- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
10th Nov 2021
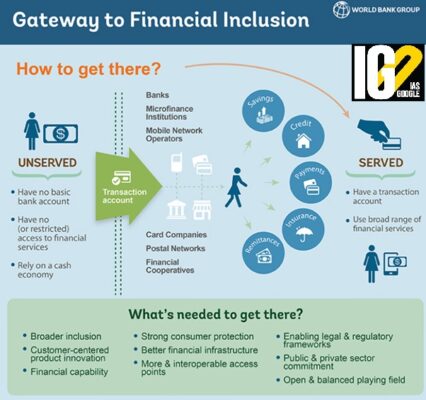
‘INDIA NOW AHEAD OF CHINA IN FINANCIAL INCLUSION METRICS’
India is now ahead of China in financial inclusion metrics, with rise in mobile and Internet banking transactions.
Financial inclusion (FI):

 ICE- Cars
ICE- Cars



 Genesis:
Genesis:

- Financial inclusion is defined as the availability and equality of opportunities to access financial services.
- It refers to a process by which individuals and businesses can access appropriate, affordable, and timely financial products and services.
- These include banking, loan, equity, and insurance products.
- National Mission for Financial Inclusion aims to ensure access to financial services in an affordable manner.
- Under the scheme, a basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account can be opened in any bank branch or Business Correspondent (Bank Mitra) outlet, by persons not having any other account.
- One basic savings bank account is opened for unbanked person.
- Jan Dhan- Aadhar- Mobile Trinity (JAM Trinity) has a positive impact on the banking sector and financial inclusion in the country.
- JAM trinity refers to the government of India initiative to link Jan Dhan accounts, mobile numbers and Aadhaar cards of Indians to plug the leakages of government subsidies.
- The Aadhar-enabled payment system (AEPS) enables an Aadhar enabled bank account (AEBA) to be used at any place and at any time.
- Under Digital India, information and communication technology has provided convenient tools to spread awareness about financial schemes and services.
- Digital payments have been made secure with the strengthening of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- The payment system has been made more accessible due to offline transaction-enabling platforms, like Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD), which makes it possible to use mobile banking services without internet, even on a basic mobile handset.
- India has also been actively engaged with other countries and multilateral fora viz. Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion (GPFI) and Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- The Basic Savings Bank Deposit (BSBD) Account has been designed as a savings account which will offer certain minimum facilities, free of charge, to the holders of such accounts.

- The strategy has been prepared by RBI under the aegis of the Financial Inclusion Advisory Committee.
- The strategy aims to provide access to formal financial services in an affordable manner, broadening & deepening financial inclusion and promoting financial literacy & consumer protection.
- The aim of this initiative is to create awareness about financial products and services, good financial practices, going digital and consumer protection.
- Opening of bank branches in remote areas
- Issuing Kisan Credit Cards (KCC)
- Using information technology to spread awareness and literacy
- Linkage of self-help groups (SHGs) with banks
- Increasing the number of automated teller machines (ATMs)
- Pocket Money is a financial literacy initiative by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the National Institute of Securities Markets (NISM).
- The objective of this is to help school-going children to understand the importance of financial management and the value of money.
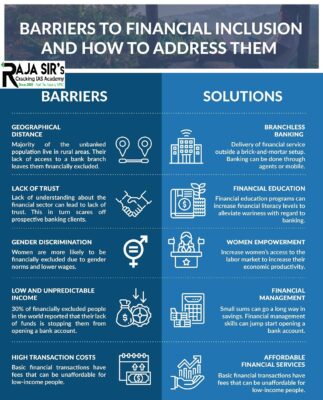
- The Bank Mitra / Banking Correspondent Agent (BCAs) at the Grass Root level has now become the extended arm of the Banks.
- These BCAs have a vital role in successful implementation of Financial Inclusion and PMJDY.
- An initial target could be set for account holders to use their accounts at least once every 90 days.
- Small corner stores should be made as agents for banks where people can deposit and withdraw money from their accounts and transact.
- However, not all those agents have equipment or are being paid enough by banks to conduct transactions.
- The acceptance network for debit cards is virtually non-existent.
- There are solutions to develop that network more rapidly and India could work with global partners to make that happen.
- The financial inclusion campaign should also make a bigger effort to emphasize mobile channels that have been a catalyst for financial inclusion elsewhere.
- Allowing Payments Banks to process government payments would break the monopoly of public sector banks and be a boon for customers.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index).
- It will assess the quality and extent of financial inclusion in India and will be published every July for the previous financial year.
- There are three broad parameters with certain assigned weights:
- Access (35 percent)
- Usage (45 percent)
- Quality (20 percent).
- Each parameter consists of various dimensions computed based on 97 indicators.
- The FI-Index doesn’t have a base year.
- The FI-Index for the year ended March 2021 is 53.9 as against 43.4 for the year ended March 2017.
- A 100 on this score would mean that all customers are fully aware of all kinds of financial services, have access to all products and do not feel constrained to make transactions.

- To halve fuel consumption of new light-duty vehicles, fuel consumption should fall 4.3 % per year on average from 2019 to 2030.
- The average rated fuel consumption fell by only 0.9 per cent between 2017 and 2019.
- This is smaller than the 1.8 per cent annual average reduction between 2010 and 2015.
- The three major car markets: China, the European Union, and the United States, accounted for 60 per cent of global sales of light-duty vehicles in 2019.
- This totalled 90 million, down seven per cent from 2017.
- Stagnating fuel economy standards in the US and the EU up to 2019.
- The rising market share of SUVs, which can use almost one-third more fuel than a medium-sized car.
- The rising cost of squeezing out further efficiency gains from mature technologies.
- The slow adoption of electric cars to compensate for larger vehicles.
 ICE- Cars
ICE- Cars
- For combustion engine cars, most emissions occur at their tailpipe.
- Less than 20 per cent of overall emissions are related to the production of their fuels.
- Battery electric vehicles had the lowest emissions in 2019, followed by plug-in hybrids and hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles.
- For battery electric and fuel cell electric vehicles, all the emissions are incurred in producing and delivering the electricity or hydrogen on which they run.
- Hybrid vehicles have the lowest emissions among vehicles with internal combustion engines using gasoline, diesel or compressed natural gas.
- GFEI is a partnership between 6 organisations that promote research, and action to improve fuel economy worldwide and zero emission technologies.
- The GFEI was first established in 2009.
- Aim: To ensure that the world’s vehicle fleet is as clean and efficient as possible in response to global concerns about clean air and climate change.
- Headquarters: London, UK.
- Accelerating the rapid transition to the most efficient, zero emission vehicles globally – saving money, energy and tackling climate change.
- Improving average fuel economy of light duty vehicles by 2030 for new vehicles.
- Expanded its focus to include Heavy Duty Vehicles, with the aim of a 35 per cent improvement by 2035 and 80 per cent by 2050.
- Decarbonizing the electricity grid to meet emissions targets for the global vehicle fleet.

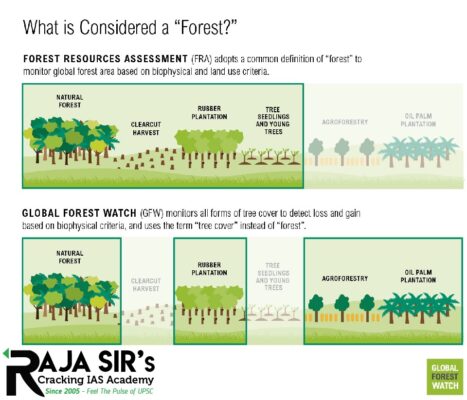
- 420 million hectares of forest has been lost since 1990.
- However, most of the deforestation was in the tropical biomes during 2000-2018.
- 90 % of deforestation worldwide was due to agricultural expansion.
- Percentage of global forests converted for other purposes:
- 3 % has been converted to cropland
- 5 % was lost to livestock grazing
- 6 % converted for urban and infrastructure development
- 6 % to other causes.

- Agriculture is the main driver of deforestation in all regions except Europe where urban and infrastructure development have a higher impact.
- Conversion to cropland dominates forest loss in Africa and Asia, with over 75 per cent of the forest area lost converted to cropland.
- Deforestation has been successfully reduced in South America and Asia.
- Tropical rainforests in these regions recorded the highest deforestation rates of all biomes.
- Russian Federation,
- Brazil
- Canada
- The United States of America
- China.

- The Demoiselle crane is a species of crane.
- They are found in central Euro- Siberia, ranging from the Black Sea to Mongolia and North Eastern China.
- These cranes are migratory birds.
- Birds from western Eurasia will spend the winter in Africa while the birds from Asia, Mongolia and China will spend the winter in the Indian subcontinent.
- It is the smallest species out of 15 crane species.
- It has a loud trumpeting call, higher-pitched than the common crane.
- It has a dancing display, more balletic than the common crane, with less leaping.
- Demoiselle cranes are primarily wetland species.
- They like to breed in marshy areas, closer to the water, but are fine with wintering in arid areas like the Thar and Rann of Kutch, so long as water is a short flight away.
- IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature): Least Concern
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora): Appendix II
- Newcastle disease is a highly contagious disease of birds.
- It is caused by a para-myxo virus.
- It infects the lungs and intestine of the infected birds.
- The disease is transmitted through infected birds' droppings and secretions from the nose, mouth and eyes and direct contact between healthy birds and the bodily discharges of infected birds.
- The virus can survive for several weeks in a warm and humid environment on birds' feathers, manure, and other materials.
- Birds affected by this disease are fowls, turkeys, geese, ducks, pheasants, partridges, guinea fowl and other wild and captive birds.
- Humans aren’t normally affected, but people in direct contact with infected birds may develop a very short-term eye infection.
- Vaccination: The vaccine contains the LaSota strain of Newcastle disease virus and applies to chickens only.

- About:
- It was launched during the UNFCCC Conference of Parties (CoP) 26adaptation day (8th November 2021), it will be the world’s first curated, open-source reference index.
- It has been launched to build a universal model for assessing resilience to climate risks.
- It will provide reference data on climate and natural hazard risksto inform and protect populations and economies, particularly in emerging and developing countries, form a basis for mobilising the trillions of investment needed to meet the Paris goals on climate-resilient development.
- It can be used in aggregated risk managementacross sectors and geographies.
- Goal: The coalition wants to achieve two immediate goals.
- First, they want to provide global open reference risk datadeveloped using insurance risk modelling principles.
- Second, they want to provide shared standards and facilities applicable to a wide range of uses:
- Corporate climate risk disclosure.
- National adaptation planning and reporting.
- Planning of pre-arranged humanitarian finance.
- Partners & Supporters: GRII has been initiated with partial funding and in-kind contributions from the insurance sector and partner institutions such as:
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI)
- Coalition for Climate Resilient Investment (CCRI)
- Need:
- Natural catastrophes cost nearly USD 200 billion globally in 2020. Since 1970, over 2 million people have died in climate-related disasters; 9 out of every 10 in developing countries.
- Almost every country has felt the harsh impact of climate change in recent years in some form or another.
- Systems and economies resilient to climate disruption can save millions of lives and livelihoods.
- Significance:
- The outcomes of this risk analysis will help close the insurance protection gap and direct investment and aid to where they are needed the most.
- It will help global economic sectors understand, in concrete terms, the value of building climate resilience and the costs of doing nothing, this will address the data emergency that is contributing to the climate crisis.
- It will enable asset owners to compare portfolio risks across geographies and hazards, as well as helping countries to prioritise national adaptation investments.
- Identify and develop solutions that have the potential to make digital payments accessible to the under-served.
- Enhance the ease of payments and user experience.
- Strengthening the security of digital payments and promoting customer protection.
- Solve the problem in the payment and settlement systems by creating;
- non-mobile digital payment solutions for converting small ticket cash transactions to digital mode.
- Context-based retail payments to remove the physical act of payment.
 Genesis:
Genesis:
- In the Chicago Convention 1944, the signatories decided to set rules to act as fundamental building blocks to international commercial aviation.
- As a part of these rules, ‘freedoms of air’ were decided.
- These freedoms or rights allow airlines of a particular country the privilege to use or land in another country’s airspace.
- The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services, granted by one State to another State or States to fly across its territory without landing.
- The right or privilege, granted by one State to another State or States to land in its territory for non-traffic purposes.
- The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services, granted by one State to another State to put down, in the territory of the first State, traffic coming from the home State of the carrier.
- The right or privilege, granted by one State to another, to take on, in the territory of the first State, traffic destined for the home State of the carrier.
- The right granted by one State to another to put down and to take on, in the territory of the first State, traffic coming from or destined to a third State.
- The right or privilege, in respect of scheduled international air services, of transporting, via the home State of the carrier, traffic moving between two other States.
- ICAO is an intergovernmental specialized agency associated with the United Nations (UN).
- Established in 1947 by the Convention on International Civil Aviation (1944).
- Aim: To developing safe and efficient international air transport for peaceful purposes and ensuring a reasonable opportunity for every state to operate international airlines.
- Headquarters: Montreal, Canada.
- An Assembly of delegates from all member countries that meets every three years.
- A Council of representatives from 33 member states, elected by and responsible to the Assembly.
- An Air Navigation Commission appointed by the Council for addressing technical matters.
- Various standing committees, like Committee on Joint Support of Air Navigation Services and a Finance Committee.
- Establishing and reviewing international technical standards for aircraft operation and design.
- Perform crash investigation, meteorology, ground facilities for air transport, and-rescue missions.
- Promoting regional and international agreements aimed at liberalizing aviation markets.
- To establish legal standards to ensure that the growth of aviation does not compromise safety.
- Encourages the development of international aviation law.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies