- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
July 19, 2024 Current Affairs
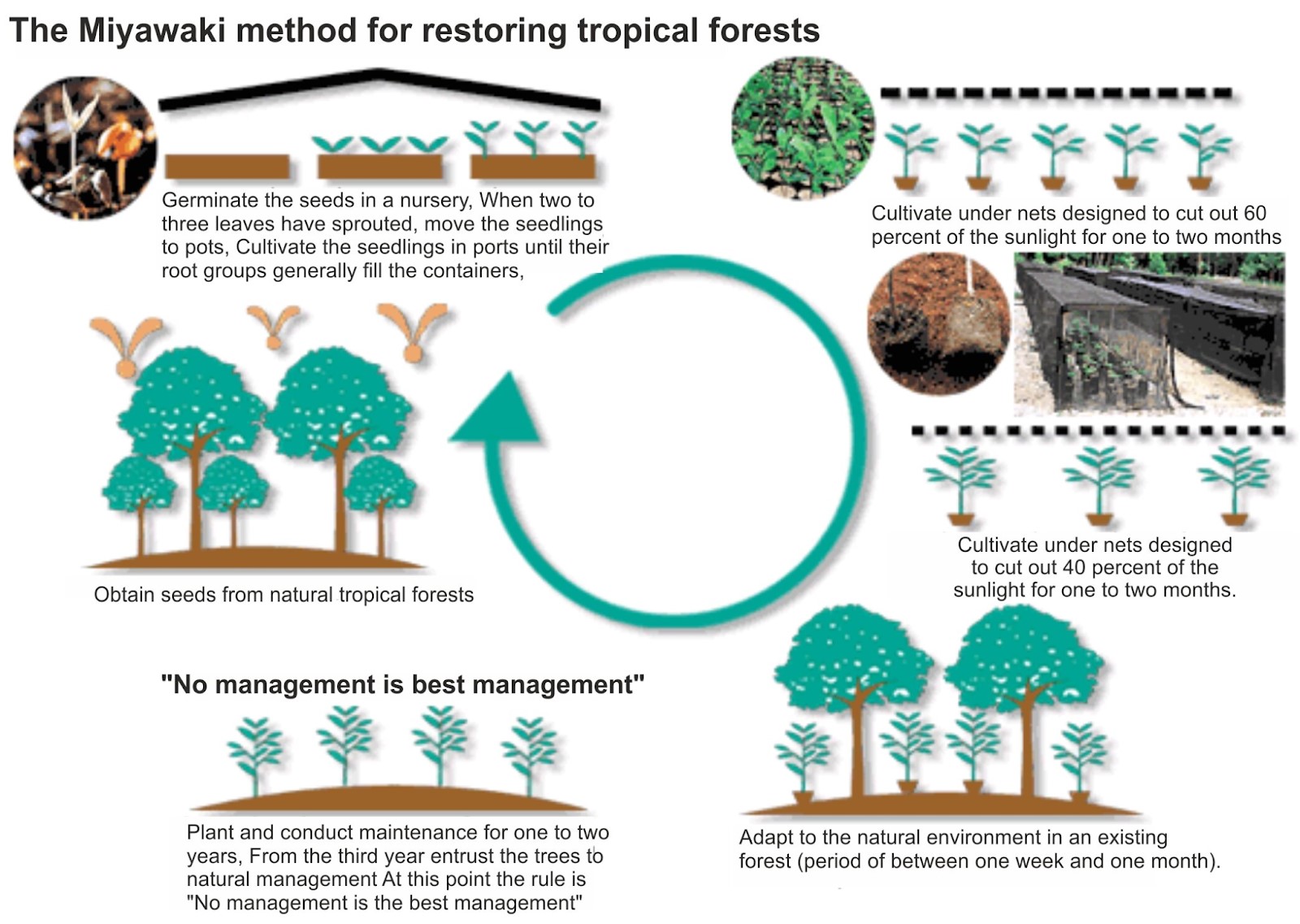
MIYAWAKI FOREST
- The methodology was developed in the 1970s, with the basic objective to densify green cover within a small parcel of land. The method involves creating dense, multi-layered forests that grow rapidly and mimic the natural biodiversity of native forests.
- This method involves planting two to four different types of indigenous trees within every square metre. The plants used in the Miyawaki method are mostly self-sustaining and don’t require regular maintenance like manuring and watering.
- In this method, the trees become self-sustaining and they grow to their full length within three years.
Benefits
- It helps in fighting the negative consequences of climate change.
- Help to reduce pollution levels in nearby areas by capturing dust and other particles.
- It increases the green cover of city enable residents to breathe fresh and pure air.
- It is a cost-effective method to grow tree and restore green cover in cities where finding space is a problem. For instance, in Mumbai, Delhi
- Promotion of indigenous variety of trees for instance Bel, Anjan, Arju, Neem, Peepal and Amala, etc.
- These forests can also sustain wildlife hence these urban forests encourage new bio diversity.
CROP RESIDUE MANAGEMENT
Crop residue are the agricultural waste that are left in the fields after the harvesting and threshing process. Stubbles, stalks, stover, husk, bran, bagasse and molasses are generally classified under the category of crop residue. These crop residues were once thought to be waste. But these are now regarded as an important natural resource.
In-situ Crop residue management
- Mulching is the practice of leaving crop residue on the soil surface to protect the soil from erosion and retain moisture. Mulching also helps to suppress weeds and provides nutrients to the soil.
- No-till farming involves planting crops without disturbing the soil. Crop residue is left on the soil surface, and seeds are planted through it. This method helps to conserve soil moisture and reduce soil erosion.
- Cover crops are planted in between cash crops to provide ground cover and add nutrients to the soil. Cover crops can also be left on the soil surface as a form of mulch.
- Crop rotation involves alternating the type of crops grown on a field each season. This method can help to reduce soil erosion and nutrient depletion while also improving soil health
Crop residue ex-situ management
- Biomass power generation: Crop residues can be used as a source of fuel for biomasspower generation. This method involves burning crop residues to produce electricity or heat.
- Animal feed: Crop residues can be used as a source of animal feed, particularly for livestock such as cattle, sheep, and goats. Crop residues can be baled and stored for use as animal feed during the dry season when forage is scarce.
- Composting: Crop residues can be composted to produce a nutrient-rich soil amendment. This method involves collecting the crop residues and mixing them with other organic materials such as manure, leaves, and grass clippings. The compost can then be used to improve soil fertility and structure.
- Biochar production:Biochar is a type of charcoal that is produced by heating crop residues in the absence of oxygen. Biochar can be used as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility, water retention, and crop productivity.
- Industrial uses: Crop residues can be used in various industrial processes, such as the production of paper, textiles, and building materials.
OVER 800 ELEPHANTS DIED IN KERALA IN 8 YEARS
The Asian elephant’s scientific name is Elephas maximus. It is the largest living terrestrial animal in Asia. Due to a population drop of at least 50% over the previous three generations of elephants, or roughly 60–75 years, the Asian elephant has been categorized as Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 1986. Its main threats are habitat loss, habitat degradation, habitat fragmentation, and poaching.
- There are three subspecies of Asian elephants: Indian, Sumatran, and Sri Lankan. India has more than 60% population of Asian elephants.
- India has the largest number of wild Asian elephants, estimated at 29,964 according to the 2017 census by Project Elephant. It is about 60% of the species’ global population.
- Karnataka has the highest number of elephants, followed by Assam and Kerala.
Conservation Status:
IUCN Red List of threatened species:
- African Forest Elephant (Loxodonta Cyclotis)- Critically Endangered
- African Savanna Elephant (Loxodonta Africana)- Endangered
- Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus)- Endangered
Initiatives in India for Elephant Conservation
1. Addressing Elephant-Human Conflict:
- Establishment of over 40 elephant corridors and 88 wildlife crossings to reduce conflicts.
- Creation of buffer zones around protected areas covering more than 17,000 sq. km.
2. Project Elephant:
- Launched in 1992, covering 23 states across India.
- Improved the status of wild elephants, with a population increase from about 25,000 in 1992 to around 30,000 in 2021.
3. Elephant Reserves:
- Establishment of 33 Elephant reserves covering approximately 80,777 Sq.km.
- These reserves play a crucial role in safeguarding wild elephant populations and their habitats.
Leader of the Opposition
The leader of the largest opposition party having not less than one-tenth seats of the total strength of the Lok Sabha is recognised as the leader of the Opposition. The ‘Leader of Opposition’ is responsible for leading the Opposition party’s efforts to critique and scrutinize the government, offering alternative policies, and ensuring a robust debate on legislative matters.
Role of Leader of Opposition in India
- To provide an alternative government i.e. being ready to form an alternative government.
- It is pretty much this role that made Ivor Jennings describe the Leader of Opposition as the ‘Alternative Prime Minister’.
- To act as a bridge and facilitate communication between the government and opposition, striving for consensus on critical issues.
- To maintain the checks and balances in the parliamentary system and ensure robust democratic discourse.
- To uphold democratic principles by ensuring robust debate, defending minority rights, and promoting democratic norms.
Status of Leader of Opposition in India
- The office of the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha was accorded statutory recognition in 1977 under the Salary and Allowances of Leaders of Opposition in Parliament Act, 1977.
- The rank of the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha is equivalent to that of a Cabinet Minister. Hence, they are also entitled to a salary, allowances, and other facilities similar to that of a Cabinet Minister.
Late Blight Disease
The Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI) has issued an advisory for potato farmers, warning of a high risk of late blight disease in the crop due to changing weather conditions.
- Late blight disease, is a fungal infection caused by Phytophthora infestans.
- The primary host is potato, but infestansalso can infect other solanaceous plants, including tomatoes, petunias and hairy nightshade.
- It poses a significant threat to potato crops. This disease can lead to substantial yield losses and diminish the quality of tubers.
- Cool, moist weather conditions are highly favourable for the spread of late blight.
Symptoms:
- When plants have become infected, lesions(round or irregularly shaped areas that range in colour from dark green to purplish black and resemble frost injury) appear on the leaves, petioles, and stems.
- A whitish growthof spore-producing structures may appear at the margin of the lesions on the under-leaf surfaces.
- Potato tubers develop rot up to 15 mm (0.6 inch) deep.
- Secondary fungi and Bacteria(particularly Erwinia species) often invade potato tubers and produce rotting that results in great losses during storage, transit, and marketing.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies