- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
26th Sep 2021
HOW A GUPTA ERA TEMPLE IN ETAH HAS PUT FOCUS BACK ON SHANKHALIPI SCRIPT
The discovery of Gupta era temple in Etah district of Uttar Pradesh by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has put back the focus on the shankhalipi script.
 Indian scientists have developed a new sustainable and affordable solution for converting keratin waste such as human hair, wool, and poultry feathers to fertilizers, pet, and animal feeds.
Indian scientists have developed a new sustainable and affordable solution for converting keratin waste such as human hair, wool, and poultry feathers to fertilizers, pet, and animal feeds.



 A 14-year-old Tamil Nadu schoolgirl’s solar-powered ironing cart project and a Delhi entrepreneur’s agricultural waste recycling concept were named among 15 finalists for the first-ever Earthshot Prize 2021.
A 14-year-old Tamil Nadu schoolgirl’s solar-powered ironing cart project and a Delhi entrepreneur’s agricultural waste recycling concept were named among 15 finalists for the first-ever Earthshot Prize 2021.



- The script in the temple was deciphered as saying, ‘Sri Mahendraditya’, the title of Kumaragupta-I of the Gupta dynasty.
- Shankhalipi or shell-script is a term used to describe ornate spiral characters assumed to be Brahmi derivatives that look like conch shells or shankhas.
- They are found in inscriptions across north-central India and date to between the 4th and 8th centuries.
- Shankhalipi is found to be engraved on temple pillars, columns and rock surfaces.
- Both Shankhalipi and Brahmi are stylised scripts used primarily for names and signatures.
- The inscriptions consist of a small number of characters, suggesting that the shell inscriptions are names or auspicious symbols or a combination of the two.
- The script was discovered in 1836 on a brass trident in Uttarakhand’s Barahat by English scholar James Prinsep.
- He was the founding editor of the Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal.
- Later, two more similar scripts were found at Nagarjuna group of caves in the Barabar Hills near Gaya, Bihar.
- Prominent sites with shell inscriptions include:
- Mundeshwari Temple in Bihar
- Udayagiri Caves in Madhya Pradesh
- Mansar in Maharashtra
- Some cave sites of Gujarat and Maharashtra
- Also reported in Indonesia’s Java and Borneo.
- The attempts to decipher shell script have not been successful.
- No such inscriptions with dates or numbers have been reported so far even as their chronology can be determined by the objects on which they are written.
- For a comprehensive review of National Cadet Corps (NCC) in order to make it more relevant in changed times.
- To suggest measures to empower NCC cadets to contribute more effectively towards nation building
- To propose ways for gainful engagement of NCC Alumni for betterment of the organisation
- To recommend best practices of similar international youth organisations for inclusion in NCC curriculum
 Indian scientists have developed a new sustainable and affordable solution for converting keratin waste such as human hair, wool, and poultry feathers to fertilizers, pet, and animal feeds.
Indian scientists have developed a new sustainable and affordable solution for converting keratin waste such as human hair, wool, and poultry feathers to fertilizers, pet, and animal feeds.
- These wastes are inexpensive sources of amino acids and protein, underlining their potential to be used as animal feed and fertilizer.
- The key technology behind this involves pre-treatment followed by hydrolysis of keratin using a technique called Hydrodynamic Cavitation.
- Hydrodynamic cavitation is the process of vaporisation, bubble generation and bubble implosion which occurs in a flowing liquid as a result of a decrease and subsequent increase in local pressure.

- Messenger RNA or mRNA technology, used in Covid-19 vaccines, works by teaching our cells to recognize and protect us against infectious diseases.
- The challenge with this technology is that it must be kept cold to maintain stability during transport and storage.
- If the project is successful, plant-based mRNA vaccines — which can be eaten —can be stored at the room temperature.
- The project is backed by a US $500,000 grant from the US National Science Foundation.
- It has three goals:
- Showing that DNA containing the mRNA vaccines can be successfully delivered into the part of plant cells where it will replicate
- Demonstrating the plants can produce enough mRNA to rival a traditional shot
- Determining the right dosage.
- The project will utilise nanotechnologies to deliver genetic material to the chloroplasts.
- Chloroplasts are small organs in plant cells that convert sunlight into energy the plant can use.
- They are also an untapped source for making desirable molecules.
- A single plant would produce enough mRNA to vaccinate a single person, with long term goal of people growing it in their own gardens.
- The Award has been instituted to promote Laboratory Quality and performance improvement in the country.
- It will ensure the laboratory’s commitment to achieve excellence in providing high precision testing and calibration services with the national/international quality systems legislations, including Health, Safety & Environment.
- It is open to all operational Laboratories pertaining to Testing, Calibration & Medical including their Proficiency Testing Providers & Reference Material Producers located in India.
- Late Prof. S.K. Joshi was a luminary in the field of Science and Academica.
- He made a significant contribution in improving scientific research in India by serving as President-INSA, DG-CSIR, Director-NPL and Chairman-NABL.
- Prof. Joshi was felicitated with Padma Bhushan, Padma Shri, CV Raman Medal of INSA and other prestigious awards.

- Petrol and diesel will not be brought under the GST regime yet.
- GST rate on biodiesel, which is supplied to oil marketing companies for blending with diesel, has been reduced from 12% to 5%.
- GST rates on Retro Fitment Kits for vehicles, used by persons with special disabilities, have also been reduced to 5%.
- Online food delivery aggregator firms Swiggy and Zomato will be liable to pay GST and not the restaurant partners.
- Food delivery apps will now collect and deposit GST with the government.
- GST rate on fortified rice kernels for schemes like integrated child development schemes has been recommended to be reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Transport of export goods by vessels and air has been exempt from GST till September 30. This exemption was given as exporters were facing difficulties in getting a refund of ITC (Input Tax Credit) due to technical glitches on the GST portal.
- National permit fees for granting permits to goods carriages (charged by the states) has been exempted from the GST regime.
- Cess to pay back compensation loans taken by Centre and then transferred to states last fiscal and this fiscal will continue till March 2026.
- Beyond June 2022, the cess will be collected only to repay the loans taken by the states
- Inverted duty structure on footwear and textiles will be corrected from January 1, 2022.
- On locomotives and certain railway parts, the GST rate has been increased to 18% from 12% to correct the inverted duty structure.
- GST of 12% will be applicable on specific renewable devices.
- Concessional GST rates on COVID-19 related drugs have been extended till December 31.
- GST rates on cancer-related drugs such as Keytruda etc. will come down from 12% to 5%.
- Expensive imported drugs such as Zolgensma and Viltesto are exempted from GST.
- They are used to treat Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), & cost around Rs 16 crores.
- GST Council is the governing body of GST having 33 members.
- Out of which 2 members are of Centre and 31 members are from 28 state and 3 Union territories with legislation.
- The council contains the following members:
- Union Finance Minister (as chairperson)
- Union Minister of States in charge of revenue or finance (as member)
- Ministers of states in charge of finance or taxation or other ministers as nominated by each state’s government (as member).
- GST Council is an apex member committee to modify, reconcile or to procure any law or regulation based on the context of goods and services tax in India.
- The council is responsible for any revision or enactment of rule or any rate changes of the goods and services in India.

- While addressing the G-33 Virtual Informal Ministerial Meeting, India stated that historical asymmetries and imbalances in the agreement must be corrected to ensure a rule-based, fair, and equitable order.
- G-33 must strive for positive outcomes on a permanent solution to public stockholding for food security purposes, finalization of a safeguard mechanism and a balanced outcome on domestic support.
- The G-33 Virtual Informal Ministerial Meeting was organised by Indonesia.
- It aimed to discuss the agricultural priority issues of G-33 and way forward for the 12th Ministerial Conference of WTO, scheduled to be held from November 30 to December 3, 2021.
- The agreement came into force in 1995.
- To address government policies that distort markets and restrict trade.
- It initiated reductions in subsidies and trade barriers to make markets fairer and more competitive.
- It guided members to continue negotiations for further reform, considering concerns like food security and the environment.
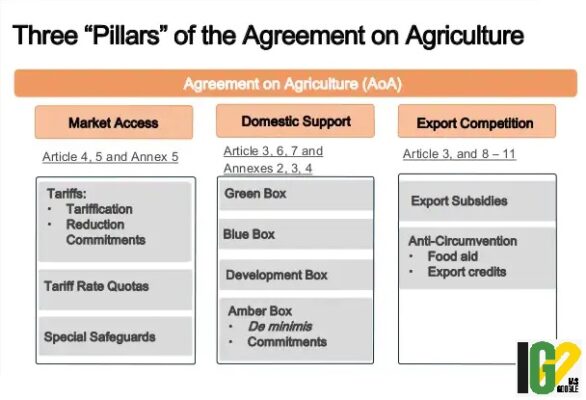
- Market Access:
- Under the reform Programme, the developing country members have converted their non-tariff measures to equivalent bound tariffs.
- Additional market access is provided through tariff rate quotas, and the tariffs are being reduced.
- Contingency protection is provided through special safeguards, and transparency works through notifications.
- Domestic Support:
- The present rules and commitments on agriculture are called the “Uruguay Round reform Programme”.
- To ensure the specific binding commitments in the areas of market access and export competition are not undermined through domestic support measures.
- a) The Green Box
- Support with no, or minimal, distortive effect on trade are referred to as “Green Box” measures.
- They have to be government-funded (not by charging consumers’ higher prices) and must not involve price support.
- The measures are exempted from reduction commitments and, can be increased without any financial limitation under the WTO.
- The Green Box applies to both developed and developing country Members.
- In case of developing countries special treatment is provided in respect of governmental stockholding programmes for food security purposes and subsidized food prices for urban and rural poor.
- It covers government service programmes including general services provided by governments, public stockholding programmes for food security purposes and domestic food aid.
- It provides for the continuation of programmes such as research, including general research, research in connection with environmental programmes, and research programmes relating to products.
- b) Amber Box
- Trade-distorting support are known as “Amber Box” measures.
- Government buying-in at a guaranteed price (market price support) is considered as amber box category.
- The aggregate monetary value of Amber Box measures is, with certain exceptions, subject to reduction commitments.
- c) Blue Box
- Direct payments under production limiting programmes are termed as “Blue Box” measures.
- They exempt from commitments if payments are made on fixed areas and yield or a fixed number of livestock.
- Such payments fit into this category if they are made on 85 per cent or less of production in a defined base period.
- Here production is required in order to receive the payments, but the actual payments do not relate directly to the current quantity of that production.
- Export competition/subsidies
- Export subsidies subject to product-specific reduction commitments within the limits specified in the schedule of the WTO Member concerned.
- Any excess of budgetary outlays for export subsidies or subsidized export volume over the limits specified in the schedule which is covered by the “downstream flexibility” provision of Article 9.2(b) of the Agreement on Agriculture.
- Subsidies consistent with the special and differential treatment provision for developing country Members.
- Subsidies other than those subject to reduction commitments if they are in conformity with the anti-circumvention disciplines of Article 10 of the Agreement on Agriculture.

- The announcement was made at the Major Economies Forum on Energy and Climate (MEF), hosted virtually by the White House.
- Countries joining the Global Methane Pledge commit to:
- A collective goal of reducing global methane emissions by at least 30% by 2030, compared with 2020 levels.
- Moving towards using best available inventory methodologies to quantify methane emissions, with a particular focus on high emission sources.
- Delivering on the Pledge would reduce warming by at least 0.2 degrees Celsius by 2050.
- As the atmospheric lifetime of methane is short, taking action now can rapidly reduce the rate of global warming.
- It will also produce benefits like improving public health and agricultural output.
- Methane is a greenhouse gas which is 80 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of its global warming capacity.
- Approximately 40% of methane emitted is from natural sources.
- About 60% comes from human-influenced sources, which include livestock farming, rice agriculture, biomass burning and so forth.
- It is the biggest cause of climate change after carbon dioxide (CO2). It accounts for about half of the 1.0 degrees Celsius net rise in global average temperature since the pre-industrial era.
- Global Methane Initiative (GMI) is a voluntary, collaborative effort to reduce methane gas emissions and advance methane recovery and use as a clean energy source.
- The initiative began as the "Methane to Markets Partnership" in November 2004. It brings together national governments, private sector entities, development banks, NGOs and other interested stakeholders.
- The initiative currently focuses on five sectors (known sources of anthropogenic methane emissions): agriculture, coal mining, municipal solid waste, municipal wastewater, and oil and gas systems.
- GMI Partner Countries together contribute approximately 70% of the world's anthropogenic methane emissions.
- India is a founder partner of GMI.
- India has announced a renewable energy capacity goal of 450 GW by 2030.
- The Indian Railways plans to fully electrify its tracks by 2023, and has committed to net-zero emissions by 2030.
- The meeting was being hosted by Tajikistan, also saw the inclusion of Iran as a new member of the SCO.
- Indian PM commended the step to include Saudi Arabia, Egypt and Qatar as new dialogue partners of the regional organisation.
- The political change in Afghanistan did not lead to an inclusive system and the process was not conducted through negotiation.
- The Taliban has declared an “interim government” in Kabul but India has not yet recognised that set-up.
- The neighbours of Afghanistan would be seriously impacted by the developments in that country.
- He expressed India’s support for the “central role” of the United Nations in the global deliberation regarding the current system in Afghanistan.
- The SCO members have been dealing with terrorism and that was why they should ensure that the territory of Afghanistan was not used to export terrorism.
- Terrorist and extremist ideologies will receive encouragement if Afghanistan continues to remain unstable and in the grip of fundamentalist forces.
- A large number of advanced weapons were left behind by western powers in Afghanistan, and cautioned that the country could emerge as the source of uncontrolled flow of drugs, illegal weapons and human trafficking.
- To deal with the fallout of the volatile situation in Afghanistan, he urged the SCO member-countries to frame a “code of conduct” to stop terror financing and cross-border terrorism.
- The SCO member-countries should adopt strong and common norms to deal with the matter.
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental political, economic and military organization founded by: China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistanin 2001 in Shanghai.
- Shanghai Five group was founded in 1996 by all the current SCO members except Uzbekistan.
- After the inclusion of Uzbekistan in 2001, it was renamed as SCO.
- Aim: Regional development and security issues (terrorism, ethnic separatism and religious extremism)
- Official Languages: Russian and Mandarin
- The Heads of State Council (HSC): Highest decision-making body in the SCO.
- The Heads of Government Council (HGC): Second highest body that deals with the grouping’s trade and economic agenda besides approving its annual budget.
- The Secretariat
- The Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS)– combats regional terrorism, separatism and
- extremism.
- 42% of the world’s population
- 20% of the global GDP.
- 4 of its members (India, Russia, China and Pakistan) are nuclear powers and 2 (Russia and China) are permanent members of the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- A counterweight to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
- It is a Russia-led military alliance of seven former Soviet states.
- Created in: 2002
- Current members: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russian Federation & Tajikistan
- Observers: Afghanistan and Serbia
- Objective: To ensure the collective defence of any member that faces external aggression.
- Counterpart of: NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
- Presidency system: Rotating presidency system
- Highest body: Collective Security Council (CSC)
- Counter cyber warfare, narcotics trafficking, the illegal circulation of weapons, transnational
- crime, and terrorism.
- Developed law enforcement training for its members.
 A 14-year-old Tamil Nadu schoolgirl’s solar-powered ironing cart project and a Delhi entrepreneur’s agricultural waste recycling concept were named among 15 finalists for the first-ever Earthshot Prize 2021.
A 14-year-old Tamil Nadu schoolgirl’s solar-powered ironing cart project and a Delhi entrepreneur’s agricultural waste recycling concept were named among 15 finalists for the first-ever Earthshot Prize 2021.
- They will now receive tailored support and resources from the Earthshot Prize Global Alliance Members, a network of private sector businesses around the world.

- The most prestigious global prize for the environment was launched by Britain’s Prince William in 2020, with a fund of 50-million-pound.
- Aim: To fund the most innovative solutions to the world’s most pressing environmental challenges.
- It is centred around five Earthshots goals:
- Protect and restore nature,
- Clean our air,
- Revive our oceans,
- Build a waste-free world and
- Fix our climate.
- Five prizes worth of one million-pound prizes will be awarded each year for the next ten years, providing at least 50 solutions to the world’s greatest environmental problems by 2030.
- Each Earthshot is underpinned by scientifically agreed targets including UN Sustainable Development Goals and other internationally recognised measures.

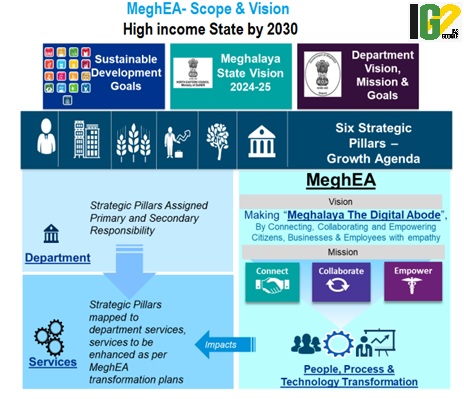
- The project aims to improve service delivery and governance for the people using power of Digital technologies.
- The initiative is spread across 6 pillars i.e. Governance, Human Resources, Entrepreneurship, Primary Sector, Infrastructure and Environment, and envision to make Meghalaya a high-income state by 2030.
- Coordinate all ICT initiatives to get a better holistic perspective, boost IT planning effectiveness and optimize costs and investments for better returns.
- Ensure that state government applications and systems provide end-users with information they need to make decisions and influence government operations.
- Craft an ecosystem for the digital economy to boost shared prosperity, by leveraging ICT for employment and growth.
- The exercise is part of an initiative to develop inter-operability and sharing expertise between the two nations.
- It is an annual military exercise between the two countries.
- Both the Armies would familiarise themselves with each other’s weapons, equipment, tactics, techniques and procedures of operating in a counter-insurgency environment in mountainous terrain.
- There would be a series of Expert Academic Discussions on various subjects such as Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief, High Altitude Warfare, Jungle Warfare etc.
- Last edition of Exercise Surya Kiran was conducted in Nepal in 2019.
- The challenge aims to bring together the tech firms and Start-ups (based out of India) with the potential to build an indigenous planetariums system software using latest technologies including Augmented Reality (A.R.), Virtual Reality (V.R.) and Merged Reality (M.R.).

- Inspired by the Chandrayaan launches, Indian Space Research Organization conducted the ISRO Quiz competition 2019 in collaboration with MyGov.
- Prime Minister was accompanied by the Quiz winners from across the country to watch Chandrayaan 2 lunar landing live from the ISRO control room.
- It is open to experts from all domains of Planetarium Technology; it includes Start-ups, Indian Legal Entities; and Individuals (or Teams) also.
- The application will be evaluated on different parameters including Approach towards problem-solving, Product Idea, Degree of Innovation, Novelty of Approach.
- The participants will be evaluated by a Grand Jury based on parameters including Innovation, Replicability, Scalability, Usability, and Ease of deployment/roll-out and potential risks involved in implementation of the solution.
- First winner, second winner and third winner under the contest will get the cash prizes of Rs.5 lakh, Rs.3 lakh and Rs.2 lakh respectively.
- In addition to that the winners and participants will get the opportunity to meet peers in the field and get to know the latest advancement in the Ecosystem.
- A high viewership platform will provide them the opportunity to showcase/promote their Innovation.
- The day is celebrated on the birthday of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi.

- The scheme aims at infusing self-sustainability in the Indian pottery sector.
- It is a no-subsidy program.
- It enables potters to get a direct loan from the banks under Pradhan Mantri Shishu Mudra Yojana.
- KVIC is acting as a facilitator for financial aid to potters through RBL bank and also providing training to the artisans.
- No financial burden on the exchequer.
- Beneficiaries can repay the loans in easy installments.
- KVIC set up “Kashi Pottery Cluster” at Village Bhatti in Varanasi under the SFURTI Scheme.
- The cluster has provided direct employment to 340 pottery artisans who have been trained by KVIC.
- The cluster is equipped with modern equipment like furnaces, electric potter wheels, blunger machines, pug mills and other modern equipment for higher production of clay pottery.

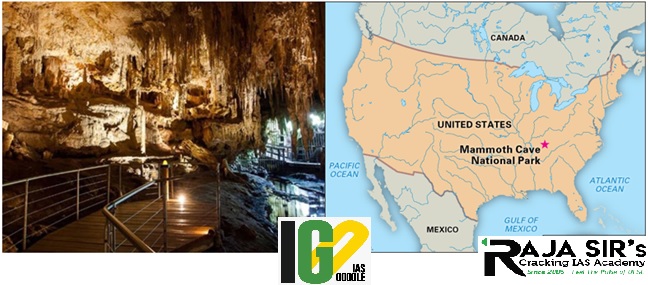
- The additional mileage was mapped and documented by the Cave Research Foundation, Mammoth Cave National Park.
- It brings the total length of the cave system in south-central Kentucky to 676 kilometers.
- It is an American National Park in west-central Kentucky, encompassing portions of Mammoth Cave, the longest cave system in the world.
- It was officially declared as a national park in 1941.
- Became a World Heritage Site in 1981 and an International Biosphere Reserve in 1990.
- The Park preserves the cave system, a part of the Green River Valley, and the rolling hills of south-central Kentucky.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies