What, Why and How of Current account deficit?.
- Balance Of Payment (BOP) is a statement which records all the monetary transactions made between residents of a country and the rest of the world during any given period.
- This statement includes all the transactions made by/to individuals, corporates and the government and helps in monitoring the flow of funds to develop the economy.
- A BOP statement of a country indicates whether the country has a surplus or a deficit of funds.
- When a country’s export is more than its import, its BOP is said to be in surplus.
- On the other hand, the BOP deficit indicates that a country’s imports are more than its exports.
Significance:
- The BOP of a country reveals its financial and economic status.
- A BOP statement can be used as an indicator to determine whether the country’s currency value is appreciating or depreciating.
- The BOP statement helps the Government to decide on fiscal and trade policies.
- It provides important information to analyze and understand the economic dealings of a country with other countries.
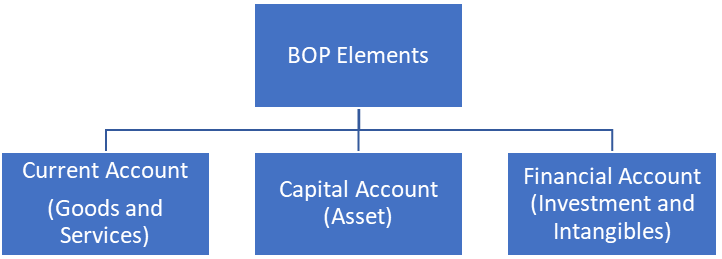 Current Account:
Current Account:
- The current account is used to monitor the inflow and outflow of goods and services between countries.
- This account covers all the receipts and payments made with respect to raw materials, manufactured goods and services.
- When all the goods and services are combined, together they make up to a country’s Balance of Trade (BOT).
- There are various categories of trade and transfers which happen across countries.
- It could be visible or invisible trading, unilateral transfers or other payments/receipts.
- Trading in goods between countries are referred to as visible items and import/export of services (banking, information technology etc.) are referred to as invisible items.
- Unilateral transfers refer to money sent as gifts or donations to residents of foreign countries.
Capital Account:
- All capital transactions between the countries are monitored through the capital account.
- Capital transactions include the purchase and sale of assets (non-financial) like land and properties.
- The capital account also includes the flow of taxes, purchase and sale of fixed assets etc. by migrants moving out/into a different country.
- The deficit or surplus in the current account is managed through the finance from the capital account and vice versa.
- There are 3 major elements of a capital account:
- Loans and borrowings – It include all types of loans from both the private and public sectors located in foreign countries.
- Investments – These are funds invested in the corporate stocks by non-residents.
- Foreign exchange reserves – Foreign exchange reserves held by the central bank of a country to monitor and control the exchange rate does impact the capital account.
Financial Account
- The flow of funds from and to foreign countries through various investments in real estates, business ventures, foreign direct investments etc. is monitored through the financial account.
- This account measures the changes in the foreign ownership of domestic assets and domestic ownership of foreign assets.
- On analyzing these changes, it can be understood if the country is selling or acquiring more assets (like gold, stocks, equity etc.).
Current Account deficit
- It is measured as a percentage of GDP. The formulae for calculating CAD is:
- Current Account = Trade gap + Net current transfers + Net income abroad
- Trade gap = Exports – Imports
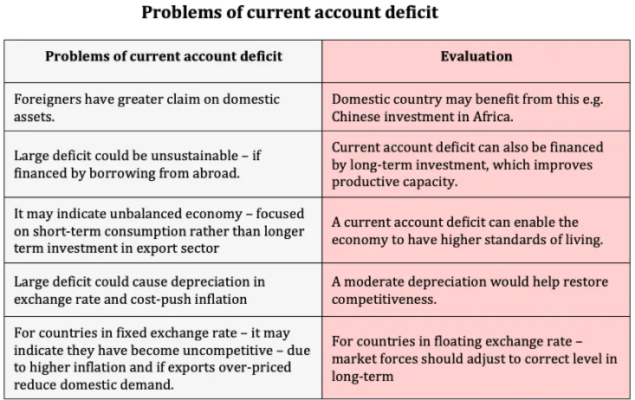
- A country with rising CAD shows that it has become uncompetitive, and investors may not be willing to invest there.
- In India, the Current Account Deficit could be reduced by boosting exports and curbing non-essential imports such as gold, mobiles, and electronics.
- Current Account Deficit and Fiscal Deficit (also known as "budget deficit" is a situation when a nation's expenditure exceeds its revenues) are together known as twin deficits and both often reinforce each other, i.e., a high fiscal deficit leads to higher CAD and vice versa.

Next
previous
 Current Account:
Current Account:











 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies