- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
10th March 2021
Uighur Muslims
Recently, several hundred Uighur Muslim women in Turkey staged an International Women’s Day march against the extradition agreement of Turkey with China and demanding the closure of mass incarceration camps in China’s Xinjiang Province.
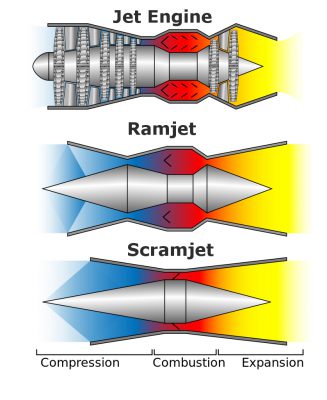 The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted the test of the Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology, which is crucial for the indigenous development of long range air-to-air missiles.
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted the test of the Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology, which is crucial for the indigenous development of long range air-to-air missiles.
 Overseas Citizen of India
Equine Herpes Virus Outbreak in Europe
Overseas Citizen of India
Equine Herpes Virus Outbreak in Europe
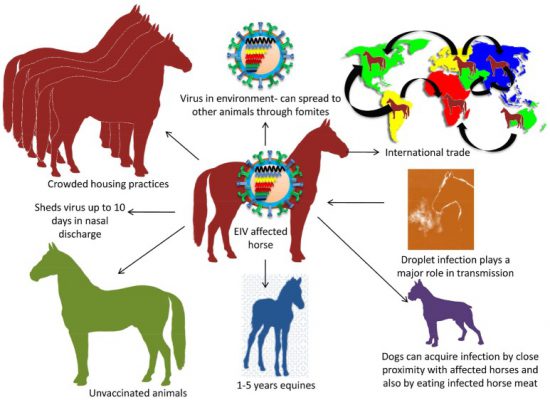 Recently, there has been an outbreak of Equine Herpes Virus (EHV-1) among horses in Europe.
Recently, there has been an outbreak of Equine Herpes Virus (EHV-1) among horses in Europe.

 The Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) celebrated the 3rd Janaushadhi Diwas (7th March 2021) to spread awareness about quality generic medicines, available at low prices.
The Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) celebrated the 3rd Janaushadhi Diwas (7th March 2021) to spread awareness about quality generic medicines, available at low prices.
- Earlier in 2020, the United States House of Representatives approved a legislation calling for sanctions on Chinese officials responsible for oppression of Uighur Muslims.
- Uighur Muslims:
- The Uighurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
- The Uighurs speak their own language, similar to Turkish, and see themselves as culturally and ethnically close to Central Asian nations.
- The Uighurs are considered to be one of the 55 officially recognized ethnic minority communities in China.
- However, China recognises the community only as a regional minority and rejects that they are an indigenous group.
- Currently, the largest population of the Uighur ethnic community lives in Xinjiang region of China.
- A significant population of Uighurs also lives in the neighbouring Central Asian countries such as Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
- Xinjiang is technically an autonomous region within China — its largest region, rich in minerals, and sharing borders with eight countries, including India, Pakistan, Russia and Afghanistan.
- The Uighurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
- Persecution of Uighurs:
- Over the past few decades, as economic prosperity has come to Xinjiang, it has brought with it in large numbers the majority Han Chinese, who have cornered the better jobs, and left the Uighurs feeling their livelihoods and identity were under threat.
- This led to sporadic violence, in 2009 culminating in a riot that killed 200 people, mostly Han Chinese, in the region’s capital Urumqi.
- Uighur Muslims for decades, under the false accusation by the Chinese government of terrorism and separatism,have suffered from abuses including persecution, forced detention, intense scrutiny, surveillance and even slavery.
- However, China claims its camps to be ‘educational centres’ where the Uighurs are being cured of “extremist thoughts” and radicalisation, and learning vocational skills.
- China claims that Uighur groups want to establish an independent state and, because of the Uighurs’ cultural ties to their neighbours, leaders fear that elements in places like Pakistan may back a separatist movement in Xinjiang.
- Over the past few decades, as economic prosperity has come to Xinjiang, it has brought with it in large numbers the majority Han Chinese, who have cornered the better jobs, and left the Uighurs feeling their livelihoods and identity were under threat.
- China’s Extradition Treaty:
- In December 2020, China approved an extradition treaty with Turkey aimed at strengthened judicial cooperation to facilitate a crackdown on transnational criminals including terrorists.
- Extradition is the formal process of one state surrendering an individual to another state for prosecution or punishment for crimes committed in the requesting country's jurisdiction.
- The extradition agreement comes amidst deepening economic and financial ties between Turkey and China.
- China is also Turkey's leading supplier of Covid-19 vaccines.
- Since 1990, the Uighur diaspora in Turkey has become more vibrant and has attracted widespread attention globally through demonstrations, conferences, meetings and briefings.
- Concerns of Uighur Muslims:
- If Turkey ratifies the treaty, this will be the last nail in the coffin of Uighur culture as China will silence the biggest Uighur diaspora outside Xinjiang.
- The treaty will become another instrument in the hands of China for the prosecution of its enslaved Uighur minority.
- In December 2020, China approved an extradition treaty with Turkey aimed at strengthened judicial cooperation to facilitate a crackdown on transnational criminals including terrorists.
- India’s Stand:
- The Indian government has maintained near silence on the Uighur crisis.
- All the countries should reconsider their position and urge China to immediately stop the persecution of Muslims and the prohibition of Islam in Xinjiang.
- China must close its “Vocational Training Centers,” release the religious and political prisoners from prisons and detention camps. It should adopt multiculturalism and accept the Uighurs and other Turkic Muslims of China as ordinary citizens equal to native Chinese.
- The Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECGLS) has helped in the credit growth for the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector.MSME Credit Health Index:
Launch: The TransUnion CIBIL in partnership with the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI)has launched MSME Credit Health Index.
-
- The Index is published quarterly.
- Aim: To provide a measure of the growth and strength of the MSME sector in India.
- The Index will provide government, policy makers, lenders and MSME market participants, a numeric indicator for benchmarking the health of the MSME sector.
- Measurement: The Index measures the credit health of India’s MSME industry on two parameters i.e, growth and strength. Both the growth and strength indices follow the principle of higher the better.
- Growth is measured by plotting increase in exposure value (outstanding balances) over time.
- An increasing Growth Index indicates improvement in credit growth.
- Strength is measured by decrease/increase in credit risk in terms of non-performing assets (NPA).
- An increasing Strength Index implies better asset quality and therefore denotes an improvement in the structural strength of the sector.
- Growth is measured by plotting increase in exposure value (outstanding balances) over time.
- Significance: This measurement model will facilitate better MSME credit risk management, formulation of strategies and policies to support the revival and resurgence of the MSME sector and the economy.
-
- Latest Data:
- The overall growth index inched up to 114 points, which is a three-point increase from 111 in June, 2020.
- The overall Strength Index also improved to 89 from 83 over the same period.
- About the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme:
- The scheme was launched as part of the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan package announced in May 2020 to mitigate the distress caused by coronavirus-induced lockdown, by providing credit to different sectors, especially Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- The ECLGS provides for the Guaranteed Emergency Credit Line (GECL) facility.
- The GECL is a loan for which 100% guarantee is provided by the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company (NCGTC) to Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) - banks, financial institutions and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- The loans are extended in the form of additional working capital term loan facility in case of banks and additional term loan facility in case of NBFCs to eligible Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)/business enterprises and interested Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) borrowers.
- NCGTC is a private limited company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 in 2014, established by the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, as a wholly owned company of the Government of India, to act as a common trustee company for multiple credit guarantee funds.
- Credit guarantee programmes are designed to share the lending risk of the lenders and in turn, facilitate access to finance for the prospective borrowers.
-
- Whale sharks are the largest shark, and indeed largest of any fishes alive today and they travel large distances to find enough food to sustain their huge size, and to reproduce.
- The whale shark is a ‘filter feeder shark’ which means it does not eat meat like other sharks. Whale sharks filter sea water and feed on tiny planktons.
- The maximum size of whale sharks is not known, but could be as large as 20m.
- Scientific Name:
- Rhincodon typus.
- Habitat:
- Whale sharks are found in all the tropical oceans of the world.
- Threats:
- Oil & gas drilling, shipping lanes etc.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
- Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
 The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted the test of the Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology, which is crucial for the indigenous development of long range air-to-air missiles.
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted the test of the Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) technology, which is crucial for the indigenous development of long range air-to-air missiles.
- Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet (SFDR) Technology:
- SFDR technology is a missile propulsion system based on the concept of Ramjet Engine principle.
- The system utilises a solid fuelled air-breathing ramjet engine.
- Unlike solid-propellant rockets, the Ramjet takes up oxygen from the atmosphere during flight. Thus, it is light in weight and can carry more fuel.
- DRDO began developing SFDR first in 2017 and had conducted successful tests in 2018 and 2019 as well.
- Significance:
- Successful demonstration of SFDR technology will enable DRDO to develop indigenous long range air-to-air missiles.
- At present, such technology is available only with a handful of countries in the world.
- Air-to-air missiles which use SFDR technology can achieve longer ranges as they do not require oxidisers (take oxygen from the atmosphere).
- The missile based on SFDR fly at supersonic speeds and high manoeuvrability ensures the target aircraft cannot get away.
- Defence Research and Development Organisation:

- Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) works under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- It is working to establish a world class science and technology base for India and provides Defence Services decisive edge by equipping them with internationally competitive systems and solutions.
- It was established in 1958 after combining Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army and theDirectorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) with the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- It is responsible for carrying out Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Some of the recent tests conducted by DRDO:
- Helina and Dhruvastra: Anti-tank Guided Missile
- Smart Anti Airfield Weapon
- Army Variant of MRSAM
- Land-attack Version of BrahMos Missile
- Quick Reaction Surface-to-Air Missile System
- Enhanced Version of Pinaka Mk-1 Missile
- NAG Missile: Anti Tank Guided Missile
- A ramjet is a form of air-breathing jet engine that uses the vehicle’s forward motion to compress incoming air for combustion without a rotating compressor.
- Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds but they are not efficient at hypersonic speeds.
- IGMDP was the brainchild of renowned scientist Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam.
- It was intended to attain self-sufficiency in the field of missile technology.
- After keeping in mind the requirements of various types of missiles by the defense forces, the program recognized the need to develop five missile systems.
- The IGMDP formally got the approval of Indian government on 26th July, 1983.
- The missiles developed under IGMDP are:
- Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Prithvi
- Intermediate-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Agni
- Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile – Trishul
- Medium-range surface-to-air missile – Akash
- Third generation anti-tank missile – Nag
- The rights and restrictions are not new, they have been notified previously in 2005, 2007, and 2009. They were also mentioned in an OCI brochure published by the Ministry of Home Affairs in November 2019.
- Multiple Entry Lifelong Visa:
- OCI cardholders will be entitled to get multiple entry lifelong visas for visiting India for any purpose.
- Prior Permission:
- OCI cards would need prior permission for a set of activities that include research, journalism, mountaineering, missionary or Tablighi work, and visits to restricted areas.
- Parity with Non Resident Indians (NRIs):
- OCI cardholders will enjoy parity with NRIs in adoption of children, appearing in competitive exams, purchase or sale of immovable property barring agricultural land and farmhouses, and pursuing professions such as doctors, lawyers, architects, and chartered accountants.
- Parity with Indian Nationals:
- They have parity with Indian nationals in the matter of domestic air fares, entry fees to monuments and public places.
- Entrance Exams and Admissions:
- OCIs can appear for all-India entrance tests such as National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET), Joint Entrance Examination (Mains), Joint Entrance Examination (Advanced) or such other tests to make them eligible for admission only against any NRI seat or any supernumerary seat.
- The OCI cardholder shall not be eligible for admission against any seat reserved exclusively for Indian citizens.
- Other Economic, Financial and Educational fields:
- In respect of all other economic, financial and educational fields not specified in the latest notification or the rights and privileges not covered by the notifications made by the Reserve Bank of India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, the OCI cardholder shall have the same rights and privileges as a foreigner.
- Exemption:
- They are exempted from registration with the Foreigners’ Regional Registration Officer (FRRO) for any length of stay in India.
- Foreigners visiting India who hold long-term visas (more than 180 days) are required to register their presence in India with the Foreigners’ Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- They are exempted from registration with the Foreigners’ Regional Registration Officer (FRRO) for any length of stay in India.
- Restrictions:
- There will be no restriction in visiting religious places and attending normal religious activities like attending religious discourses.
- However, preaching religious ideologies, making speeches in religious places, distribution of audio or visual display/pamphlets pertaining to religious ideologies, spreading conversion etc. will not be allowed.
 Overseas Citizen of India
Overseas Citizen of India
- The Ministry of Home Affairs defines an OCI as a person who:
- Was a citizen of India on or after 26th January 1950; or
- Was eligible to become a citizen of India on 26th January 1950; or
- Is a child or grandchild of such a person, among other eligibility criteria.
- According to Section 7A of the OCI card rules, an applicant is not eligible for the OCI card if he, his parents or grandparents have ever been a citizen of Pakistan or Bangladesh. The category was introduced by the government in 2005.
- The Government of India via Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2015 merged the Person of Indian Origin (PIO) category with OCI category in 2015.
- A Non-Resident Indian (NRI) means a person resident outside India who is a citizen of India or is a person of Indian origin.
- An Indian citizen residing outside India for a combined total of at least 183 days in a financial year is considered to be an NRI.
- NRIs enjoy voting rights and are required to pay and file the income tax return on their Indian income like resident Indians.
- NRI is more of a technical classification for taxation purposes and investment purposes.
- However, in case an NRI wishes to take up foreign citizenship, he/she will have to give up Indian citizenship as the Indian constitution does not allow dual citizenship.
- A person cannot hold Indian as well as foreign citizenship simultaneously.
- As per the the Foreigners Act, 1946, foreigner means a person who is not a citizen of India.
- The Fundamental Rights guaranteed by Articles 14, 20, 21, 21A, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27 and 28 are available to all persons whether citizens or foreigners. The Fundamental Rights guaranteed by Articles 15, 16, 19, 29, and 30are available only to citizens of India.
 Recently, there has been an outbreak of Equine Herpes Virus (EHV-1) among horses in Europe.
Recently, there has been an outbreak of Equine Herpes Virus (EHV-1) among horses in Europe.
- So far seven countries have confirmed EHV-1 cases: Spain, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Sweden and Qatar.
- Equine Herpes Virus (EHV):
- Equine Herpes Virus is a common DNA virus that occurs in horse populations worldwide.
- EHV is a family of viruses which are named by numbers such as EHV 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
- There are more viruses in this family, but EHV 1, 3, and 4 pose the most serious health risks for domestic horses.
- Health Risks:
- EHV1 can cause manifestations of disease in horses, including respiratory disease, abortion and neonatal death.
- This strain can also cause neurological problems, leading to paralysis and in some cases, death. Horses that contract this virus can develop a lack of coordination, weakness, loss of appetite and are unable to stand.
- Spread of EHV-1 Virus:
- It is contagious and spread by direct horse-to-horse contact via the respiratory tract through nasal secretions.
- This virus can also be spread indirectly through contact with physical objects that are contaminated with the virus.

- Equine Herpesvirus Myeloencephalopathy (EHM) is another name for the neurologic disease associated with Equine Herpes Virus (EHV) infections.
- Precautions and Treatment:
- As the infection has a high transmission rate, keeping a diseased horse in isolation is required.
- Treatments may include anti-inflammatory drugs.
- He was awarded for his commitment to expanding India's leadership in sustainable development to meet the country's, and the world's, future energy needs.
- He addressed the CERAWeek conference and highlighted the steps taken by India to address the issue of climate change and attaining the target of achieving clean fuel.
- CERAWeek Global Energy and Environment Leadership Award:
- The Award was instituted in 2016.
- It recognises the commitment of leadership on the future of global energy and environment, and for offering solutions and policies for energy access, affordability and environmental stewardship.
- Cambridge Energy Research Associates (CERA):
- It is a consulting company in the United States that specializes in advising governments and private companies on energy markets, geopolitics, industry trends, and strategy.
- CERAWeek:
- It was founded in 1983 by Dr. Daniel Yergin.
- It is an annual energy conference, organized in Houston (USA) in March, since 1983.
- CERAWeek by IHS Markit is the annual international gathering of energy industry leaders, experts, government officials and policymakers, leaders from the technology, financial and industrial communities - and energy technology innovators.
- CERAWeek 2021 was convened virtually from 1st-5th March, 2021.
- Theme: The New Map: Energy, Climate, and Charting the Future.
- Highlights of PM Address:
- The Prime Minister in his address discussed the key initiatives taken by India to attain climate justice:
- National Hydrogen Mission,
- PM KUSUM,
- Bharat - 6 emission norms,
- Give It Up Subsidy Movement,
- SATAT initiatives,
- Blending of ethanol,
- Modern techniques of irrigation,
- Organic farming,
- International Solar Alliance,
- India’s commitment towards the Paris Climate Accord, and
- Talked of Mahatma Gandhi’s Principle of Trusteeship.
- At the core of Trusteeship is collectivism, compassion and responsibility.
- The Prime Minister in his address discussed the key initiatives taken by India to attain climate justice:
 The Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) celebrated the 3rd Janaushadhi Diwas (7th March 2021) to spread awareness about quality generic medicines, available at low prices.
The Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) celebrated the 3rd Janaushadhi Diwas (7th March 2021) to spread awareness about quality generic medicines, available at low prices.
- Theme of Janaushadhi Diwas was “Seva Bhi – Rozgar bhi”. The Janaushadhi week was celebrated across the country from 1st-7th March 2021.
- As a part of celebrations, the Prime Minister inaugurated the 7,500th Janaushadhi Kendra at NEIGRIHMS, Shillong.
- Janaushadhi Kendra:
- Bureau of Pharma PSUs in India (BPPI) supports Janaushadhi Kendras as a part of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana.
- These are the centres from where quality generic medicines are made available to all.
- The number of stores has grown to more than 7400 and all 734 districts of the country have Janaushadhi Kendras.
- Government grants of up to Rs. 2.5 lakhs are provided for setting up of Pradhan Mantri Janaushadhi Kendras, which can be set up by doctors, pharmacists, entrepreneurs, Self Help Groups (SHGs), NGOs, charitable societies, etc. at any suitable place or outside the hospital premises.
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP):
- PMBJP is a campaign launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals in 2008 under the name Jan Aushadhi Campaign.
- The campaign was revamped as PMBJP in 2015-16.
- Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI) is the implementation agency for PMBJP.
- The Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India works under the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
- BPPI has also developed the Janaushadhi Sugam Application.
- PMBJP stores have been set up to provide generic drugs, which are available at lesser prices but are equivalent in quality and efficacy as expensive branded drugs.
- It also intends to extend the coverage of quality generic medicines so as to reduce the out of pocket expenditure on medicines and thereby redefine the unit cost of treatment per person.
- A medicine under PMBJP is priced on the principle of a maximum of 50% of the average price of top three branded medicines. Therefore, the price of Janaushadhi Medicines is cheaper at least by 50% and in some cases, by 90% of the market price of branded medicines.
- PMBJP is a campaign launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals in 2008 under the name Jan Aushadhi Campaign.
- Performance Analysis:
- In the current financial year 2020-21, PMBJP has already achieved sales of Rs. 593.84 crores. This has led to savings of approximately Rs. 3600 crores of the common citizens of the country.
- This scheme is also providing a good source of self-employment with sustainable and regular earnings.
- This Summit saw participation from several regional officials including infrastructure Ministers from Afghanistan, Armenia, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia and Uzbekistan.
- India’s Proposal:
- Pitching for Chabahar in the INSTC which goes via Iran’s biggest port Bandar Abbas, India proposed that the land route via Kabul (Afghanistan) and Tashkent (Uzbekistan) would form the INSTC’s “Eastern corridor”.
- India’s push to include Chabahar in the INSTC could have been made with an eye on the new Biden administration’s push for restoring talks with Iran on the JCPOA nuclear agreement, and the possible easing of some sanctions.
- Establishing an eastern corridor through Afghanistan would maximise its potential.
- India highlighted Chabahar’s role in recent years in sending Indian humanitarian aid and emergency supplies to Afghanistan and Iran and in opening up trade opportunities.
- Pitching for Chabahar in the INSTC which goes via Iran’s biggest port Bandar Abbas, India proposed that the land route via Kabul (Afghanistan) and Tashkent (Uzbekistan) would form the INSTC’s “Eastern corridor”.
- Chabahar Port:
- Location:
- It is located on the Gulf of Oman and is only 72 km away from the Gwadar port in Pakistan which has been developed by China.
- About:
- It is the only Iranian port with direct access to the Indian ocean and consists of two separate ports named Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
- Afghanistan, Iran and India signed a tripartite agreement on developing Chabahar port and setting up a trilateral transport and transit corridor in 2016.
- Significance:
- For India:
- Connectivity:
- It is a key part of India’s plans to enhance connectivity to Afghanistan and the Central Asian states.
- Countering China and Pakistan:
- It opens up a permanent alternative route for trade with Afghanistan and Central Asia, given the hurdles in the direct route through Pakistan.
- China and Pakistan are striving to increase their economic and trade cooperation through the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and Gwadar port, which both are part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Part of Indo-Pacific Strategy: Chabahar Port is a key element in India's Indo-Pacific strategy that also includes Eurasia's connection with the Indian Ocean Region.
- Connectivity:
- For Afghanistan:
- It will facilitate India’s role in Afghanistan’s development through infrastructure and education projects and also allow Afghanistan to have a commercial fleet under the Afghan flag sailing from Chabahar.
- For Central Asian Countries:
- Central Asian countries like– Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan– also view Chabahar Port as their gateway to the Indian Ocean Region.
- For India:
- Location:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC):
- It is a multi-modal transportation established on 12th September 2000 in St. Petersburg, by Iran, Russia and India for the purpose of promoting transportation cooperation among the Member States.
- The INSTC was expanded to include eleven new members, namely: the Republic of Azerbaijan, Republic of Armenia, Republic of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Republic of Tajikistan, Republic of Turkey, Republic of Ukraine, Republic of Belarus, Oman, Syria, Bulgaria (Observer).
- It envisions a 7,200-km-long multi-mode network of ship, rail and road route for transporting freight, aimed at reducing the carriage cost between India and Russia by about 30% and bringing down the transit time from 40 days by more than half.
- This corridor connects India Ocean and the Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea via the Islamic Republic of Iran and then is connected to St. Petersburg and North Europe via the Russian Federation.
- Quasars:
- Quasars are very luminous objects in faraway galaxies that emit jets at radio frequencies.
- The word quasar is short for "quasi-stellar radio source".
- The name, which means star-like emitters of radio waves, was given in the 1960s when quasars were first detected.
- The name is retained today, even though astronomers now know most quasars are faint radio emitters. In addition to radio waves and visible light, quasars also emit ultraviolet rays, infrared waves, X-rays, and gamma-rays.
- Most quasars are larger than our solar system. A quasar is approximately 1 kiloparsec in width.
- They are only found in galaxies that have supermassive blackholes which power these bright discs.
- Black hole refers to a point in space where matter is so compressed as to create a gravity field from which even light cannot escape.
- Most active galaxies have a supermassive black hole at the centre which sucks in surrounding objects.
- Quasars are formed by the energy emitted by materials swirling around a blackhole right before being sucked into it.
- They are further categorised into the "radio-loud" and the"radio-quiet" classes.
- Radio-loud:
- They are with powerful jets that are strong sources of radio-wavelength emission.
- These make up about 10% of the overall quasar population.
- Radio-quiet :
- They are those quasars lacking powerful jets, with relatively weaker radio emission than the radio-loud population.
- The majority of quasars (about 90%) are radio-quiet.
- Radio-loud:
- Recently Discovered Quasar/P172+18:
- Named P172+18, the quasar emitted wavelengths which had a redshift of 6.8.
- It took 13 billion years for the quasar’s light to reach earth.
- This particular quasar appears to the scientists as it was when the universe was just around 780 million years old.
- The glowing disc around a blackhole is 300 million times more massive than our Sun.
- It is also one of the fastest accreting quasars, which means it is accumulating objects from the galaxy at an enormous speed.
- Only three other ‘radio-loud’ sources with redshift greater than six have been discovered so far and the most distant one had a redshift of 6.18.
- The higher the redshift of the radio wavelength, the farther away is the source.
- Named P172+18, the quasar emitted wavelengths which had a redshift of 6.8.
- Inference:
- The blackhole at its centre is consuming from its galaxy at a stunning rate.
- Significance:
- A detailed study of these ‘radio-loud’ super bright objects can lead astronomers to understanding how the supermassive blackholes in their core grew to be as big so rapidly since the Big Bang.
- It also holds clues about the ancient star systems and astronomical bodies.
- About the ESO’s VLT:
- The Very Large Telescope used to observe the P172+18 is located at Paranal Observatory in the Atacama Desert.
- The four Unit Telescopes boast 8.2-meter (27 feet) mirrors.
- Just one of these instruments can spot objects that are 4 billion times fainter than what can be seen with the unaided eye.
- According to the European Southern Observatory, the Very Large Telescope is the world's most advanced optical telescope.
- The Very Large Telescope used to observe the P172+18 is located at Paranal Observatory in the Atacama Desert.
- Gravitational redshift occurs as particles of light (photons) climb out of a gravitational well like a black hole and the light's wavelength gets drawn out. This shifts the wavelength to the red part of the light spectrum - hence"redshift".
- In order to escape intense gravity, particles of light (photons) must expend energy.
- However, at the same time, these photons must travel at a constant speed - the speed of light.
- Therefore, the photons can't lose energy by slowing down but must expend it in another way.
- This lost energy manifests itself as a shift towards the red end of the light spectrum.
- PLI Scheme:
- In order to boost domestic manufacturing and cut down on import bills, the central government in March 2020introduced a scheme that aims to give companies incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in domestic units.
- Apart from inviting foreign companies to set shop in India, the scheme also aims to encourage local companies to set up or expand existing manufacturing units.
- The Scheme has been approved for many sectors including electronic products, IT hardware, pharmaceuticals, automobiles and components, etc.
- PLI Scheme for Telecom Sector :
- About:
- This Scheme is for domestic manufacturing of telecom and networking products such as switches, routers, 4G/5G radio access network, wireless equipment and other internet of things (IoT) access devices.
- It will be operational from 1st April, 2021.
- Eligibility for the Scheme:
- It is subject to achieving a minimum threshold of cumulative incremental investment and incremental sales of manufactured goods.
- The cumulative investment can be made at one go, subject to annual cumulative threshold as prescribed for four years being met.
- 2019-20 will be treated as the base year for computation of cumulative incremental sales of manufactured goods net of taxes.
- Incentives:
- An investor who qualifies for the scheme will be incentivised up to 20 times the minimum investment threshold,enabling them to utilise their unused capacity.
- Higher Incentives for MSMEs:
- For Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), the minimum investment threshold has been kept at Rs. 10crore, while for others it is Rs. 100 crore.
- For MSMEs, a 1% higher incentive is also proposed in the first three years.
- About:
- Significance :
- The scheme is expected to lead to an incremental production of about Rs. 2.4 lakh crore, with exports of about Rs. 2 lakh crore over five years and bring in investments of more than Rs. 3,000 crore.
- Scheme is also likely to generate 40,000 direct and indirect employment opportunities and generate tax revenue of Rs. 17,000 crore from telecom equipment manufacturing.
- Through this scheme, India will move towards self-reliance. Currently, India imports over 80% of its telecom and wireless networking equipment.
- Vaccine Passports:
- A vaccine passport is an e-certificate that stores and records jabs and Covid-19 test status.
- It can be kept in a smartphone app or in other digital formats.
- Its contents can be flashed at security checkpoints when people travel across borders.
- The idea is modelled on the proof of vaccination that several countries required even before the pandemic.
- Travellers from many African countries to the USA or India are required to submit proof that they have been vaccinated against diseases such as yellow fever.
- In February 2021, Israel became the first country to introduce a certification system that allows those who have been vaccinated against Covid-19 to access certain facilities and events.
- A vaccine passport is an e-certificate that stores and records jabs and Covid-19 test status.
- Function of Vaccine Passports:
- Will digitise vaccination records across countries.
- Supposed to function as proof that the holder has been vaccinated against Covid-19 and is, therefore, safe.
- Potential Beneficiary of the Vaccine Passports:
- The primary benefit will be to the tourism and the hospitality industries, which are both seen as being at the heart of Covid-19 spread and are the worst hit by the pandemic.
- The international air travel, which suffered massively because of the outbreak.
- Similar Initiative: Several associations and non-profits have been issuing their own versions for international travel:
- IATA Travel Pass: The global trade body representing airlines (The International Air Transport Association) is developing an app called IATA Travel Pass that will provide airlines and other aviation industry stakeholders with a common platform to check for the proof of vaccination and its validity.
- CommonPass: Non-profit Commons Project has been trying out an app called CommonPass, which contains a passenger’s vaccination record.
- Concerns Raised in Instituting Vaccine Passport:
- WHO’s Stand:
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) is against the introduction of Covid-19 vaccination proofs as a requirement for international travel.
- There are still critical unknown facts regarding the efficacy of vaccination in reducing transmission.
- Lack of Uniformity: The major difficulty in implementation will be the lack of uniformity across jurisdictions in requirement and issuance of proofs of vaccination.
- Inadequate Availability of Vaccines: Preferential vaccination of travellers could result in inadequate supplies of vaccines for priority populations considered at high risk of severe Covid-19 disease.
- Introducing a requirement of vaccination as a condition for travel has the potential to hinder equitable global access to a limited vaccine supply and would be unlikely to maximize the benefits of vaccination for individual societies and overall global health.
- Perpetuate Discrimination and Inequality: Experts argue that vaccine passports, in any form, might make travel inequitable. Adoption of these digital passports can perpetuate discrimination and inequality, increasing the divide between socioeconomic groups.
- Rich countries that have already bought millions of doses from pharmaceutical companies are ahead in the race. The poorer nations may have to wait for months, if not years, to start inoculations.
- This means that if vaccine passports become a norm, then these lower-income nations will lose out on the advantage.
- It will lead to exclusion of the younger generation who would be last in line to be vaccinated.
- Privacy Concerns: These are mainly digital certificates that are accessed by a particular service provider to check for proof of vaccination, there is a possibility that they would be used by authorities to track the movement of their holders.
- WHO’s Stand:
-
- Counter Insurgency (CI) and Counter Terrorism (CT) operations in mountainous, rural and urban scenarios under the United Nations (UN) mandate.
- First Edition:
- Took place in Tashkent, Uzbekistan in November 2019.
- Significance:
- Uzbekistan is important to India for security and connectivity to the Central Asian region and also Iran, it is also one alternative India has with respect to Afghanistan.
- Security concerns stemming from the conflict in Afghanistan is one of the major challenges for India’s involvement in Central Asia.
- Uzbekistan is important to India for security and connectivity to the Central Asian region and also Iran, it is also one alternative India has with respect to Afghanistan.
| Joint Military Exercises of India with Other Countries | |
| Name of Exercise | Country |
| Garuda Shakti | Indonesia |
| Ekuverin | Maldives |
| Hand-in-Hand | China |
| Bold Kurukshetra | Singapore |
| Mitra Shakti | Sri Lanka |
| Nomadic Elephant | Mongolia |
| Shakti | France |
| Surya Kiran | Nepal |
| Yudh Abhyas | USA |









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies