- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
NOVEMBER 13, 2025
Global Inequality Report 2025
- The Global Inequality Report 2025 was recently commissioned by the South African Presidency of the G20.
- It was prepared by the G20 Extraordinary Committee of Independent Experts on Global Inequality, led by Nobel laureate Joseph E. Stiglitz.
Key Findings of the Report
The Scale of Inequality
- Wealth Gap: The wealthiest 1% gained 41% of all new global wealth since 2000, while the bottom half received only 1%.
- Income Divide: Around 83% of countries, covering 90% of the world’s population, face high income inequality with Gini scores above 0.4.
- Food Crisis: One in four people (2.3 billion) experience moderate or severe food insecurity, an increase of 335 million since 2019.
- Inherited Wealth: About $70 trillion will be transferred via inheritance in the next decade, continuing intergenerational inequality.
Key Drivers of the Inequality
- Capital Dominance: Since 1990, 56% of countries have seen a rise in income share for capital, while the overall labour share has declined globally.
- Concentrated Ownership: Nearly 85% of the population derives no income from capital, highlighting the extreme concentration in capital ownership.
- Wage Disparity: Between 2019 and 2024, the average CEO pay increased by 50%, while the average worker’s income rose by less than 1%.
- Public Wealth Erosion: Rapid private wealth growth outpaced public asset expansion, leading to governments with high net debt and limited investment capacity.
Consequences of High Inequality
- Democracy Collapse: High inequality makes democratic systems seven times more likely to weaken or eventually collapse.
- Health & Social Gaps: Health and social outcomes decline sharply under inequality; e.g. African American women are twice as likely to die in childbirth as white women or women in Kerala.
|
India-Specific Findings
|
Key Policy Recommendations
- New Global Body: Establish an International Panel on Inequality (IPI), modelled on the IPCC, to provide authoritative and data-driven assessments on inequality.
- Global Tax Reform: Implement a global minimum tax on ultra-rich individuals and promote stronger progressive taxation on income and wealth.
- Fair Trade Rules: Revise global trade and IP laws to give developing countries better access to health and clean-energy technologies.
- Public Investment: Increase funding for universal education, healthcare, and social protection to build fair and equal opportunity systems.
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPV&FRA) Act, 2001
‘Plant Genome Saviour Awards Ceremony’ was held to celebrate 25 years of the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPV&FRA) Act, 2001.
About PPV&FRA Act, 2001
- Objectives: To establish an effective protection system for plant varieties, farmers'' and breeders'' rights; encourage new variety development and seed industry growth.
- It recognizes following rights:
- Farmers’ rights: Registration and protection of new, farmers'', and extant varieties; rewards for conservation.
- Researchers’ rights: Use of any registered variety for experiments.
- Breeders’ rights: Exclusive rights to produce, sell, import or export etc.
- Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers'' Rights Authority (PPV&FRA): Established in 2005 as a statutory body under Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Functions: Registration of new plant varieties, national gene bank etc.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters
- The Union Cabinet approved the Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters (CGSE) under the Ministry of Finance to enhance India’s export sector.
- Objective: Enhance the global competitiveness of Indian exporters and promote market diversification.
- Credit Guarantee: It provides a 100% credit guarantee to Member Lending Institutions (MLI) that provide additional credit facilities to exporters.
- Credit Support: It offers up to ₹20,000 crore in collateral-free credit support to eligible exporters, including Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Implementation: The Department of Financial Services (DFS) will carry out the scheme through the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Limited (NCGTC).
- Significance: The initiative advances India’s progress toward the USD 1 trillion export target, thereby strengthening the vision of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
|
India’s Export Landscape
|
CBSE Draft Curriculum for AI and Computational Thinking
- A draft curriculum for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computational Thinking (CT) has been created by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) for Classes III to XII.
|
Computational Thinking (CT) is a structured approach to problem-solving that applies core computer science concepts to address challenges across various subjects and real-life contexts. |
- Objective: The curriculum aims to develop an AI-ready mindset and skill set in learners, promoting critical thinking, ethical awareness, and career readiness for a technology-driven future.
- Teacher Training: Structured, time-bound training modules under NISHTHA will be used to enhance teacher capacity for effective AI curriculum delivery.
- Implementation: By the Department of School Education and Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, in coordination with CBSE and NCERT.
- Timeline: Classes 3–6 will adopt the new AI curriculum in 2026–27, expanding to Classes 9–10 by 2027–28, with senior-secondary electives added later.
- Significance: It is India’s first comprehensive, nationwide integrated literacy framework aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features
- Early Integration: Computational-thinking concepts, currently confined to mathematics, will be introduced across all subjects, for Classes 3–5.
- Phased Learning: AI awareness and foundational CT will be introduced from Classes 6–8, progressing to advanced applications in Classes 9–10.
- Elective Option: Core AI and machine learning modules will be offered as electives for Classes 11–12 to deepen conceptual understanding.
- Experiential Learning: The framework encourages practical learning through games, projects, and activities that teach the AI Project Cycle, data analysis, and model evaluation.
Aurora
Auroras were witnessed in Northern America, Australia etc. due to a cannibal solar storm.
- A cannibal solar storm happens when a faster solar storm catches up with an earlier storm, resulting in a stronger storm, affecting GPS and power systems.
- An aurora is a natural light display in the night sky, usually only appearing in lower Polar Regions.
- They occur when high-energy charged particles from the Sun collide with atoms in the upper atmosphere.
- E.g. Oxygen (green and red light), Nitrogen (blue and purple).
- Near the North Pole, it is called an aurora borealis or northern lights and near the South Pole, it is called aurora australis or the southern lights.
India–Cuba Sign Memorandum of Understanding
- India and Cuba signed a MoU that includes a Treaty on Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters and a Protocol on Cultural Exchange and Cooperation.
- The Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty facilitates the sharing of legal information and support between the judicial systems of both countries.
- The Cultural Exchange Protocol promotes partnerships in arts, heritage, sports, and education, strengthening people-to-people ties.
India–Cuba Relations
- Diplomatic Recognition: India was one of the first countries to recognise the new Cuban government after the 1959 Revolution.
- Strategic Solidarity: As founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), both nations consistently promote collaboration among Global South countries in international forums.
- Bilateral Assistance: India has provided over $243 million in Lines of Credit to Cuba for projects in key sectors like agriculture and renewable energy. It also consistently provides humanitarian aid.
- Focus Areas: Cuba’s membership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) strengthens bilateral energy ties; other areas include biotechnology and traditional medicine.
Ricin and Ammonium Nitrate
Recently terror attacks were averted related to Ricin poison and Ammonium Nitrate.
Ricin
- It is a protein found naturally in castor beans and can be made from waste residue of castor beans.
- Lethal poison: Even 1 mg mixed in food can kill an adult. There is no antidote or specific treatment for ricin poisoning.
- It works by getting inside the cells of a person''s body and preventing the cells from making the proteins they need.
Ammonium Nitrate
- Pure ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) is a white, water-soluble, crystalline substance with a melting point of 170°C.
- It is not explosive by itself. However, it is one of the ingredients used for the manufacture of explosives.
SEBI Warns Against Digital Gold Investments
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has issued a public advisory cautioning investors against investing in digital gold and e-gold products.
What is Digital Gold?
- Digital gold refers to the online purchase of gold without physically possessing it.
- The value of digital gold is linked to the price of physical gold, and it is often created and traded using blockchain technology.
- It allows investors to buy, sell, and store gold electronically and even convert holdings into physical gold, such as coins, bars, or jewellery.
- Advantages: Eliminates storage and security concerns, enables investment in small denominations and offers quick liquidity during emergencies.
Why Did SEBI Issue a Warning?
- SEBI noted that several digital platforms are marketing digital gold as an investment alternative to physical gold, without regulatory oversight.
- Such products are neither classified as securities nor regulated as commodity derivatives, meaning they operate outside SEBI’s jurisdiction.
Risks Associated with Digital Gold
- Lack of Regulation: Operates outside SEBI’s framework, making redressal difficult in case of disputes or fraud.
- Counterparty Risk: Since digital gold is not traded on exchanges, investors depend entirely on the platform’s reliability. A default or insolvency can lead to a total loss.
- Operational Risk: Issues such as mismanagement, technical glitches, or fraudulent storage claims pose additional threats.
- No Transparency: Absence of standardised pricing and storage audits increases investor vulnerability.
- Market Influence: Aggressive marketing & social media promotions often obscure the associated risks.
SEBI-Approved Avenues for Safe Gold Investment
- SEBI recommends investors opt for regulated gold investment products such as:
- Gold Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Traded on stock exchanges, backed by physical gold holdings, and governed by SEBI norms.
- Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs): Issued by the RBI on behalf of the government, offering fixed interest and capital appreciation.
- Electronic Gold Receipts (EGRs): Tradeable instruments on exchanges representing actual gold holdings.
- Commodity Derivatives (MCX/NSE): Offer exposure to gold prices with risk management, mark-to-market settlements, and clearing corporation guarantees, reducing default risks.
DNA Identification
DNA Identification/profiling used to identify suspects or victims at Red fort blast site.
- It is a technique used to identify individuals by analyzing unique patterns in their DNA.
Key Methods
- Short Tandem Repeat (STR): Examines short repeating DNA sequences in the nucleus.
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): Used if nuclear DNA is degraded. mtDNA is abundant and maternally inherited, allowing matches with maternal relatives.
- Y Chromosome: Focuses on STRs on the Y chromosome, inherited father to son. Identifies male victims by matching paternal male relatives.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used for highly degraded DNA.
- SNPs are single-base differences unique to individuals, matched with personal items like toothbrushes.
India’s First Vanadium Redox Flow Battery System
- The Union Minister of Power inaugurated India’s largest and first MWh-scale Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB) system.
- The system has been installed at NETRA, NTPC’s R&D centre in Greater Noida, with a capacity of 3 MWh.
- Developed By: NTPC’s R&D team under the Ministry of Power.
- Significance: It marks a significant step in the country’s progress towards long-duration energy storage (LDES) solutions to improve renewable energy integration and grid resilience.
Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB)
- A VRFB is a large-scale flow battery that stores and releases energy using vanadium ions in different oxidation states.
- Key Features: It offers a scalable, safe, and long-lasting design, making it well-suited for extended, grid-level energy storage.
- Applications: To integrate renewable energy sources such as solar and wind into existing power grids.
- Li-Ion Alternative: They are increasingly replacing lithium-ion batteries in stationary grid storage due to their durability and safety.
|
Flow batteries are rechargeable storage systems with two separate liquid electrolytes stored in external tanks. These solutions are pumped through an electrochemical cell where chemical reactions charge or discharge the battery. |
Union Cabinet approved the Export Promotion Mission (EPM) for six years
This initiative, first announced in the Union Budget 2025–26, is designed to serve as a comprehensive and flexible framework to bolster India''s export ecosystem amidst evolving global trade challenges.
Key Features of Export Promotion Mission (EPM)
- Financial Outlay and Timeline: Rs. 25,060 crore from FY 2025–26 to FY 2030–31.
- Mission Objective: To enable Affordable trade finance (particularly for MSMEs); Enhanced competitiveness through compliance and certification; Greater international market access, job creation, etc.
- Target: To support MSMEs, first-time exporters, and labour-intensive sectors, such as Textiles, Leather, Gems & Jewellery, etc.
- Mission Architecture: The mission will operate through two distinct but integrated sub-schemes:
- Interest subvention, collateral guarantees, credit cards for e-commerce exporters, etc.
- Export quality and compliance support, assistance for international branding, export warehousing and logistics, etc.
- Niryat Protsahan (Financial Support): Improving access to affordable trade finance through financial instruments, such as
- Niryat Disha (Non-Financial Support): Designed to enhance the market readiness and competitiveness of Indian exporters through
- Implementing Agency: The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) in collaboration with Department of Commerce, Ministry of MSME, Ministry of Finance, Financial Institutions, Export Promotion Councils, State Governments, etc.
- Consolidation of Schemes: Integrates and modernizes key existing schemes, such as the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) and the Market Access Initiative (MAI).
|
Cabinet approves Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters (CGSE)
|
Gynandromorphism
Scientists in Thailand discovered a rare spider that is half-female and half-male (gynandromorphism) named Damarchus inazuma.
- It is an abnormal reproductive condition in which both female and male characteristics are displayed in the same individual.
- It is most frequently recognized in organisms that have strong sexual dimorphism such as certain butterflies, spiders and birds.
- Cause: It is typically an event in mitosis during early development.
- One of the dividing cells does not split its sex chromosomes, producing mixed male/female cell lines.
UNESCO’s Neurotechnology Ethics Framework
- UNESCO released the world’s first global framework on the ethics of neurotechnology, set to enter into force on November 12, 2025, to regulate brain-related innovations.
|
Neurotechnology Definition: Devices and procedures that access, assess, or act on the human neural system to restore or enhance brain function. Applications: Includes brain-computer interfaces, neuroimaging, and AI-based brain data analysis used in healthcare, rehabilitation, and human enhancement. |
Key Recommendations of the UNESCO Framework
- Ethical Governance: Ensure beneficence, autonomy, privacy, and accountability in neurotech R&D.
- Ban on Misuse: Prohibits using brain data for political manipulation or employment screening.
- Human Rights: Recognises freedom of thought and mental privacy as emerging “neurorights”.
- Open Science Promotion: Advocates the sharing of research data under open-access models.
- Responsible Research & Innovation (RRI): Encourages researchers to evaluate long-term impacts.
- Vulnerable Groups: Calls for safeguards for children, the elderly, and the mentally ill in neurotech testing.
- Self-Regulation: Urges companies to adopt ethics-by-design and independent ethics boards.
Global Precedents of Neurotechnology Frameworks
- Chile (2021): First country to enshrine “mental integrity” in its Constitution.
- California (2024): Passed a law protecting brain data privacy from corporate misuse.
- OECD (2019): Developed the first guidelines for responsible innovation in neurotechnology enterprises.
Pratyush Sinha Committee
A SEBI-appointed High-Level Committee (HLC), under the chairmanship of Pratyush Sinha recommended stronger rules to prevent conflicts of interest among top officials within SEBI.
Key Recommendations of the Committee
- Mandatory Disclosure: Of assets and liabilities by the Chairperson, whole-time members and senior officers.
- Insider Classification: Top SEBI leadership to be categorised as “insiders” under insider-trading regulations.
- Investment Restrictions: Senior officials and dependent family members allowed investing only through pooled, professionally-managed funds.
- Ethics Oversight: Creation of an Office of Ethics & Compliance, digital disclosure registry, and formal recusal reporting.
- Dedicated whistleblower channel for conflict-of-interest reporting.
ARISE Programme
- At the UNFCCC COP30 Climate Summit, Germany and Spain pledged $100 million to support a new climate change adaptation programme under the Climate Investment Funds (CIF).
- Accelerating Resilience Investments and Innovations for Sustainable Economies (ARISE).
- Objective: To help developing countries integrate resilience into economic planning, strengthen adaptive capacity, and mobilise climate finance.
- Implementing Body: Climate Investment Funds (CIF), a $13 billion multilateral financing mechanism housed within the World Bank.
|
COP30 UNFCCC Summit
|
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Recent reports highlight the use of FTIR spectroscopy as a rapid and effective tool for detecting material evidence in post-blast forensic investigations.
- It is a technique used to analyze materials by measuring how they absorb infrared light.
- It uses a special device called an interferometer to record data, which is then processed by a computer to make a graph (called a spectrum).
- Significance: non-destructive (preserve sample); require minimal material, provides both qualitative & quantitative data etc.
- Applications: Commonly used across fields such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, environmental analysis, and forensics.
Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters (HVICs)
Union Minister of Science and Technology announced that 4 HVICs are being developed across the country to demonstrate complete green hydrogen value chain.
HVICs
- Aim: To demonstrate full hydrogen value chain (production, storage, transport and utilization) and India’s first large-scale hydrogen demonstration projects.
- Originally conceptualized by the Department of Science and Technology, they are now integrated under the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM).
- NGHM is an Umbrella programme launched in 2023 to create a Green Hydrogen ecosystem. It targets to produce 5 MMT of Green Hydrogen annually by 2030.
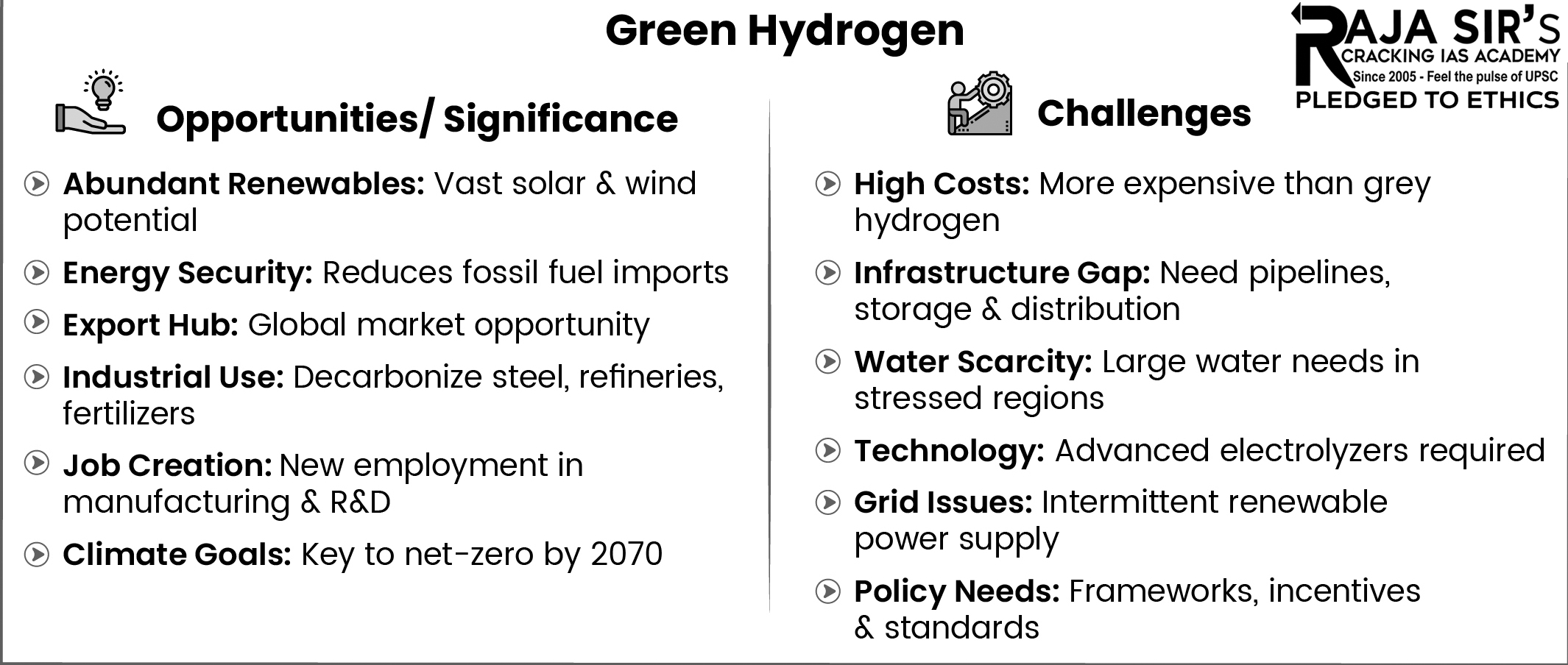
Green Hydrogen
- Hydrogen produced using renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, instead of fossil fuels.
- Process: By electrolysis (splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen) or gasification of biomass.
- Criteria: Emissions from the process should not be more than 2 kg of CO₂ equivalent for every 1 kg of Hydrogen produced.
- India’s First 3 Green Hydrogen Hubs: Deendayal Port (Gujarat), V.O. Chidambaranar Port (Tamil Nadu), and Paradip Port (Odisha).
Humboldt Penguin (Spheniscus humboldti)
- Chile’s Ministry of the Environment has reclassified the Humboldt penguin as ‘endangered’ within the country, due to a decline of over 50% in its population since the late 1990s.
Humboldt Penguin (Spheniscus humboldti)
- The Humboldt penguin is a medium-sized seabird native to the Pacific coasts of Chile and Peru. It is named after the cold Humboldt Current.
- Habitat Preference: They inhabit rocky coastal areas and offshore islands, and nest in burrows, caves, or rock crevices.
- Distribution: Their range follows the cold, nutrient-rich Humboldt Current, with nearly 80% of the global population found along Chile’s Pacific coast.
- Behavioural Traits: Humboldt penguins are highly social and monogamous, with both parents sharing responsibilities for egg incubation and offspring care.
- Physical Features: They have black heads, white facial stripes, and pink skin patches near the bill.
- Unique Adaptation: Spines on their tongues help grip slippery fish underwater, while patches of bare skin dissipate excess heat.
- Ecological Role: As mid-level predators, they help maintain marine ecosystem balance by regulating the small schooling fish population.
- Major Threats: Fishing net entanglement, guano extraction, food competition, avian influenza, etc.
- Conservation Status: IUCN: Vulnerable; CITES: Appendix I
Quantum Diamond Microscope
IIT Bombay develops India’s first Quantum Diamond Microscope under the National Quantum Mission.
- Technology: Uses nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres in diamond to image magnetic fields at nanoscale resolution at room temperature.
- Applications: Enables advanced research in neuroscience, materials science and non-destructive semiconductor testing.
- Significance: Secures India’s first patent in quantum sensing and strengthens national capabilities in frontier instrumentation.
Global Climate Risk Index 2025
- At the COP 30 Summit in Belém, Germanwatch has published the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, showcasing the effects of climate-related disasters (1995–2024).
Key Findings of the Report
- India ranked 9th globally among nations worst hit by climate disasters (1995–2024)
- Over 80,000 deaths in India due to extreme weather events, which is about 9.6% of global deaths.
- Around 430 extreme events were recorded in India, including floods, droughts, cyclones, and heatwaves.
- Economic Losses for India are estimated at USD 170 billion over 30 years due to climate disasters.
- Improved Annual Rank from 10th (2023) to 15th (2024), indicating gradual progress in resilience.
- The most affected countries include Pakistan, Philippines, Bangladesh, Haiti, and Myanmar.
- The 1999 Odisha cyclone, 2013 Uttarakhand floods, Cyclone Hudhud (2014), Cyclone Amphan (2020), and the 2015 heatwave were major events.
|
Germanwatch
|
Parachute System Test for Gaganyaan Mission
- ISRO recently conducted an Integrated Main Parachute Airdrop Test (IMAT) as part of qualification trials for the Gaganyaan mission’s parachute system.
- A test article simulating the mass of the Gaganyaan Crew Module was dropped from an Indian Air Force (IAF) IL-76 aircraft.
- The test confirmed that the crew module is capable of a stable descent even if one of the four main parachutes fails or opens late.
Gaganyaan Mission
- The Gaganyaan Mission is India’s first human spaceflight program by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Objective: It aims to send a crew of three astronauts into Low Earth Orbit (LEO), about 400 km above Earth, for a three-day mission and to ensure their safe return.
- Launch Vehicle: The mission will use the human-rated LVM3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3), India’s heaviest and most powerful operational rocket, earlier known as GSLV Mk-III.
- Launch Timeline: The first uncrewed test flight is scheduled for late 2025, with the first crewed mission planned for 2027.
India-Botswana Announces Cheetah Translocation Pact
India-Botswana formally announced translocation of eight cheetahs to India as a part of ‘Project Cheetah’.
Project Cheetah
- About: Launched in 2022, Project Cheetah aims to translocate African cheetahs to India. It is the world’s first intercontinental large wild carnivore translocation initiative.
- In 2022, eight cheetahs from Namibia were translocated to Kuno National Park, followed by twelve cheetahs from South Africa in 2023.
- Implementing agency: National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
- NTCA is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change constituted under enabling provisions of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006.
- Cheetah Project Steering Committee: Established by NTCA in 2023 to oversee, evaluate, and advise on implementation of Project Cheetah.
- It operates under the umbrella of Project Tiger.
Significance of Re-introducing Cheetah in India
- Ecological Restoration: Cheetahs are apex predators and play a vital role in maintaining the balance of prey species and the overall health of grassland ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Cheetah will serve as a flagship to save not only its prey-base, but also other endangered species of the grassland and semi-arid ecosystems.
|
Cheetah (Acinonyx Jubatus Venaticus)
|









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies