- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
Dec 26, 2021
INDIAN ARMY LAUNCHES INDIGENOUS MESSAGING APPLICATION CALLED ASIGMA
Recently, Indian Army has launched Indian Army launches in-house messaging application named, ASIGMA (Army Secure IndiGenous Messaging Application).

 The Karnataka Right to Freedom of Religion Bill, 2021
The Karnataka Right to Freedom of Religion Bill, 2021
 Abhyas:
Abhyas:
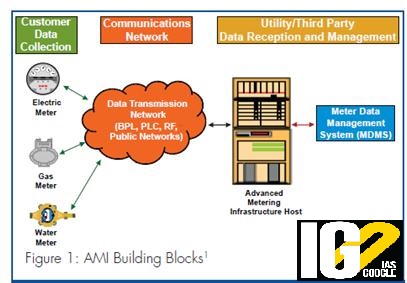 Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
 What are three forms of hunger?
What are three forms of hunger?
 Highlights
Highlights
 Need of the scheme:
Need of the scheme:
 What is bottom trawling?
What is bottom trawling?

- It is a new generation web-based application.
- It is a replacement of Army Wide Area Network (AWAN) messaging application which has been in service for past 15 years.
- It is developed by team of officers of the Corps of Signals of the Army.
- It will meet real time data transfer and messaging requirements of the Army in the backdrop of current geo political security environment.
- It has multi-level security, message
- prioritisation and tracking, dynamic global address book.
 The Karnataka Right to Freedom of Religion Bill, 2021
The Karnataka Right to Freedom of Religion Bill, 2021
- It prohibits conversion from one religion to another by misrepresentation, force, fraud, allurement or marriage.
- However, it provides an exemption for those who reconvert to his immediate previous religion.
- Reconversion shall not be deemed to be a conversion under this Act.
- Family members or any other person who is related to the individual, who is getting converted, can file complaint regarding conversion.
- Punishment:
- Conversion from general category, a jail term of three to five years and a fine of Rs 25,000 has been proposed for those violating the law.
- Conversion from SC/St category, a jail term of three to 10 years and a fine of Rs 50,000.
- Double punishment for repeat offence.
- Compensation: It envisages payment of Rs 5 lakh (on court orders) to victims of conversion by the persons attempting the conversion.
- The offence of conversion has been deemed to be a cognizable and non-bailable, that can be tried in a magistrate’s court under the proposed law.
- Marriages conducted with the intention of conversion can be declared null and void by a family court or a jurisdictional court.
- Any person intending to convert to another religion after the law comes into force will have to notify the district magistrate two months in advance.
- The person who is carrying out the conversion must provide one-month notice to district magistrate.
- District magistrate must conduct an enquiry through the police on the real purpose of the conversion.
- Not informing the authorities will result in a prison term of six months to three years for persons who convert, and a term of one to five years for those carrying out conversions.
- The person who gets converted to inform the district magistrate of the conversion within 30 days, and he/she must appear before the district magistrate to confirm their identity.
- Not informing the district magistrate will lead to the conversion being declared null and void.
- It violates the constitutional guarantee of equality because making religious conversions the sole ground for terming the marriage as void.
- It violates article 15 which mandates that the state shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them.
- Article 25 of the Constitution of India guarantees the freedom to profess, propagate, and practice religion, and allows all religious sections to manage their own affairs in matters of religion; subject to public order, morality, and health. Thus, it is in contrast with Article 25.
 Abhyas:
Abhyas:
- It is an Indigenously developed High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT).
- It is an unmanned aerial target system, operated from the ground. It will be used in future tests and practices of aerial weapons.
- It has a gas turbine engine to sustain a long endurance flight at subsonic speed.
- It is in the development stage.
- The loan money will be used for the implementation of smart meters & Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI).
 Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- AMI is a complex system or infrastructure of technologies that connect different technological networks for making a two-way communication network.
- It includes technological networks like Customer Information Systems (CIS), Geographical Information Systems (GIS), Outage Management Systems (OMS), Work Management (WMS), Mobile Workforce Management (MWM) etc.
- System Reliability: Effective monitoring will minimize power outages, making the system more reliable.
- Energy Costs: Easy monitoring will reduce costs and wastages in long term.
- Electricity theft will be reduced.
- Apart from electricity, AMI can be used in other fields like gas and water distribution and billing infrastructure.
- High cost.
- Technological integration and management.
- Interoperability and standardization.
 What are three forms of hunger?
What are three forms of hunger?
- Under Nutrition:
- Insufficient intake of basic foods requirement, causing undernourishment.
- Insufficient Macronutrients.
- Malnutrition:
- Insufficient intake of essential quality vitamins and minerals.
- Micronutrient deficiencies.
- Over Nutrition:
- Intake of excess food causes overnutrition, resulting in Obesity.
- Poverty is the leading economic factor behind it. Poverty causes other co-related problems like ‘Food Deserts’ and ‘Poverty Trap’.
- Food Deserts are the areas where people have limited access to a variety of healthful foods.
- Poor people often live in aggregated poor neighborhoods where merchants have weak incentives to offer higher-cost nutritious products. This creates ‘food deserts.
- The poverty trap or Poverty cycle makes a poor to remain poor for generations.
- It is a self-enforcing mechanism, where due to the unaffordability of good food and quality standard of leaving, a poor could not escape poverty.
- Food Deserts are the areas where people have limited access to a variety of healthful foods.
- Increasing income of people by economic growth and development.
- Social sector schemes by the government distribute quality food.
- Reducing chemical fertilizers used in agriculture.
- De-agrarianizing food production and doing vertical farming for nutritious foods.
- When people abandon agriculture, it is referred to as de-agrarianizing.
- Vertical farming is a method of Off-farm agriculture that focuses on growing crops in vertically stacked layers.
- Aim: To provide safe, reliable, affordable and environment friendly public Mass Rapid Transit System for Agra city.
- It will improve mobility for planned urban development in Agra.
- The project will also enhance economic productivity of the city and catalyze job creation.
- EIB is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States.
- It focuses on the areas of climate, environment, small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs), development, cohesion and infrastructure.
 Highlights
Highlights
- It is a protocol of waste management for garbage free cities.
- Aim- To give effect to the vision of creating “Garbage Free Cities” (GFC) under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0.
- A total of 299 cities have been certified–
- 9 cities rated as 5-star,
- 143 cities rated as 3-star
- 147 cities as 1-star
- The earlier 25 components/ indicators have now been reduced to 24,
- Only 16 indicators are mandatory for 1-star and 3-star levels.
- The remaining 8 indicators will be relevant for 5-star and 7-star aspirants.
- Multi-step calculation of the previous GFC protocol has now been changed to a single step
- Higher weightages (50%) allotted to Door-to-Door Collection, Source Segregation, Waste processing & Dumpsite remediation;
- The entire process of applying for certification and subsequent assessment have been simplified and made completely digital.
- Capacity building, revenue from sale of waste by-products have been added to strengthen the waste management system.
- Continuous assessment has been introduced to help cities plan assessment.
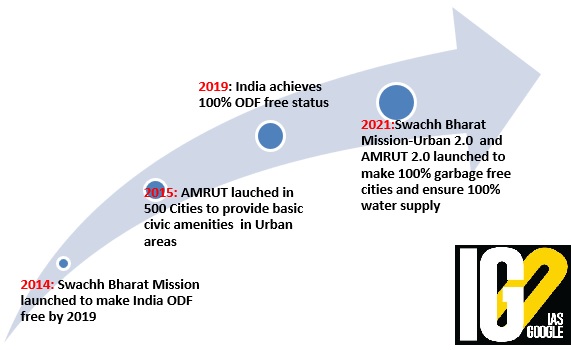
- Swachh Bharat Mission is a nation-wide campaign in India.
- Launched- 2014
- Phase 1of the mission lasted till October 2019. Phase 2 has been implemented between 2020–21 and 2024-25.
- Objectives-
- Eliminating open defecation through the construction of household-owned and community-owned toilets.
- Establishing an accountable mechanism of monitoring toilet use.
- 4,324 Urban local bodies have been declared Open Defecation Free through the construction of more than 66 lakhs individual household toilets and over 6 lakhs community/public toilets.
- Digital enablement's such as Swachhata App has introduced by MoHUA in 2016.
- It is the digital grievance redressal platform
- Swachh Survekshan, the world’s largest urban cleanliness survey covering over 4,000 Urban Local Bodies was initiated under SBM-Urban in 2016.
- Launched- 2021
- Nodal Ministry- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
- Implementation year-2021 to 2026
- To tap other aspects under the Swachh Bharat mission including safe containment, transportation, disposal of fecal sludge, and septage from toilets.
- All wastewater will be treated properly before it is discharged into water bodies, and the government is trying to make maximum reuse a priority.
- It also focuses on source segregation of garbage, reduction in single-use plastic.
- To ensure complete access to sanitation facilities.
- All statutory towns will become (open-defecation free) ODF+ certified.
- All statutory towns with less than 1 lakh population will become ODF++ certified (focus on toilets with sludge and septage management).
- 50% of all statutory towns with less than 1 lakh population will become Water+ certified.
- All statutory towns will be at least 3-star Garbage Free rated as per Star Rating Protocol for Garbage Free cities.
- Remediation of all legacy dumpsites.
- All the 25 High Courts of India have different usage of the phrases to identify different cases.
- This creates ambiguity in the interpretation leading to delayed justice.
- Different High Courts follow different procedures in matters pertaining to virtual courts, started during the pandemic.
- Court fees differ for the same type of cases in different States.
 Need of the scheme:
Need of the scheme:
- National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) have been involved in certification of Process and Products
- NDDB has been awarding Quality Mark to the dairy plants of cooperatives.
- BIS has a product certification scheme for manufacturers, including dairy product processors allowing licensees to use ISI Mark on their products.
- However, there was no unification of product and process certification- making it difficult to dairy plants to avail end to end certification.
- Further the consumer awareness was also lacking towards quality of milk and products.
- Milk and milk products are perishable nature and has short shelf-life, increasing the difficulty for conformity assessment.
- With the initiative of the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairy, Conformity Assessment Scheme was unveiled by BIS with the help of NDDB.
- It is a first of its kind certification scheme for milk and milk product.
- It has brought ‘Product–Food Safety Management System–Process’ certification under one umbrella with a unified logo featuring the earlier respective logos BIS-ISI mark & NDDB-Quality Mark and Kamdhenu Cow.
- Government of India has notified various products for compulsory compliance to Indian Standards through Quality Control Orders (QCOs);
- These are: Public interest, protection of human, animal or plant health, safety of the environment, prevention of unfair trade practices, national security etc.
- Simplify the certification process.
- Create an instantly recognizable logo for public to be reassured about dairy product quality.
- Increase the sales of milk and milk products in organized sector and in turn enhancing income of farmers.
- Develop a quality culture in the dairy sector.
- Monetary policy refers to the policy of the central bank with regard to the use of monetary instruments under its control to achieve the goals specified in the Act.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI)is vested with the responsibility of conducting monetary policy.
- This responsibility is explicitly mandated under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- It is the (fixed) interest rate at which the Reserve Bank provides overnight liquidity to banks against the collateral of government and other approved securities under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF).
- It is the (fixed) interest rate at which the Reserve Bank absorbs liquidity, on an overnight basis, from banks against the collateral of eligible government securities under the LAF.
- It is a facility that allows banks to borrow money through repurchase agreements (repos) or to make loans to the RBI through reverse repo agreements.
- The LAF consists of overnight as well as term repo auctions.
- Aim of term repo: To help develop the inter-bank term money market, which in turn can set market-based benchmarks for pricing of loans and deposits, and hence improve transmission of monetary policy.
- RBI also conducts variable interest rate reverse repo auctions, as necessitated under the market conditions.
- It is a facility under which scheduled commercial banks can borrow additional amount of overnight money from the Reserve Bank by dipping into their Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) portfolio up to a limit at a penal rate of interest.
- This provides a safety valve against unanticipated liquidity shocks to the banking system.
- The MSF rate and reverse repo rate determine the corridor for the daily movement in the weighted average call money rate.
- It is the rate at which the Reserve Bank is ready to buy or rediscount bills of exchange or other commercial papers.
- The Bank Rate is published in Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- This rate has been aligned to the MSF rate and, therefore, changes automatically as and when the MSF rate changes alongside policy repo rate changes.
- It is the average daily balance that a bank is required to maintain with the Reserve Bank as a share of such per cent of its Net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) that the Reserve Bank may notify from time to time.
- It is the share of NDTL that a bank is required to maintain in safe and liquid assets, such as, unencumbered government securities, cash and gold.
- Changes in SLR often influence the availability of resources in the banking system for lending to the private sector.
- These include both, outright purchase and sale of government securities, for injection and absorption of durable liquidity, respectively.
- Surplus liquidity of a more enduring nature arising from large capital inflows is absorbed through sale of short-dated government securities and treasury bills.
- The cash so mobilised is held in a separate government account with the Reserve Bank.
- Financial inclusion is the process of extending the reach of formal banking services and products to the unbanked population in the country.
- Financial inclusion appeared to be the lowest in rural, agriculture-dependent areas where food was the main source of income.
- Financial inclusion leads to preference shifts from cash to interest-bearing bank deposits and other financial assets.
- Financial inclusion is expected to expand the access to bank credit, which is interest sensitive and affected by changes in the policy rate.
- Hence financial inclusion enhances the potency of interest-rate based monetary policy by causing an increasing number of people to become responsive to interest rate cycles.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) to gauge the accessibility of banking and financial services and products and the usage and quality of such facilities to Indian population.
- The index rose from 49.9 in March 2019, to 53.1 in March 2020, and further to 53.9 in March 2021.
 What is bottom trawling?
What is bottom trawling?
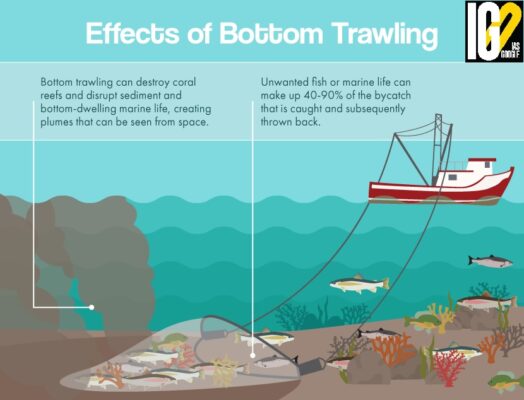
- It is a method of fishing that involves dragging heavy weighted nets across the sea floor, in an effort to catch fish.
- It is a favoured method by commercial fishing companies as it can catch large quantities of product in one go.
- It drags the large, weighted nets across the seafloor, everything that happens to be in the way gets swept up in the net too.
- In addition to the turtles, juvenile fish and invertebrates, deep sea corals are also get swept up in trawling nets.
- Trawlers targets seamounts because they are known hot spots for fish and other marine life.
- Coral forests, often found on seamounts, act as nurseries for juvenile fish and other invertebrates.
- It changes the flow of nutrients and carbon through the food web and alter geomorphological landscapes.
- How: Bottom trawling can both resuspend and bury biologically recyclable organic material.
- Example: Resuspension of nutrient solids like phosphorus can result in oxygen deficient dead zones.
- The boats should be designed in such a way that fishermen get access to the deeper parts of the ocean and fish species.
- A knowledge can be given to fishermen for the construction of tuna long liners with gill nets.
- Imposing a limit on the amount of sponge and coral individual vessels and the entire fleet can pull up as bycatch.
- A system to warn other trawling vessels of an area with high concentrations of coral or sponge can be used.
- A habitat review committee that will meet annually to ensure the measures are working, and potentially improve the fishery even further can be formed.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies