- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 Latest News
Latest News
April 26, 2024 Current Affairs
Global Report on Food Crises: acute hunger remains persistently high in 59 countries.
- Nearly 282 million people faced high levels of acute food insecurity in 59 countries with 1-in-5 people assessed in need of critical urgent action in 2023, according to the 2024 Global Report on Food Crisis (GRFC), released recently.
Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) 2024:
- GRFC is produced annually by the Food Security Information Network(FSIN) and launched by the Global Network Against Food Crises, a multi stake holder initiative that includes United Nations agencies, the European Union, the United States Agency for International Development, and non-governmental agencies working to tackle food crises.
Highlights of GRFC 2024:
- The report analyzed a population of 1.3 billion in 2023 across 59 countries.
- 2023 was the fifth consecutive year of rises in the number of people suffering acute food insecurity, defined as when populations face food deprivation that threatens lives or livelihoods, regardless of the causes or length of time.
- Nearly 282 million people faced high levels of acute food insecurity in 59 countries in 2023.
- The report identifies conflicts, extreme weather events, and economic shocks as the three main drivers behind the exacerbation of food crises in the world.
- With food crisis escalating alarmingly in conflict hotspots in 2023, notably Palestine (Gaza Strip) and Sudan, conflict / insecurity became the primary driver in 20 countries, directly affecting 135 million people.
- The Gaza Strip became the area with the most severe food crisis in the last eight years of GRFC reporting.
- Sudan is facing one of the worst food crises in the world, with almost a third of the population in need of emergency food aid.
- Meanwhile, weather extremes were the main driver for 18 countries, with over 72 million people facing high levels of acute food insecurity because of such extreme weather events.
- The 10 countries with the world’s largest food crisis in 2023 were the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Nigeria, Sudan, Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Yemen, the Syrian Arab Republic, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Myanmar.
- On a positive note, the situation improved in 17 countries in 2023, including the Democratic Republic of Congo and Ukraine.
Antarctica''s France-Sized Ice Shelf Makes Daily Jumps, Raising Icequake Concerns.
- Researchers have uncovered a surprising phenomenon in Antarctica: the massive Ross Ice Shelf, roughly the size of France, lurches forward several centimetres once or twice a day.
Ross Ice Shelf:
- Location: It is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica.
- It is situated in the Ross Sea, extending off the continent’s coast into the ocean.
- It is the world’s largest floating body of ice, covering approximately 487,000 square kilometres, about the size of France.
- Only ten percent of the ice shelf is visible, with the majority hidden in several hundred metres of ice below the surface.
- Thickness: Its thickness varies significantly, ranging from about 100 meters to several hundred meters. The thickest parts are generally found where the shelf anchors against the continent.
Formation:
- It is formed by the accumulation and compaction of snow, which, over time, turns into ice.
- It is being fed a constant flow of ice from glaciers draining from both the East and West Antarctic Ice Sheets.
- As new ice is added, existing ice is being removed through melting at the base and ice calving at the front.
- It plays an important role in stabilising the Antarctic ice sheet, buttressing the ice that is constantly moving over the land surface.
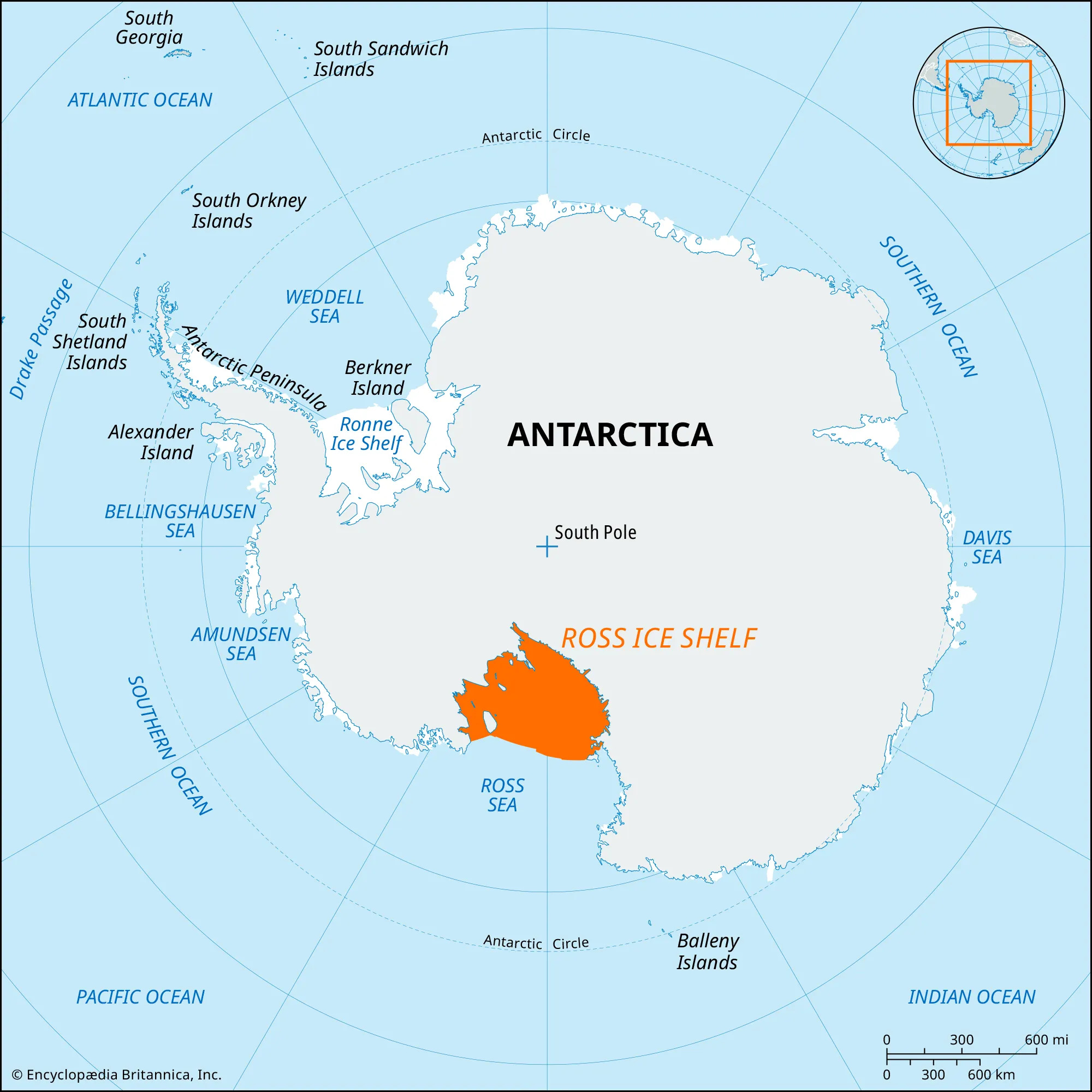
Ross Sea:
- It is a giant bay just 320 kms from the South Pole.
- The sea is remote and positioned south and slightly east of New Zealand.
- It is the largest polar marine ecosystem in the world.
- The Ross Sea is relatively shallow, and it accounts for an area of approximately 960,000 square km (370,000 square miles).
- A large portion of the sea is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf.
- It is strongly influenced by the coastal East-Wind Drift that sets up a vast clockwise gyre accompanied by deep water upwelling.
- It is the first protected area in Antarctica and home to most of the world’s penguins and many species of whale.
- Numerous scientific research stations are located along its coasts.
FSSAI order has raised the Maximum residue limit (MRL) of pesticides in herbs.
- The Food Safety Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) order has raised the Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) for pesticides in herbs and spices from 0.01 mg/kg to 0.1 mg/kg.
Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) of pesticides in herbs and spices:
- MRL is the highest level of a pesticide residue that is legally tolerated in or on food or animal feed when pesticides are applied correctly in accordance with Good Agricultural Practice.
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) sets MRLs for all food and animal feed based on recommendations from the FAO/WHO Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR).
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) established the CAC in 1963.
Indian Scenario of MRL:
- The FSSAI is responsible for fixing the MRL of pesticides in India.
- The MRLs are outlined under the Food Safety and Standards (Contaminants, Toxins and Residues) Regulation, 2011.
- These limits are set based on data from field trials conducted or reported by the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC), under the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Family Welfare.
Issues with increasing MRL:
- It allows for more pesticides to be ingested into the human body with severe health implications.
- Differing MRLs can cause trade issues, with importing countries imposing strict limits raising costs for producers, consumers, and possibly halting trade.
FSSAI:
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India is a statutory body under the administration of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It regulates the manufacture, storage, distribution, sale, and import of food articles, while also establishing standards to ensure food safety.
- It was established by the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, which consolidated all former acts and orders related to food safety that were previously handled by various ministries and departments.
PayU receives RBI's in-principle approval for payment aggregator role.
Payment Aggregator (PA):
- Payment aggregator is a financial technology company that enables businesses to accept various payment methods, including debit cards, credit cards, UPI, and bank transfers.
- They act as intermediaries between merchants and financial institutions.
- PAs are incorporated under the Companies Act, either 1956 or 2013.
Authorization and Regulation:
- Non-bank payment aggregators must obtain authorization from the RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
Types of Payment Aggregators in India:
- Third-party payment aggregators: Independent companies that offer a wide range of payment options through partnerships with multiple payment providers.
- Bank payment aggregators: Owned and operated by banks, offering a more limited range of payment options but potentially higher security and reliability.
Features and Functions:
- Payment aggregators assist businesses in setting up sub-merchant accounts, which are essential for processing transactions.
Operational Process:
- To accept payments, businesses first create an account with a PA, which then provides them with merchant accounts.
- At the checkout page, customers choose their preferred payment method. The acquiring bank receives the transaction details, and the card company conducts a fraud check.
- After approval, the issuer sends funds to the acquiring bank, which then transfers them to the merchant's account.
Security and Efficiency:
- Payment aggregators prioritize security measures to prevent fraud and protect customer data.
- The onboarding process for merchants is streamlined to be efficient, often completed within a few days.
RBI issues Master Direction for Asset Reconstruction Companies.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC):
- ARCs are financial institutions that buys the Non Performing Assets (NPA) or bad assets from banks and financial institutions so that the latter can clean up their balance sheets.
- In the Union Budget 2021-22, Finance Minister announced the setting up of ARCs in India to take care of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) of stressed banks.
- They are registered under the RBI and regulated under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
RBI's New Master Direction for ARCs:
- The Master Direction for ARCs has been issued under the authority granted by the SARFAESI Act, 2002.
- Objective: To ensure ARCs operate prudently and efficiently, protecting investor interests and maintaining financial stability.
- Minimum Net Owned Funds (NOF): ARCs must maintain a minimum NOF of Rs 300 crore to commence business in securitization or asset reconstruction.
- Registration Requirement: ARCs need to apply for and obtain a Certificate of Registration (CoR) from the RBI before starting their operations.
- Investment Restrictions: ARCs are not allowed to invest in land or buildings, except for their own use, which should not exceed 10% of their owned funds.
- Prohibition on Deposits: ARCs cannot raise funds through deposits.
- Capital Adequacy: A capital adequacy ratio of at least 15% of total risk-weighted assets must be maintained.
- Leadership Age and Tenure Limits: The maximum age for MD/CEO or Whole-time Director (WTD) is capped at 70 years, with a tenure limit of five years at a time and a maximum continuous tenure of fifteen years.
- Reporting Malpractices: ARCs must report serious professional misconduct by chartered accountants, advocates, and valuers to the Indian Banks Association (IBA) for inclusion in a fraud database.
Significance of ARCs:
- Encourage prompt resolution of stressed assets, facilitating better value realization.
- Inject liquidity into the economy by addressing distressed assets.
- Enhance bank valuation and strengthen their capacity to raise market capital.
IAF successfully tests air-launched ballistic missile in Andamans, significantly boosts stand-off capabilities.
- Recently, under the aegis of Strategic Forces Command a new version of Medium-Range Ballistic Missile successfully launched in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Crystal Maze 2:
- It is an extended stand-off range air-to-surface ballistic missile of Israeli origin, also known as ROCKS.
Features:
- This missile has the ability to strike targets located at distances exceeding 250 kilometers.
- It is designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- It is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
- It operates effectively in GPS-denied areas like the one India faced during the Kargil War.
- It can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
Ballistic Missile and Why is it Named So?
A Ballistic missile follows a ballistic flight path which comprises three phases of flight:
- First phase or the Boost Phase: The solid-fuel rocket engine propels the missile upward, requiring it to swiftly attain velocity and altitude as it penetrates through the dense layers of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Second and unpowered phase of flight: It happens in the upper reaches of the earth’s atmosphere or in space, where the missile travels along its pre-determined path, but without the power of its engines.
- It is known as the coast phase or mid-course phase and during this time, it travels along a horizontal path.
- During the coasting, the missile is either in space or the upper atmosphere, where it faces minimal resistance or drag.
- Third and final phase or the terminal phase: The missile descends and gets back into the earth’s atmosphere and flies towards its target, while being guided by its on-board systems.
- Significance for India: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative. This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
Other similar missiles:
- Popeye Missile : The Israeli-built Popeye is a medium-range conventional missile which can be fired from a stand-off distance of around 90 km, i.e., the aircraft doesn’t need to be vertically above the target to hit it.
- SPICE: SPICE (Smart Precise Impact and Cost Effective guidance kit)-2000 is mounted on a standard 2000-pound Mk 84 unguided bomb. This converts it into smart guided air-to-surface munition that can be dropped from a stand-off distance of up to 60 km.
- It is a “fire and forget” weapon that automatically goes to its target once launched relying only on its navigation/seeker system.
- The missile, launched from a Su-30 fighter jet by the IAF.
- This missile inherits many technologies from Popeye and SPICE which was used in the Balakot strike.
Strategic Forces Command (SFC):
- It is also sometimes known as Strategic Nuclear Command, forms part of India’s Nuclear Command Authority (NCA,which is responsible for command and control decisions regarding India’s nuclear weapons programme).
- The SFC is incharge of handling the country’s nuclear arsenal, while the DRDO is responsible for developing weapons systems and related military technologies.
- It was created on 4th of January, 2003.
- It comprises personnel from the Indian Army, Navy and Air Force.
- The Commander-in-Chief (CinC), a 3-star General, is appointed on a rotational basis from the three services.
A few days after Meta unveiled its Llama 3 Large Language Model (LLM), Microsoft unveiled the latest version of its ‘lightweight’ AI model – the Phi-3-Mini.
Phi-3-Mini
- It is believed to be first among the three ‘small models’ that Microsoft is planning to release.
- Other Two Models : Phi-3-small (7B) and Phi-3-Medium will be available shortly.
- It has outperformed models of the same size and the next size up across a variety of benchmarks, in areas like language, reasoning, coding, and math.
- Variants : It is available in two variants, one with 4K context window, and another with 128K tokens.
- Theses model is instruction-tuned, which means that it is trained to follow the different types of instructions given by users.
- This also means that the model is ‘ready to use out-of-the-box’.
Potential uses :
- Providing summaries of long documents or trends within market research reports.
- Also, marketing and sales departments could use it to write product descriptions or social media posts.
- It could also underpin a customer chatbot to answer basic questions about products and services.
What are Language Models ?
- Language models are the backbone of AI applications like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, etc. These models are trained on existing data to solve common language problems such as text classification, answering questions, text generation, document summarisation, etc.
- Large Language Models(LLMs) : LLMs are large general-purpose language models that can be pre-trained and then fine-tuned for specific purposes.
- ‘Large’ in LLMs has two meanings — the enormous size of training data; and the parameter count.
- In the field of Machine Learning, where machines are equipped to learn things themselves without being instructed, parameters are the memories and knowledge that a machine has learned during its model training.
- They define the skill of the model in solving a specific problem.
- Small Language Models(SLMs) : SLMs are more streamlined versions of large language models.
- When compared to LLMs, smaller AI models are also cost-effective to develop and operate, and
- They perform better on smaller devices like laptops and smartphones.
- SLMs are great for resource-constrained environments including on-device and offline inference scenarios.










 General Studies
General Studies