- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
May 27, 2024 Current Affairs
Earlier in May 2024, a team of researchers at Banaras Hindu University (BHU) had conducted a one-year follow-up study on Covaxin vaccine.
- The Covaxin vaccine was developed by the Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) to fight against coronavirus.
- The participants were interviewed over phone about long-term adverse events of special interest (AESI) after one year of vaccination.
- The study found nearly one third of the individuals who received Covaxin were reported to have faced AESI.
- These include viral upper respiratory tract infections, menstrual abnormalities and Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
ICMR:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is the premier national agency in India for the formulation, coordination, and promotion of biomedical research.
- The ICMR was originally established in 1911 by the name of the Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA). It was redesignated as the ICMR in 1949.
- Objective: To conduct and support research that addresses the health challenges faced by the Indian population.
- Funding and Support: The organization provides funding and support for research projects undertaken by various institutions, including universities, medical colleges, and research laboratories across India.
- Ethics and Standards: ICMR sets ethical standards for conducting medical research, ensuring that studies are carried out in a responsible and ethical manner.
ICMR’s Response to the BHU’s Study:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has distanced itself from the Banaras Hindu University (BHU) researchers.
- The ICMR said that the BHU’s study was poorly designed with critical flaws.
- The ICMR said the body has not provided any financial or technical support for the research.
Covaxin:
- Covaxin is India''s indigenous COVID-19 vaccine developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) - National Institute of Virology (NIV).
- The vaccine is developed using Whole-Virion Inactivated Vero Cell derived platform technology.
- It is an “inactivated” vaccine that uses the dead virus.
- It is incapable of infecting people but still able to instruct the immune system to mount a defensive reaction against an infection.
- It is a 2-dose vaccination regimen.
- It is a vaccine with no sub-zero storage and is stable at 2-8 ℃.
- The efficacy against COVID-19 disease is shown to be 81%.
- It has proven to neutralize the variants – Alpha, Gamma, Zeta, Kappa, Beta and Delta.
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS):
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare disorder where the body’s immune system damages nerve. The damage to the nerves causes muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis. While its cause is not fully understood, the syndrome often follows infection with a virus or bacteria.
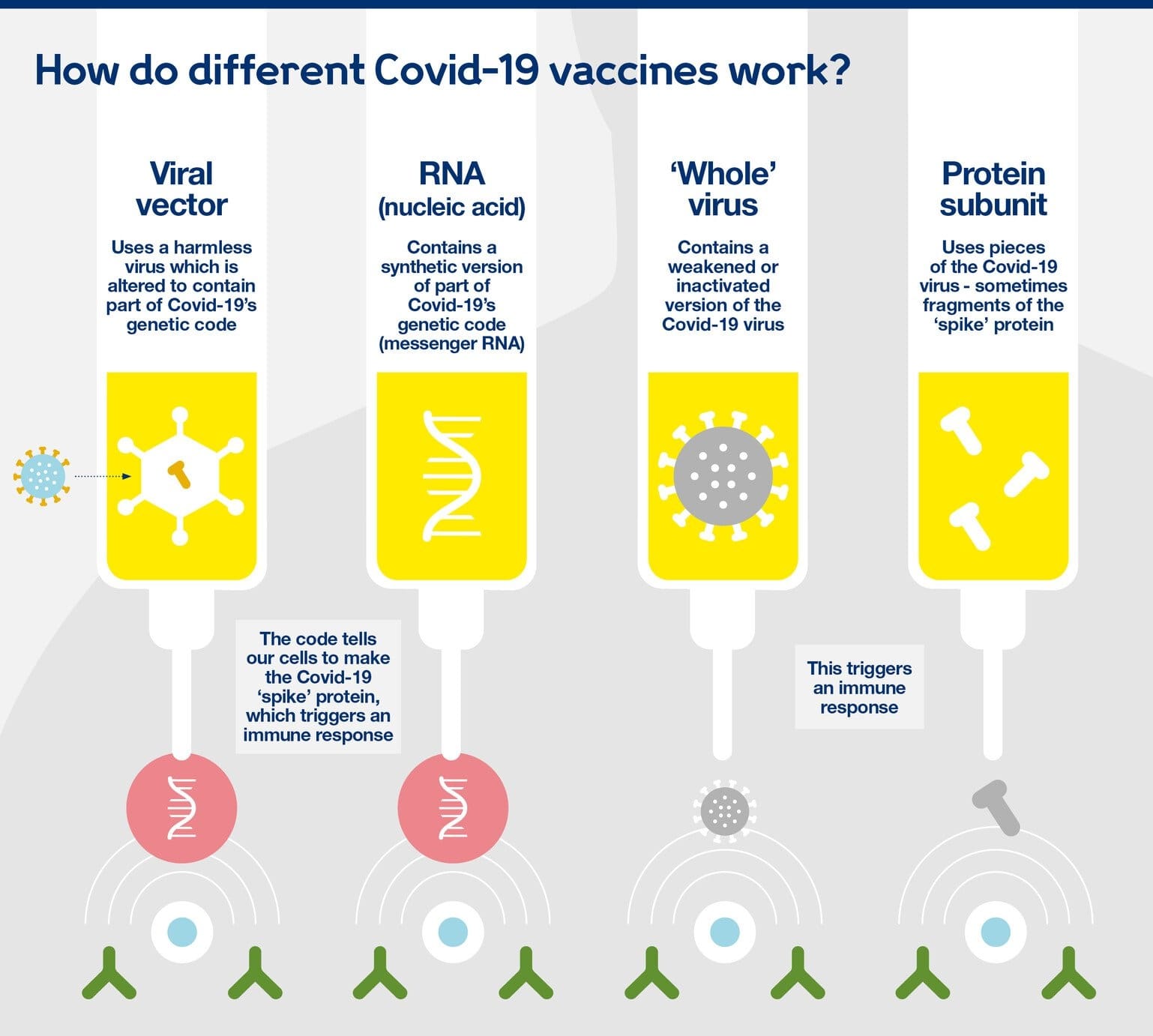
What are the stages of testing vaccines?
Vaccines are meant to follow a testing process of four stages
- Pre-Clinical- In this phase medical professionals use cell or tissue culture systems and animal testing to determine whether the candidate vaccine will produce immunity.
- Clinical Development- Now, a sponsor, usually a private company, applies for approval of the vaccine.
Once the proposal has been approved, the candidate vaccine needs to three trial stages of human testing.
- Phase I- A small group of people is injected with this candidate vaccine to determine how safe it is and to learn more about the responses it provokes among test subjects.
- Phase II- A group of more than hundreds of human test subjects are injected to determine more information about immunogenicity, safety, dose size, and immunization schedule.
- Phase III- In this phase, more than thousands of human test subjects are injected to determine rare side effects which sometimes don’t appear in smaller groups.
- Regulatory review and approval- Once a vaccine passes all the phases, the vaccine developer submits a license application to the regulatory authority.
- Quality control- The firm has to continue monitoring the use of its vaccine on patients and submit post-marketing surveillance details, which checks for any long-term unintended adverse effects.
SKAMPI, a prototype telescope of the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO), has achieved its first light.
Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO):
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organization with member states and partners from five continents.
- The organization is headquartered in the United Kingdom.
Member Countries:
- It currently has 9 member countries: Australia, China, Italy, Netherlands, Portugal, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, and the UK.
- Prospective members in the process of joining include Canada, France, Germany, India, Japan, South Korea, and Sweden.
Construction and Locations:
- SKAO plans to construct the world''s largest radio telescope with facilities in South Africa and Australia.
- In South Africa, 197 mid-frequency antennas will form the SKA-Mid telescope.
- In Western Australia, 1.31 lakh low-frequency antennas will form the SKA-Low telescope.
- Both sites are situated in radio-quiet zones to avoid interference.
Technology and Capabilities:
- The SKAO aims to use interferometry, connecting numerous smaller antennas via optical fiber networks to function as a single vast virtual telescope.
- SKAO will be the most powerful radio telescope, capable of observing up to 3,000 trillion km into the universe.
Science Goals and Functions:
- SKAO’s main science objectives include studying the evolution of the universe, tracking gravitational waves, and examining cosmic magnetism.
- It will enable detailed studies of galaxies and stars, test theories of gravity, and more.
Prototypes and Testing:
- The SKAMPI prototype in South Africa captured images at 2.5GHz wavelength, revealing characteristic radio emissions from the Milky Way and external galaxies like Centaurus A.
- This prototype aims to refine the design of the SKA-Mid dishes and has delivered high-quality data during its testing phase.
- The first antenna of the SKA-Low was installed in March 2024 in Western Australia.
- Contributions and Development
- Over ten countries are involved in this multi-billion-dollar project, including key players like Canada, China, Germany, France, and India.
- India has committed to contribute Rs. 1,250 crore to the project.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have developed a pioneering zero-emission cement production method.
Zero-Emission Cement:
- Zero-emission cement refers to cement produced using methods that eliminate greenhouse gas emissions throughout the production process, primarily by recycling materials and utilizing renewable energy-powered technologies.
- Cement production is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, responsible for about 8% of total emissions.
- Traditional cement production involves creating "clinker," which requires heating limestone and other raw materials to 1450°C. This process contributes 90% of the cement''s carbon footprint.
- The conventional method includes superheating limestone in kilns, typically powered by burning fossil fuels, and the limestone itself releases significant CO2 when heated.
- The new method repurposes cement paste from demolished buildings and employs an electric arc furnace—traditionally used in steel recycling—to produce clinker.
- This innovative approach modifies the steel recycling process to create cement without the high carbon emissions associated with traditional methods.
- If these electric furnaces are powered by renewable energy, the production process could achieve zero emissions.
- This breakthrough could significantly impact the cement industry by providing a low-cost, low-emission cement production method at scale, marking a substantial shift towards achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
- According to Allwood, this method offers a "big bright hope" for reducing concrete''s substantial environmental impact. It surpasses the emissions of entire nations like China and the United States except for their outputs.
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) is addressing a case regarding high-tension electrical lines being laid through the eco-sensitive zone of Mrugavani National Park.
Mrugavani National Park:
- It is situated in Chilkur, Moinabad Mandal, Hyderabad, Telangana.
- It was declared a National Park in 1994.
- Area: The park covers an area of 3.6 square kilometers (1211 acres).
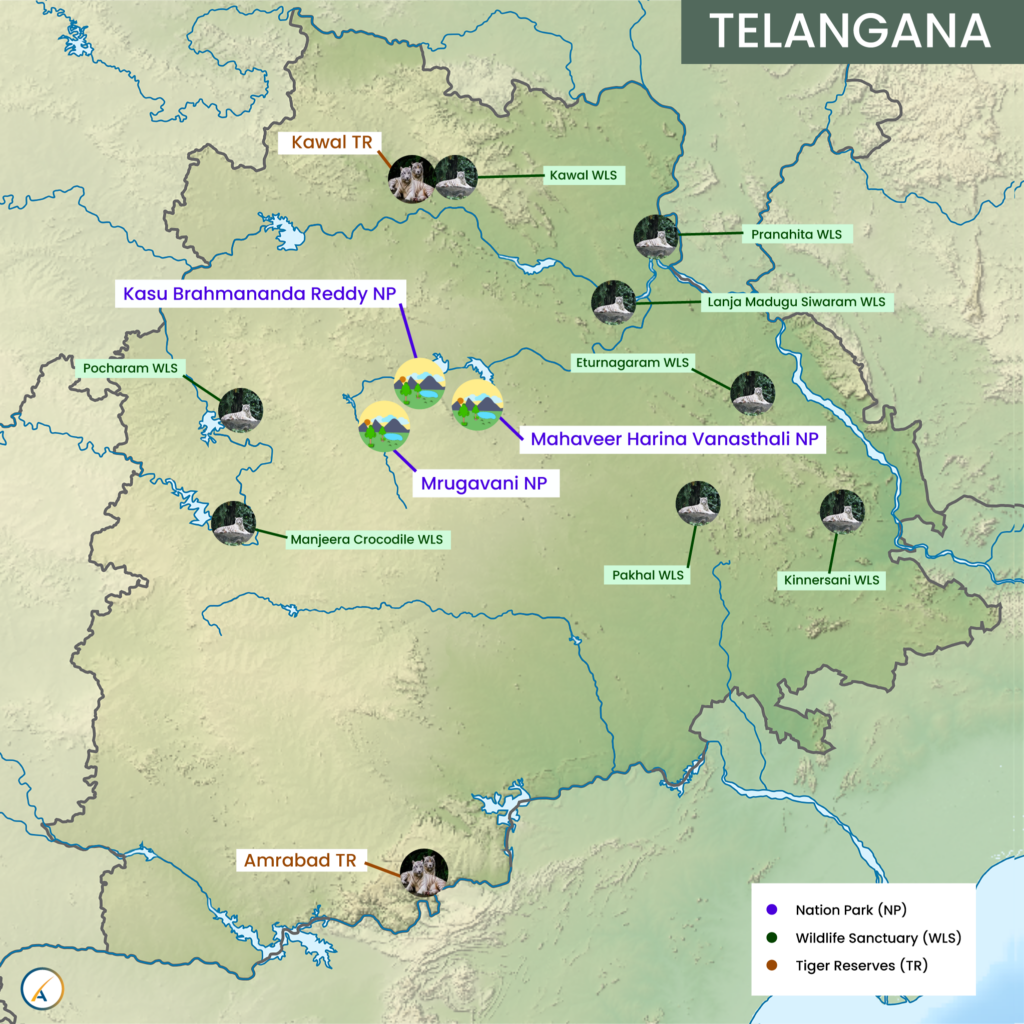
Vegetation:
- Characterized as tropical dry deciduous forest, it includes a variety of plant life forms such as bryophytes, pteridophytes, herbs, shrubs, climbers, and trees.
- The dominant flora includes teak, bamboo, sandalwood, Picus, Palas, and Rela.
Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, hosting about 350 spotted deer, and other animals like Indian hare, forest cat, civet, Indian rat snake, Russell’s viper, cheetal, wild boar, jungle cat, mongoose, monitor lizard, python, and king cobra.
- The park also supports over 100 bird species including warblers, peacocks, lapwings, and flowerpeckers.
Conservation Issues: It was recently reported to NGT that the park''s area has been reduced by 80 hectares on paper, which impacts the integrity of its eco-sensitive zone.
Recently Meme Coins are Garnering considerable popularity within the cryptocurrency realm.
- The term “meme coin” originated with Dogecoin, conceived as a playful response to the Doge meme featuring a Shiba Inu dog.
Memecoins:
- Meme coins, also known as ‘memetic tokens’ or ‘community coins’, are digital currencies created as a form of satire or humorous tribute to the internet culture.
- They often feature quirky names, logos, and branding that reference popular memes, jokes, or internet phenomena.
- Presently, the market boasts over 300 different meme coins.
- For Example: Dogecoin (DOGE), Shiba Inu (SHIB), Retik Finance (RETIK).
Working of Meme Coins:
- Meme coins function similarly to traditional cryptocurrencies, leveraging blockchain technology to operate.
- They are commonly established on platforms like Ethereum and Solana, which facilitate their functionalities.
Advantages and disadvantages of Meme Coins:
Pros:
- Highly Volatility: Possibility of earning a profit if values rise
- Extensive or uncapped supply: Minimal values per token due to extensive supply.
- Exploring Blockchain Technology: An Engaging Approach to Understanding Cryptocurrency, Smart Contracts, and Platforms such as Ethereum and Solana.
- Straightforward creation process: Comparatively straightforward creation process when juxtaposed with traditional cryptocurrencies.
- Increase participation in Trading: Potential participation in an active investing and trading community
Cons:
- Lacks intrinsic value or unique utility: These coins are primarily driven by speculation and community engagement.
- High risk and volatility: Due to rapid price fluctuations it poses risks of High Volatility.
- Lack of Regulation: As it operates within a largely unregulated environment, heightening susceptibility to fraud and manipulation.
- Limited adoption: Compared to leading cryptocurrencies, thereby restricting practical applicability.
- Technologically complex for some users









 Latest News
Latest News
 General Studies
General Studies