- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
2nd January 2021
IFSCA becomes member of IOSCO
Recently, the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has become an Associate Member of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO).
International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA)
 Occurring of Lightning
Occurring of Lightning
- It has been established in 2020 under the International Financial Services Centres Authority Act, 2019.
- It is headquartered at GIFT City, Gandhinagar in Gujarat.
- It is a unified authority for the development and regulation of financial products, financial services and financial institutions.
- The GIFT IFSC is the maiden international financial services centre in India.
- The main objective of the IFSCA is to develop a strong global connect and focus on the needs of the Indian economy as well as to serve as an international financial platform for the entire region and the global economy as a whole.
- The membership of IOSCO would provide IFSCA the platform to exchange information at the global level and regional level on areas of common interests.
- The IOSCO platform would enable IFSCA to learn from the experiences and best practices of the regulators of other well established financial centres.
- The IOSCO’s membership is a significant milestone in connecting IFSCA with the regulators of securities markets globally.
- It would contribute immensely towards the development and regulation of the financial products, financial services and financial institutions at the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City International Financial Services Centre.
- It is the international organization that brings together the world's securities regulators, covering more than 95% of the world’s securities markets.
- It is the global standard setter for the securities sector.
- It works closely with the G20 and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in setting up the standards for strengthening the securities markets.
- The IOSCO Objectives and Principles of Securities Regulation have been endorsed by FSB as one of the key standards for sound financial systems.
- It is a savings scheme launched in 2015 as part of the Government initiative Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao campaign.
- It enables guardians to open a savings account for their girl child with an authorised commercial bank or India Post branch.
- The individuals can open an account with as low as Rs. 250 and they also have to invest a minimum of Rs. 250 to keep the account active.
- The maximum amount that an individual can deposit per year in a Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana account is Rs. 1.5 Lakh.
- The maturity period of an SSY account is 21 years.
- An account holder (the girl) will be able to withdraw from her account once she reaches 18 years of age.
- The account holder can only withdraw 50% of the accumulated amount once after she reaches this specified age only for the purpose of higher education.
- The SSY account can be opened by legal guardians of the girl child provided the following conditions are met:
-
- The girl must be an Indian resident
- The girl shouldn’t be more than 10 years of age
- Upto two accounts can be opened in a family with two girl children.
- It is one of the most popular schemes owing to the high-interest rate as well as the tax benefits it offers.
- Under Section 80 C of the Income Tax Act, 1961, individuals can claim tax exemption up to Rs 1.5 Lakh from the amount contributed to SSY account.
- The interest income generated from investing is tax-exempt as well and tax benefits are extended to the maturity amount too.
- The GST revenue collections had been posting a contraction and were at a lower level than the previous year following the outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic.
- The GST revenue collections remained in negative territory for the first five months of FY 2020-21.
- The month of December marked the fourth month in which GST revenue collectionshave posted a year-on-year growth.
- The GST collections in December have gained support from higher festive season sales on account of Diwali in November.
- The rollout of new technological systems of e-invoicing and action against tax evaders has up-ticked the GST collections.
- The tax experts noted that the government should provide a breakup of the GST revenues collected through the filing of returns and through recovery drives by the GST authorities to help in assessing the true picture of the extent of economic recovery.
- The proposed extension of electronic invoicing to all businesses will further prevent leakages in GST revenues.
- Under GST laws, e-invoice for B2B transactions has been made mandatory for companies with turnover of over Rs 500 crore in 2020.
- It was notified to be extended to businesses with over Rs 100 crore turnover from January 2021 and is likely to be extended for all businesses beginning April 1 2021.
- The E-invoicing system is connected to a central portal that receives and validates invoices in real-time and over time will eventually replace the e-way bill system.
- The revenues from import of goods was 27% higher and the revenues from domestic transactions (including import of services) are 8% higher that the revenues from these sources during the same month last year.
- Uttar Pradesh with 293 deaths, Madhya Pradesh 248, Bihar 221, Odisha 200 and Jharkhand 172 deaths together accounted for more than 60 per cent of the numbers.
- In 2018-19 period, there were 2,800 deaths and the drop has been attributed to the efforts of various stakeholders, including CROPC.
- The report suggests states “aggressively participate in Lightning Resilient India Campaign and undertake lightning risk management more comprehensively” in order to further reduce deaths.
- According to report, the Government of India and most states have not notifiedlightning as a disaster.
- The report mentions that the rapid degradation of environment like global warming, deforestation, depletion of water bodies, concretizations, rising pollution and aerosol levels have cumulatively pushed the environment to extremes.
 Occurring of Lightning
Occurring of Lightning
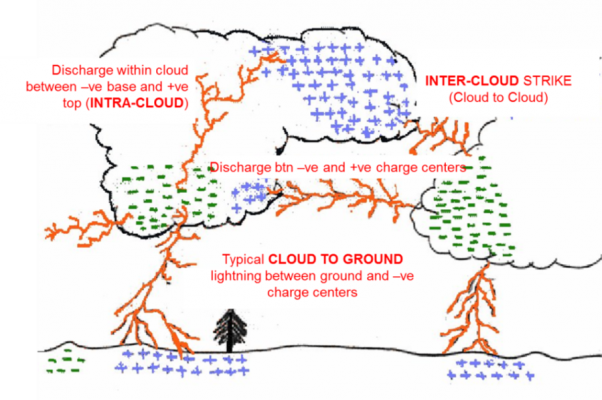
- Lightning is the process of occurrence of a natural ‘electrical discharge of very short duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud’.
- Inter cloud or intra cloud (IC) lightning which are visible and are harmless.
- It is cloud to ground (CG) lightning, which is harmful as the ‘high electric voltage and electric current’ leads to electrocution.
- CROPC has a MOU with the India Met Department (IMD) to disseminate early lightning forecasts which uses satellite observations, inputs from ‘network of Doppler and other radars’, ‘lightning detection Sensors’ among others.
- It makes Lightning Forecast unique with best possible lead time of even a week taking into account the devastations caused by the severe thunderstorms during pre-monsoon.
- The NDMA has issued comprehensive guidelines for preparations of Lightning action plans to states, but the large number of fatalities show the implementation also needs a more ‘scientific and focused community centric approach’.
- The mapping of lightning is a major breakthrough in identifying the precise risk in terms of lightning frequency, current intensity, energy content, high temperature and other adverse impacts.
- The climatology of lightning would yield a Lightning Risk Atlas map for India which will form the basis for a lightning risk management programme.
- The exchange of information comes despite the ongoing tensions between India and Pakistan.
- The relationship dipped after India's war planes pounded a terrorist training campdeep inside Pakistan in February 2019 in response to the Pulwama terror attack.
- Tensions between the two nations spiked further after New Delhi abrogated provisions of Article 370 of the Constitution to withdraw Jammu and Kashmir's special status and bifurcated it into two Union Territories.
- Pakistan downgraded its diplomatic relations with India and expelled the Indian high commissioner following the revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is Non-nuclear aggression agreement and nuclear weapons control treaty between India and Pakistan.
- The practice of exchanging the list of nuclear installations was carried out under a bilateral arrangement that prohibits them from attacking each other's atomic facilities.
- The exchange was made in accordance with Article-II of the Agreement on Prohibition of Attacks against Nuclear Installations and Facilities between Pakistan and India.
- According to Foreign Office (FO), the exercise is carried out consecutively since January 1, 1992.
- Each party shall refrain from undertaking, encouraging or participating in, directly or indirectly, any action aimed at causing the destruction of, or damage to, any nuclear installation or facility in the other country.
- The term "nuclear installation or facility" includes nuclear power and research reactors, fuel fabrication, uranium enrichment, isotopes separation and reprocessing facilities.
- It covers any other installations with fresh or irradiated nuclear fuel and materials in any form and establishments storing significant quantities of radio-active materials.
- Each Contracting Party shall inform the other on 1st January of each calendar year of the latitude and longitude of its nuclear installations and facilities and whenever there is any change.
- The RBI-DPI has been constructed with March 2018 as the base period.
- The DPI for March 2019 and March 2020 work out to 153.47 and 207.84 respectively, indicating appreciable growth.
- The RBI-DPI comprises five broad parameters that enable the measurement of deepening and expansion of digital payments in the country over different time periods.
- The parameters are including Payment Enablers (weight 25%), Payment Infrastructure – Demand-side factors and (10%), Payment Infrastructure – Supply-side factors (15%), Payment Performance (45%) and Consumer Centricity (5%).
- The RBI-DPI shall be published on RBI’s website on a semi-annual basis from March 2021 onwards with a lag of 4 months.
- According to the latest RBI data, digital transactions exhibited a sustained recoveryand momentum picked up in November 2020, supported by both wholesale and retail transactions.
- In the retail segment, national electronic funds transfer (NEFT) transactions volume grew 24.6 percent year-on-year in November 2020, much higher than the growth (13.9 percent).
- In value terms, UPI transactions to the tune of Rs 3.9 lakh crore has happened while IMPS transactions worth Rs 2.76 lakh crore has happened.
- The data showed that RTGS transactions worth Rs 79.8 lakh crore and NEFT worth Rs 22.18 lakh crore were reported.
- Among other digital transaction modes, national electronic toll collection (NETC) held on to a buoyant growth trajectory and immediate payment service (IMPS) showed stronger growth in November 2020 than in the previous month.
- It aims to capture the extent of digitisation of payments across the country.
- Under payment performance, which carries the highest weight in the index, the regulator would measure factors such as the volume and value of digital payments, unique users, paper clearing, and currency in circulation and cash withdrawals.
- The RBI and government have been pushing for digital transactions over the years to bring in more transparency and efficiency in the financial system.
- The objective of DPI is to reflect accurately the penetration and deepening of various digital payment modes.
- A special ‘Police K9 Cell’ was established in November 2019 under the Police Modernization Division of the Ministry of Home Affairs with the mandate of ‘Mainstreaming and Augmentation of Police Service K9s in the country’.
- It is the first such publication in the country on the subject of Police Service K9s (PSKs) i.e. Police Dogs.
- It is a unique initiative that will further enrich the subjects related to Police Service Dog (K-9) (PSK) teams in the country.
- The police dog squad can act as a force multiplier to ensure the safety of societysimilar to drones or satellites are being used in the country.
- The publication of the Police K9 Journal is a step in creating an ecosystem in the country to train and learn on augmenting this vital resource.
- It is a biannual journal which will be released in April and October every year.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies