- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
27th Oct 2021
GOVERNMENT AMENDS INDIAN TELEGRAPH RIGHT OF WAY RULES, 2021
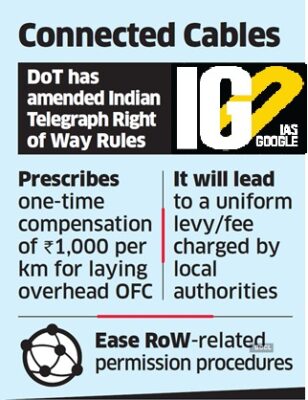 The Central Government has notified the Indian Telegraph Right of Way (Amendment) Rules, 2021 recently.
The Central Government has notified the Indian Telegraph Right of Way (Amendment) Rules, 2021 recently.
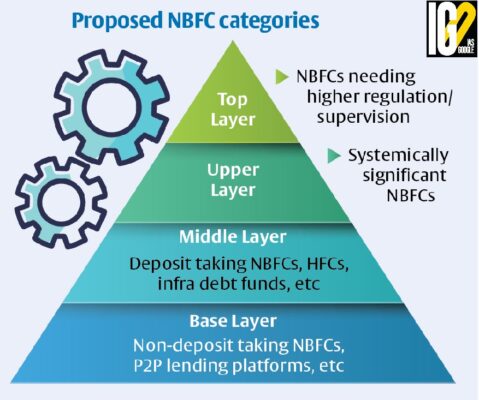 NBFCs will be split into four layers depending on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness, to determine scale-based regulation.
NBFCs will be split into four layers depending on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness, to determine scale-based regulation.




 With an aim to boost liquidity in the corporate bond market, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has suggested further capping the number of ISINs for such bonds issued on a private placement basis.
With an aim to boost liquidity in the corporate bond market, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has suggested further capping the number of ISINs for such bonds issued on a private placement basis.

 The Central Government has notified the Indian Telegraph Right of Way (Amendment) Rules, 2021 recently.
The Central Government has notified the Indian Telegraph Right of Way (Amendment) Rules, 2021 recently.
- It incorporates the provisions related to nominal one-time compensation and uniform procedure for establishment of Overground Telegraph Line in the Indian Telegraph Right of Way Rules, 2016.
- The amount of one-time compensation for establishment of overground telegraph line will be maximum one thousand rupees per kilometre.
- Documentation for RoW application for overground telegraph line has been made simple.
- There will be no fee other than Administrative fee and Restoration charges for establishing, maintaining, working, repairing, transferring or shifting the underground and over ground telegraph infrastructure.
- These amendments will ease Right of Wayrelated permission procedures for establishment and augmentation of Digital Communications Infrastructure across the country.

- With a robust pan India digital infrastructure, the digital divide between rural-urban and rich-poor will be bridged.
- E-governance and financial inclusion will be strengthened; doing business will be easy; information and communication needs of citizens and enterprises will be fulfilled.
- Ultimately, the dream of India’s transition to a digitally empowered economy and society will be translated into reality.

- Banni buffaloes are also known as “Kutchi” or “Kundi”.
- The breeding tract includes the Banni area of Kutch district of Gujarat.
- The breed is maintained by Maldharis, under locally adapted extensive production system in its breeding tract.
- They are trained to graze on Banni grassland during night and brought to the villages in the morning for milking.
- The buffalo is mostly black in color.
- Forehead is elongated and straight with no slope towards horn base.
- The body size ranges from medium to large, and generally covered with hairs.
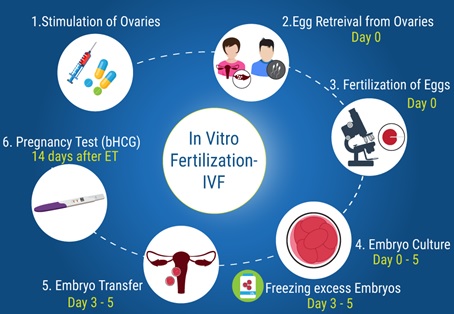
- IVF is a series of procedures used to help with fertility or prevent genetic problems and assist with the conception of a child.
- It is the most effective form of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). IVF may involve eggs, sperm, or embryos from a known or anonymous donor.
- During IVF, mature eggs are collected from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab.
- The fertilized egg (embryo) is transferred to a uterus, one full cycle of IVF takes about three weeks.
- IVF is a treatment for infertility or genetic problems.
- Sometimes, it is offered as a primary treatment for infertility in women over age 40.
- Multiple births
- IVF increases the risk of multiple births if more than one embryo is transferred to uterus.
- Premature delivery
- Use of IVF increases the risk, that the baby will be born early or with a low birth weight.
- Miscarriage
- The rate of miscarriage for women who conceive using IVF is about 15% to 25%. But the rate increases with maternal age.
- Egg-retrieval procedure
- Use of a needle to collect eggs could possibly cause bleeding, infection or damage to the bladder and blood vessel.
- Birth defects
- Age is the primary risk factor in the development of birth defects.
- More research is needed to determine whether babies conceived using IVF might be at increased risk of certain birth defects.
- The new guidelines will be applicable from October 2022.
 NBFCs will be split into four layers depending on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness, to determine scale-based regulation.
NBFCs will be split into four layers depending on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness, to determine scale-based regulation.
- Base Layer
- It includes NBFCs with an asset size below Rs 1,000 crore.
- It will include peer-to-peer lending platforms, account aggregators, NBFCs not accessing public funds nor having any public interface.
- Middle Layer
- It consists of all deposit-taking and non-deposit taking NBFCs with an asset size of Rs 1,000 crore and above, primary dealers, infrastructure debt fund NBFCs, housing and infrastructure finance companies.
- Upper Layer
- It comprises of NBFCs which are identified by the RBI as warranting enhanced regulatory requirement based on a set of parameters and scoring methodology.
- Top Layer
- NBFCs in the upper layer may be moved to the top layer if the potential systemic risk from specific companies rises.
- The top 10 NBFCs will automatically fall into the upper layer.
- NBFCs in the Upper Layer must maintain a minimum common equity tier-1 capital of 9% of risk weighted assets.
- Upper Layer NBFCs will be required to hold differential provisioning towards different classes of standard assets.
- They must follow the exposure framework of the RBI.
- Large exposure of an NBFC to all counterparties and groups of connected counterparties will be considered for exposure ceilings.
- The RBI has prescribed an internal limit for exposure toward other NBFCs.
- NBFCs in the base layer are subject to regulations as currently applicable to non-deposit-taking NBFCs.
- In the middle layer they will follow regulations as applicable for non-deposit-taking systemically important NBFCs.
- NBFCs must move to a 150-day NPA recognition norm by March 31, 2024.
- NPA recognition at 120 days of overdue must be achieved by March 31, 2025.
- NBFCs must follow 90-day NPA recognition cycle by March 31, 2026.
- NBFCs are required to make an internal assessment of the need for capital, commensurate with the risks in their business, like commercial banks.
- They must follow a uniform exposure limit of 25% and 40% of Tier-1 capital for single borrower and group borrowers, respectively.
- 27 States and UTs improved their scores compared to SEEI 2019.
- Out of these, seven States — Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Punjab, Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu — improved by more than 10 points.

- The index categorized States into four based on the score.
- Those with above 60 points are ‘front-runners’, states with 50-60 points are ‘achievers’, 30-49.5 points are ‘contenders’ and less than 30 points would get ‘aspirant’ status.
- The performance has been measured through 68 indicators across six sectors: buildings, industry, municipalities, transport, agriculture and distribution companies (Discoms), and cross sector initiatives.
- Help drive Energy Efficiency (EE) policies at the state and local level.
- Highlight best practices and encourage healthy competition among states.
- Track progress in managing the states’ and India’s energy footprint.
- Set a baseline for EE efforts and provide a foundation to set state specific EE targets.
- Institutionalize data capture and monitoring of EE activities by states.

- The declaration accused China of a litany of human rights violations against the Uighurs, including torture, forced sterilisation and forced disappearances.
- It was signed by the United States, several European and Asian member states and others.
- In answer, China accused the U.S. for “ethnic cleansing” against Native Americans and accused France of committing “crimes against humanity” in its former colonies.
- The Uyghurs are a group of people who live mostly in the Xinjiang area of China.
- There are about 12 million Uyghurs, mostly Muslim, living in Xinjiang, which is officially known as the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR).
- They have been living there for at least several hundred years.
- They are generally regarded as a Turkic people, which means they speak a language related to Turkish and have ancestors who came from the traditional homeland of the Turks - north of central Asia.
- But studies of their genetic make-up suggest that they also have ancestors who came from other parts of the world, with European DNA mixed with Chinese, south Asian, Siberian, and central Asian.
- They see themselves as culturally and ethnically close to Central Asian nations.
- Recent decades have seen a mass migration of Han Chinese (China's ethnic majority) into Xinjiang, allegedly orchestrated by the state to dilute the minority population there.
- Xinjiang lies in the north-west of China and is the country's largest region.
- Xinjiang is a mostly desert region and produces about a fifth of the world's cotton.
- It is autonomous, meaning - in theory - it has some powers of self-governance. But in practice, both regions are subjected to major restrictions by the central government.
- The region is also rich in oil and natural gas and because of its proximity to Central Asia and Europe.
- In the early 20th Century, the Uyghurs briefly declared independence for the region but it was brought under the complete control of China's new Communist government in 1949.
- The small island nations suffer losses to as much as 10% of their GDP due to natural disasters.
- Two-thirds of the countries in the world suffer the highest relative losses due to disasters.
- The highest hazard risks relative to the size of their capital stock.
- Some countries have lost 80% to 90% of their GDPs in single disaster events in the past.

- Launched by: Prime Minister of India at the 2019 UN Climate Action Summit in September 2019.
- Aim:
- To promote disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- To promote research and knowledge sharing in the fields of infrastructure risk management, standards, financing, and recovery mechanisms.
- Secretariat: New Delhi
- Responsibility:
- Its focus is on developing disaster resilience in ecological, social, and economic infrastructure.
- It goals to achieve substantial changes in member country's policy frameworks and future infrastructure investments, along with a major decrease in the economic losses suffered due to disasters.
- Significance:
- It is the second major coalition launched by India outside of the UN.
- It is seen as India's attempts to obtain a global leadership role in climate change matters.
- Members: 22 countries and 7 organisations.
- Main thematic areas that guide CDRI's work: Governance and Policy, Risk Identification and Estimation, Standards and Certification, Capacity building, Innovation & Emerging Technology, Recovery and Reconstruction, Finance and Community based approaches.

- Melioidosis (Whitmore’s disease) is an infectious disease that can infect humans or animals.
- Caused by: Bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei
- This bacterium is commonly found in soil and fresh surface water in South Asia, Southeast Asia, and northern Australia.
- It was originally identified in Burma, in 1911 among morphine addicts.
- It is spread to humans and animals through direct contact with the contaminated water or soil.
- Symptoms: Fever, skin changes, pneumonia, and abscesses, to severe with inflammation of the brain, inflammation of the joints, and low blood pressure that causes death.
- Person-to-person or animal-to-human transmission is extremely rare.
- No vaccination has been found yet.
- It is found especially in males from rural areas.
- Diabetes and alcoholism being the commonest risk factors.
 With an aim to boost liquidity in the corporate bond market, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has suggested further capping the number of ISINs for such bonds issued on a private placement basis.
With an aim to boost liquidity in the corporate bond market, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has suggested further capping the number of ISINs for such bonds issued on a private placement basis.
- Six ISINs maturing per financial year should be allowed for plain vanilla debt securities as compared to 12 at present.
- An International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) is a 12-digit alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies a specific security.
- The organization that allocates ISINs in any particular country is the country's respective National Numbering Agency (NNA).
- It is used for uniquely identifying securities like stocks, bonds warrants and commercial papers. It is a unique number assigned to a security that is universally recognizable.
- ISINs are used for numerous reasons including clearing and settlement. The numbers ensure a consistent format so that holdings of institutional investors can be tracked consistently across markets worldwide.
- IIGF will be conducted jointly by Ministry of Electronics and IT, NIXI and Multistakeholder Group from 8th to 11th of November, 2021.

- The India Internet Government Forum is an initiative associated with the UN Internet Governance Forum (UN-IGF).
- The Internet Governance Forum (IGF) is a multi-stakeholder platform bringing representatives together from various groups to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
- The multi-stakeholder concept is well adopted by IGF (Internet Governance Forum) under UN and by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
- Theme of IIGF 2021: ‘Empower India through Power of Internet’
- The event will witness enlightening discussions on the road to Digitization in India.
- IIGF has been constituted in conformance to IGF-Paragraph 72 of the Tunis Agenda of the UN-based Internet Governance forum (IGF).
- India & Internet- India’s Digital Journey and her Global Role,
- Equity, Access & Quality – High-speed Internet for All and
- Cyber Norms and Ethics in Internet Governance.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies