- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
15th Aug 2021
PM MODI LAUNCHES VEHICLE SCRAPPAGE POLICY, SAYS IT WILL PROMOTE A CIRCULAR ECONOMY
Recently, the Prime Minister has launched the Vehicle Scrappage Policy at the Investors Summit in Gujarat.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy








- India is committed to provide global standard safety and quality to its citizens and this thinking is behind the transition from BS4 to BS6.
- The government is taking continuous steps to make Indian Industry sustainable and productive for speeding the process of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
- India had to import 23,000 crore worth of scrap steel during 2020 as India’s scrapping is not productive and India is not able to recover energy and rare earth metals.
- When it comes to vehicles which are older than 20 years, India is home to 2.1 crore such vehicles.
- Karnataka has the highest number (39.4 lakh) in the country which is followed by Delhi (36.1 lakh), Uttar Pradesh (26.2 lakh), Kerala (20.6 lakh), Tamil Nadu (15.9 lakh) and Punjab (15.3 lakh).

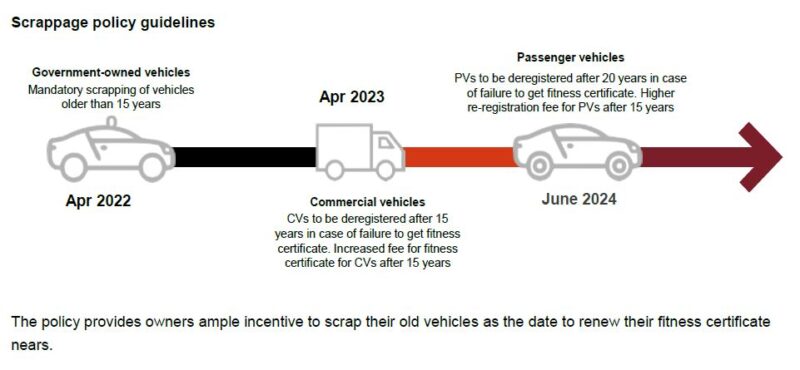
- The policy implementation will begin with heavy commercial vehicles, which will need to undergo mandatory fitness tests starting April 1, 2023.
- All other vehicles, including private ones, will be included in the mandatory fitness test criteria from June 1, 2024, in a phased manner.
- The policy aims to scrap old, unfit and polluting vehicles by creating an infrastructure for automated testing of vehicles that have completed the registration period.
- As per law, a registration certificate for a passenger vehicle is valid for 15 years from date of issue. For a commercial vehicle, it is valid for a period of 10 years.
- The scrappage policy will come into effect after the expiry of this 10 or 15 year period.
- A valid fitness certificate will be necessary for renewal of registration certificates after 15 years.
- The renewed certificate will be issued for a period of 5 years in case of private vehicles.
- Unfit vehicles will be scrapped scientifically which will ensure that registered vehicle scrapping facilities all over the country are technology driven and transparent.
- The term 'unfit' vehicles include those:
- Who fail to qualify a fitness test;
- Who have been damaged due to fire, riot, natural disaster, accident or any other calamity;
- Declared obsolete or beyond repair; and
- Vehicles which have outlived their utility
- Holding on to vehicles older than 15 years will become an expensive affair for owners as cost for renewal of fitness certificate might go up by 62 times for commercial vehicles and by 8 times for private vehicles.
- The states will impose green tax over and above the road tax that every vehicle owner needs to pay.
- The first advantage will be that a certificate will be given on scrapping the old vehicle.
- Whoever has this certificate will not have to pay any money for registration on the purchase of a new vehicle and he will also be given some exemption in road tax.
- The second benefit will be that the maintenance cost, repair cost, fuel efficiency of the old vehicle will also be saved in this.
- The third benefit is directly related to life because there will be some relief from the high risk of road accidents due to old vehicles and old technology.
- The fourth benefit is that it will reduce the harmful impact of pollution on our health.

- The vehicle scrapping will help phase out unfit and polluting vehicles in an environment friendly manner.
- Its objective is to create a viable circular economy and bring value for all stakeholders while being environmentally responsible.
- It is expected to give a new identity to the auto sector and to the mobility of New India.
- It will play a big role in the modernization of the vehicular population in the country, removing unfit vehicles from the roads in a scientific manner.
- The new scrapping policy is an important link in the circular economy and in the waste to wealth campaign.
- The policy uses the principle of Reuse, Recycle and Recovery to promote the country's self-reliance in the auto sector and in the metal sector.
- Pollution due to single use plastic items has become an important environmental challenge confronting all countries.
- India is committed to take action for mitigation of pollution caused by littered Single Use Plastics.
- In the 4th United Nations Environment Assembly held in 2019, India had piloted a resolution on addressing single-use plastic products pollution, recognizing the urgent need for the global community to focus on this very important issue.
- The adoption of this resolution at UNEA 4 was a significant step.

- According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) report 2018-19, 3.3 million metric tonnes of plastic waste was generated in India in 2018-19.
- The total municipal solid waste generation is 55-65 million tonnes; plastic waste is approximately 5-6 per cent of the total solid waste generated in the country.
- Goa has the highest per capita plastic waste generation at 60 grams per capita per day, which is nearly double of what Delhi generates (37 grams per capita per day).
- The manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale and use of following single-use plastic, including polystyrene and expanded polystyrene, commodities shall be prohibited with effect from the 1st July, 2022
- Ear buds with plastic sticks, plastic sticks for balloons, plastic flags, candy sticks, ice-cream sticks, polystyrene (Thermocol) for decoration;
- Plates, cups, glasses, cutlery such as forks, spoons, knives, straw, trays, wrapping or packing films around sweet boxes, invitation cards, and cigarette packets, plastic or PVC banners less than 100 micron, stirrers
- The thickness of plastic carry bags has been increased from fifty microns to seventy five microns with effect from 30th September, 2021 and to one hundred and twenty microns with effect from the 31st December, 2022.
- The plastic packaging waste shall be collected and managed in an environmentally sustainable way through the Extended Producer Responsibility of the Producer, importer and Brand owner (PIBO).
- For effective implementation of Extended Producer Responsibility, the Guidelines for Extended Producer Responsibility being brought out have been given legal force through Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021.
- In Rule 3 (na), (qa) & (va), (vb) & (vc) which specifies “non-woven plastic bag”, “Plastic waste processing”, “Single-use plastic commodity”, “Thermoset plastic” and “Thermoplastic” the following has been inserted:
- The “non-woven plastic bag” means a bag made up of plastic sheet or web structured fabric of entangled plastic fibers or filaments bonded together by mechanical or thermal or chemical means.
- The “non-woven fabric” means a flat or tufted porous sheet that is made directly from plastic fibres, molten plastic or plastic films.
- The “Plastic waste processing” means any process by which plastic waste is handled for the purpose of reuse, recycling, co-processing or transformation into new products.
- The “Single-use plastic commodity” means a plastic item intended to be used once for the same purpose before being disposed of or recycled.
- The “Thermoset plastic” means a plastic which becomes irreversibly rigid when heated and hence cannot be remoulded into desired shape.
- “Thermoplastic” means a plastic which softens on heating and can be moulded into desired shape.
- The “non-woven plastic bag” means a bag made up of plastic sheet or web structured fabric of entangled plastic fibers or filaments bonded together by mechanical or thermal or chemical means.
- It prohibits identified single use plastic items which have low utility and high littering potential by 2022.

- It is the first nasal vaccine that has received the regulatory approval for Phase 2 trials.
- It is the first of its kind COVID-19 jab to undergo human clinical trials in India.
- BBV154 is an intranasal replication-deficient chimpanzee adenovirus SARS-CoV-2 vectored vaccine.
- Bharat Biotech International Limited (BBIL) has in-licensed technology from Washington University in St Louis, USA.
- The phase 1 clinical trial has been completed for the 18-60 years age group.
- The intranasal vaccines aim to overcome barriers to delivery and administration that come with producing and distributing injectable vaccine.
- The intranasal vaccines are able to tap an additional set of immune cells found in the tissues lining the nose, mouth and lungs.
- Intranasal vaccines cut down on the need for syringes, needles and other components like alcohol swabs, as they are not injected.
- The vaccine was found to be safe, immunogenic, and well tolerated in pre-clinical toxicity studies.
- It was able to elicit high level of neutralizing antibodies in animal studies.
- An intranasal vaccine stimulates a broad immune response – neutralizing IgG, mucosal IgA, and T cell responses.
- The past attempts to develop intranasal vaccines, including for measles flu, have not been very successful.
- The intranasal vaccines have mostly been made using live, weakened viruses, but have never cleared clinical trials.
- The experts have also said that, because such a vaccine is being administered through the nose, the amount given in one shot has to be smaller than the quantity that can be delivered when injected.

- Under this operation, people with disabilities from across the country will undertake an expedition till Siachen Glacier.
- The Operation aims to create a new World Record for the largest team of people with disabilities to reach the world’s highest battlefield.
- The selected people with disabilities from across the country will undertake an expedition till Kumar Post (Siachen Glacier) to create a new World Record for the largest team of people with disabilities to reach the world’s highest battlefield.
- The team of people with disabilities has been trained by ‘Team CLAW’ which is a team of Armed Forces veterans.
- It shall subsequently undergo three stages of acclimatisation, training and medical screening before being inducted into the Siachen Base Camp for the final expedition.
- Those selected will undergo all the three stages of acclimatisation and training at Leh (Stage 1), Siachen base camp (Stage 2) and North Pullu (Stage 3) after which the final expedition team would be selected.

- It shall firmly place India on the global stage as a leader in empowering Divyangjan and set a benchmark for other nations to emulate.
- It will drive the Prime Minister’s vision for Divyangjan and MSJE’s pursuit to harness the immense productive potential of people with disabilities.
- It will powerfully portray the skill and heart of India’s Armed Forces not only on the Battlefield but off it as well.
- CLAW Global was set up in January 2019 by Major Vivek Jacob, a retired Para Special Forces officer.
- It was established with an aim of teaching life skills to adventurers and people with disabilities.
- It is an India-based organization helping people with disabilities follow their passions in adventurous activities.
- The organization, which stands for Conquer Land Air Water, has worked with people with disabilities across India to help them partake in activities like scuba diving etc.


- It is a bilateral exercise between Indian Navy and Qatar Emiri Naval Force (QENF).
- The present edition of the exercise included a three-day harbour phase followed by a two-day sea phase.
- The sea phase comprised of tactical maritime exercises involving Surface Action, Anti-Piracy exercises, Air Defence, Maritime surveillance, Boarding operations and SAR exercises.
- In the sea phase of the exercise, Indian Navy Stealth Frigate INS Trikand, QENF Missile Boats of Barzan and Damsah class, Fast-Attack Crafts of MRTP 34 class and Rafale Fighter Aircraft participated.
- Indian Navy remains committed towards ensuring peace, stability and security in the region and is ever-ready to cooperate and collaborate with partner Navies on issues of Maritime safety and security.
- The 2nd edition of exercise Zair-Al-Bahr will contribute towards the Indian Navy’s efforts to consolidate Inter-operability and forge strong bonds of friendship with the Qatari Navy.
- The bilateral maritime exercise between two navies would further strengthen the maritime exchanges between the two countries and enhance maritime security in the region.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies