- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
June 16, 2024 Current Affairs
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Programme
- Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) informed that it is all set to carry out the third and final RLV Landing Experiment (RLV LEX) under the Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Programme.
- RLV-LEX missions involve taking an unmanned winged prototype, christened Pushpak, to a designated height and releasing it to land safely under varying conditions.
- The configuration of RLV-TD is similar to that of an aircraft and combines the complexity ofboth launch vehicles and aircraft.
- The winged RLV-TD has been configured to act as a flying test bed to evaluate various technologies, namely, hypersonic flight, autonomous landing, and powered cruise flight.
- In the future, this vehicle aims to be scaled up to become thefirst stage of India’s reusable two-stage orbital launch vehicle.
|
Third and Final RLV LEX |
Significance of the Experiment
- It marked a significant milestone in ISRO’s journey towards achieving low-cost access to space. The successful execution of the landing experiment demonstrated ISRO’s capability to develop a reusable launch vehicle, which is expected to significantly reduce the cost of launching satellites into orbit.
- The RLV-TD programmeis a testament to ISRO’s commitment to innovation and technological advancement. With the successful completion of this landing experiment, ISRO has moved one step closer to realising its vision of developing a fully reusable launch vehicle.
- After the successful completion of the RLV-LEX series, ISRO plans to proceed with the next stage of tests under the RLV-TD Programme, involving an unmanned Orbital Re-entry Vehicle (ORV)that is 1.6 times the size of ‘Pushpak’ used in the LEX missions.
- The ORV will be placed in a 400-kilometre orbit around Earth using a modified Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV)
|
Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Technology |
Longitude Prize on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- Recently, PA-100 AST System(a high-tech, transformative, rapid, point-of-care test for Urinary Tract Infections) has won the Longitude Prize on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
PA-100 Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST) System
- It is an automated analyserthat combines phase contrast microscopy and nanofluidics to make available antibiograms, for the first time, at the point of care.
- It relies on nanofluidics to perform rapid AST, and uses the most advanced phenotypic diagnostic performance possible.
- Cell growth is monitored in real time using contrast phase microscopy.
- Resistant bacteria keep a higher growth rate during incubation, while susceptible ones grow slowly or lyse.
- It provides targeted antibiotic treatmentin less than one hour, reducing the risk of AMR.
- It has been evaluated with the most common uropathogenic bacterial speciesin uncomplicated UTI:
- Gram negative: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Proteus mirabilis;
- Gram positive:Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecalis;

|
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) |
Truenat Platform
- Recently, the Truenat platformhas been hailed for its role in combating TB at the 77th World Health Assembly in Geneva, a decision-making body of WHO.
- It was developed by Goa-based Molbio Diagnostics, is a ground-breaking innovation in thefield of molecular diagnostics.
- Truenat is a real-time quantitative micro-PCR system.
- It is a portable, battery-operated machinethat can be deployed at labs, health centres, and even in the field that can test for over 40 diseases, including Covid-19, HCV, HBV, HIV, HPV, dengue, malaria, influenza, herpes, typhoid, and TB.
Game-Changer in TB Diagnostics
- The platform provides a rapid molecular test for the diagnosis of pulmonary, extrapulmonary, and rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis.The Global Fund, which collaborates with the WHO to build stronger health systems across the globe, appreciated India’s commitment to eliminating TB by creating mass awareness, and intensive monitoring programmes using digital technologies.
|
Tuberculosis in India |
25th anniversary of Kargil war victory
- As part of the 25th year celebration of Kargil war victoryover Pakistan, a team of the Indian Army has embarked on a pan-India motorcycle expedition from Dhanuskhodi (Tamil Nadu) to Dras (UT of Ladakh).
Kargil War
- The Kargil War, fought from May to July 1999in the Kargil region and elsewhere along the Line of Control (LoC), was a testament to the resilience and bravery of the Indian armed forces.
- It commenced shortly after the signing of the Lahore declaration in 1999,when the Pakistan Army surreptitiously occupied the winter-vacated posts of the Indian Army.
- The conflict was triggered by the infiltration of Pakistani troops — disguised as Kashmiri militants — into strategic positions on the Indian side of the LoC.
- The Indian Army, later supported by the Indian Air Force, recaptured a majority of the positions on the Indian side of the LoC.
Operation Vijay
- In India, the conflict is also referred to as Operation Vijay,which was the codename of the Indian military operation in the region.
- The Indian Air Force acted jointly with the Indian Army to flush out the Pakistan Army and paramilitary troops from vacated Indian positions along the LoC.
- It was a unique display of bravery, resolve, and commitment under inhospitable conditions of terrain and weather.
Aftermath
- The war came to an end on 26 July 1999, marking a significant victory for India.
- Ever since the victory in Operation Vijay, 26 July is celebrated as the ‘Kargil Vijay Diwas’every year.
GST Council
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council is likely to consider a review of 28% tax on online gaming.
GST Council
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council is a constitutional body established under Article 279A of the Indian Constitution through the 101st Amendment Act of 2016.
- The Union Finance Minister is the Chairperson of the GST Council.
- The GST Council makes recommendations to the Union and the States on key GST-related issues, including:
- Taxes, cesses, and surcharges to be subsumed under GST
- Goods and services to be subject to or exempt from GST
- Model GST laws, principles of levy, and apportionment of IGST
- Tax rates, thresholds, special provisions, and any other matter relating to GST
- Dispute resolution: The Council also serves as a platform to resolve disputes between the Centre and the States or among the States themselves on GST-related matters.
- The Centre has one-third of the total voting power, while the States collectively have two-thirds.
- A recent Supreme Court ruling has clarified that the recommendations of the GST Council are not binding on either Parliament or state legislatures.
Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND)
- The Financial Intelligence Unit has fined Axis Bank for “failing” to put in place a mechanism to detect and report suspicious transactions in the name of counter-terrorist commando force NSG.
FIU-IND
- Established in 2004 under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- An independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC)headed by the Finance Minister.
- Responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing, and disseminating information related to suspect financial transactions.
- Plays a pivotal role in India’s anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) efforts.
- Works closely with various domestic and international agencies to combat financial crimes.
Greater Adjutant Stork

- The greater adjutant stork also known as ‘Garuda’, one of the most endangered bird species, is facing severe threats due to rapid urbanization in Assam.
- The Greater Adjutant Stork is also known as the “Hargila” in Assam, India.
- They are known for their ability to soar high in the sky for long periods.
Scientific Name: Leptoptilos dubius
Genus: Part of the stork family, Ciconiidae, which includes about 20 species of large, long-necked birds.
Habitat: Historically found across southern Asia and mainland Southeast Asia.
- Now mainly confined to small regions, primarily in Assam, India.
- There are three known breeding sites: one in Cambodia and two in India (Assam and Bihar).
- In Assam, they inhabit the Brahmaputra valley, especially in Guwahati, Morigaon, and Nagaon districts.
- In Bihar, a smaller population is found around Bhagalpur.
Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List:Endangered
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972:Schedule IV
Diet:
- Primarily carnivorous.
- Feeds on fish, frogs, snakes, other reptiles, eels, birds, offal, and carrion.
- Exhibits scavenging behavior similar to vultures.
Significance:
- Regarded as the mount of Vishnu, a major deity in Hinduism. Revered by some as “Garuda Maharaj” (Lord Garuda) or “Guru Garuda” (Great Teacher Garuda).
- Assists farmers by killing rats and other farm pests.
Conservation:
- Several conservation organizations are working to protect the Greater Adjutant Stork, including the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) and the Assam Forest Department.
- Efforts include habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and community education initiatives.
Mercy Petition
- President Droupadi has turned down the mercy petition of a terrorist who was sentenced to death in the December 2000 Red Fort attack.
- Article 72: Grants the President of India the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites, or remissions of punishment, or to suspend, remit or commute the sentence of any person convicted of any offense.
- In all cases where the punishment or sentence is by a Court Martial.
- In all cases where the punishment or sentence is for an offence against any law relating to a matter to which the executive power of the Union extends.
- In all cases where the sentence is a sentence of death.
- Article 161: Provides similar powers to the Governor of a state.
- There is no time limit given in these two Articles for Mercy Plea.
- These Articles have no binding effect on the President and the Governors of the states to accept all the Mercy Petitions.
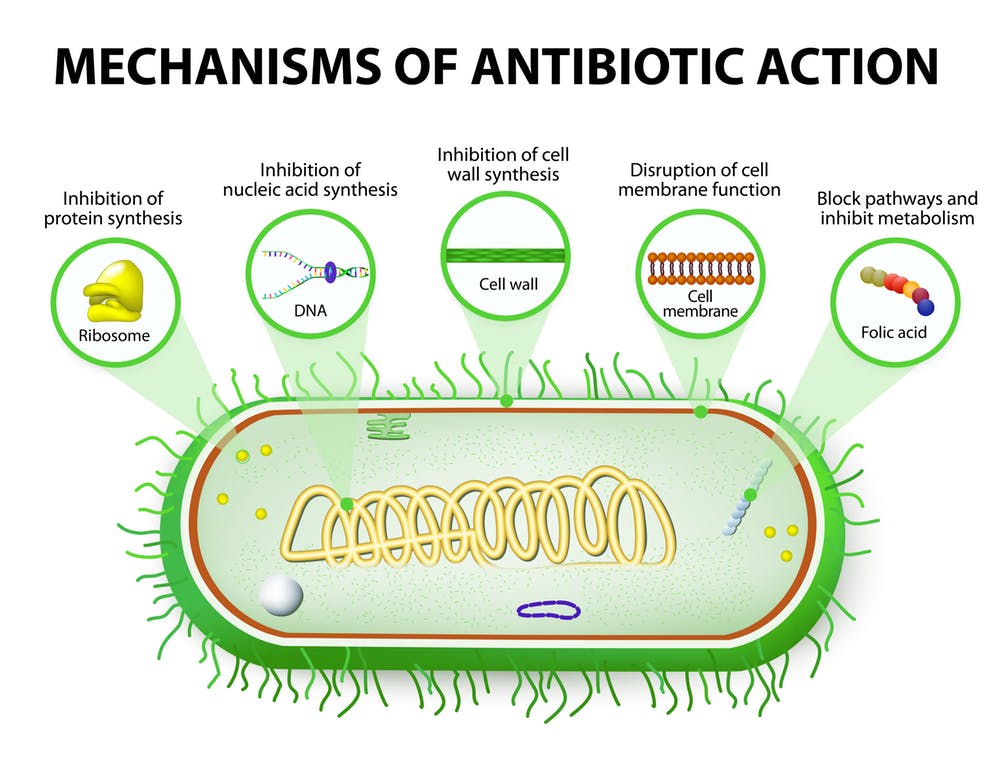
Enterobacter bugandensis
- A recent study by IIT Madras and NASA discovered a dangerous bacteria called Enterobacter bugandensison the International Space Station (ISS).
- This bacteria is known for causing hard-to-treat infections in hospitals. In the unique conditions of space, like zero gravity and increased radiation, the bacteria changed and became even more difficult to treat with antibiotics.

Multidrug-resistant organisms
- Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) are bacteria that have developed resistance to multiple antibiotics, making them difficult to treat. These bacteria are often called “superbugs” because they can cause infections that are easy to spread and hard to cure.









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies