- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
5th January 2021
National Metrology Conclave
Recently, the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has delivered inaugural address at the National Metrology Conclave 2021.
Key Highlights of National Metrology Conclave 2021
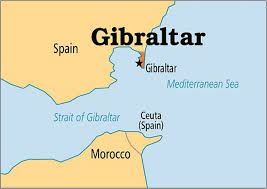 Recently, Spain has signed a deal before the Brexit transition period ended with United Kingdom to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar.
Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula that Britain controls but Spain claims as its own.
Recently, Spain has signed a deal before the Brexit transition period ended with United Kingdom to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar.
Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula that Britain controls but Spain claims as its own.
 Recently, the Odisha Forest department has stressed the need for stricter monitoring of social media platforms to check pangolin poaching and trading.
Recently, the Odisha Forest department has stressed the need for stricter monitoring of social media platforms to check pangolin poaching and trading.
- The Conclave was organised by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Physical Laboratory (CSIR-NPL).
- The theme of the conclave is ‘Metrology for the Inclusive Growth of the Nation’.
- The Prime Minister dedicated National Atomic Timescale and Bhartiya Nirdeshak Dravya Pranali to the Nation.
- It would help the industry to make quality products in sectors like Heavy metals, Pesticides, Pharma and Textiles by drafting a 'Certified Reference Material System'.
- He also laid the Foundation Stone of National Environmental Standards Laboratory.
- Manufacturing of Quality Products: Metrology allows manufacturers to produce products more accurately, more quickly and to a higher standard.
- Increase in Knowledge: The research will need measurements even in the final phases of his or her research which usually involve determining whether the results obtained after a research are accurate or significant.
- Characterization of gravitational fields, rock dating, determination of certain physical or chemical constants is all areas of research that call for metrology.
- Protection of People: Measurement of radiation in radiotherapy and dosage of drugs stand out as vital areas in the health sector.
- They call for measuring units that are vital for the safety of patients and precision is important because it can save lives.
- Helps in Different Areas of The Law: Labor law involves systems designed to monitor the hours worked, lighting levels in professional premises, noise levels and measurement of ambient atmospheres such as fibres and mercury vapors.
- Environmental law is yet another legal field that cannot survive without metrology because protection of the environment solely requires statutory requirements on the quality of air and water.
- The CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, India (NPLI) is committed to ensure thequality of products in every manufacturing and consumer sector by providing SI traceable measurements.
- Reference materials (RM) play pivotal role in maintaining the quality infrastructure of any economy through testing and calibration with precise measurements traceable to SI units.
- NPLI has released two important certified RMs as Bharatiya Nirdeshak Dravyas (BNDs) i.e. BND-4201 for 4N purity gold and BND-5101A for Bituminous coal.
- The Certified Indian Reference Material program was started in 1986 by CSIR-NPLI.
- The Seaplane Service is already in operation between Kevadia and Sabarmati Riverfront in Ahmedabad, which was inaugurated by Prime Minister on 31st October 2020.
- The project aims at initiating the process of commencing operations of the Seaplane services, on the select routes, under a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) framework through prospective airline operators.
- The project execution and implementation would be through Sagarmala Development Company Ltd (SDCL).
- The SDCL is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Shipping.
- The proposed Origin-Destination pairs under Hub and Spoke model include:
- Islands of Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep,
- Guwahati Riverfront & Umranso Reservoir in Assam,
- Yamuna Riverfront / Delhi (as Hub) to Ayodhaya, Tehri, Srinagar (Uttarakhand), Chandigarh and many other tourist places of Punjab & HP;
- Mumbai (as Hub) to Shirdi, Lonavala, Ganpatipule;
- Surat (as Hub) to Dwarka, Mandvi & Kandla, Khindsi Dam, Nagpur & Erai Dam and Chandrapur (in Maharashtra)
- The joint development and operation of “Sagarmala Seaplane Services (SSPS)” will be undertaken by forming a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) with Sagarmala Development Company Limited (SDCL).
- SDCL is exploring plans to leverage the potential of the vast coastline and numerous water bodies/rivers across India by commencing seaplane operations to provide connectivity and easier accessibility to remote locations.
- The Sea Plane will utilize the nearby water bodies for take-off and landing and thus connect those places in a much economical way as conventional airport infrastructure.
- The seaplanes services will be a game-changer providing a supplementary means of faster and comfortable transportation across the nation.
- It will boost tourism for domestic and international holidaymakers.
- It will save travel time and stimulate localized short distance travelling especially in the hilly regions or across the rivers/lakes etc.
- It is being started for boys and girls coming out of child care institutions and having completed 18 years of age.
- The objective of the scheme is to provide such a platform to these youth, through which they will be able to become self-reliant by continuing their education and training.
- Under the launch pad scheme, 52 districts of the state have been divided into 5 clusters.
- The five divisional headquarters are being started in Indore, Sagar, Gwalior, Jabalpur and Bhopal.
- Under this scheme, the District Administration will provide space to these youths for opening of coffee shops, stationery, photocopying, computer typing and DTP work.
- An amount of Rs 6 lakh will be provided by the Women and Child Development Department for the installation of each launch pad.
- The launch pads will be operated through non-governmental organizations.
- The Nile, Africa’s longest river, has been at the center of a decade-long complex dispute involving several countries that are dependent on the river’s waters.
- At the forefront of this dispute are Ethiopia and Egypt, with Sudan having found itself dragged into the issue.
- The main waterways of the Nile run through Uganda, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt, and its drainage basin runs through several countries in East Africa, including Ethiopia.
- The construction of the dam was initiated in 2011 on the Blue Nile tributary of the river that runs across one part of Ethiopia.
- The Nile is a necessary water source in the region and Egypt has consistently objected to the dam’s construction, saying it will impact water flow.
- Given the dam’s location on the Blue Nile tributary, it would potentially allow Ethiopia to gain control of the flow of the river’s waters.
- Egypt lies further downstream and is concerned that Ethiopia’s control over the water could result in lower water levels within its own borders.
- Egypt proposed a longer timeline for the project over concerns that the water level of the Nile could dramatically drop as the reservoir fills with water in the initial stages.
- Sudan’s location between Egypt up north and Ethiopia down south has caused it to become an inadvertent party to this dispute.
- It was formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as Hidase Dam.
- It is a gravity dam which is situated on Blue Nile River in Benishangul-Gumuz region of Ethiopia.
- The reservoir and dam will offer major benefits to Ethiopia, Egypt and Sudan.
- After completion, it will be Africa’s biggest hydroelectric power plant.
- It is a bone of contention between Egypt and Ethiopia.
- It empties into Mediterranean Sea after traveling for over 6,600 kilometers (4,100 miles).
- It flows from south to north through eastern Africa.
- It begins in the rivers that flow into Lake Victoria (located in modern-day Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya).
- In addition to Egypt, the Nile runs through or along the border of 10 other African countries, namely, Burundi, Tanzania, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and South Sudan.
- Its three main tributaries are the White Nile, the Blue Nile and the Atbara.
- It is a river originating in natural springs above Lake Tana in Ethiopia.
- Along its upper reaches in Ethiopia the river is called the Abbai.
- The Blue Nile joins the White Nile at Khartoum, Sudan, and, as the Nile, flows through Egypt to the Mediterranean Sea at Alexandria.
 Recently, Spain has signed a deal before the Brexit transition period ended with United Kingdom to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar.
Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula that Britain controls but Spain claims as its own.
Recently, Spain has signed a deal before the Brexit transition period ended with United Kingdom to maintain free movement to and from Gibraltar.
Gibraltar is a small portion of land on the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula that Britain controls but Spain claims as its own.
- Officially remaining a British Overseas Territory, Gibraltar will now be part of the Schengen zone and follow EU rules.
- Gibraltar, with an area of just 6.8 sq km and a population of around 34,000 people, has been the subject of intense dispute between Spain and Britain for centuries.
- The territory, which is connected to Spain by a small strip of land and surrounded by sea on three sides, serves as the only opening from the Atlantic Ocean into the Mediterranean Sea.
- It is a key location on the shortest sea route between Europe and Asia via the Suez Canal.
- Gibraltar fell into British hands after a war in 1713, and has since remained with Britain despite several attempts by Spain to retake it.
- Due to its strategic importance, Gibraltar came to be highly fortified by Britain since the 18th century, thus earning its commonly known name “the Rock”.
- Gibraltar’s port was critically important for the Allies during the World War II and it continues to be a key base for NATO.
- The result of the 2016 Brexit referendum gave rise to the possibility of a hard border coming up between Gibraltar and the rest of Europe.
- Gibraltarians mainly voted ‘Remain’ because the territory’s economy depends on an open border with Spain, which sends over 15,000 workers and 200 trucks there daily.
- The free movement will now continue because of the Spain-UK deal, as Gibraltar is being placed in the Schengen area, with Spain acting as a guarantor.
- The Schengen passport-free zone includes 22 countries from the EU, and four others i.e. Norway, Switzerland, Iceland and Liechtenstein.
- The EU will now place Frontex border guards for the next four years to ensure free movement to and from Gibraltar.
- The territory’s port and airport would become the external borders of the Schengen area.
 Recently, the Odisha Forest department has stressed the need for stricter monitoring of social media platforms to check pangolin poaching and trading.
Recently, the Odisha Forest department has stressed the need for stricter monitoring of social media platforms to check pangolin poaching and trading.
- The Athagarh Forest Division in Odisha’s Cuttack district had tasted success in pinning down the active gang of pangolin smugglers during November 2019.
- The investigations revealed that the accused were trading pangolin and scales online by forming WhatsApp groups in which videos and photos were shared with potential customers.
- The trafficking of live pangolin and its scales is a highly lucrative business for organised mafia, who exploit poor and vulnerable forest dwelling communities for their criminal interests.
- Pangolins are solitary, primarily nocturnal animals and are easily recognized by their full armor of scales.
- Pangolins are the only mammals wholly-covered in scales and they use those scales to protect themselves from predators in the wild.
- There are eight species of pangolins which are found on two continents:
- The four species live in Africa: Black-bellied pangolin (Phataginus tetradactyla), White-bellied pangolin (Phataginus tricuspis), Giant Ground pangolin (Smutsia gigantea) and Temminck's Ground pangolin (Smutsia temminckii).
- The four species found in Asia: Indian pangolin (Manis crassicaudata), Philippine pangolin (Manis culionensis), Sunda pangolin (Manis javanica) and the Chinese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla).
- The Indian Pangolin is listed as Endangered in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species and protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The annual mean land surface air temperature averaged over India during 2020 was nearly 0.3 degree Celsius above normal but was substantially lower than the highest warming observed over India during 2016.
- The monsoon and post-monsoon seasons contributed to most of the temperature rise in 2020 with mean temperature in winter also above normal.
- The pre-monsoon season temperature was below normal (-0.030C).
- India's 0.3 degree rise was less than the average global temperature rise of 1.2 degree.
- The 2020’s monsoon rainfall was 9% above its seasonal normal.
- The 2020 annual rainfall over the country as a whole was 109 per cent of its Long Period Average (LPA) based on the data of 1961-2010.
- The 2020 Northeast monsoon season (October-December) rainfall over the country as a whole was normal (101 per cent of LPA).
- The five cyclones formed over the North Indian Ocean in 2020 including the super cyclonic Storm AMPHAN, Very Severe Cyclonic Storms NIVAR & GATI, Severe Cyclonic Storm NISARGA, and Cyclonic Storm ‘BUREVI’.
- Bihar and Uttar Pradesh were the most adversely affected States by natural disasters during the year which claimed more than 350 deaths from each State mainly due tothunderstorm, lightning and cold waves.
- Heavy rainfall and flood related incidents reportedly claimed over 600 lives from different parts of the country during pre-monsoon, monsoon and the post-monsoon seasons.
- Of these, 129 deaths were in Assam, 72 from Kerala , 61 from Telangana, 54 lives from Bihar, 50 from Maharashtra, 48 Uttar Pradesh, & 38 from Himachal Pradesh.
- Thunderstorms and lightning reportedly claimed 815 lives from different parts of the country.
- In the Union Budget 2019, the Finance Minister proposed the introduction of a scheme of faceless e-assessment.
- The scheme seeks to eliminate the human interface between the taxpayer and the income tax department.
- The scheme lays down the procedure to carry out a faceless assessment through electronic mode.
- All provisions introduced under Faceless Assessment, under the Income Tax Act, 1961, are introduced to:
- Eliminate the interface between the Assessing Officer and the assessee during the course of proceedings, to the extent that is technologically feasible;
- Optimise the utilisation of resources through the economies of scale and functional specialisation; and
- Introduce a team-based determination of arm’s length price with dynamic jurisdiction.
- As per the Taxation and Other Laws (Relaxation and Amendment of Certain Provisions) Bill, 2020, Faceless Assessment will now bring other provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961 under its purview.
- The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) decides the scope of the faceless assessment such as territorial area, persons, class of persons, incomes, class of incomes, cases or class of cases to whom this faceless assessment is applicable.
- It is an attempt of the government to remove individual tax officials’ discretion and potential harassment for income tax payers.
- In the faceless regime, the main objective is to remove physical interaction as much as possible, and the taxpayers may not have the opportunity to explain (in person) business-related complexities and explain various positions they have taken while filing their income-tax returns.
- The Central Government introduced the Faceless Assessment Scheme to provide greater transparency, efficiency and accountability in Income Tax assessments.
- The Section 130 gives power to the Central Government to make a scheme by notifying the same in the Official Gazette, for the purposes of:
- The exercise of any or all powers and performance of any or all the functionsconferred on or assigned to the income-tax authorities under the Income Tax Act, as referred to in section 120; or
- To vest the jurisdiction with the Assessing Officer, as referred to in section 124; or
- To exercise the power to transfer cases under section 127; or
- To exercise jurisdiction in case of change of incumbency, as referred to in section 129









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies