- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
JANUARY 15, 2026 Current Affairs
India’s Bioeconomy and India’s first state-funded BSL-4 lab for deadliest pathogens in Gujarat
- India’s bioeconomy touched billion in 2024, up from billion in 2014, as announced by Union Minister while inaugurating a BSL-4 biocontainment facility in Gujarat.
India’s Bioeconomy:
- India’s bioeconomy refers to the economic value generated from biotechnology, biopharma, agriculture biotech, bio-industrial products, bio-energy, and health sciences.
Key facts & data:
- India’s bioeconomy has achieved a remarkable 16-fold growth over the last decade, surging from billion in 2014 to billion by 2026.
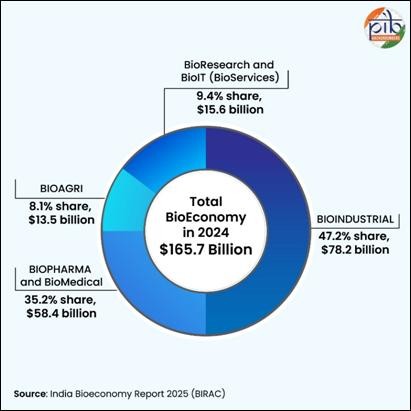
As of 2026, the market is distributed across four critical segments:
- Bio-Industrial (47%): The largest share, led by the Ethanol Blending Program which achieved its 20% (E20) target in 2025, five years ahead of schedule.
- Bio-Pharma (35%): India remains the “Pharmacy of the World” , supplying 65% of the WHO’s vaccine requirements.
- Bio-Research & IT (9%): The fastest-growing segment, fuelled by AI-driven drug discovery.
- Bio-Agri (8%): Cantered on climate-resilient crops and bio-fertilizers.
- The number of biotech start-ups has skyrocketed from 50 in 2014 to over 11,000 in 2026.
- In addition to the NIV in Pune, 2026 marks the operationalization of state-led BSL-4 Bio-Containment facilities (1st such as in Gujarat).
UGC’s new rules against caste discrimination
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has notified the Promotion of Equity in Higher Education Institutions Regulations, 2026 to curb caste-based discrimination on campuses.
UGC’s new rules against caste discrimination:
- The University Grants Commission (Promotion of Equity in Higher Education Institutions) Regulations, 2026 is a revised legal framework to prevent caste-based discrimination in universities and colleges across India. It updates and strengthens the earlier 2012 anti-discrimination regulations.
Key features:
- Expanded definition of caste-based discrimination: Discrimination now explicitly includes acts against SCs, STs and OBCs, correcting the exclusion of OBCs in the draft rules.
- Broad definition of discrimination: Covers unfair or biased treatment based on caste, tribe, religion, gender, disability, place of birth, and includes actions that harm human dignity or equality in education.
- Mandatory Equal Opportunity Centres (EOCs): Every higher education institution must set up an EOC to promote equity, inclusion and access for disadvantaged groups.
- Equity Committees in each institution: Headed by the institution’s chief, with mandatory representation of SCs, STs, OBCs, women and persons with disabilities, to handle complaints and monitor inclusion.
- Regular monitoring and reporting: EOCs must submit bi-annual reports, and equity committees must meet at least twice a year.
- Strong penalties for violations: Institutions violating the rules can be debarred from offering degrees or academic programmes, and may even lose recognition.
- National-level oversight: A UGC monitoring committee with professional councils will oversee compliance across the country.
Nipah Virus
- Two nurses in West Bengal have tested positive for the Nipah virus, with one in coma and another on ventilator support, triggering emergency contact tracing and isolation of over 120 people.
About Nipah Virus:
- Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus (animal-to-human) that can also spread between humans, causing illnesses ranging from mild fever to fatal encephalitis and severe respiratory disease.
Natural Host
- Primary reservoir: Fruit bats (Pteropus species – flying foxes)
- Intermediate hosts: Pigs, horses, goats, dogs (can infect humans)
- Human transmission:
- Contact with bat-contaminated food (e.g., fruits, date-palm sap)
- Contact with infected animals
- Human-to-human via respiratory droplets, body fluids, or close care
Symptoms
- Early symptoms: Fever, headache, muscle pain, sore throat, vomiting
- Progressive symptoms: Dizziness, drowsiness, confusion
Severe disease:
- Acute respiratory distress
- Encephalitis (brain inflammation)
- Seizures and coma within 24–48 hours
Key Features
- Case fatality rate: 40%–75% (very high)
- Incubation period: 4–14 days (can extend up to 45 days)
- WHO Priority Pathogen: Listed under WHO R&D Blueprint for urgent vaccine and drug research.
Treatment:
- No specific antiviral drug or vaccine available.
- Supportive care is the mainstay:
- Oxygen and ventilator support
- Intensive care for brain and lung complications
- Symptom-based management
- Early isolation, contact tracing, and infection control are critical to stop outbreaks.
US regional bases in the Middle East
- Iran has warned it will strike U.S. military bases in the Middle East if Washington intervenes in Iran’s internal unrest, after President Donald Trump publicly backed Iranian protesters.
US regional bases in the Middle East:
- The United States maintains a network of permanent and rotational military bases across the Middle East to secure oil routes, protect allies, counter terrorism, and deter Iran and other regional threats under the US Central Command (CENTCOM) framework.
Major US bases in the region
1. Bahrain – Fifth Fleet Headquarters
- Hosts the US Navy’s Fifth Fleet, which controls naval operations across the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, Arabian Sea and parts of the Indian Ocean, ensuring maritime security and oil flow.
2. Qatar – Al Udeid Air Base
- The largest US base in the Middle East, serving as CENTCOM’s forward headquarters with around 10,000 troops, coordinating air, missile defence and regional military operations.
3. Kuwait – Camp Arifjan & Ali Al Salem Air Base
- Camp Arifjan is the forward HQ of US Army Central, while Ali Al Salem is a key air logistics hub near the Iraq border, supporting deployments to Iraq and Syria.
4. United Arab Emirates – Al Dhafra Air Base & Jebel Ali Port
- Al Dhafra supports US air operations, surveillance and anti-ISIS missions; Jebel Ali is the US Navy’s busiest port in the Middle East, hosting aircraft carriers and warships.
5. Iraq – Ain Al Asad & Erbil Air Base
- Ain Al Asad supports Iraqi and NATO missions and was hit by Iranian missiles in 2020; Erbil is a key logistics, intelligence and training hub in northern Iraq.
6. Saudi Arabia – Prince Sultan Air Base
- Hosts US air defence systems such as Patriot and THAAD to protect the Kingdom and regional US assets from missile attacks.
7. Jordan – Muwaffaq al Salti Air Base
- Base of the US 332nd Air Expeditionary Wing, supporting air operations across Syria, Iraq and the Levant.
8. Turkey – Incirlik Air Base
- Jointly run by the US and Turkey, it hosts US nuclear weapons and supports NATO and anti-ISIS operations in West Asia.
Similipal National Park
- Similipal National Park in Odisha recorded a rise in its mugger crocodile population to 84 during the three-day census, reversing a declining trend seen in recent years.
Similipal National Park:
- Similipal is a National Park, Tiger Reserve and Biosphere Reserve forming part of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
- It is one of India’s most biodiverse protected landscapes and is part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves (since 2009).
Location:
- Located in Mayurbhanj district of northern Odisha, it lies in the Eastern Ghats and spreads over about 2,750 sq km, making it one of India’s largest tiger reserves.
Key geographical features:
- Similipal is a high-plateau forested massif with an average elevation of about 900 m.
- It contains prominent peaks such as Meghasani (1,158 m) and Khairiburu (1,178 m) and famous waterfalls like Barehipani (217 m) and Joranda (181 m).
- The landscape is drained by rivers such as Budhabalanga, Salandi, Deo and Khairi, which create ideal wetland habitats for crocodiles and other wildlife.
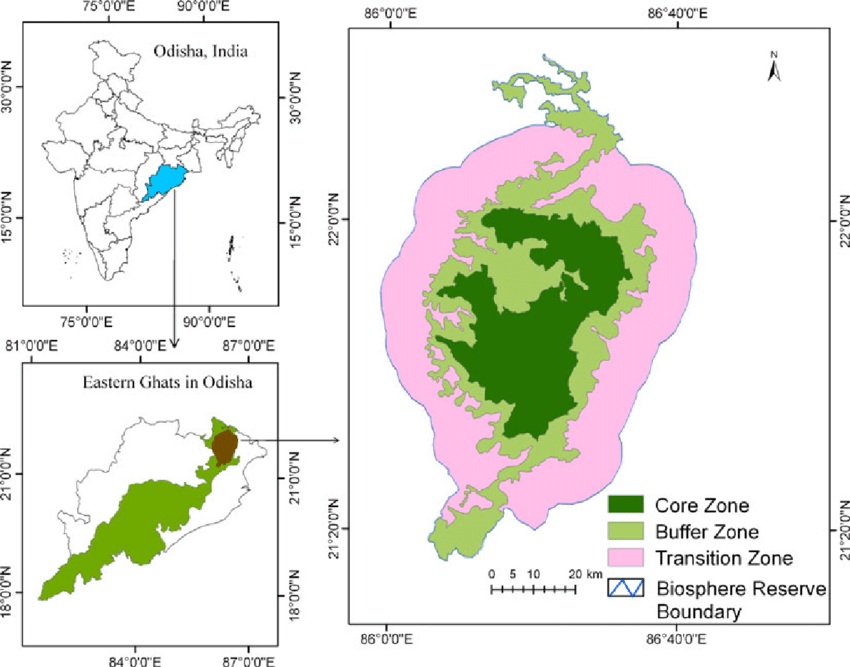
Crocodile census and conservation:
- The 2026 census counted 84 mugger crocodiles, up from 81 in 2025, with West Deo River alone hosting around 60 individuals.
- The recovery is attributed to the Ramtirtha Mugger Crocodile Breeding Centre, which releases hatchlings annually into Similipal’s rivers.
Malayalam Language Bill, 2025
- An inter-state debate between Kerala and Karnataka arose after the Kerala Legislative Assembly passed the Malayalam Language Bill, 2025.
- Language Transition: The Bill seeks to replace Kerala’s English-Malayalam bilingual system with Malayalam as the sole official language.
- Karnataka’s Opposition: Karnataka argues the Bill violates Articles 29 and 30, which protect linguistic minorities’ fundamental rights to preserve language and script.
The Malayalam Language Bill, 2025
- Official Status: Malayalam is designated as the exclusive official language for all state administrative and governmental purposes.
- School Language: The Bill mandates Malayalam as the compulsory first language in government and aided schools up to Class X.
- Legislative Drafting: All State Bills and Ordinances must be drafted and introduced in Malayalam.
- Judicial Language: Judicial orders and court proceedings, particularly in District and Sessions Courts, will be progressively translated into Malayalam.
- Digital Enablement: The IT Department will develop open-source software and AI tools that are natively functional in Malayalam.
- Public Signage: Government department signboards, advertisements, and public notices will prioritise Malayalam usage.
- Product Labelling: All products manufactured or sold in Kerala must carry directions and labels written in Malayalam.
Safeguards for Linguistic Minorities
- Minority Communication: In designated areas, Tamil, Kannada, Tulu, and Konkani speakers may communicate with the government in their mother tongues.
- Exam Exemptions: Non-Malayali and foreign students are exempt from Malayalam examinations in Classes 9, 10, and higher secondary levels.
- Student Choice: Students whose mother tongue is not Malayalam may choose other languages offered in the National Education Curriculum.
Criticisms of the Bill
- Border Access: Kannada- and Tamil-speaking residents in border districts like Kasaragod may face barriers to access government services and courts.
- Learning Burden: Declaring Malayalam as the compulsory first language may impose a cognitive load on students from minority communities.
- Drafting Process: The Bill’s drafting phase reportedly lacked adequate representation of district-level linguistic diversity.
Jobless Growth Risks
- ILO in its World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2026 report warned that global unemployment may remain low, but job quality is worsening, especially for youth and women.
Key Findings of the ILO Report
- Unemployment Flat: Global unemployment projected at 4.9%, affecting about 186 million people in 2026, staying similar till 2027.
- Jobs Gap High: Wider labour underutilisation (“jobs gap”) projected at 408 million, showing hidden distress beyond headline unemployment.
- Working Poor: Around 284 million workers still live in extreme poverty, earning below $3/day.
- Poverty Slowdown: Worker extreme poverty share fell only 3.1 percentage points (2015–25) to 7.9%, far slower than the 15 percentage points drop in the previous decade.
- Informality Rising: Informal employment is projected at 2.1 billion workers by 2026.
- Informality Shift: Global informality rate increased by 0.3 percentage points (2015–25), mainly due to higher employment share in Africa and Southern Asia.
Gender Concerns
- Low Participation: Women form only two-fifths of global employment, showing structural barriers.
- Labour Force Gap: Women are 24.2 percentage points less likely than men to be in the labour force.
- NEET Burden: Young women are 14.4 percentage points more likely than young men to be NEET (Not in Employment, Education or Training).
Youth Concerns
- Youth Unemployment: Global youth unemployment rose to 12.4% in 2025 from 12.3% in 2024, signalling weak entry-level job creation.
- Youth NEET Rise: Youth NEET share rose to 20.0% in 2025, up from 19.9% in 2024.
Emerging Drivers of Risk
- Trade Uncertainty: Rising trade uncertainty may cut returns to labour and reduce real wages for both skilled and unskilled workers.
- Income Loss Zones: Estimated wage/income losses could be up to 0.45% in South-Eastern Asia and up to 0.3% in Europe and Southern Asia due to trade-policy uncertainty shocks.
ILO Roadmap for Tackling Jobless Growth
- Decent Work Push: Align recovery policies with the ILO Decent Work Agenda to expand quality jobs, wages and protections to all sectors.
- Women Workforce Entry: Expand childcare, paid leave, and safe work norms to close labour force gaps; E.g., Nordic childcare systems that sustain high female participation.
- Minimum Income Floor: Protect the working poor through cash-support frameworks; E.g., the ILO Social Protection Floors Recommendation (2012) used by countries to ensure basic income security.
- Formalisation Drive: Expand formal work through ILO Recommendation 204 (Transition from Informal to Formal Economy, 2015) and universalised social protection.
Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2024
- Context (PIB): NITI Aayog released the 4th edition of the Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2024.
- It assesses export readiness across States and Union Territories, identifying structural gaps, growth drivers, and policy opportunities to enhance competitiveness.
- EPI 2024 is structured around four pillars—Export Infrastructure, Business Ecosystem, Policy and Governance, and Export Performance.
- These pillars are further divided into 13 sub-pillars and 70 indicators for a detailed assessment.
- New Metrics: The 2024 edition adds indicators for Macroeconomic Stability, Cost Competitiveness, Human Capital, Financial Access, and the MSME Ecosystem.
- Categories: States and UTs are grouped into Large States, Small States, North-Eastern States, and Union Territories; each category is classified as Leaders, Challengers, or Aspirers.
- District Focus: Districts have been highlighted as core units of competitiveness, translating national export goals into local strategies.
- Significance: EPI provides an evidence-based framework to support India’s USD 1 trillion in merchandise exports by 2030 and Viksit Bharat @2047.
Key Highlights
- Export Scale: India’s FY2023-24 exports hit a record ₹65 lakh crore, with global trade share rising from 1.7% to 1.8%, driven by IT and business services.
- Top Performer: Maharashtra ranked first among Large States, followed by Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
- Landlocked State: Uttar Pradesh emerged as the top performer, ranking fourth nationwide.
- Small States & UTs: Uttarakhand ranked first, followed by Jammu and Kashmir and Nagaland.
Warmest La Niña Year
- Berkeley Earth Annual Temperature Report 2025 reports that 2025 became the warmest La Niña year on record, despite La Niña’s usual cooling influence.
Key Findings of the Report
- High Global Anomaly: The global annual average temperature anomaly in 2025 reached +1.44°C, despite months of La Niña influence. It ranked as the 3rd warmest year globally.
- Record Heat Footprint: About 9.1% of Earth’s surface recorded its highest annual average temperature in 2025, showing widespread extreme heat conditions.
- Land Vs Ocean Extremes: Record warmth covered 10.6% of land areas and 8.3% of ocean areas, showing widespread heating across systems.
- Population Exposure: Around 770 million people (8.5% of the global population) experienced record warm annual temperatures, mainly across Asia.
- No Record Cold: The report noted no regions recorded a record cold year.
- Warmest-Year Streak: The last 11 years include all 11 warmest years in the instrumental record.
|
La Niña
|
Ultracold Atoms
- Ultracold atoms are enabling the world’s most precise atomic clocks and are emerging platforms for quantum simulation and quantum computing.
Ultracold Atoms
- Meaning: Atoms cooled to just a few billionths of a degree above absolute zero (absolute zero is minus 273.15 degrees Celsius).
- Quantum Behaviour: At such low temperatures, atoms behave like overlapping waves, so quantum effects become visible at a larger scale.
How They Are Made?
- Laser Cooling: Laser light is tuned slightly below an atomic transition so atoms absorb photons opposite to motion & slow down. Repeated absorption & re-emission works like a braking force, reducing speed.
- Nobel Link: Cooling and trapping atoms using laser light was recognised with the 1997 Nobel Prize in Physics. It laid the foundation of modern cold-atom physics.
- Deep Cooling: Laser cooling alone cannot reach the lowest temperatures, so hottest atoms are allowed to escape in a second step. The remaining atoms redistribute energy and cool further.
- Dark Spot Trap: A “dark spot” inside the light trap shelters the coldest atoms from stray light that causes heating. This prevents re-heating and helps reach absolute temperature.
Key Applications
- Atomic Clocks: Cold atoms improve time precision since atoms are nearly motionless, stabilising “tick”.
- Navigation Link: Atomic clocks are essential for GPS timing and internet synchronisation.
- Gravity Sensors: Cold-atom gravimeters can detect underground structures and monitor volcanoes.
78th Indian Army Day Parade Held Outside Cantonment
- The 78th Indian Army Day parade in Jaipur marked the first time the main event was held outside a military cantonment.
- Historic Venue: Traditionally, the parade was held at Cariappa Parade Ground in Delhi Cantonment until 2023, when it adopted a rotating city format.
- New Unit: The parade showcased the first public appearance of the newly raised Bhairav Battalion.
Indian Army Day
- Indian Army Day is observed annually on January 15 to honour the selfless service of soldiers.
- Command Transition: It marks the day when K. M. Cariappa was appointed the first Indian Commander-in-Chief of the Army in 1949.
- He succeeded Sir Francis Roy Bucher, the last British Commander-in-Chief of the Indian Army.
- Annual Theme: The theme for 2026 is “Year of Networking and Data Centricity.”
Global Risks Report 2026 by World Economic Forum
- The World Economic Forum released the Global Risks Report 2026 with the central theme “Age of Competition.”
- Global Warning: The report warns against “multipolarity without multilateralism,” where fragmentation and confrontation increasingly replace international cooperation.
- World Economic Forum releases the Global Risks Report annually to assess major threats to global stability over the short term (2 years) and the long term (10 years).
Key Findings of Global Risk Report 2026
- Short-Term Risks: Geoeconomic confrontation ranks first over the next two years, followed closely by misinformation and disinformation.
- Economic Weaponisation: The report identifies the “weaponisation of economic determinants” as a central driver of current global instability.
- Long-Term Risks: Extreme weather events remain the top ten-year risk, with biodiversity loss and ecosystem collapse following.
- AI Disruptions: Adverse outcomes of AI are the fastest-rising long-term risk, driven by labour displacement and autonomous warfare.
- Social Polarisation: Technological risks are increasingly intensifying political and social polarisation within countries.
India-Specific Findings
- Cyber Insecurity: Cyber insecurity is India’s most significant national risk, ahead of inequality and weak public services.
- Water Conflict: The Indus River Basin is flagged as a potential flashpoint for future water conflicts between India and Pakistan.
- Digital Success: India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is recognised as a global best practice in digital public infrastructure.
Henley Passport Index
- In the 2026 Henley Passport Index, the Indian passport rose five places to rank 80th globally, up from 85th in 2025.
- Indian passport holders can now travel to 55 destinations without a pre-approved visa.
- Singapore remains the world’s strongest passport, with access to 192 destinations, followed by Japan and South Korea in second place.
- The Index is published by Henley and Partners, ranking passports by the number of destinations accessible without a visa.
- The index relies on data from the International Air Transport Association (IATA), which maintains the world’s largest travel information database.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies