- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
NOVEMBER 28, 2025
PM Jan Vikas Karyakram
- The Ministry of Minority Affairs held a nationwide review of PM Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK) to improve last-mile outcomes in minority-concentrated areas.
PM Jan Vikas Karyakram
- A Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented by the Ministry of Minority Affairs to bridge development deficits in Minority Concentration Areas (MCAs) across India.
- Covers both urban and rural minority clusters across 700+ MCAs and targets MCAS where the minority population exceeds 25% and socio-economic indicators lag behind national averages.
- Funding Pattern is 90:10 for NE/Hill States, 60:40 for others, 100% for UTs (as per CSS norms).
Objectives of PMJVK
- Reduce regional development deficits through education, health, civic amenities, skill infrastructure.
- Ensure equitable access to public infrastructure for minority communities.
- Strengthen social inclusion, area development, women-focused facilities, and youth-skill infrastructure.
Achievements of PMJVK Implementation
- Asset Creation: Over 12,000+ social infrastructure projects sanctioned since inception.
- Education Boost: Over 800 facilities, including smart classrooms, have been developed.
- Health Infrastructure: 500+ PHCs and maternal-health facilities established or upgraded.
- Gender Inclusion: Women’s hostels and skill centres constitute 15–20% of total project approvals.
- Digital Transparency: 100% fund releases routed through the PMJVK Portal and SNA-SPARSH in 2025.
- Community Facilities: 2,000+ community assets like Sadbhav Mandaps and skill centres for public use.
Issues in PMJVK Implementation
- Utilisation Delays: Only 62–65% of annual allocations utilised on schedule.
- Capacity Shortage: Nearly 40% MCAs have inadequate project-preparation capacity.
- Land Constraints: 25–30% PMJVK works are stuck due to land/permission bottlenecks.
- State Variation: Huge differences in fund utilisation and asset completion. E.g., Some States show above 90% utilisation, others remain below 50%.
Way Forward
- Digital Strengthening: Scale PMJVK Portal with automated alerts and public dashboards for accountable delivery. E.g., Adopt monitoring templates similar to Geo-MGNREGA for real-time verification.
- Community Ownership: Institutionalise social audits and community consultations to ensure transparency and inclusion. E.g. Follow participatory frameworks of the Aspirational Districts Programme.
- Quality Assurance: Enforce third-party audits, digital photo-evidence, and QR-tagging of assets to strengthen accountability and reduce leakages. E.g. QA models seen in the National Health Mission.
- Convergence Models: Integrate PMJVK projects with PM-SHRI schools, PM-KVK skill hubs, NHM health facilities, and Smart Cities infrastructure for greater developmental impact.
IMF Assigns Second-Lowest ‘C’ Rating to India’s National Accounts Statistics (NAS) and Inflation Data
IMF Grading is divided into four grades:
- A: The data provided are adequate for surveillance.
- B: Data have some shortcomings but is broadly adequate for surveillance.
- C: Data have some shortcomings that somewhat hamper surveillance.
- D: Data have serious shortcomings that significantly hamper surveillance.
Key Issues highlighted by IMF
- Outdated Base Year (2011-12) for GDP calculation: fails to reflect current production technology and user preferences, which can lead to over or underestimating economic activity.
- Need to use updated data sources: E.g. Household consumption and expenditure survey (HCES), Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), etc. to better capture the structural changes in the economy.
- Lack of Seasonally Adjusted Data: National accounts are not seasonally adjusted, making it difficult to interpret short-term quarterly movements.
- Outdated statistical techniques in the quarterly national accounts data.
- Lack of Producer Prices Indices (PPI): Excessive use of single deflation i.e. Wholesale Price Index (WPI), may introduce cyclical biases.
- Outdated CPI Components: The IMF highlights that the current CPI base year, items basket, and weights are outdated (2011/12).
IMF’s Recommendation:
- Going forward, regular benchmark revisions of national account, price, and other key statistics should be conducted according to international best practices.
|
Key Statistical Indicators of Economy
|
Improvised Explosive Device (IED) Used in Red Fort Car Blast
- Investigators suspect that the recent car blast near the Red Fort in New Delhi may have been caused by an improvised explosive device (IED).
Improvised Explosive Device (IED)
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) is a homemade or non-standard explosive weapon assembled from commercial or military components to cause damage.
- Wide Range: IEDs can be built using pressure cookers, metal pipes, chemical fertilisers, cell phones, vehicle parts and other readily available items.
- Size Variation: Their size ranges from small improvised devices to large vehicle-concealed bombs known as Vehicle-Borne IEDs (VBIEDs).
- Core Components: A typical IED contains five elements: Switch (Trigger), Initiator (Detonator), Main Charge (Explosive Material), Power Source (Battery), and Container (Casing).
- Lethal Enhancements: Many IEDs include nails, ball bearings, or hazardous chemicals to maximise casualties during detonation.
- Trigger Methods: Common triggering systems include command-operated remote methods, timer-based systems, and victim-operated mechanisms (i.e., pressure plates).
Why IEDs Are Often Preferred Weapons of Choice?
- Cheap Components: The materials used for IEDs (e.g., fertiliser, hydrogen peroxide, and gunpowder) are inexpensive, dual-use and commercially available.
- Easy Fabrication: IEDs can be assembled with minimal training and permit wide variation in size, form, and concealment techniques.
- Low Detectability: Their improvised design and use of non-military components make them difficult for conventional screening technologies to identify.
- Remote Detonation: Many IEDs can be triggered remotely, allowing perpetrators to maintain distance and evade immediate capture.
Factors Contributing to the Decline of IED Use in India
- Ammonium Nitrate Rules: Designating ammonium nitrate as a deemed explosive has imposed tighter licensing controls and curtailed pilferage from mining sites.
- Border Controls: Enhanced border surveillance and interdiction measures have disrupted smuggling routes carrying military-grade explosives from Pakistan.
- Rule Amendments: Recent amendments to the Explosives Rules tightened transport tracking and closed logistics loopholes used to siphon legally sourced materials.
- Fertiliser Safeguards: Mandatory neem-coating and added chemical inhibitors in fertilisers have made separating ammonium compounds for explosive use technically unviable.
Way Forward for a Holistic National Counter-IED Policy
- Nodal Agency: Empower the National Bomb Data Centre (NBDC) as the central authority to integrate intelligence and remove information silos across state police and central security forces.
- Uniform RSP: Mandate a standard national Render Safe Procedure (RSP) to prevent casualties caused by inconsistent IED handling and disposal practices.
- Signature Bank: Create a digital National Bomb Signature Bank to link forensic signatures across incidents and identify recurring bomb-maker networks.
- Component Law: Enact specific legal provisions criminalising the possession of unauthorised IED sub-components such as detonator circuits and triggering switches.
Centre Gets CEC Push for Tiger Reserve in Goa
- A Supreme Court-appointed Central Empowered Committee (CEC) recommended notifying a tiger reserve in Goa through a two-phase implementation plan.
- First Phase: Around 300 sq km of Cotigao and Netravali Wildlife Sanctuaries (WLS), adjoining Karnataka’s Kali Tiger Reserve, will be notified as the core area.
- Second Phase: The inhabited parts of Mhadei WLS and the southern part of Bhagwan Mahavir WLS will subsequently be notified as buffer zones.
- Legal Requirement: The state must issue the notification within three months and prepare a Tiger Conservation Plan under Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- State Objection: Goa argued that (a) nearly 1,00,000 residents oppose relocation and (b) the state currently has no resident tigers.
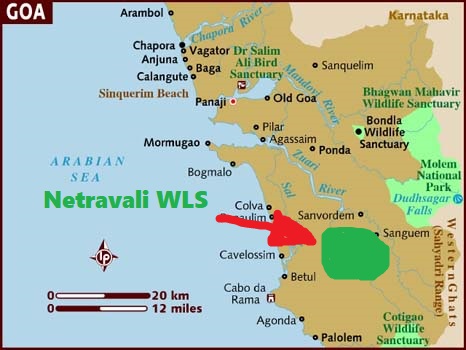
Tiger Landscape in Goa
- Reserve Status: Goa has no formally notified tiger reserve, yet its Western Ghat belt remains a crucial tiger landscape.
- Tiger Corridor: Mhadei and Bhagwan Mahavir Wildlife Sanctuaries (WLS) create a continuous tiger corridor linking Karnataka’s Bhimgad WLS and Kali Tiger Reserve.
- Recognised Habitat: The Western Ghats stretch from Sattari to Netravali was officially recorded as tiger habitat in the 2018 National Tiger Census.
- Mortality Concern: NTCA recommended a tiger reserve after four tigers were deliberately poisoned in Mhadei WLS in 2020.
- Legal Mandate: A 2023 Bombay High Court order directed Goa to notify Mhadei and adjoining areas as a Tiger Reserve under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
Tex-RAMPS Scheme
Government has approved the Textiles Focused Research, Assessment, Monitoring, Planning and Start-up (Tex-RAMPS) Scheme.
‘Tex-RAMPS’ Scheme
- Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Funding: ₹305 crore from 2025-26 to 2030-31.
- Aim: To future-proof India’s textiles and apparel (T&A) ecosystem by strengthening Research, Innovation and Competitiveness in Textiles Sector.
Key Components
- Research & Innovation: in smart textiles, sustainability etc.
- Data, Analytics & Diagnostics: including employment assessments, supply chain mapping, etc.
- Real-time Integrated Textiles Statistical System (ITSS): to support structured monitoring and strategic decision-making.
- Capacity Development & Knowledge Ecosystem: Strengthening of State-level planning, dissemination of best practices.
- Start-up & Innovation Support: Support for incubators, hackathons, and academia-industry collaborations.
New Fruit Fly Species Euphranta undulata
- A new fruit fly species, Euphranta undulata, was recently discovered in the Ri-Bhoi district of Meghalaya.
- Etymology: The name, undulata, derives from the Latin word for “wavy,” referring to the wavy margin of the female aculeus tip (the pointed part of the egg-laying ovipositor).
- Physical Traits: It is a slender-bodied insect with a brown or grey abdomen and patterned hyaline (transparent) wings.
- Ecological Niche: Native to the bamboo ecosystem of Northeast India, it is frugivorous (fruit-eating) and monophagous (feeding on a single type of food).

NGT directs CPCB to trace hundreds of missing Endosulfan barrels
- The NGT has directed the CPCB, Kerala SPCB and Plantation Corporation of Kerala to trace hundreds of missing barrels of banned pesticide Endosulfan.
National Green Tribunal (NGT):
- A specialised judicial body for speedy disposal of environmental disputes, functioning with expertise in environmental science and law.
- Established in: Set up on 18 October 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 to provide dedicated and time-bound environmental justice.
- Aim: To ensure effective environmental protection, conservation of natural resources, and provide relief and compensation for environmental damage.
Jurisdiction:
- Handles civil cases involving substantial environmental questions linked to laws listed in Schedule I (e.g., Water Act, Air Act, EPA, Forest Conservation Act, Biodiversity Act).
The following important Acts are NOT within NGT’s jurisdiction:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Wildlife crimes, poaching, sanctuary matters fall outside NGT’s powers and go to regular courts.
- Indian Forest Act, 1927: Issues of forest offences, transit rules, and forest land rights are not heard by the NGT.
- Forest Rights Act, 2006 (FRA): Claims, titles, individual/community forest rights are outside NGT jurisdiction.
- Has appellate jurisdiction over decisions relating to environmental clearances, pollution control orders, and biodiversity benefit-sharing disputes.
Governance Structure
- Chairperson: Head of the Tribunal – must be a retired Supreme Court Judge or Chief Justice of a High Court and appointed by the Central Government in consultation with the CJI.
- Judicial Members: Retired Judges of SC/HC and handle adjudication of environmental disputes based on legal principles.
- Expert Members: Specialists in environmental science, forestry, pollution control, or related fields; ensure interdisciplinary decision-making.
Powers & Functions
- Can provide relief, compensation, and restitution for victims of pollution, environmental damage, and hazardous substance accidents.
- Applies the polluter pays, precautionary, and no-fault liability principles while awarding compensation.
- Not bound by the Civil Procedure Code; guided instead by principles of natural justice for faster adjudication.
- Aims to decide cases within six months, reducing burden on High Courts and the Supreme Court.
- Can enforce environmental rights, impose penalties, direct restoration work, and monitor compliance with its orders.
ICMR Report Warns of Rising Antibiotic Resistance in India
- ICMR’s AMRSN Report 2024 warns that common infections in India—UTIs, pneumonia, sepsis, diarrhoea are becoming harder to treat as routine antibiotics fail.
- Superbugs like coli, Klebsiella, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas now show high resistance to fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins and even last-line carbapenems.
Superbugs
- A superbug is a bacteria or fungus that becomes resistant to multiple antibiotics or antifungals, making routine infections extremely difficult to treat.
How Superbugs Form?
- They evolve resistance due to misuse/overuse of antibiotics, incomplete dosing, hospital overexposure to high-end drugs, and gene transfer between microbes.
Types of Common Superbugs:
- Bacterial: coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, MRSA, CRE.
- Fungal: Candida auris, Aspergillus fumigatus with rising antifungal resistance.
Symptoms of Superbug Infections:
- Symptoms vary by organ but include persistent fever, chills, septic shock, painful skin lesions, breathing difficulty, extreme fatigue, rapid heart rate or low blood pressure.
Implications:
- Treatment Failure: Even strong antibiotics stop working, forcing toxic or expensive drug combinations.
- Higher Mortality: ICU infections like ventilator-associated pneumonia become life-threatening.
- Longer Hospital Stays: Patients require prolonged isolation, raising healthcare burden.
- Economic Loss: Increased cost of treatment, lost productivity, and higher burden on public hospitals.
- Threat of Untreatable Infections: Everyday illnesses could become fatal like in the pre-antibiotic era.
Significance
- Highlights urgent need for India-wide antibiotic stewardship and infection-control protocols.
- Signals rising global AMR threat, jeopardising SDG targets on health and well-being.
- Calls for surveillance strengthening, new drug discovery, and regulated antibiotic sales.
G.V. Mavalankar (1888 - 1956)
- Lok Sabha Speaker paid floral tributes to Shri Ganesh Vasudev Mavalankar, the first Speaker of Lok Sabha.
- Popularly known as Dadasaheb, he was conferred the title ‘Father of the Lok Sabha’ by Jawaharlal Nehru.
Key Contributions:
- He was active in Gujarat Education Society, Gujarat Sabha, and joined Swaraj Party.
- He played active role in Non-Cooperation movement and ‘Khaira No-Rent’ campaign.
- Remained Speaker of Bombay Legislative Assembly (1937-1946), elected to preside over Central Legislative Assembly (1946) and became speaker of Provisional Parliament in 1949.
- He was the founder Chairman of the National Rifle Association as also of the Institute for Afro-Asian Relations.
- Books: Manavatana Jharna, Sansmarano, A great Experiment.
- Values: Nonpartisanship, leadership, integrity, patriotism etc.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies