- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
01st Sep 2021
8TH MEETING OF AGRICULTURAL EXPERTS OF BIMSTEC COUNTRIES
Recently, India hosted the 8th Meeting of Agriculture Experts of Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Countries.
Highlights




- It highlighted the UN Food System Summit 2021 and the transformations that are happening in the agriculture and food systems globally.
- It exhorted to enhance the engagement and deepen the cooperation in agriculture and allied sectors amongst the BIMSTEC Member States by encouraging the exchange of knowledge, germplasm, students and experts.
- It emphasized addressing biosafety and biosecurity concerns and promoting digital agriculture along with the trade of technologies for developing resilient agriculture, food systems and value chains.
- The BIMSTEC Member States appreciated the greater engagement of India offering six slots of scholarships each for Master and PhD programmes in agriculture and its other initiatives for capacity development and training.
- It discussed cooperation in the areas of high impact transboundary diseases of livestock and poultry; aquatic animal diseases and bio-security in aquaculture and digitalization to promote precision farming.

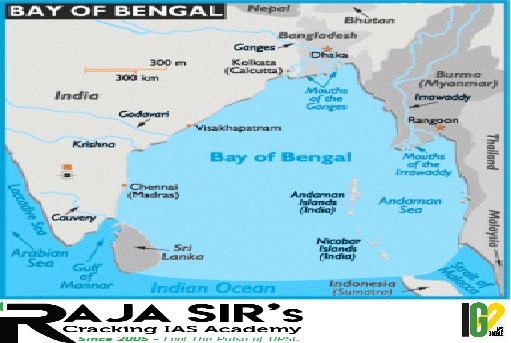
- It is a regional organization comprising seven Member States lying in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- It came into being in 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration and headquartered in Dhaka.
- It constitutes seven Member States: five deriving from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- Formally, the economic bloc was formed with four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- The regional group constitutes a bridge between South and South East Asia and represents reinforcement of relations among these countries.
- The BIMSTEC has also established a platform for intra-regional cooperation between SAARC and ASEAN members.
- The BIMSTEC region is home to around 1.5 billion people which constitute around 22% of the global population with a combined gross domestic product (GDP) of 2.7 trillion economy.
- Its objective is to harness shared and accelerated growth through mutual cooperation in different areas of common interests by mitigating the onslaught of globalization.
- The Bay of Bengal has grown in strategic significance within the Indo-Pacific, especially due to the contest between India and China.
- In 2016, India held a joint BRICS-BIMSTEC Summit in Goa for the latter’s regional outreach and after this, the support for BIMSTEC gained further momentum.
- An India-Myanmar-Thailand highway is one of the key projects that figures in a big way in theUN Food System Summit 2021(earlier Look East) policy.
- The groupings such as BIMSTEC can take forward the concept of regional cooperation in a different manner with the India-Pakistan bickering coming in way of a smooth functioning of the SAARC.
- It has come under scrutiny mainly due to dormancy in initial years and a stalled Free Trade Agreement (FTA) process.
- The lack of involvement of Malaysia, Singapore and Indonesia in BIMSTEC, even as dialogue partners has also been a point of contention.
- India aggressively pushed for the conclusion of a long-pending FTA among BIMSTEC nations but differences between India and Thailand over market access for professionals, duty cuts on traded goods and policy relaxation stalled the process.
- BIMSTEC has been slow on the come-up because unlike bodies like the EU or ASEAN, it is based on consensus-building which takes time.

- It is required to curb e-commerce entities’ dominant position in the market.
- There was increased incidence of the ban on misleading users by manipulating search results.
- The government also seeks to ban ‘flash sales’ on e-commerce platforms if such sales are organised by fraudulently intercepting the ordinary course of business using technological means.
- It is required to purify e-commerce landscape of the country which has been greatly vitiated by various e-commerce global companies.
- It proposed that every e-commerce entity which intends to operate in India must register itself with the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- The new draft proposed the appointment of chief compliance officer and resident grievance officer.
- The e-commerce entities are also required to provide information not later than 72 hours of the receipt of an order from a government agency for prevention, detection and investigation and prosecution of offences under any law.
- The government has proposed a ban on ‘mis-selling’ of goods and services offered on such platforms.
- The proposed amendment defines ‘flash sale’ as that organised by an e-commerce entity at significantly reduced prices, high discounts or any other such promotional offers for a predetermined period of time.
- The e-commerce entities should ensure that such registration number and invoice of orders are displayed prominently to their users in a clear and accessible manner on their platform.
- The E-commerce entities offering imported goods/services will also have to mention the name and details of the importers and the country of origin.
- It is claimed that the draft rules could go beyond consumer protection which could cause delays in the finalization of India’s consumer protection legislation for the growing E-commerce in the country.
- It is pointed out that matters such as competition, law enforcement, intermediary liability, and data protection did not fall under the Department of Consumer Affairs’ purview.
- Fallback Liability affects investor sentiments: The reason for such failure may be due to negligent conduct, omission or commission or any act done while fulfilling the duties and liabilities in the manner as prescribed by the marketplace e-commerce entity.
- Rules at variance with FDI Policy: As per Aayog, the proposed definition of e-commerce firms, including related parties, is in conflict with the term under the foreign direct investment (FDI) policy.
- Creates unequal playing field in the market: The draft rules propose registration of e-commerce entities that intend to operate in India, with the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- As per Aayog, these norms are not applicable to brick-and-mortar stores and will create a non-level playing field against a sector that has played a critical role during the pandemic.
- The combined Index of Eight Core Industries stood at 134.0 in July 2021, which increased by 9.4 per cent (provisional) as compared to the Index of July 2020.

- Coal –Coal production (weight: 10.33 per cent) increased by 18.7 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 10.5 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over corresponding period of the previous year.
- Crude Oil–Crude Oil production (weight: 8.98 per cent) declined by 3.2 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index declined by 3.4 per cent during April to July, 2021-22over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Natural Gas - Natural Gas production (weight: 6.88 per cent) increased by 18.9 per cent in July, 2021over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 21.0 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Petroleum Refinery Products–Petroleum Refinery production (weight: 28.04 per cent) increased by 6.7 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 13.1 per cent during April to July, 2021-22over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Fertilizers – Fertilizers production (weight: 2.63 per cent) increased by 0.5 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index decreased by 1.1 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Steel –Steel production (weight: 17.92 per cent) increased by 9.3 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 59.4 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Cement –Cement production (weight: 5.37 per cent) increased by 21.8 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 45.6 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over the corresponding period of previous year.
- Electricity –Electricity generation (weight: 19.85 per cent) increased by 9.0 per cent in July, 2021 over July, 2020.
- Its cumulative index increased by 14.6 per cent during April to July, 2021-22 over the corresponding period of previous year.
- It is an index of the eight most fundamental industrial sectors of the Indian economy and it maps the volume of production in these industries.
- It gives the details of eight sectors namely Coal, Natural Gas, Crude Oil, Refinery Products (such as Petrol and Diesel), Fertilisers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- The Refinery Products have the largest weight while Cement has the lowest weight.
- The eight industries are the essential “basic” and/or “intermediate” ingredient in the functioning of the broader economy.
- It measures combined and individual performance of production in selected eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- It comprises 40.27 percent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The mapping of health of eight core industries provides a fundamental understanding of the state of the economy.
- Dara Shikoh was born in Ajmer, the land of Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti, to whom, his father Shah Jahan had prayed for a son.
- Dara Shikoh, who was Mughal emperor Shah Jahan’s son and expected heir, was killed on the orders of his brother Aurangzeb in 1659 after losing the war of succession.
- At the age of twenty-five, Dara wrote his first book, Safinat-ul-Awliya, a concise document detailing the lives of the Prophet and his family, the Caliphs and of saints belonging to the five major Sufi orders then popular in India.
- Dara Shikoh is described as a “liberal Muslim” who tried to find commonalities between Hindu and Islamic traditions.
- Dara Shikoh, who had a deep understanding and knowledge of major religions, particularly Islam and Hinduism, is known as a pioneer of the academic movement for interfaith understanding in India.
- He strove to develop cordial relationships between people by finding commonalities between Hinduism and Islam and bringing their cultures into dialogue.
- His most important works, Majma-ul-Bahrain (Mingling of Two Oceans) and Sirr-i-Akbar (Great Mystery), are devoted to the cause of establishing connections between Hinduism and Islam.
- He not only discovered commonalities but even said that the foundation of the two religions is the same, which is the belief, “One Reality and One God”.
- Dara Shikoh acquired proficiency in Sanskrit and Persian, which enabled him to play a key role in popularising Indian culture and Hindu religious thought.
- He translated the Upanishads and other important sources of Hindu religion and spirituality from Sanskrit to Persian.
- He wrote ‘Risala-i-hak Numa’ (The Compass of the Truth), the ‘Shathiyat or Hasanat-ul-Arifin’ and the ‘Iksir-i-Azam’.
- He also commissioned the ‘Jug Bashist’ and the ‘Tarjuma-i-Akwal-i-Wasili’.

- The Indian Navy was represented by INS Tabar.
- It held off the Algerian coast and saw participation of a frontline Algerian warship, 'Ezzadjer'.
- It included diverse activities such as coordinated manoeuvring, communication procedures and steam past.
- It enabled the two navies to understand the concept of operations followed by each other.
- It provides enhanced interoperability and opened the possibility of increasing interaction and collaboration between them in future.
- The naval exercise with Algeria is very important for India as it is strategically located in the Maghreb region and is the largest country of Africa.
- India has been gradually increasing its engagements with the navies in the African continent through frequent naval deployments and port visits.
- An inclusive regional maritime security infrastructure has been set up with the participation of the island states which are strategically located and there are constant interactions at the operational level.
- A robust information sharing mechanism has been set up by India to monitor the activities in the IOR.
- An Indian- led initiative Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), is headquartered in Mauritius and has eight African members including the strategic island states like Madagascar and Comoros.
- The main aim of the Strategy is to foster increased wealth creation from Africa’s oceans and seas.
- It can be done by developing a sustainable thriving blue economy in an environmentally sustainable and secure manner.
- A secure maritime environment in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) is crucial for both India and African countries for securing national interests and achieving sustained national development.
- India has a vast coastline of 7,500 kilometers and an EEZ of two million square kilometers and it occupies a central position in the IOR, straddling the main international shipping lanes.
- Africa’s maritime environment is globally significant as huge amounts of international shipping activities pass through its seas.
- Around 90 percent of the continent’s trade is carried out by sea, thereby making the African Maritime Domain (AMD) crucial for commercial, security, environmental, and developmental reasons.
- It is a Talwar-class stealth Frigate built for the Indian Navy in Russia.
- It is equipped with a versatile range of weapons and sensors.
- It is a part of the Indian Navy's Western Fleet which is based in Mumbai under Western Naval Command.
- It was commissioned in 2004 in Kaliningrad, Russia.

- It is a pearly white or pale yellow-coloured cohesive mixture of honey and secretions from the hypopharyngeal and mandibular glands of worker honeybees.
- It contains moisture or water (60-70 per cent), lipids (1-10 per cent), minerals (0.8-3 per cent), proteins (9-18 per cent), sugar (7 per cent) and other elements.
- It is produced artificially by stimulating bee colonies to produce queen bee, grown outside its natural habitat.
- It needs to be stored in sub-zero temperatures immediately after production, during packaging and also at the consumer’s end.
- The perfect time to harvest royal jelly is when the maximum amount gets accumulated upon the larva turning 5 days old.
- The recommended temperature for fresh royal jelly is below –20 degrees Celsius.
- It meets the ISO-prescribed standards imposed by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) in 2019.
- The standards are laid down based on the concentration of moisture, sugars, protein and Hydroxy acids with 10 carbon atoms (10 HDA).
- The country-specific standards of royal jelly standards are available only in Switzerland, Bulgaria, Brazil and Uruguay whereas other countries are in the process of devising the same with the help of International Honey Commission.

- In the 1940s, the production techniques of royal jelly were first developed by Japan.
- At 600 metric tonnes/year, China tops the production charts and is followed by Taiwan (350 metric tonnes/year).
- Thailand and Italy are among the other top producers in the world.
- With over 400 metric tonnes/ year, Japan is the world’s largest importer followed by Germany, America and some other European nations.
- Delhi and north Indian markets mostly supply Chinese-manufactured royal jelly whereas markets in Mumbai have imports available from Thailand.
- Royal jelly is no medicine but a nutritious substance.
- An average healthy person needs to consume only about 500 mg (fresh) and 200mg (powder) in a day to get maximum health benefits.
- Royal jelly is known for its antioxidant properties.
- It cures damaged cells in the body and rejuvenates them and some cancer patients are advised consumption of royal jelly up to 10mgs.
- Its consumption is suggested to women for improving their fertility.
- It is found effective for women suffering from premenstrual and post-menopausal problems.
- Significance of Indian Royal Jelly meeting ILO standards%3









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies