- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
18th Aug 2021
GATI SHAKTI MASTER PLAN THAT PM MODI ANNOUNCED ON INDEPENDENCE DAY
Recently, the Prime Minister has launched the PM Gati Shakti Master Plan on the 75th Independence Day.
Need for PM Gati Shakti Master Plan
 Govt to launch Rs 100 lakh cr 'Gati Shakti' national master plan.(photo:BJP twitter)[/caption]
Govt to launch Rs 100 lakh cr 'Gati Shakti' national master plan.(photo:BJP twitter)[/caption]





- India has been working for a reset of its logistics sector involving railways, highways, inland waterways and airports to put in place an effective transportation grid.
- The logistics make up about 13% of costs for Indian companies, making exports uncompetitive vis-a-vis China.
- India needs to increase both manufacturing and exports because every product that is sold globally from India is attached to India.
 Govt to launch Rs 100 lakh cr 'Gati Shakti' national master plan.(photo:BJP twitter)[/caption]
Govt to launch Rs 100 lakh cr 'Gati Shakti' national master plan.(photo:BJP twitter)[/caption]
- It is a Rs. 100 lakh-crore project for developing ‘holistic infrastructure’.
- It is a national infrastructure master plan which will make a foundation for holistic infrastructure.
- It will help raise the global profile of local manufacturers and help them compete with their counterparts worldwide.
- It raises possibilities of new future economic zones.
- It is aimed at easier interconnectivity between road, rail, air and waterways to reduce travel time and improve industrial productivity.
- It is aimed at breaking silos within the transport network to reduce travel time and improve industrial productivity.
- It aims at improving industrial productivity, making manufacturing globally competitive, facilitating future economic zones and creating employment.
- The earthquakes have been wreaking havoc in Haiti since at least the 18th century, when the city of Port-au-Prince was destroyed twice in 19 years.
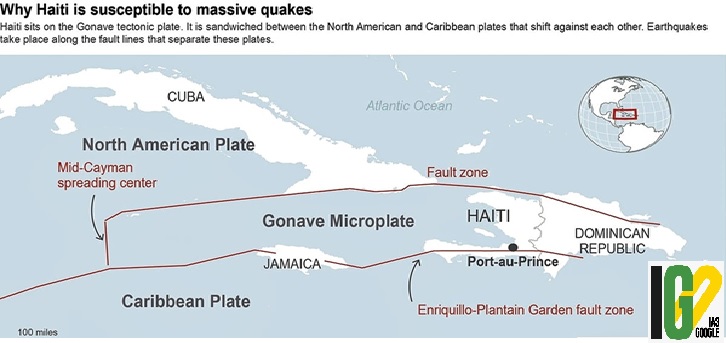
- In 2010, devastating earthquake had occurred along the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone, which cuts across Haiti’s southwestern Tiburon Peninsula.
- It is likely the source of three other big earthquakes in Haiti between 1751 and 1860, two of which destroyed Port-au-Prince.

- Haiti sits near the intersection of two tectonic plates i.e. the North American plate and the Caribbean plate that make up the Earth’s crust.
- The earthquakes can occur when those plates move against each other and create friction.
- The multiple fault lines between those plates cut through or near the island of Hispaniola, which Haiti shares with the Dominican Republic.
- Hispaniola sits in a place where plates transition from smashing together to sliding past one another.
- It is a combination of factors that include a seismically active area, a high population density of 11 million people and buildings that are often designed to withstand hurricanes and not earthquakes.
- Faults are discontinuities or cracks that are the result of differential motion within the earth’s crust.
- The vertical or lateral slippage of the crust along the faults causes an earthquake.
- When compressional or tensional force is beyond the elastic limit of rocks, they break and get displaced. This process is called faulting.
- Normal Fault: It is created because of tensional force. In such type of fault, crustal blocks/rocks are displaced away from each other causing expansion of crust.
- Reverse Fault: It is created due to compressional force. When the compressional force is beyond the elastic limit of rocks, they break and gets displaced towards each other. It leads to contraction of crust.
- Thrust Fault: It is a special type of reverse fault in which fault angle is low.
- Transcurrent Fault: When the crustal blocks are displaced parallel to each other, transcurrent faults are formed.

- It is a new scheme that is applicable with effect from January 1st, 2021, formed to replace the existing MEIS (Merchandise Exports from India Scheme).
- The rebate will be issued in the form of a transferable duty credit/ electronic scrip (e-scrip) which will be maintained in an electronic ledger by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC).
- It is to be implemented by Customs through a simplified IT System.
- Refund of the previously non-refundable duties and taxes: Mandi tax, VAT, Coal cess, Central Excise duty on fuel etc. will now be refunded under this particular scheme.
- All the items under the MEIS and the RoSTCL (Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies) are now under the purview of the RoDTEP Scheme.
- Automated system of credit: The refund will be issued in the form of transferable electronic scrips.
- These duty credits will be maintained and tracked through an electronic ledger.
- Quick verification through digitisation: Through the introduction of the digital platform, the clearance happens at a much faster rate.
- Verification of the records of the exporters will be done with the help of an IT-based risk management system to ensure speed and accuracy of transaction processing.
- Multi-sector scheme: Under RoDTEP, all sectors, including the textiles sector, are covered, so as to ensure uniformity across all areas.
- The Employment Oriented Sectors like Marine, Agriculture, Leather, Gems & Jewellery etc. are covered under the Scheme.

- Duties/ taxes/ levies, at the Central, State & local level, borne on the exported product, including prior stage cumulative indirect taxes on goods & services used in production of the exported product, and
- Such indirect Duties/ taxes/ levies in respect of distribution of exported products.
- The Scheme shall not be available in respect of duties and taxes already exempted or remitted or credited.
- The determination of ceiling rates under the Scheme will be done by a Committee in the Department of Revenue/Drawback Division with suitable representation of the DoC/DGFT.
- The Scheme will operate in a Budgetary framework for each financial year and necessary calibrations and revisions shall be made to the Scheme benefits.
- All sectors, including the textiles sector, may enjoy the benefits of the RoDTEP Scheme. Labor-intensive sectors that enjoy benefits under the MEIS Scheme will be given a priority.
- Manufacturer exporters and merchant exporters (traders) are both eligible for the benefits of this scheme.
- There is no particular turnover threshold to claim the RoDTEP.
- Re-exported products are not eligible under this scheme.
- To be eligible to avail the benefits of this scheme, the exported products need to have the country of origin as India.
- Special Economic Zone Units and Export Oriented Units are also eligible to claim the benefits under this scheme.
- Where goods have been exported via courier through e-commerce platforms, RoDTEP scheme applies to them as well.

- The scheme for zero rating of exports will boost India’s exports & competitiveness in the global markets and the rates of RoDTEP will cover 8555 tariff lines.
- The export centric industries are being reformed and introduced to better mechanisms so as to increase their competitiveness, boost exports, generate employment and contribute to the overall economy.
- It is going to give a boost to Indian exports by providing a level playing field to domestic industry abroad.
- Its support will be available to eligible exporters at a notified rate as a percentage of Freight On Board (FOB) value.

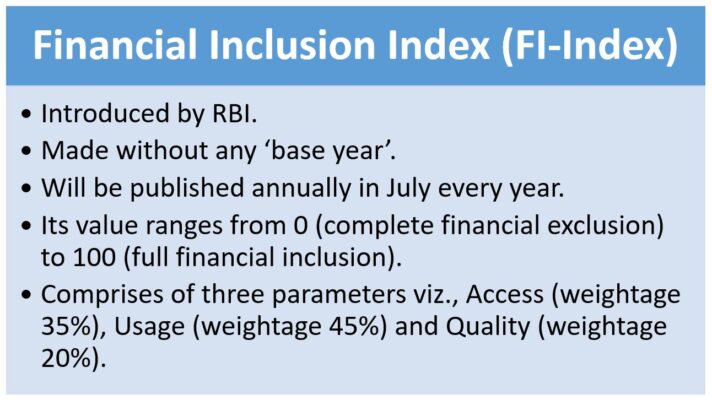
- It is an annual publication of Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- It captures information on various aspects of financial inclusion in a single value ranging between 0 and 100, where 0 represents complete financial exclusion and 100 indicates full financial inclusion.
- It comprises three broad parameters i.e. Access (35%), Usage (45%), and Quality (20%), with each of these consisting of various dimensions computed based on a number of indicators.
- It has been constructed without any ‘base year’ and it reflects cumulative efforts of all stakeholders over the years towards financial inclusion.
- The annual FI-Index for the period ending March 2021 is 53.9 as against 43.4 for the period ending March 2017.
- There has been a very good improvement of 10.5 points in the FI Index between 2017 and 2021 because this was the period when the government and RBI gave a big push to financial inclusion.

- It has a unique feature of the quality parameter, which captures the quality aspect of financial inclusion as reflected by financial literacy, consumer protection, and inequalities and deficiencies in services.
- It has been conceptualized as a comprehensive index incorporating details of banking, investments, insurance, postal, and the pension sector.
- It is responsive to ease of access, availability and usage of services, and quality of services, comprising 97 indicators in all.

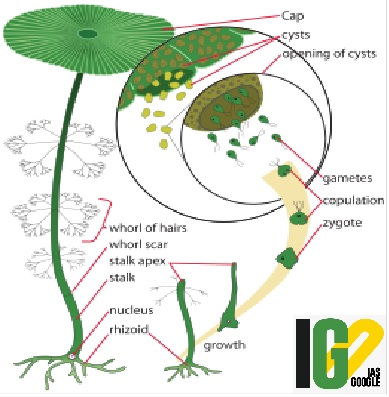
- It is a stunning bright green algae, resembling an umbrella or a mushroom.
- It is measured as small as 20 to 40 mm and has grooves on its cap measuring 15 to 20mm in diameter.
- It is named after the imaginary sea mermaid, Acetabularia jalakanyakae.
- Jalakanyakae is a Sanskrit word that literally means a mermaid.
- It is very primitive and is a single-cell organism.
- Its characteristic feature is that its nucleus forms a rhizoid structure, which facilitates the algae to attach itself to shallow rocks.

- It is a member of a very diverse group, the green algae.
- The other members of the same group that we will consider are Oedogonium, Chlamydomonas and Cladophora, all of which are quite different in form and structure.
- It has an unusual structure by being large, unicellular and possessing features that might be considered organs i.e. ‘roots, stems and leaves’.
- The single cell is attached to the substrate by root-like cellular extensions.
- It is a typical photoautotroph, using the energy of sunlight to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and then using the carbohydrates as an energy source in cellular respiration.
- It is generally found in warm, marine waters.

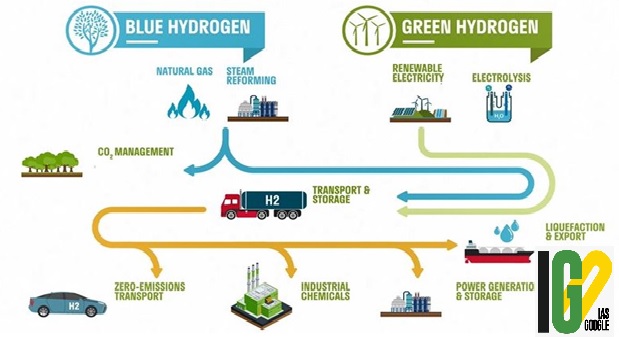
- It is produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrolyzer that may be powered by electricity generated from renewable energy sources.
- It is distinct from grey hydrogen, which is produced from methane and releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Green Chemicals like ammonia and methanol can directly be utilised in existing applications like fertilisers, mobility, power, chemicals, shipping among others.
- Green Hydrogen blending up to 10 per cent may be adopted in City Gas Distribution (CGD) networks to gain widespread acceptance.
- Cost competitive: The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) has said in a recent report that currently all hydrogen consumed in India comes from fossil fuels. However, by 2050, nearly 80% of India's hydrogen is projected to be green.
- It is clear that green hydrogen will become the most competitive route for hydrogen production by around 2030 which would be driven by dramatic cost declines in key production technologies such as electrolyzers and solar PV.
- Power source of energy-intensive industries: While wind and solar energy can provide the electricity to power homes and electric cars, green hydrogen could be an ideal power source for energy-intensive industries like concrete and steel manufacturing.
- Addresses the problem of intermittency in existing renewable energy plants: The renewable energy to create the fuel can help solve the problem of intermittency that plagues wind and solar power, and so it is essentially efficient storage.
- Zero emissions from aircraft: The energy density of green hydrogen is three times that of jet fuel, making it a promising zero-emissions technology for aircraft.
- Production centres are situated away from demand centres: The most renewable energy resources that can produce low-cost electricity are situated far from potential demand centres.
- Lack of decarbonization ability of Indian industries: The near-term promise of hydrogen lies in “hard-to-abate” industrial sectors like steel, refining, fertilizer & methanol.
- These industries contribute to 11 per cent of India’s total emissions and have limited opportunities to decarbonize because fossil fuels play an integral role in their core processes.
- Massive expansion of renewable generation: It is noted that hydrogen fuels need renewable energy to be green, which will require a massive expansion of renewable generation to power the electrolysis plants that split water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Lack of storage infrastructure: The green hydrogen is hard to store and transport without a pipeline and in some places, hydrogen is lot more expensive than other fuels such as natural gas.
- Its storage requires compression to 700 times atmospheric pressure, refrigeration to 253 degrees Celsius.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies