- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
News Information Bureau | 29th July 2020
India’s involvement in ITER reflects capabilities for advanced design and manufacturing: PM Modi
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has written a message to the scientific community of many nations on the historic occasion of the beginning of the ITER Assembly activities.
ITER Project
 HRD Minister Launches India Report On Digital Education During COVID-19
Union Minister for HRD has launched India Report on Digital Education, 2020. The report elaborates the innovative methods adopted by the Ministry of HRD, Education Department of States and Union Territories for ensuring accessible and inclusive education to children at home and reducing learning gaps.
Initiatives by Ministry of HRD
Ministry of Human Resource Development has initiated many projects to assist teachers, scholars and students in their pursuit of learning like DIKSHA platform, Swayam Prabha TV Channel, Online MOOC courses, On Air – Shiksha Vani, DAISY by NIOS for differently-abled, e-PathShala, National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) to develop e-content and energised books, telecast through TV channels, E-learning portals , webinars, chat groups, distribution of books and other digital initiatives along with State/ UT Governments.
Initiatives by State Governments/UTs
HRD Minister Launches India Report On Digital Education During COVID-19
Union Minister for HRD has launched India Report on Digital Education, 2020. The report elaborates the innovative methods adopted by the Ministry of HRD, Education Department of States and Union Territories for ensuring accessible and inclusive education to children at home and reducing learning gaps.
Initiatives by Ministry of HRD
Ministry of Human Resource Development has initiated many projects to assist teachers, scholars and students in their pursuit of learning like DIKSHA platform, Swayam Prabha TV Channel, Online MOOC courses, On Air – Shiksha Vani, DAISY by NIOS for differently-abled, e-PathShala, National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) to develop e-content and energised books, telecast through TV channels, E-learning portals , webinars, chat groups, distribution of books and other digital initiatives along with State/ UT Governments.
Initiatives by State Governments/UTs

 What is the long-term solution to the problem?
What is the long-term solution to the problem?
- ITER is international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject, which will be the world’s largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment. The goal of ITER is to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of fusion energy for peaceful use.
- It is an experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor that is being built next to the Cadarache facility in Saint-Paul-lès-Durance, in Provence, southern France.
- The project is funded and run by seven member entities—the European Union, India, Japan, China, Russia, South Korea and the United States.
- Construction of the ITER Tokamak complex started in 2013 and the building costs were over US$14 billion by June 2015.
- The EU, as host party for the ITER complex, is contributing about 45 per cent of the cost, with the other six parties contributing approximately 9 per cent each.
- Scientists have long sought to mimic the process of nuclear fusion that occurs inside the Sun, arguing that it could provide an almost limitless source of cheap, safe and clean electricity.
- Unlike in existing fission reactors, which split plutonium or uranium atoms, there is no risk of an uncontrolled chain reaction with fusion and it does not produce long-lived radioactive waste.
- The ITER aims to use a strong electric current to trap plasma inside a doughnut-shaped enclosure long enough for fusion to take place.
- Hydrogen plasma will be heated to 150 million degrees Celsius, ten times hotter than the core of the Sun, to enable the fusion reaction.
- The process happens in a doughnut-shaped reactor, called a tokamak 1, which is surrounded by giant magnets that confine and circulate the superheated, ionised plasma, away from the metal walls.
- The superconducting magnets must be cooled to -269°C (-398°F), as cold as interstellar space.
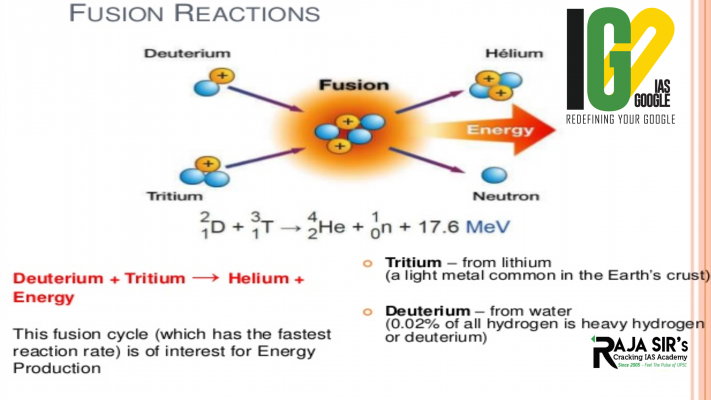
- Nuclear fusion is the process of making a single heavy nucleus (part of an atom) from two lighter nuclei.
- The nucleus made by fusion is heavier than either of the starting nuclei. It releases a large amount of energy.
- Fusion is what powers the Sun. Atoms of Tritium and Deuterium (isotopes of hydrogen, Hydrogen-3 and Hydrogen-2, respectively) unite under extreme pressure and temperature to produce a neutron and a helium isotope. Along with this, an enormous amount of energy is released, which is several times the amount produced by fission.
- Scientists continue to work on controlling nuclear fusion in an effort to make a fusion reactor to produce electricity.
- While nuclear fission is the division of one atom into two (by neutron bombardment), the fusion is the combination of two lighter atoms into a larger one (at a very high temperature).
 HRD Minister Launches India Report On Digital Education During COVID-19
Union Minister for HRD has launched India Report on Digital Education, 2020. The report elaborates the innovative methods adopted by the Ministry of HRD, Education Department of States and Union Territories for ensuring accessible and inclusive education to children at home and reducing learning gaps.
Initiatives by Ministry of HRD
Ministry of Human Resource Development has initiated many projects to assist teachers, scholars and students in their pursuit of learning like DIKSHA platform, Swayam Prabha TV Channel, Online MOOC courses, On Air – Shiksha Vani, DAISY by NIOS for differently-abled, e-PathShala, National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) to develop e-content and energised books, telecast through TV channels, E-learning portals , webinars, chat groups, distribution of books and other digital initiatives along with State/ UT Governments.
Initiatives by State Governments/UTs
HRD Minister Launches India Report On Digital Education During COVID-19
Union Minister for HRD has launched India Report on Digital Education, 2020. The report elaborates the innovative methods adopted by the Ministry of HRD, Education Department of States and Union Territories for ensuring accessible and inclusive education to children at home and reducing learning gaps.
Initiatives by Ministry of HRD
Ministry of Human Resource Development has initiated many projects to assist teachers, scholars and students in their pursuit of learning like DIKSHA platform, Swayam Prabha TV Channel, Online MOOC courses, On Air – Shiksha Vani, DAISY by NIOS for differently-abled, e-PathShala, National Repository of Open Educational Resources (NROER) to develop e-content and energised books, telecast through TV channels, E-learning portals , webinars, chat groups, distribution of books and other digital initiatives along with State/ UT Governments.
Initiatives by State Governments/UTs
- Some of the major digital initiatives by State Governments are SMILE (Social Media Interface for Learning Engagement) in Rajasthan, Project Home Classes in Jammu, Padhai Tunhar duvaar (Education at your doorstep) in Chhattisgarh, UnnayanInitiatives in Bihar through portal and mobile application, Mission Buniyaad in NCT of Delhi, Kerala’s own educational TV channel (Hi-Tech school programme), E-scholar portal as well as free online courses for teachers in Meghalaya. Telangana has online certificate programs for teachers on ‘Management of mental well-being during COVID’.
- Assam has launched the Biswa Vidya Assam Mobile Application for class 6 to 10. Bihar has launched Vidyavahini App with e-books for class 1 to 12. Under Unnayan Bihar Initiative, Bihar has also launched Mera Mobile Mera Vidyalaya for students, and Unnayan Bihar Teacher App. Chandigarh has launched Phoenix Mobile application to assess the learning outcome for the students of class 1 to 8. Maharashtra has launched the Learning Outcomes Smart Q Mobile App to facilitate learning for students in the state. Punjab has launched iScuela Learn Mobile Application for class 1 to 10. Sikkim Edutech App connects all the schools of Sikkim under the State Education Department, Parents also have login access along with students, teachers and administrative units. Tripura has an application titled ‘EmpowerU Shiksha Darpan’ in order to facilitate student’s appraisal. Uttar Pradesh launches ‘Top Parent’ app targeting children from 3-8years age. The application currently houses three high-quality EdTech apps for children – Chimple, Maths Masti and Google Bolo.

- During the release, the Environment Minister has confirmed that the Ministry is working on a programme in which efforts would be made to provide water and fodder to animals in the forest itself to deal with the challenge of human-animal conflict which is causing deaths of animals.
- For this LIDAR based survey technology will be used for the first time. Lidar is a method for measuring distances by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflection with a sensor.
- It was highlighted that with the presence of nearly 30 percent of India’s tigers outside tiger reserves, India had embarked upon assessing management interventions through the globally developed Conservation Assured | Tiger Standards (CA|TS) framework, which will now be extended to all fifty tiger reserves across the country.
- The day is celebrated on July 29 each year to create awareness for tiger conservation. It promotes a system to protect natural habitats of tigers and raise public awareness. This year, the Global Tiger Day is celebrated with the slogan, “Their Survival is in our hands”.
- Saint Petersburg Summit – The summit was held to increase the awareness about declining tiger population in the world. Also, the leaders attended the summit pledged to make efforts to double the tiger population by 2022.
- In 2010, with tiger numbers at an all time low, the tiger range governments committed to an ambitious and visionary goal of Tx2- to double wild tigers by 2022.
- The initiative was started in 2010 at the St. Petersburg Tiger Summit.
- The Tx2 approach looks at doubling the number of tigers in the wild, rather than just saving the animal in each of the countries in which it is present. This strategic focus looks at not only protecting tigers but protecting landscapes including source sites and corridors, according to World Wildlife Fund.
- It also encourages trans-boundary collaboration between countries for tiger conservation.
- The Tx2 initiative marks the first time that all tiger range countries have come together to collaborate and work together towards a global goal of protecting this apex predator.
- India has fulfilled its resolve to double the tiger numbers four years before the target. The country now has an estimated 2967 tigers as per the latest census.
- With this number, India is home to nearly 75% of the global tiger population and has already fulfilled its resolve of doubling tiger numbers, made at St. Petersburg in 2010, much before the target year of 2022.
- The latest results of 2018 had shown that India now has an estimated 2967 tigers out of which 2461 individual tigers have been photo captured, a whopping 83% of the tiger population, highlighting the comprehensive nature of the survey.
- The All India Tiger Estimation done quadrennially is steered by the National Tiger Conservation Authority with technical backstopping from the Wildlife Institute of India and implemented by State Forest Departments and partners.
- Abundance index of co-predators and other species has been carried out which hitherto was restricted only to occupancy
- Sex ratio of tigers in all camera trap sites has been carried out for the first time.
- Anthropogenic effects on tiger population have been elaborated in a detailed manner.
- Tiger abundance within pockets in tiger reserves has been demonstrated for the first time.
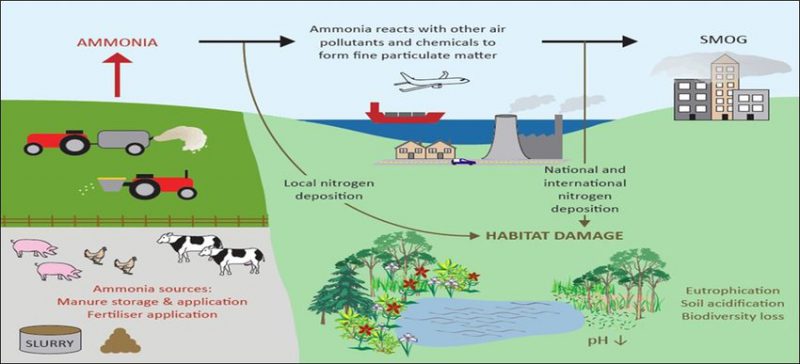
- Ammonia is a colourless gas and is used as an industrial chemical in the production of fertilisers, plastics, synthetic fibres, dyes and other products.
- Ammonia occurs naturally in the environment from the breakdown of organic waste matter, and may also find its way to ground and surface water sources through industrial effluents or through contamination by sewage.
- If the concentration of ammonia in water is above 1 ppm it is toxic to fishes. In humans, long term ingestion of water having ammonia levels of 1 ppm or above may cause damage to internal organs.
- The Delhi Jal Board (DJB) at present does not have any specific technology to treat ammonia. The only solution it adapts is to reduce production at three water treatment plants — Wazirabad, Chandrawal and Okhla — which are largely affected by the pollutant.
- In addition to this, the board mixes raw water that carries high concentration of ammonia with fresh supply from Munak canal, which brings Yamuna water from Munak area in Haryana to Delhi. The amount of chlorine added to disinfect raw water is also increased when high levels of ammonia are detected.
- With the completion of a new unit of the Chandrawal water treatment plant by 2022, fitted with advanced technologies and filters, the DJB expects it can treat ammonia levels up to 4 ppm.
 What is the long-term solution to the problem?
What is the long-term solution to the problem?
- Stringent implementation of guidelines against dumping harmful waste into the river, and making sure untreated sewage does not enter the water are two things pollution control bodies are expected to do. However, neither Haryana nor Delhi have been able to ensure the same.
- But, a more organic method agreed upon by environmentalists and experts is to maintain a sustainable minimum flow, called the ecological flow. This is theminimum amount of water that should flow throughout the river at all times to sustain underwater and estuarine ecosystems and human livelihoods, and for self regulation.
- The lack of a minimum ecological flow also means accumulation of other pollutants. After water is extracted from the river for treatment in North East Delhi, what flows is mostly untreated sewage and refuse from homes, run off from storm water drains and effluents from unregulated industry.
- In the appeal made to the Expert Appraisal Committee for River Valley Projects, the signatories pointed out that “The Kundah watershed region in the Nilgiris supports important last remaining vestiges of the Shola-grassland mosaic vegetation, which is one of the most endangered vegetation types in India. This region has crucial amounts of green cover in terms of forested tracts (plantations) which have been naturalised and serve as important habitat and corridors for endangered populations of wildlife.”
- The proposed Sillahalla project, once implemented, will result in the construction of an upper and a lower reservoir along the Sillahalla stream and also past the existing Kundah Palam dam, and could lead to the direct submergence of 170 hectares of land.
- Toda Tribe is a pastoral tribe of the Nilgiri Hills of southern India.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but is the most unusual and different among the languages belonging to the Dravidian family.
- They live in settlements of from three to seven small thatched houses.
- They traditionally trade dairy products, as well as cane and bamboo articles, with the other Nilgiri peoples.
- The traditional Toda dress is a distinctive shawl which is called putukuli. In the Toda language it is called pohor. It enjoys a ‘Geographical Indication Tag’.
- The embroidery is done by Toda women and has distinctive red and black (and occasionally blue) thread work in geometric designs on unbleached white cotton fabric.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies