- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
September 07, 2024 Current Affairs
Union Health Ministry approves introduction of new shorter and more efficacious treatment regimen for drug-resistant TB in India
Key highlights of the introduction of the BPaLM regimen for MDR-TB treatment in India
Introduction of BPaLM Regimen:
- New Treatment: The Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare has introduced the BPaLM regimen for Multi-Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB).
- Components: The regimen includes a combination of three existing drugs—Bedaquiline, Linezolid, and the newly approved Pretomanid, with optional Moxifloxacin.
Benefits of BPaLM Regimen:
- Treatment Duration: The BPaLM regimen offers a shorter treatment duration of six months compared to traditional MDR-TB treatments, which can last up to 20 months.
- Effectiveness: It has shown higher efficacy and a better safety profile compared to previous treatments.
- Cost Efficiency: The new regimen is expected to reduce overall treatment costs and improve the cost-effectiveness of TB management.
National TB Elimination Program (NTEP):
- Objective: The program aims to eliminate TB in India by 2025, five years ahead of the global target under the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Previous Program: NTEP was formerly known as the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP).
Support Initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (PM TBMBA): Launched by the President of India to foster collective efforts for TB elimination.
- Ni-kshay Mitra Initiative: Provides additional support such as diagnostics, nutrition, and vocational aid for TB patients, encouraging community and corporate involvement.
- Ni-kshay 2.0 Portal: Facilitates community support and engagement in TB care.
MultiDrug Resistant TB
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB) can develop resistance to the antimicrobial drugs used to cure the disease.
- Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is TB that does not respond to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful anti-TB drugs.
- Most people with TB are cured by a strictly followed, 6-month drug regimen that is provided to patients with support and supervision.
- Inappropriate or incorrect use of antimicrobial drugs, or use of ineffective formulations of drugs (such as use of single drugs, poor quality medicines or bad storage conditions), and premature treatment interruption can cause drug resistance, which can then be transmitted, especially in crowded settings such as prisons and hospitals.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB, XDR-TB, is a rare type of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB) that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). It has been reported in 1117 countries worldwide.
About Tuberculosis (TB)
- Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person.
- It mainly affects the lungs, but it can affect any part of the body, including the tummy (abdomen), glands, bones and nervous system.
- TB is a potentially serious condition, but it can be cured if it''s treated with the right antibiotics.
Current status of TB in India:
- Incidence Rate: As of 2022, the incidence rate of TB in India was reported at 199 cases per 100,000 population, a decline from 237 per lakh population in 2015. This reflects a 16% decrease in new TB cases since 2015.
- Prevalence: The estimated prevalence of tuberculosis infection (TBI) among individuals over 15 years of age was around 31% according to a national survey conducted from 2019 to 2021.
- Global Contribution: India accounted for approximately 26% of the global incidence of TB cases in 2020. In that year, India also represented 38% of global TB deaths among HIV-negative individuals.
- Mortality Rate: The mortality rate due to TB decreased from 28 per lakh population in 2015 to 23 per lakh population in 2022, indicating progress in managing the disease.
- Total Cases: Estimates suggest that the total number of TB cases in India has increased from 2.2 million to 2.6 million in recent years, reflecting ongoing challenges in detection and treatment.
Union Minister Shri Ram Mohan Naidu Inaugurates Digi Yatra Facility at 9 More Airports
- Digi Yatra Facility Launched at Bhubaneswar, Coimbatore, Dabolim (Goa), Indore, Bagdogra, Ranchi, Patna, Raipur, and Visakhapatnam
- The Total Number of Digi Yatra-Enabled Airports Increases to 24
- 5 Lakh Users Downloaded Digi Yatra App; 3 Crore Passengers Have Used the Digi Yatra.
DIGI YATRA
- It is a project conceived to achieve contactless, seamless processingof passengers at Airports, based on Facial Recognition Technology (FRT).
- The project envisages that any traveller may pass through various checkpoints at the airport through a paperless and contactless processing,using facial features to establish the identity which would be linked to the boarding pass.
- It provides a decentralized mobile wallet-based identity management platformwhich is cost effective and addresses privacy/data protection issues in implementation of Digi Yatra.
- The Digi Yatra Foundation, a joint venturewith stakeholders including the Airports Authority of India and major Indian airports, is implementing the project.
Key Pillars
Digi Yatra platform will be built on 4 key pillars, like Connected Passengers, Connected Airports, Connected Flying and Connected Systems which can make it possible over a period of time for passengers to:
- Plan their trips efficiently by identifying price trends and estimate future airfares at the time of ticket booking,
- Optionally link their Aadhaar to airlines and other ecosystem players at the time of booking for faster airport entry and automated check-ins without requiring any paper-based interventions,
- Walk-through security scanners swiftly owing to advanced biometric security solutions,
- Receive relevant information pertaining to various facilities, protocols, airline timings, queue lengths at airports etc.,
- Engage in customized digital offerings at experience zones,
- Get real time notifications about congestion and delays to have greater visibility on the next step of journey,
- Conveniently navigate through the airport using digital guidance systems, interactive kiosks and augmented reality apps,
- Stay connected during flights and indulge in immersive experiences. Also book in-flight services and destination-based offerings digitally,
- Get a prompt when their luggage reaches the baggage claim belt, and
- Submit grievances, share experiences and provide feedback.
Concerns and Issues Related to Digi Yatra
- Privacy Infringement: There are few incidents which suggest biometric data collection without clear and informed consent are raising concerns about passenger privacy.
- Data Security: When Data is the new oil, Digi yatra heightened worries regarding personal data protection, fueled by previous instances of data breaches in the aviation industry.
- Narrow adoption: Many people are in the habit of following the traditional format of paper work verification to keep themselves aloof from technical complications in application.
- Technology Reliability: The facial recognition system may face potential challenges, including errors or biases, requiring ongoing scrutiny to ensure reliability.
Way Forward
- Expansion of Digi Yatra: Due to the high volume of people at the airport there is a need to diversify the scope of Digi Yatra. Digi Yatra facility should be available at all major airports and offered by all airlines operating in India.
- Integration with Service Providers: Linking Digi Yatra portal with other travel platforms like booking portals and ride-hailing apps can further give a more holistic experience to passengers.
- Enhancing Security Features: Regular improvement of biometric authentication and data security measures is vital.
- Protection of Data of Passengers: Encouraging more airlines, airports, and passengers to participate is crucial for wider acceptance.
78th Meeting of Network Planning Group under PM GatiShakti evaluates 18 road projects
Key highlights from the 78th Network Planning Group (NPG) meeting under the PM GatiShakti initiative
- Evaluation: Review of 18 significant road infrastructure projects proposed by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Objective: To ensure these projects align with the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan (NMP) principles of integrated and multimodal infrastructure development.
Project Highlights
- Tamil Nadu and Kerala:
- Madurai-Kollam ICR: 129.92 km, 4-lane; reduces travel distance by 10 km, enhances connectivity.
- Madurai-Dhanushkodi Highway: 46.67 km, 4-lane; improves access to tourist destinations.
- Chennai-Mahabalipuram-Pondicherry Corridor: 46.05 km, 4-lane; boosts tourism and local industries.
- Thoppur Ghat Section: 6.60 km, 8-lane; enhances safety and efficiency in hilly terrain.
- Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh:
- Belagavi Ring Road: 75.39 km, 4-lane; decongests urban traffic.
- Tumkur Bypass: 44.10 km, 4-lane; streamlines traffic around Tumkur city.
- Bhopal-Sagar Economic Corridor: 138.00 km, 4-lane; facilitates central MP connectivity.
- Western Bypass of Gwalior City: 56.90 km, 4-lane; reduces congestion in Gwalior.
- Ayodhya Nagar Bypass: 16.44 km, 6-lane; enhances connectivity in Bhopal.
- Maharashtra and Telangana:
- Ahmednagar-Solapur Corridor: 59.22 km, 4-lane; supports regional industrial growth.
- Talegaon-Chakan-Shikrapur Corridor: 54.00 km, 4-lane; streamlines freight movement near Pune.
- Jagtial-Karimnagar Highways: 58.87 km, 4-lane; improves state connectivity.
- Armoor-Jagtial-Mancherial Highway: 131.90 km, 4-lane; enhances access to markets in Telangana.
- Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Bihar:
- Badvel-Nellore Corridor: 108.13 km, 4-lane; boosts Agri-economy by improving market access.
- Sambalpur Ring Road: 35.38 km, 4-lane; reduces congestion and supports industrial growth.
- Cuttack-Paradip Corridor: 86.79 km, 4-lane; critical for port connectivity and regional development.
- Bakarpur-Manikpur-Sahebgunj-Areraj-Bettiah Highway: 162.95 km, 4-lane; improves access to economic opportunities in Bihar.
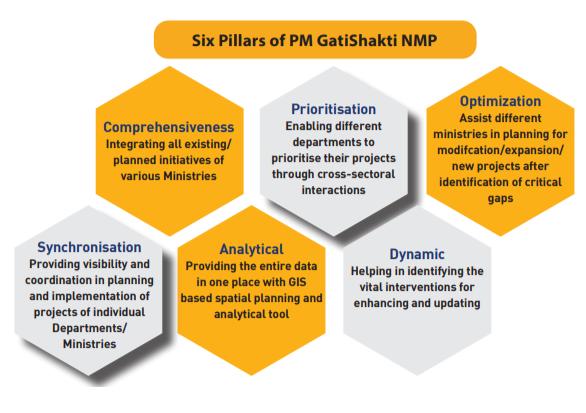
Network planning group
- It is one of the institutional structures of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- It is an Integrated Multimodal Network Planning Group (NPG) with heads of the Network Planning Division of all connectivity infrastructure Ministries & Departments.
- It is responsible for unified planning and integration of the proposals and assists the Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGOS) in respect of its mandate.
- It will guide all the Departments/ Ministries responsible for the creation of economic zones and connectivity infrastructure during the planning phase itself.
- NPG’s role will be to ensure:
- Integration of networks.
- Enhance optimization through modification/expansion/new network creation.
- Avoid duplication of work for the holistic development of any region.
- Reduction of logistics costs through micro-plan detailing.
PM Gati Shakti
- PM Gati Shaktiis a master plan for multi-modal connectivity (launched in October 2021), to give more speed (Gati) and power (Shakti) to infrastructure projects by connecting 16 Ministries, including Railways and Roadways, on one digital platform.
- While the Government has not specified the size of the programme in financial terms, it will subsume the Rs 110 lakh crore National Infrastructure Pipeline (launched in 2019).
INDIA - FRANCE BILATERAL NAVAL EXERCISE VARUNA
- Indian Naval Ship Tabar & LRMR P8I Aircraft Participate in the 22nd edition of IN - FN Bilateral Exercise VARUNA in the Mediterranean Sea’
Key Activities:
- Tactical Manoeuvres: Advanced naval operations integrating air, surface, and sub-surface assets.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare Exercises: Enhanced drills targeting submarine threats.
- FLYEX: Air exercise involving tactical air operations.
- Air Defence Exercise: Simulation and execution of defensive measures against aerial threats.
- Live Weapon Firings: Demonstration of real-time weapon capabilities.
- PHOTO-EX: Aerial and surface photography exercises.
- Steam Past: Naval tradition showcasing ships'' capabilities.

VARUNA Exercise
- The Indian and French Navies have been conducting bilateral maritime exercises since 1993. Since 2001, these exercises have been called ‘VARUNA’. This is an annual event.
- These interactions further underscore the shared values as partner navies, in ensuring freedom of seas and commitment to an open, inclusive Indo-Pacific and a rules-based international order.
Importance of the VARUNA Exercise
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Enhances strategic ties and deepens diplomatic relations between India and France.
- Improving Interoperability: Facilitates joint operations, standardizing procedures and tactics for seamless coordination.
- Showcasing Capabilities: Demonstrates advanced naval assets and technological integration, highlighting operational strengths.
- Enhancing Readiness: Provides realistic training scenarios, improving the skills and readiness of naval personnel.
- Promoting Best Practices: Encourages exchange of best practices and innovative strategies between the navies.
- Regional and Global Security: Contributes to maritime security and demonstrates strategic presence in key regions.
- Building Long-Term Partnerships: Reinforces strategic alliances and sets the foundation for future collaborations.
- Operational Flexibility: Enhances adaptability to various maritime scenarios and challenges.
INS Tabar: A stealth frigate with advanced weaponry and sensors, designed for multi-role naval operations including anti-submarine and anti-aircraft warfare.
LRMR P-8I: A maritime reconnaissance aircraft equipped with advanced sensors and armament for long-range surveillance and anti-submarine warfare.
Successful launch of Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile, Agni-4 conducted in Odisha
- Defence Ministry said, the launch successfully validated all operational and technical parameters.
- He said, the launch was conducted under the aegis of Strategic Forces Command.
The Agni-IV
- It is an Indian solid-fueled intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with a range of up to 4,000 km.
- The two-stage missile, previously named Agni-II Prime, is a derivative of the Agni-II MRBM with extended range.
- India has flight tested the Agni-IV eight times since its first test in 2010.
Key Features
- Range: Approximately 3,500 to 4,000 kilometers, making it capable of reaching targets across most parts of South Asia and beyond.
- Guidance System: Equipped with advanced inertial navigation systems and satellite guidance for high accuracy.
- Warhead: Can carry a variety of payloads, including conventional and nuclear warheads.
- Propulsion: Powered by solid rocket propellants for reliable performance and extended range.
Strategic Significance
- Deterrence: Enhances India''s strategic deterrence capability with its long range and precision.
- Defense: Provides India with a credible second-strike capability, ensuring a robust response to any potential threat.
Operational Capabilities
- Accuracy: High precision due to advanced guidance systems, ensuring effective targeting.
- Versatility: Capable of being launched from various platforms, including mobile launchers, which increases its strategic flexibility.
Agni Missile
- The Agni missiles are solid-propelled ballistic missiles, ranging from short-range missiles to intercontinental ballistic missiles, with road and rail mobility providing greater chances of survivability during an enemy attack.
- The development of the Agni missile series was started in early 1980 as part of the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programled by former President APJ Abdul Kalam.
- Since then, India has developed many variants of the Agni missile series.
- Over the last two decades, India has worked to improve its strategic deterrent capability by developing a variety of ballistic missiles,precision-guided munitions, and related platforms.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies