- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
15th Oct 2021
POWER MINISTRY MANDATES ENERGY ACCOUNTING OF DISCOMS TO CUT ELECTRICITY LOSSES
The Ministry of Power has mandated energy accounting of Distribution Companies (Discoms) on a periodic basis to reduce electricity losses.
Highlights:




Index of Industrial Production (IIP):





- The regulations have been issued by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Objective: To reduce distribution sector inefficiency and losses, hence moving towards the economic viability of discoms.
- It stipulates quarterly energy accounting by discoms through a certified energy manager within 60 days.
- There will an annual energy audit by an energy auditor. The reports will be published in the public domain.
- The reports will provide information about electricity consumption by consumers, the transmission and distribution losses in various areas.
- It will identify areas of high losses and theft and enable corrective actions.
- It will enable the fixation of responsibility on officers for losses and theft.
- The data will enable the discoms to take appropriate measures for reducing their electricity losses.
- The discoms will be able to plan, suitable infrastructure up-gradation and demand-side management (DSM) efforts in an effective manner.
- This initiative will contribute towards India’s climate actions in meeting Paris Agreement goals.
- Energy accounting is a system to record, analyse and report energy consumption and cost on a regular basis.
- The energy flow to various segments.
- Energy consumption by various categories of consumers.
- Energy losses including both technical and commercial losses at various stages.
- Energy required for meeting the technical requirements of the system out of the total energy available over a specified time period.
- To segregate losses into technical/non-technical losses.
- To identify areas of mismatch between billing and revenue collection and improve metering, billing, and collection.
- To identify high loss areas and remedial steps for reduction of both technical and commercial losses.
- Initiate benchmarks of actual system losses with the standards.
- Monitoring conformity with meeting requirements.
- Preparing energy flow diagrams and energy balancing.
- Performance Degradation analysis and benchmarking.
- Fuel procurement and handling efficiency.
- Estimation of Non-Metered Consumption.
- Generating management information systems reports.
- It helps to establish the energy input consumed by various consumers, identify high loss areas, and evolve strategies to reduce losses.
- It is as fundamental to energy management as cost accounting is to financial management.
- It is one of the most cost-effective tools to cut energy costs and conserve energy.
- It can raise awareness about reducing energy demand and help in energy conservation efforts.
- The notification is expected to release on 6th December 2021.

- It has specified a system whereby makers and users of plastic packaging can collect Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates and trade in them.
- Plastic such as multi-layered and multi-material will be eligible to be sent for end-of-life disposal such as road construction, waste to energy, waste to oil and cement kilns.
- Rigid Plastic.
- Flexible plastic packagingof single-layer plastic sheets and covers made of plastic, carry bags, pouches etc.
- Multi-layered plastic packaging.
- They will inform the government about how much plastic they produce annually.
- Companies will have to collect at least 35% of the target in 2021-22, 70% by 2022-23 and 100% by 2024.
- In 2024, they will have to recycle 50% of their rigid plastic (category 1) and 30% of category 2 and 3 plastics.
- After 2026-27, 80% of category 1 and 60% of the other two categories will need to be recycled.
- If entities cannot fulfil their obligations, they will be permitted to buy certificates for their shortfall from the organisations that have used recycled content.
- In case of Non-compliance, there will be no fine. Instead, an “environmental compensation” will be levied.
- Entities that do not meet their targets must pay a fine & if they meet their targets within three years, they will get a 40% refund.
- Funds collected in this way will be put in an account and can be used to collect and recycle plastic packaging waste on which the environmental compensation is levied.
- It is observed annually on 11thOctober. It was declared by the United Nations (UN), which was first observed in 2012.
- A resolution to declare 11thOctober as the International Day of the Girl Child was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 19th December 2011.
- The day is dedicated to raising awareness on gender equalitywhile assuring rights and improving opportunities for girls.
- Child marriage kills more than 60 girls a dayglobally, 26 girls a day in West and Central Africa and six girls a day in South Asia.
- South Asia is followed byEast Asia and the Pacific and Latin American and the
- The deaths are majorly caused from pregnancy and childbirthresulting from child marriage.
- With school closures, health services under strain or closed, and more families being pushed into poverty, women and girls face an increased risk of violence during lengthy lockdowns.
- A further 10 million girlsare now expected to marry by 2030, leaving more girls at risk of dying.
- Earlier, according to a report published by ChildLine India the pandemic and the subsequent lockdown have proved to be new drivers of child marriagesin rural Madhya Pradesh.
- Also some activists and organisations of Karnataka have raised the issue of increased child marriages in Lockdownwith the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Ensure the safe and unrestricted participation of female humanitarian staff in all humanitarian response efforts, including needs assessments and the design, implementation, and monitoring, and evaluation of all humanitarian services at every level.
- The movement is working to deliver on the Global Acceleration Plan for Gender Equality(launched by Generation Equality Forum), which set a target to prevent nine million child marriages in five years.
- The Child Marriage Restraint Act of 1929restricts the practice of child marriage.
- The Special Marriage Act, 1954and the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006 prescribe 18 and 21 years as the minimum age of consent for marriage for women and men respectively.
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006was enacted to address and fix the shortcomings of the Child Marriage Restraint Act.
- The Union Ministry for Women and Child Development has set up a committee to examine matters pertaining to age of motherhood, imperatives of lowering Maternal Mortality Ratio and the improvement of nutritional levels among women. The Committee is headed by Jaya Jaitely.
- The Committee was proposed in the Union Budget 2020-21.
- Prevention of Child Marriage is a part of SDG 5which deals with gender equality and empowerment of all women and girls.
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)estimates suggest that each year, at least 5 million girls under 18 get married in India, which makes it home to the largest number of child brides in the world - accounting for a third of the global total.
- Nearly 16% of adolescent girls aged 15-19 are currently married.
- While the prevalence of girls getting married before age 18 has declined from 47% to 27% between 2005-2006 and 2015-2016.
- The CCEA also approved the inclusion of Potash derived from Molasses (0:0:14.5:0) under the NBS Scheme.


- The subsidy on P&K fertilisers is governed by the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme from April 2010.
- The subsidy on P&K fertilizers will be provided based on the NBS rates approved by the CCEA to ensure smooth availability of these fertilizers to the farmers at affordable prices.
- Government is making available fertilizers, namely Urea and 24 grades of P&K fertilizers to farmers at subsidized prices through fertilizer manufacturers/ importers.
- The subsidy on P&K fertilizers is being governed by NBS Scheme w.e.f. 01.04.2010.
- In accordance with its farmer friendly approach, the Govt. is committed to ensure the availability of P&K fertilizers to the farmers at affordable prices.
- This will enable smooth availability of all P&K fertilizers to the farmers during Rabi Season 2021-22 at the subsidized/affordable prices.
- It will support the agricultural sector by continuing the present subsidy levels and giving special packages of additional subsidy for DAP and three mostly consumed NPK grades.

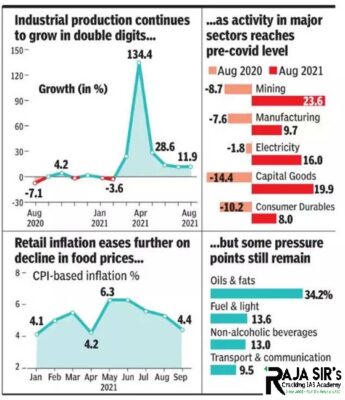
- Food inflation based on the Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI) eased to 0.68% in September from 3.11% in August.
- Within the food prices, Vegetables registered a de-growth of minus 22%, while food and beverages segment grew 1.01%.
- Inflation in the fuel and light category remained elevated at 13.63%.
- Index of industrial production (IIP) for the month of August surged 11.9%.
- The Central bank (RBI) in its latest monetary policy meeting lowered the inflation forecast at 5.3% for the current financial year (2021-22) from an earlier estimate of 5.7%.

- CPI is a measure of change in retail prices of goods and services consumed by a defined population group in a given area with reference to a base year.
- This basket of goods and services represents the level of living or the utility derived by the consumers at given levels of their income, prices and tastes.
- The consumer price index number measures change only in prices.
- Published and developed by: The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- Base Year: 2011-12.
- Importance:
- Used as an economic indicator of:
-
-
- Inflation.
- Monitoring price stability.
- Deflator in national accounts.
- Determining dearness allowance of Government employees and wage contracts between labour and employer.
- Inflation targeting in Monetary Policy by RBI.
-
- The formula for calculating Consumer Price Index is Laspeyre’s index which is measured as follows:
- [Total cost of a fixed basket of goods and services in the current period * 100] divided by Total cost of the same basket in the base period.
- Presently the consumer price indices compiled in India are:
- CPI for Industrial workers CPI(IW)
- CPI for Agricultural Labourers CPI (AL)
- CPI for Rural Labourers CPI (RL)
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees (UNME)
- CFPI is a measure of change in retail prices of food products consumed by a defined population group in a given area with reference to a base year.
- CFPI have been widely used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation.
- Published and developed by: The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Base Year: 2011-12.
- Consumer Food Price Index (CFPI) is a component of all-items Consumer Price Index.
- Three categories -rural, urban and combined - separately on an all-India basis.
- CFPI is also calculated on a monthly basis, and methodology remains the same as CPI.
| Headline Inflation | Core Inflation |
|
|
- It is an index that tracks manufacturing activity in different sectors of an economy. It is released monthly by NSO.
- Mining, manufacturing, and electricity are the three broad sectors in which IIP constituents fall.
- IIP index is currently calculated using 2011-2012 as the base year.
- It consists of 8 core Industries that constitute 38% of the total IIP.
- Electricity (Highest weightage)
- Steel
- Refinery Products
- Crude Oil
- Coal
- Cement
- Natural Gas
- Fertilizers
- Cicadas are members of the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- They are physically distinguished by their stout bodies, broad heads, clear-membraned wings, and large compound eyes.
- There are more than 3,000 species of cicadas. They occur in deserts, grasslands, and forests.
- Male cicadas produce loud noises by vibrating membranes near the base of the abdomen.
- They occur in deserts, grasslands, and forests.
- Cicadas have been used in folk medicines, religious and monetary symbols, and an important source of food.
- They act as indicators of a healthy forest ecosystem, but there are no conservation measures for them at present.
- Major threat: Rapidly diminishing natural habitat

- On May 22, 2012, a large meteor shower occurred near the town of Katol in Nagpur.
- The shower caused sonic booms or thunder-like noises, initially spreading rumours that an aircraft had crashed.
- The next day, researchers from the Geological Survey of India collected about 30 meteorite fragments with the largest weighing around a kilogram.
- International team of scientists examined a section of the highly-shocked meteorite from Katol.
- The first natural occurrence of a mineral called bridgmanite. The mineral was named in 2014 after Prof. Percy W. Bridgman, recipient of the 1946 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- About 80% of the Earth’s lower mantle is made up of bridgmanite.
- By studying this meteorite sample, scientists can decode how bridgmanite crystallized during the final stages of our Earth’s formation.
- The host rock was mainly composed of olivine, an olive-green mineral.
- Olivine is the most abundant phase in our Earth’s upper mantle.
- Our Earth is composed of different layers including the outer crust, followed by the mantle and then the inner core.
- The composition expected to be present in the Earth’s lower mantle which is at about 660 km deep.
- Studying the meteorite could also tell us more about how our Earth evolved from being a magma ocean to a rocky planet.

- A small sample of the meteorite is examined using special microscopy techniques. The mineralogy was determined using a laser micro-Raman spectrometer.
- These techniques helped identify, characterise the crystal structure of the meteorite and determine its chemical composition and texture.
- The bridgmanite in the meteorite was found to be formed at pressures of about 23 to 25 gigapascals generated by the shock event.
- High temperature and pressure in Earth’s interior have changed over billions of years causing crystallisation, melting, remelting of the different minerals before they reached their current state.
- He inaugurated the Quantum Communication Lab in C-DoT and unveiled the indigenously developed Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) solution.
- C-DoT has become India's first organisation to offer a complete portfolio of indigenous quantum secure telecom products and solutions.
- Samsung, Huawei, LG and some other companies have started working on 6G technologies which is said to be 50 times faster than 5G and is expected to be commercially launched between 2028-2030.

- 6G, or the sixth-generation wireless communications system will be built upon the shortcomings of 5G.
- It is said to be 50 times faster than 5G.
- It is expected to roll out for consumers by 2030.
- Higher millimeter-wave
- Microsecond latency
- Autonomous wireless systems
- 6G will selectively use different frequencies to measure absorption and adjust frequencies accordingly.
- This is based on the phenomenon that atoms and molecules emit and absorb electromagnetic radiation at characteristic frequencies, and the emission and absorption frequencies are the same for any given substance.
- Able to use higher frequencies than 5G networks
- To provide substantially higher capacity
- To support one microsecond-latency communication
- Extremely high data rates per device
- A very large number of connected devices
- Global connectivity
- Lowering the energy consumption with battery-free IoT devices
- It can integrate a set of previously disparate technologies, including deep learning and big data analytics.
- To handle IoT and mobile device data, strong relation has to be maintained between High Performance Computers (HPC) and 6G.
- It will provide the communication and data gathering necessary to accumulate information.
- Capacity of supporting data rate of 1 Terrabyte per second and latency will expand the scope of capabilities to support innovative applications in wireless connectivity, cognition, sensing and imaging.
- 6G will have big implications for many government and industry approaches to public safety and critical asset protection such as:
- Threat detection
- Health monitoring
- Feature and facial recognition
- Decision-making in areas like law enforcement and social credit systems
- Air quality measurements
- Gas and toxicity sensing
- Terahertz (THz) Signal:
- Generation of continuous THz signal is difficult and expensive because it has more strict requirements regarding size and has more complexity in designing the antenna/transmitter.
- The energy loss of signal is too much.
- Underwater Communication:
- 6G is also aiming to provide underwater communication.
- Radio signals are highly attenuated in salt water.
- Therefore, acoustic communication is the only option for communication which is expensive.
- Global Coverage:
- 6G will rely on the low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite having a height of 500 to 2000 km from the orbit for providing global coverage.
- LEO satellites travel very fast compared to the rotation of Earth. This leads to doppler variation and doppler shift in the network communication and cause random access, synchronization, signal detection, and signal measurement issues.
- Heavy Computation:
- 6G will combine communication with computation.
- To solve that 6G will rely on new technologies such as edge computing, federated AI, etc.
- However, implementing these technologies also has many sets of issues.
- Lack of Technology:
- The 6G has many promises to deliver, but hindered by underdeveloped real technology which could drastically advance 6G technology from 5G.
- Artificial Technology:
- 6G will be truly AI-driven mobile wireless communication.
- Implementing AI in physical layer is difficult due to the complexity of the physical layer and bounded learning capacity of AI algorithms.

- The resolution was first discussed in the 1990s. The framework proposed by Costa Rica, the Maldives, Morocco, Slovenia, and Switzerland, was passed with 43 votes in favour and 4 abstentions from Russia, India, China, and Japan.
- UNHRC consists of 47 members, elected yearly by the UN General Assembly for staggered three-year terms.
- It has the potential to shape global standards towards the environment and human rights.
- It will send a message to communities around the world struggling with climate hardship.
- As per WHO, 24.3% of the global deaths, occur due to environmental risks like air pollution and chemical exposure.

- Tatarstan is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe.
- It is a part of the Volga Federal District.
- It is one of the most important cultural centres of Russia.
- "Tatarstan" derives from the name of the ethnic group Tatars and stan means state.
- The summit aims to establish a new accord setting out targets for 2030 and 2050.
- A key proposal being debated at the conference is the “30 by 30” agenda that would afford 30% of the Earth’s land and oceans protected status by 2030.
- Global spending to protect and restore nature needs to triple this decade to about $350 billion annually by 2030 and $536 billion by 2050 to meet this target.
- Some rich country donors say a new fund for conservation is unnecessary because the United Nations’ Global Environment Facility already helps developing nations finance green projects.
- This comes at a time when calls to further regulate Facebook have intensified across the world following revelations by whistle-blower Frances Haugen.
- India is closing in on 750 million internet users and is the largest market in terms of users for many technology giants, including Facebook.
- Under Section 79 of the IT Act, intermediaries including social media firms get immunity from content posted on their platforms by third-party users.
- India’s IT Rules, which were notified in May, put in place a mechanism for social media users to flag problematic content as soon as they see it and asks companies to submit compliance reports on such complaints each month.

- The regulations follow the National Green Tribunal's advice to the environment ministry on May 20, 2019 that it should come out with regulation on appropriate use of RO-based water purification systems.
- Manufacturers of Reverse Osmosis-based water purifiers will now have to rate their appliances on efficiency and water wastage.
- Water supply agencies will have to declare the total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water being supplied.
- The move is aimed at allowing consumers to make informed decisions on the kind of water purifier needed.
- The water purifier will now come with a 'conformance label'-a star rating like label- declaring its efficiency level as well as water rejection/wastage levels.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies