- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
17th Oct 2021
GLOBAL TUBERCULOSIS REPORT 2021
World Health Organization (WHO) has released the Global Tuberculosis Report 2021 recently.
Highlights:



- India (41%) contributed the biggest drop in detection of new cases. Indonesia (14 per cent), the Philippines (12 per cent) and China (8 per cent) and 12 other countries accounted for 93 per cent of the total global drop of 1.3 million cases.
- The number of deaths due to tuberculosis (TB) has increased in 2021 as compared to 2019.
- Fewer people with the disease were diagnosed and treated, compared to 2019.
- Overall spending on essential TB services also dropped.
- 1.5 million people died from TB in 2020 (including 2,14,000 among HIV positive people).
- The increase in the number of TB deaths occurred mainly in the 30 countries with the highest burden of TB, including India.
- TB was ranked the 13th leading cause of death globally till 2019. It is now estimated to be the second leading cause, only after COVID-19.
- Disruption in access to TB services and a reduction in resources due to COVID pandemic.
- Lack of funding for 98% of reported TB cases in low- and middle-income countries.
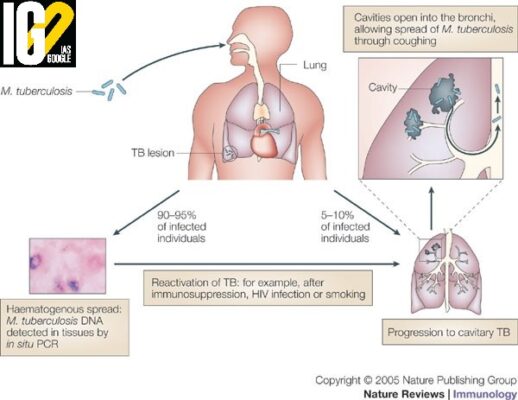
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria.
- TB generally affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain.
- It is spread from one person to the next through the air via sneeze or cough of the infected person.
- TB infection happens in four stages: the initial macrophage response, the growth stage, the immune control stage, and the lung cavitation stage.
- Active TB Disease: Active TB is an illness in which the TB bacteria are rapidly multiplying and invading different organs of the body. It is symptomatic and contagious.
- Miliary TB: Miliary TB is a rare form of active disease that occurs when TB bacteria find their way into the bloodstream.
- Latent TB Infection: The bacteria in the body are inactive and cause no symptoms. It is not contagious. Latent TB can turn into active TB, in absence of treatment.
- Fever, chills, night sweats, loss of appetite, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Significant nail clubbing may also occur.
- It is treatable and curable.
- It is treated with six-month course of four antimicrobial drugs.
- Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) disease.
- First-line anti-TB drugs: Isoniazid and rifampicin.
- Drug-resistant tuberculosis is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to at least first-line treatment anti-TB drugs.
- Tuberculosis is one of India’s most critical health challenges. It accounts for 30% of the world’s TB cases.
- State TB Index:
- Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh were the best performing states for TB control in category of states with 50 lakh population.
- Tripura and Nagaland were best-performing in the category of states having less than 50 lakh population.
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu were selected as the best performing Union Territories.
- WHO’s End TB Strategy sets targets to reduce TB deaths by 95% and to cut new cases by 90% between 2015 and 2035, and to ensure that no family is burdened with catastrophic expenses due to TB. It sets interim milestones for 2020, 2025, and 2030.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare releases the annual TB report with an aim to eliminate TB form the country by 2025, five years ahead of WHO’s target.
- They also release a Joint Monitoring Mission (JMM) report, a manual on Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) to TB patients under NIKSHAY system, a Training Module, and the quarterly newsletter NIKSHAY Patrika.
- National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- Nikshay Yojana:
- It is a direct benefit transfer (DBT) scheme for nutritional support to Tuberculosis (TB) patients rolled out in April 2018 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme under National Health Mission (NHM).
- Nikshay Ecosystem:
- It is a one-stop National TB information system to manage patients’ information and monitor program activity.
- Saksham Project:
- It is a counselling project for DR- TB (drug resistant) patients undertaken by Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign:
- It has three strong pillars which include clinical approach, public health component and active community participation.
- It aims to improve and expand the reach of TB care services across the country by 2022.
- It has been working to set common standards toward issuing CBDCs as some proceed with experiments.
- Any digital currency issued by a central bank must "support and do no harm" to the bank's ability to fulfil its mandate on monetary and financial stability, and must also meet rigorous standards.
- If issued, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) would complement cash and could act as a liquid, safe settlement asset and an anchor for the payments system.
- But the currencies must be issued in a way that do not infringe upon the central banks' mandates, and meet rigorous standards of privacy, transparency and accountability for protection of user data.
- Any central bank digital currency (CBDC) should be grounded in long-standing public commitments to transparency, rule of law and sound economic governance.
- While CBDCs could enhance cross-border payments, a "shared responsibility to minimize harmful spillovers to the international monetary and financial system."

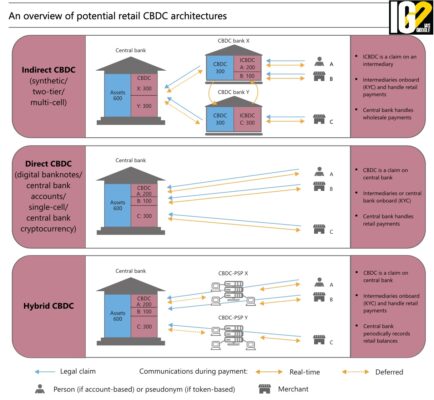
- The term CBDC refers to the virtual form of a fiat currency.
- A CBDC is an electronic record or digital token of a country's official currency.
- It is issued and regulated by the nation's monetary authority or central bank. They are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government.
- CBDCs can simplify the implementation of monetary and fiscal policy and promote financial inclusion in an economy by bringing the unbanked into the financial system.
- Because they are a centralized form of currency, they may erode the privacy of citizens.
- It is considered a form of legal tender that can be used for the sale and purchase of goods and services along with kinds of transactions.
- A central bank digital currency is the virtual form of fiat money.
- The goal is to provide users with convenience and security of digital as well as the regulated, reserve-backed circulation of the traditional banking system.
- They are designed to function as a unit of account, store of value, and medium of exchange for daily transactions.
- Global central banks have stepped up efforts to develop their own digital currencies to modernize financial systems and speed up domestic and international payments. China has been leading the pack.
- The implementation of standards facilitate access to national and international markets for Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Standards form the foundation of international trade and play a key role in strengthening global partnerships for sustainable development.
- BIS formulate need-based standards considering the need of consumers, ensuring efficient, reliable goods and promote supply chains under the Sustainable Development Goals.
- World Standards Day is observed on 14 October every year.
- Aim: To spread awareness about the importance of standardization to the global economy among regulators, consumers, and industry.
- Theme: ‘Standards for sustainable development goals - shared vision for a better world’.
- Delegates from 25 countries on 14 October 1946 in London, decided to design a global organisation for facilitating Standardisation.
- In 1970 the first World Standards Day was inaugurated by, the then President of the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO).
- The process of Standardisation is an important tool for facilitating trade and overcoming technical challenges.
- It honors the contributions of organisations like:
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
- International Ethics Standards Board for Accountants (IESBA)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- It creates awareness about the importance of Standardisation in today’s globalized world.
- The ISO is an international nongovernmental organization made up of national standards bodies.
- It develops and publishes a wide range of proprietary, industrial, and commercial standards.
- It comprised of representatives from various national standards organizations.
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was founded in 1947.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- It publishes technical reports, technical specifications, publicly available specifications, and guides.
- It plays an important role in facilitating world trade by providing common standards among different countries.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is the National Standard Body of India.
- It was established on 23rd December 1986.
- Headquarters: Manak Bhawan, Delhi.
- BIS through its activities of standardization, benefiting the national economy by providing:
- Safe, reliable, and quality goods
- Minimizing health hazards to consumers
- Protecting the environment
- Promoting exports and imports substitute
- Controlling over proliferation of varieties etc.
- Harmonious development of the activities of standardization.
- Marking and quality certification of goods.
- To provide thrust to standardization and quality control for growth and development of industry, to meet the needs of consumers.
- Standards formulation
- International activities
- Product Certification
- Hallmarking
- Laboratory services
- Training services - National Institute of Training for Standardisation
- Consumer Affairs and Publicity
- For every $100 spent on development aid, only 50 cents are invested in protecting countries from the impact of disasters.
- Financing for disaster risk reduction makes up a small fraction of the overall investments in development aid.
- $133 billion of disaster-related Overseas Development Assistance (ODA) made available between 2010 and 2019, which is only 11 per cent of the overall aid ($1.17 trillion).
- Human-induced climate change affects weather and climate extremes in every region of the globe.
- Of the overall disaster-related ODA between 2010 and 2019.
- The $5.5 billion spent on Disaster Risk Reduction, accounts for just 0.5 per cent of the total amount spent on disaster-related aid.
- International Day for Disaster Risk Reduction is observed on October 13, every year.
- Aim: To promote a global culture of risk awareness and disaster reduction.
- Theme: “International cooperation for developing countries to reduce their disaster risk and disaster losses”.
- The day celebrates, how communities around the world are reducing their exposure to disasters and raising awareness about the importance of risks they face.
- The International Day for Disaster Risk Reduction was started in 1989, after a call by the United Nations General Assembly to promote a global culture of risk-awareness and disaster reduction.
- In 2015, during the Third UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction in Sendai, Japan, the community focused on the catastrophes that severely impact at the local level, causing loss of life and significant social and economic turmoil.
- Highlighting and spotting emerging trends
- Revealing disturbing patterns, examining behavior
- Presenting progress in reducing risk.
- India got 184 votes in the 193-member assembly, while the required majority was 97.

- The 76th UN General Assembly held elections for 18 new members of the U.N. Human Rights Council who will serve for a period of three years, starting in January 2022.
- India’s current term was set to end on December 31 2021.
- For election for the term 2022-2024, there were five vacant seats in the Asia-Pacific States category - India, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Qatar and United Arab Emirates.
- It is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system.
- It was created by the United Nations General Assembly on 15 March 2006.
- It meets at the UN Office at Geneva, Switzerland.
- It replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- The Council’s work is reviewed in every five years by the UN General Assembly.
- The UNHRC holds regular sessions three times a year, in March, June, and September.
- The Council is made up of 47 United Nations Member States which are elected by the UN General Assembly.
- The 193-member General Assembly elected by secret ballot Argentina, Benin, Cameroon, Eritrea, Finland, Gambia, Honduras, India, Kazakhstan, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Montenegro, Paraguay, Qatar, Somalia, UAE and the USA for the 2022-2024 term on the Council.
- The members of the Council shall serve for a period of three years and shall not be eligible for immediate re-election after two consecutive terms.
- The membership is based on equitable geographical distribution, and seats are distributed among regional groups.
- Group of African States (13), Group of Asia-Pacific States (13), Group of Eastern European States (6), Group of Latin American and Caribbean States (8) and Group of Western European and other States (7).
- It investigates allegations of breaches of human rights in United Nations member states
- Addresses important thematic human rights issues such as:
- Freedom of association and assembly
- Freedom of expression
- Freedom of belief and religion
- Women's rights
- LGBT rights
- Rights of racial and ethnic minorities

- The fund will be available to accredited party delegates, civil society observers and journalists from developing countries.
- Participants who contract Covid-19 will be required to isolate for 10 full days in their accommodation, which could extend their stay in Glasgow.
- COP26 organisers are expecting up to 25,000 people to attend the conference while 120 heads of state have confirmed they will participate in a two-day leaders’ summit on 1-2 November.
- Under the code of conduct, all COP26 participants need to wear a face covering unless they are eating, drinking, sitting in an office or meeting space or negotiating and ensure one meter of physical distancing.
- Every day negative result will be required to enter the conference center.
- The UK has among the highest levels of reported Covid infection in the world, averaging 55 daily cases for every 100,000 people.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies