- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 Latest News
Latest News
September 28, Current Affairs
Ministry of Tourism Launches Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi – A National Responsible Tourism Initiative
- Objective: To promote responsible tourism and enhance the tourist experience by training locals to act as ambassadors and storytellers of their destinations.
Vision and Goals
- Alignment with PM''s Vision: The initiative is rooted in the Prime Minister''s vision of using tourism for social inclusion, employment, and economic development.
- Focus on Local Engagement: Aims to create a welcoming environment for tourists through well-trained local individuals who can share stories and insights about their destinations.
Pilot Locations
The initiative was piloted in six tourist destinations:
- Orchha, Madhya Pradesh
- Gandikota, Andhra Pradesh
- Bodh Gaya, Bihar
- Aizawl, Mizoram
- Jodhpur, Rajasthan
- Sri Vijaya Puram, Andaman & Nicobar Islands
Training and Capacity Building
- Target Audience: Training was provided to a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Cab and auto drivers
- Railway, airport, and bus station staff
- Hotel and restaurant workers
- Homestay owners
- Tour guides and street vendors
- Local students and shopkeepers
- Training Content:
- Importance of tourism and hospitality
- General cleanliness and safety protocols
- Sustainable tourism practices
- Local history and hidden tourism gems
- Creation of unique tourism experiences (e.g., heritage walks, food tours).
Special Emphasis on Women and Youth
- Empowerment Through Training: A significant focus on training women and youth to foster new tourism products and experiences, enhancing their employability in the tourism sector.
- Innovative Products: Encouraging locals to develop experiences that reflect their culture and environment, such as:
- Food and cuisine experiences
- Cultural and nature treks
- Craft tours and homestays.
Digital Literacy and Marketing
- Incorporating Technology: Training also includes digital literacy to ensure that local experiences can be effectively marketed to a national and global audience.
Training Outcomes
- Participation: As of now, around 3,000 individuals have been trained in the pilot destinations.
- Community Engagement: Increased enthusiasm among locals to participate in tourism training programs, integrating them into the tourism ecosystem.
Future Plans and Recognition
- Expansion: The initiative will be launched across 50 additional tourist destinations.
- Recognition System: Introduction of dedicated badges for Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi to assure tourists of quality experiences when engaging with trained locals.
Significance of the Initiative
- Tourism Development: Supports sustainable tourism development and enhances local economies by creating job opportunities.
- Cultural Preservation: Empowers communities to preserve and share their cultural heritage.
- Positive Tourist Experience: Aims to ensure that every interaction between tourists and locals contributes to a memorable travel experience.
Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Sh. Nitin Gadkari to inaugurate Oxygen Bird Park (Amrit Mahotsav Park)
- Inauguration: Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways, Nitin Gadkari, will inaugurate the park along the Nagpur-Hyderabad National Highway-44.
- Location: Near Jamtha, Nagpur, Maharashtra.
- Area: The park spans 23 hectares, including 2.5 hectares designated for social forestry.
Key Features
- Eco-Initiative: Developed by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) as part of a broader effort to promote environmental sustainability along national highways.
- Natural Habitat: The park serves as a habitat for various bird species, contributing to biodiversity conservation.
- Recreational Space: Designed for both locals and tourists, the park provides a serene environment for recreation and relaxation.
- Sustainability Focus: The "Oxygen Park" feature emphasizes:
- Planting fast-growing, oxygen-producing trees.
- Reducing air pollution and promoting a healthier environment.
- Social Forestry: The Social Forestry Division of Nagpurplays a vital role in the development and maintenance of the park’s green spaces.
Financial Aspects
- Development Cost: The project has a budget of ₹14.31 crores.
- Approval Date: The initiative was formally approved in March 2023.
Significance
- Environmental Impact: The park contributes to ecological balance and air quality improvement.
- Community Engagement: It promotes awareness and engagement with nature among residents and visitors.
- Tourism Development: Enhances the recreational offerings along the busy Nagpur-Hyderabad route, potentially boosting local tourism.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission marks a Transformative Three-Year Journey towards enabling Digital Health
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance accessibility, efficiency, and transparency in India’s healthcare ecosystem.
Background
- National Health Policy (2017): Laid the groundwork for a wellness-centric approach and the integration of digital technologies in healthcare.
- National Health Stack (2018): Introduced components like unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019): Provided guidance for implementing the ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Each citizen receives a unique ID for managing and accessing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across various medical systems.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of health facilities, including public and private entities, such as hospitals and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Enables secure access and sharing of health records with informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Streamlines the discovery and delivery of health services, enhancing accessibility.
- National Health Claims Exchange (NHCX): Standardizes insurance payments and expedites claims processing.
- Data Privacy and Security: Upholds confidentiality and privacy, adhering to the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Facilitates secure data exchange among stakeholders, enhancing seamless healthcare delivery.
- Transparency: Promotes informed choices regarding health services and ensures pricing transparency.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration minimizes waiting times and reduces data entry errors, recording over 5 crore OPD tokens.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives introduced to encourage adoption of ABDM, with potential earnings of up to ₹4 crores.
- Microsites for Private Sector: Operationalized 106 microsites to assist private providers in ABDM adoption.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing public and private healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected facilitiesas of September 2024.
Achievements
- Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) created.
- More than 42 crore health records linked to ABHA.
- 236 private entities integrated into the ABDM ecosystem, including leading healthcare chains and institutions.
- More than 3 lakh facilities ABDM-enabled, with over 17,000 private facilities participating.
- Registered 3 lakh health facilitiesand 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals through the National Healthcare Providers Registry (NHPR).
Moving Towards Transformation
- Partnerships: Collaborations with organizations like IIT Kanpur for AI in healthcare and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences for digital health education.
- Training and Sensitization: Initiatives to educate stakeholders on digital health practices, including a WhatsApp Chatbot for training.
- Digital Health Standards: NABH launched its first edition of Digital Health Standards for HIS/EMR Systems to promote technology adoption.
- eSwasthya Dham Portal: Integrated with ABDM to benefit Char Dham Yatris.
Future Vision
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem where every citizen can access their health records via a unique ABHA ID. This infrastructure facilitates better healthcare delivery by:
- Reducing registration queues and streamlining appointments.
- Providing Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) for healthcare professionals to enhance decision-making and patient outcomes.
Directorate General of Quality Assurance celebrates its 68th Raising Day
- The 68th Raising Day marks a key milestone in DGQA’s mission to ensure the quality of defence armaments, stores, and equipment for the Indian Armed Forces.
Key Highlights
- Quality Standards: DGQA has played a crucial role in setting and enforcing stringent quality standards for equipment used by the Indian Army.
- Reorganization for Aatmanirbharta:
- The DGQA is undergoing a significant restructuring aimed at enhancing the Ease of Doing Business and achieving Aatmanirbharta (self-reliance) in defence.
- The new structure focuses on expediting quality assurance processes and trials while reducing layers of decision-making.
- Single Point Technical Support: The reorganization will enable a streamlined approach, providing single-point technical support for each equipment or weapon platform at all levels.
- Shift to Prevention-Based QA:
- Transitioning from a conventional inspection-based system to a prevention-focused quality assurance and risk mitigation framework.
- Emphasizing proactive measures to improve overall product quality.
- Adoption of Innovative Technologies: DGQA has implemented new QA methodologies and technologies to address emerging challenges in the defence sector.
- New Directorate for Testing and Evaluation:
- Establishment of a Directorate of Defence Testing and Evaluation Promotion to facilitate transparent allocation of proof ranges and testing facilities.
- Aimed at improving collaboration with the defence industry and ensuring efficient testing processes.
- Enhanced Engagement with Private Industry: Domestic private industries are now allowed to use DGQA''s testing facilities, which promotes the Ease of Doing Businessand supports local manufacturing efforts.
- Automation and Digitization: Standardized QA processes are being automated and digitized, enhancing efficiency and transparency in operations.
Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA):
- DGQA is an Inter-Service Organisation functioning under the Department of Defence Production in the Ministry of Defence.
- This organisation is more than a hundred years old and is responsible for second-party Quality Assurance (QA) of all defence stores and equipment, both imported as well as indigenous, for the Army, Navy (excluding Naval Armaments), and common user items for the Air Force procured from Private Sector, Public Sector Undertakings, and Ordnance Factories.
- DGQA approval implies that the products have been subjected to extensive testing, including simulations of extreme conditions.
- Apart from QA activities, the organisation is responsible for import substitutionand associates with DRDO in the development projects.
- It also ensures Documentation, Codification and Standardisation Actionfor minimizing the variety of components/equipment.
- The other servicesrendered are promotion of small-scale industries, post-procurement services,Defect Investigations and Technical Consultancy to the users, the Ministry and the production agencies.
Organisational Structure:
- DGQA Organisation is structured into eleven Technical Directorates, eachresponsible for a distinct range of equipment.
- The Technical Directoratesare structured in two tiers for functional purposes, comprising of Control lerates and Field Quality Assurance Establishments.
- In addition, there are Proof Establishments in Armament Discipline for carrying out proof of weapons and ammunition.
Union Textiles Minister Shri Giriraj Singh says roadmap set for textiles industry to grow to US$350 bn by 2030
- Union Minister Shri Giriraj Singh emphasized the significant progress made by the textiles sector in the first 100 days, outlining ambitious growth targets and various initiatives aimed at enhancing the industry''s contribution to the economy.
Key Projections and Goals
- Projected Industry Growth: The textiles industry is expected to reach US$350 billion by 2030, creating millions of job opportunities.
- Foundation for Future Success: The achievements over the past 100 days are foundational for meeting the 2030 targets, with a comprehensive focus on all aspects of the textiles value chain.
Major Initiatives and Achievements
- PM MITRA Park:
- Anticipated investment of ₹70,000 croreis expected to generate 21 lakh jobs.
- Aimed at establishing India as a global hub for textile manufacturing and exports, the parks will provide world-class industrial infrastructure.
- Bharat Tex Initiative:
- This platform is designed to attract foreign investment by promoting 4S: style, scale, skill, and sustainability.
- It positions India as a key player in the global textiles market.
- Design Importance: Emphasized the role of the National Institute of Fashion Technology in fostering innovation and design in the textiles sector.
- Technical Textiles Export Target: Set an export target of US$10 billion for technical textiles by 2030, recognizing their potential across various sectors.
- Support for Artisans: Engaged approximately 1 crore artisans in the handloom and handicraft sectors, with initiatives aimed at improving their livelihoods and market presence.
Initiatives Launched
- Skilling Program:
- The ‘Bunkar and Karigar Utthan Upskilling Programme’ was launched to enhance technical and soft skills among artisans and weavers.
- About 3,600 artisans and weavers benefited from this initiative, receiving certificates and toolkits to boost their competitiveness in the market.
- 10th National Handloom Day:
- Celebrated on August 7, 2024, with the Vice-President awarding the Sant Kabir Handloom Awards and National Handloom Awards to recognize excellence in the sector.
- Included various awareness programs, exhibitions, and campaigns to promote the significance of handloom weaving.
- Shilp Didi Mahotsav:
- Inaugurated on August 22, 2024, this marketing event was dedicated to the Shilp Didi Programme, focusing on empowering women artisans.
- Shilp Didis showcased their crafts at Dilli Haat, enhancing their marketing opportunities and e-commerce presence.
- Textile Gallery Inauguration:
- A new Textile Gallery was opened at the Crafts Museum on August 8, 2024, highlighting various Indian weaving techniques and innovations.
- Craft Tourism Village: Inaugurated in Prayagraj, this initiative supports traditional artisans, promoting sustainable livelihoods and improving their socio-economic status.
- Eri Sericulture Promotional Project: Launched in Gujarat on August 10, 2024, to encourage castor-growing farmers to adopt sericulture as an additional income source, expanding Eri culture in the region.
- Central Silk Board Platinum Jubilee Ceremony: Celebrated on September 20-21, 2024, this event highlighted the growth of the silk sector and introduced new technologies and partnerships to enhance the silk value chain.
- New Pricing Methodology for Jute: Announced on August 28, 2024, this new pricing strategy for jute sacking bags aims to provide better pricing to jute mills, benefiting around 4 lakh workers and 40 lakh farmer families.
- VisioNxt Initiative: Launched on September 5, 2024, this AI-driven fashion trend forecasting system supports industry professionals by providing insights into market trends and consumer preferences.
- Bharat Tex 2025: The Ministry unveiled the website and brochure for this global textile event, expecting participation from over 5,000 exhibitorsand 6,000 international buyers.
- International Conference on Technical Textiles: Held on September 6-7, 2024, to discuss the future of technical textiles, promote indigenous products, and explore new markets.
- Support for Startups in Technical Textiles: The Ministry approved 11 startup proposals under the GREAT initiative, providing grants for innovative projects in technical textiles.
- PM MITRA Park in Amravati: Laid the foundation for a 1000-acre PM MITRA Park in Maharashtra on September 20, 2024, aimed at attracting large-scale investments and fostering innovation within the textiles sector.
Union Health Ministry Releases Revised Operational Guidelines and Training Manual of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Key Highlights:
- Public Health Concern:
- NAFLD is recognized as a major non-communicable disease (NCD) in India, with prevalence rates ranging from 9% to 32% in the community.
- 1 to 3 out of 10 individuals may be affected by NAFLD, closely linked to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Government Initiative:
- The revised guidelines aim to enhance patient care and outcomes through evidence-based practices.
- India is the first country to integrate NAFLD into the National Programme for Prevention and Control of NCDs (2021).
- Comprehensive Framework:
- The guidelines and training modules are designed for healthcare workers at all levels, emphasizing early detection and management of NAFLD.
- A multidisciplinary approach is advocated, encouraging collaboration among various healthcare providers.
Focus Areas:
- Health promotion and lifestyle modification are critical for reducing NAFLD prevalence.
- The training module covers topics such as epidemiology, risk factors, screening, diagnosis, and treatment protocols.
- Capacity Building: The training module aims to equip healthcare professionals with necessary knowledge and skills to manage and prevent NAFLD effectively, particularly at the primary care level.
- Associated Risks: NCDs, including liver-related diseases, account for over 66% of deaths in India, with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, inactivity, and tobacco use contributing significantly.
- Expert Involvement: The initiative involves contributions from various experts and institutions including WHO, ILBS, and major medical colleges, reflecting a collaborative effortto address the rising burden of NAFLD in India.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
- It is the abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of secondary causes of fatty liver, such as harmful alcohol use, viral hepatitis.
- It is a serious health concern as it encompasses a spectrum of liver abnormalities, from a simple non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL, simple fatty liver disease) to more advanced ones like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis and even liver cancer.
- Steatohepatitisis characterized by inflammation of the liver with concurrent fat accumulation in the liver. Mere deposition of fat in the liver is termed steatosis.
- Cirrhosisis a complication of liver disease that involves loss of liver cells and irreversible scarring of the liver.
- NAFLD acts as an independent predictor of future risk of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetesand other metabolic syndromes like hypertension, abdominal obesity, dyslipidaemia, glucose intolerance.
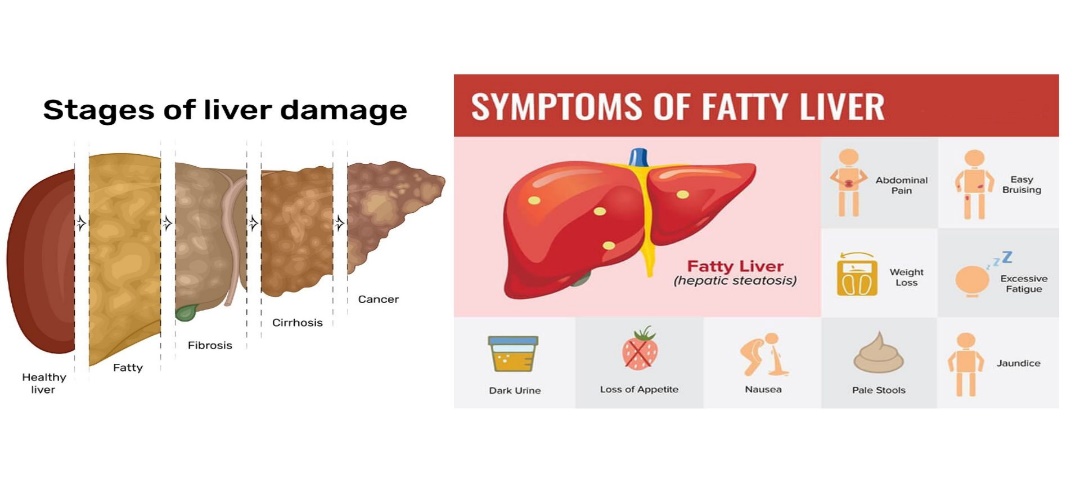
Treatment:
- There''s currently no specific medication for NAFLD.
- Doctors recommend weight loss to treat NAFLD.
- Weight loss can reduce fat, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver.
- Treatment may also be recommended for associated conditions(high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol) or complications.











 General Studies
General Studies