have been excluded from the scheme such as Income Tax payers in last assessment year, professionals like Doctors, Engineers, Lawyers, Chartered Accountants etc and pensioners pensioners drawing at least Rs.10,000/- per month (excluding MTS/Class IV/Group D employees).
- The list of 101 embargoed items comprises of not just simple parts but also some high technology weapon systems like artillery guns, assault rifles, corvettes, sonar systems, transport aircrafts, light combat helicopters (LCHs), radars and many other items to fulfil the needs of our Defence Services.
- The list also includes, wheeled armoured fighting vehicles (AFVs) with indicative import embargo date of December 2021, of which the Army is expected to contract almost 200 at an approximate cost of over Rs 5,000 crore.
- Similarly, the Navy is likely to place demands for submarines with indicative import embargo date of December 2021, of which it expects to contract about six at an approximate cost of almost Rs 42,000 crore.
- For the Air Force, it is decided to enlist the light combat aircraft LCA MK 1A with an indicative embargo date of December 2020. Of these, 123 are anticipated at an approximate cost of over Rs 85,000 crore.
- In another relevant step, the MoD has bifurcated the capital procurement budget for 2020-21 between domestic and foreign capital procurement routes. A separate budget head has been created with an outlay of nearly Rs 52,000 crore for domestic capital procurement in the current financial year.
- It offers a great opportunity to the Indian defence industry to rise to the occasion to manufacture the items in the negative list by using their own design and development capabilities or adopting the technologies designed and developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) to meet the requirements of the Armed Forces in the coming years.
- With latest embargo on import of 101 items, it is estimated that contracts worth almost Rs 4 lakh crore will be placed upon the domestic industry within the next five to seven years. Of these, items worth almost Rs 1,30,000 crore each are anticipated for the Army and the Air Force while items worth almost Rs 1,40,000 crore are anticipated by the Navy over the same period.
- The embargo on imports is planned to be progressively implemented between 2020 to 2024. The aim behind promulgation of the list is to apprise the Indian defence industry about the anticipated requirements of the Armed Forces so that they are better prepared to realise the goal of indigenisation.
 Concern
Concern
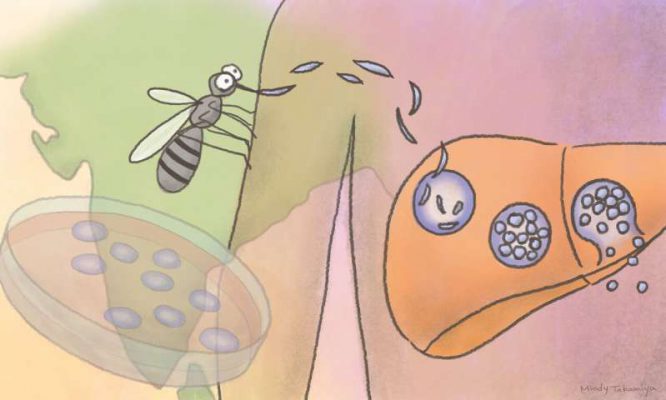
- Mosquitoes inject the sporozoite (spore-like) stage of the parasite into the skin when they bite, and the sporozoites travel to the liver.
- Imagine some 50 parasites enter our liver, each infect one liver cell or hepatocyte and multiply enormously to 10,000 or more. These can then move out and infect blood cells.
- As the number is very low in the liver, our immune system barely notices it. The parasite can remain in the liver in a dormant stage and relapse later. So there is an urgent need to find drugs for P. vivax which will kill both the blood and liver stages.
- Another complication is the emergence of drug-resistant malaria parasites. Certain malaria-endemic countries have even abandoned chloroquine for P. vivax treatment. Fortunately chloroquine is still effective in India. Therefore, there is an urgent need for development of a new class of drugs. The researchers add this assay could also be used to test if a specific anti-malarial drug would work for an individual.
- Documenting every single wingbeat of the birds, researchers have found that and Andean condors can sustain soaring for long hours without flapping their wings.
- Studying individual wingbeats for over 216 hours of flight, researchers found that they flap their wings for only 1% of their flight time. Even this flapping was specifically during take-off and when close to the ground; over 75% of flapping flight was associated with takeoffs.
- It is predicted that condors can soar long distances by flapping for about 2 seconds per kilometre. Since flapping imposes an economic cost, the overall flight effort of condors is constrained by the requirements for take-off.
- Even the wandering albatross (Diomedia exulans), which weighs about 9.4 kg and flaps minimally, spends 1.2-14.5% of its flight (outside take-off) in slow, flapping flight.
- Currents of warm rising air and streams of air pushed upward by ground features help these birds soar. Ability to ride air currents allows them to travel long distances with minimal exertion.
 Global magnetic field of the solar corona measured for the first time
A significant advance has been made by an international team of solar physicists led by those from Peking University, China, and National Center for Atmospheric Research of the U.S. The group has measured the global magnetic field of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, for the very first time. This research has been published in the journal Science.
What does the research aim to study?
Global magnetic field of the solar corona measured for the first time
A significant advance has been made by an international team of solar physicists led by those from Peking University, China, and National Center for Atmospheric Research of the U.S. The group has measured the global magnetic field of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, for the very first time. This research has been published in the journal Science.
What does the research aim to study?
- There are two main puzzles about the Sun which this advancement will help address. First is the coronal heating problem. Though the core of the Sun is at a temperature of about 15 million degrees, its outer layer, the photosphere is a mere 5700 degrees hot.
- However, its corona or outer atmosphere, which stretches up to several million kilometres beyond its surface, is much, much hotter than the surface. It is at a temperature of one million degrees or more.
- What causes the atmosphere of the Sun (corona) to heat up again, though the surface (photosphere) is cooler than the interior. That is the question which has baffled solar physicists. Popular attempts to explain this puzzle invoke the magnetic field of the corona. Hence the present work will help understand and verify these theories better.
- The other set of questions concerns the mechanisms of eruptions of the Sun, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These are driven by magnetic reconnections happening in the sun’s corona.
- The team used a technique known as coronal seismology or magnetoseismology to measure the coronal magnetic field which has been known for a few decades. This method requires the measurement of the properties of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves and the density of the corona simultaneously.

- Our Sun is surrounded by a jacket of gases called an atmosphere. The corona is the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere.
- The corona is usually hidden by the bright light of the Sun’s surface. That makes it difficult to see without using special instruments. However, the corona can be seen during a total solar eclipse.
- The corona extends far out into space. From it comes the solar wind that travels through our solar system. The corona’s temperature causes its particles to move at very high speeds. These speeds are so high that the particles can escape the Sun’s gravity.
- It has a temperature of approximately two million kelvins and an extremely low density.










 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies