- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
07th Nov 2021
HARYANA GOVT'S 75% JOB RESERVATION TO COME INTO FORCE FROM 15 JAN
Recently, Haryana government issued a notification saying that Haryana State Employment of Local Candidates Act, 2020 will come into effect from January 15, 2022.
Key features of the Act:



 Cause of mass extinction:
Cause of mass extinction:


- Provides 75 % reservation for local youth in private sector jobs.
- Covers private companies, societies, trusts and partnership firms and any person who employs 10 or more persons for manufacturing, carrying on business or rendering any service in Haryana.
- Reduced the upper limit of gross monthly salary to Rs 30,000 a month.
- It is mandatory for employers to register all such employees, who draw gross monthly salary of not more than Rs 30,000 per month”.
- The government of Madhya Pradesh is mulling a law to ensure that 70% jobs in the private sector go to local youths.
- In 2018, Gujarat government stated, it would bring a law to make it mandatory for manufacturing and service sector entrepreneurs to hire 80% of their workforce from the state.
- The agrarian sector is under tremendous stress across the country, and young people are desperate to move out of the sector. Thus, there is a serious dearth of jobs in private and government sector.
- Discrimination is one of the reasons for under-representation of Dalits and Muslims in the corporate sector. Thus, providing local jobs to these population might over there under-representation.
- Weakness in the employment situation: the unemployment rate had shot up to more than 30 percent in April, with 122 million people losing their jobs.
- The hardest hit were migrant workers in cities, who are employed in construction, restaurants, malls, courier services etc.
- There is inherent xenophobia, which is a fear or hatred of foreign people. This is not unique to India or Indian States, but is universal.
- For example, in the Brexit vote, Britons thought that foreigners were taking away local jobs, and hence voted to secede from the European Union.
- Allowing people to buy seats via capitation fee is a kind of an anti-reservation move, one that grants privileges to those who have money.
- Allowing capitation fee to enrich private institutes seldom causes outrage.
- India must ensure all its citizens opportunity in all spaces; giving preference and quotas for socially and educationally deprived sections in the private space.
- With the number of jobs generated in the state sector shrinking steadily, for the promise of quotas in the Constitution may be inevitable to extend it to the private sector.
- less than one percent (only .69 per cent) of jobs in the country for educated citizens are covered by reservations.

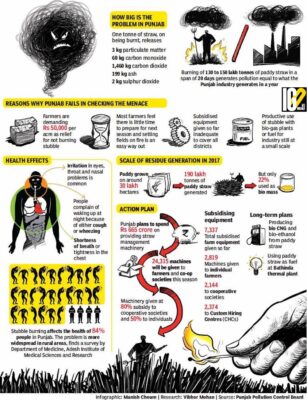
- The study was conducted in six villages of Patiala, Punjab and spanned in two phases.
- The concentrations of PM2.5, increased more than twice, from 100 g/m3 to 250 g/m3.
- These are around 10-15 times higher than the World Health Organisation’s prescribed air quality standards.
- The WHO’s guidelines prescribe annual PM2.5 average at 5 ug/m3 and PM10 annual average at 15 ug/m3.
- A two to three-fold increase was noted in most of the respiratory symptoms including wheezing, breathlessness on exertion, cough, skin rashes, runny nose, or itchiness of eyes etc.
- The highest number of respiratory complaints were reported by the elderly population (>40-60).
- It was lowest in the younger age group (>10-18) during crop burning period.
- There was decline in lung function with increase in PM2.5 concentration across all age groups.
- There was a 10-14% decline in lung function in men and nearly 15-18% decline in women.
- Stubble burning is the act of removing paddy crop residue from the field to sow wheat.
- It’s usually required in areas that use the ‘combine harvesting’ method which leaves crop residue behind.
- Crop residue burning release
- 24 million tonnes of carbon dioxide(CO2)
- Over 9 million tonnes of carbon monoxide (CO)
- 25 million tonnes of oxides of Sulphur (SOX)
- 28 million tonnes of particulate matter
- 07 million tonnes of black carbon.
- The heat from burning paddy straw penetrates 1 centimeter into the soil, elevating the temperature to 33.8 to 42.2 degree Celsius.
- This kills the bacterial and fungal populations critical for a fertile soil.
- Burning of crop residue causes damage to other micro-organisms present in the upper layer of the soil as well as its organic quality.
- 84.5 per cent people suffer from health problem due to increased incidence of smog.
- 76.8 per cent people reported irritation in eyes, 44.8 per cent reported irritation in nose, and 45.5 per cent reported irritation in throat.

- It means the rate of increase in prices over a given period of time.
- Monetary Policy: It determines the supply of currency in the market. Excess supply of money leads to inflation. Hence decreasing the value of the currency.
- Fiscal Policy: It monitors the borrowing and spending of the economy. Higher borrowings (debt), result in increased taxes and additional currency printing to repay the debt.
- Demand-pull Inflation: Increases in prices due to the gap between the demand (higher) and supply (lower).
- Cost-push Inflation: Higher prices of goods and services due to increased cost of production.
- Exchange Rates: Exposure to foreign markets is based on the dollar value. Fluctuations in the exchange rate have an impact on the rate of inflation.
- Demand-pull Inflation: Rising demand in economy.
- Cost-push Inflation: It occurs when the cost of production increases.
- Core Inflation: Inflation rate excluding temporary factors.
- Hyperinflation: Inflation over 1000% a year
- Wage inflation: Inflation caused by rising real wage.
- Imported Inflation: Inflation caused by rising price of import, e.g., due to devaluation.

 Cause of mass extinction:
Cause of mass extinction:
- The cooling climate during Late Ordovician period likely changed the ocean circulation pattern.
- This caused a disruption in the flow of oxygen-rich water from the shallow seas to deeper oceans, leading to a mass extinction of marine creatures.
- The Devonian mass extinction (about 375 million years ago) wiped out about 75% of the world’s species.
- The Permian mass extinction (about 250 million years ago) also known as the Great Dying caused the extinction of over 95% of all species.
- The Triassic mass extinction (200 million years ago) eliminated about 80% of Earth’s species, including some dinosaurs.
- The two countries had entered into a Strategic Partnership with the areas of defence & security cooperation, space cooperation and civil nuclear cooperation constitute the principal pillars of the Strategic Partnership.
- India and France have important bilateral investments and trade and commercial cooperation, particularly in sectors involving IT corridors, smart-cities, railways, capital and trade exchanges, skill development etc.
- France has emerged as a major source of Foreign Direct Investment for India.
- France has continued to support India’s claim for permanent membership of the United Nations Security Council and the reforms of the United Nations.
- France’s support was vital in India’s accession to Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), Wassenaar Arrangement (WA) and Australia Group (AG).
- France continues to support India’s bid for accession to the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- There exist vibrant bilateral cultural and educational linkages as also growing people-to-people contacts. Indian diaspora also has a sizeable presence in metropolitan France and its overseas departments/territories.
- The three services also have regular defence exercises; viz.
- Exercise Shakti (Army),
- Exercise Varuna (Navy),
- Exercise Garuda (Air Force).
- The Indian Navy also participated in the French led La Perouseexercise, along with other Quad members.
- Various staff courses, training programmes etc. also take place regularly.
- ISRO and the French Space Agency, CNES have been carrying on various joint research programmes and collaborating in satellite launches
- As part of the ongoing bilateral cooperation between ISRO and Arianespace, GSAT-11 was launched from Kourou (French Guyana).
- France continues to be a major supplier of components and equipment for the Indian space programme
- France is a founding member of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), announced by India in 2015 at UN Climate Change CoP21.
- Both countries have announced to celebrate 2021-22 as Indo French Year of Environment.
- Agence Française de Développement (AFD) and Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI) signed a letter of intent for developing 150 MW floating solar power system.
- In the field of S&T, the Indo-French Centre for the Promotion of Advance Research (CEFIPRA) based in New Delhi, plays a major role by identifying and funding joint proposals for research projects.
- The two sides set the student exchange target to 20,000 by 2025.
- A Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement between India and France.
- It has been ratified by India and is soon to be ratified by the French Parliament as well.
- The Indo French Roadmap on Cybersecurity and Digital Technology lays down areas of cooperation such as cybersecurity, fight against cybercrime, regulation of Artificial Intelligence, protection of personal information and digital governance.
- In the field of exascale computing, Atos in collaboration with CDAC has developed “PARAM-Siddhi- AI”, India’s fastest supercomputer.
- Additionally, there exist immense potential in collaborating in future technologies such as 5G and beyond, developing global tech standards.
- India supplied France with nearly 2 million hydroxychloroquine tablets and 36 MT of paracetamol (API).
- France expressed its gratitude by sending 120 ventilators, 50 thousand serological tests and 50 thousand nose/throat swabs as aid.
- France also announced a 200-million-euro loan to India to help the vulnerable sections most severely affected by the pandemic.
- An Indian Cultural Centre, named Vivekananda Cultural Centre, is being opened in Paris.
- Namaste France was held across France displaying various facets of Indian art and culture.
- Similarly, the Bonjour Indiafestival will be held in India in 2022.
- Government of India has also offered five scholarships for study of Sanskrit in India to French nationals.
- The International Day of Yoga has been organized by the Embassy of India, Paris in Paris and in other cities of France since 2016.

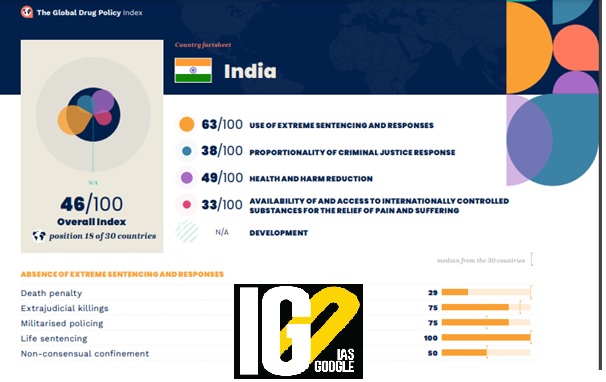
- Out of 30 countries ranked, Norway has topped, while Mexico was placed at the bottom.
- India was ranked at 18th position.
- The Global Drug Policy Index is a unique tool that measures national-level drug policies.
- It provides each country with a score and ranking that shows how much their drug policies and their implementation align with the UN principles of human rights, health and development.
- As such, the Index provides an essential accountability and evaluation mechanism in the field of drug policy.
- It is a data-driven global analysis.
- It is composed of 75 indicators running across five broad dimensions of drug policy:
- Criminal justice
- Extreme responses
- Health and harm reduction
- Access to internationally controlled medicines
- Development
- It is a project of the Harm Reduction Consortium, whose partners include:
- The European Network of People Who Use Drugs
- The Eurasian Harm Reduction Association (EHRA)
- The Eurasian Network of People who Use Drugs (ENPUD)
- The Global Drug Policy Observatory (GDPO) / Swansea University
- Harm Reduction International (HRI), the International Drug Policy Consortium (IDPC)

- Chumbi Valley lies in Yadong country in Tibetan region.
- It is also known as Dromo, Tromo or Chomo
- It is the trijunction of India, China and Bhutan.
- The inhabitants of the valley are called Promowa and are of Tibetan descent.
- Maintaining national security on border frontiers.
- Protecting the Siliguri corridor (also called 'Chicken's neck') which connects India to the north-eastern states.
- India has formally agreed to come to Bhutan's rescue in case of any aggression by foreign power under Indo-Bhutan Friendship Treaty,2007.
- It is close to Nathu-La pass which is important trade point.
- It is a narrow stretch of land located in the West Bengal, that connects India’s north-eastern states to the rest of India.
- It borders Nepal, Bangladesh and Kingdom of Bhutan.
- The corridor extends from the Darjeeling, Jalpaiguri and Terai areas of West Bengal towards the North East.
- It is the only bridge between the eight north-eastern states of India and the rest of the country.
- The region is important for trade, commerce and tourism for West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh.
- The corridor is the hub of a rail and road network connecting West Bengal and the rest of India to the North East.
- It is also the hub of the railway network that connects to the strategic military formations along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies