- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
29th April 2021
NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation)
Recently, the National Telecommunications Institute for Policy Research, Innovation and Training (NTIPRIT) has conducted webinar on "NavIC: Opportunities for the Telecom Industry".
 Recently, several houses and buildings were damaged after an earthquake of magnitude 6.4 on the Richter scale hit Assam.
Recently, several houses and buildings were damaged after an earthquake of magnitude 6.4 on the Richter scale hit Assam.
 Types of Fault
Types of Fault
- It is jointly conducted by NTIPRIT in collaboration with ISRO and Telecom Industry.
- The NRIPRIT has highlighted that there are plans to make NavIC available on L-1 bandin addition to the presently used L-5 band.
- It is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system established and maintained by ISRO.
- It is also known as Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
- It covers India and a region extending up to 1500 km beyond Indian mainland (primary coverage area).
- It provides position accuracy better than 20 m (20) and timing accuracy better than 50 ns (20).
- The actual measurements demonstrate accuracy better than 5 m and 20 nsrespectively.
- NavIC based applications are being used in various civilian sectors, including, transport, map applications, and timekeeping.
- NavIC is an indigenous positioning system that is under Indian control.
- The three satellites are located in suitable orbital slots in the geostationary orbit and the remaining four are located in geosynchronous orbits.
- It is the apex training institute of Department of Telecommunications.
- It was established in the year 2010 as National Telecom Academy.
- It is involved in conduction of induction Training for probationary officers of Indian Telecommunication Service Group A (ITS Group A).
- It conducts various In-Service Trainings, Management Development Programmes, Regional and International Trainings, Capacity Building workshops for Officers of Government of India in various aspects of IT.
- It is 5th generation Air-to-Air Missile (AAM).
- It can be launched from very short to beyond visual ranges with greater kill probability, excellent resistance to countermeasures, irrespective of evasive target maneuvers or deployment of countermeasures.
- The missile comes with a 5G imaging seeker.
- It provides “full sphere launch capability” with lock-on-after-launch and excellent acquisition and targeting capabilities.
- It is manufactured by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems (Israel).
- The trial was aimed to validate enhanced capability of the already integrated Derby Beyond Visual Range (BVR) AAM on Tejas.
- It is the most accurate and reliable AAM of the Israeli Air Force and one of the most sophisticated guided missiles in the world.
- It incorporates the aerodynamic airframe of the Python-4 missile and also retains theinertial navigation system (INS), rocket motor, warhead and proximity fuse of its predecessor.
- It is a dual use missile suitable for air-to-air and surface-to-air missions.
- It integrates a fifth-generation imaging seeker, modern software, advanced infrared counter-countermeasure (IRCCM) and flight control systems.
- It features a new electro-optical infrared seeker with high off-boresight capability.
 Recently, several houses and buildings were damaged after an earthquake of magnitude 6.4 on the Richter scale hit Assam.
Recently, several houses and buildings were damaged after an earthquake of magnitude 6.4 on the Richter scale hit Assam.
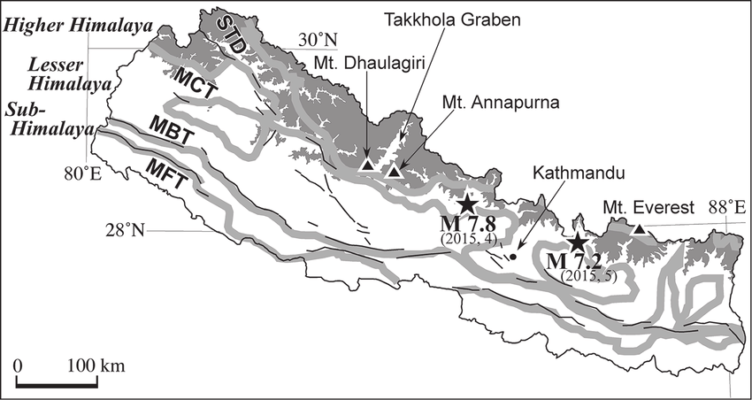
- The preliminary analysis shows that the events are located near to Kopili Fault closer toHimalayan Frontal Thrust (HFT).
- It is also known as the Main Frontal Thrust (MFT).
- It is a geological fault along the boundary of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- It demarcates a sharp physiographic and tectonic boundary between the Himalayan foothills and the Indo-Gangetic Alluvial Plains.
- It represents a discontinuous zone of active faulting between the Sub-Himalaya and the alluvial plain.
- The Kopili is the main river of the Kopili Valley.
- Geologically, Kopili Valley area comprises Neogene-Quaternary sediments which were deposited directly over the Archean basement.
- The Kopili Fault is a 300-km northwest-southeast trending fault from the Bhutan Himalaya to the Burmese arc.
- The Kopili Fault is a NW–SE trending strike-slip fault where intense seismic activity occurs down to a depth of about 50 km beneath the Kopili Fault, and the activity continues to the Main Central Thrust (MCT) in the Bhutan Himalaya.
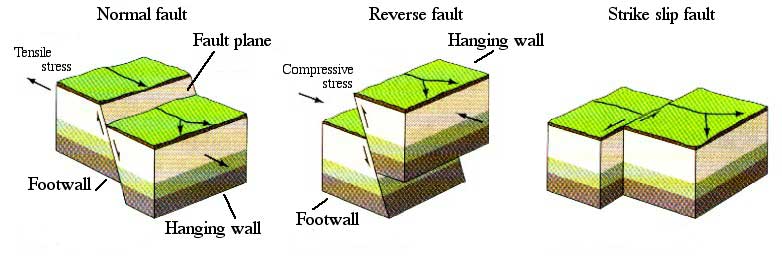
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines a fault as a fracture along which the blocks of crust on either side have moved relative to one another parallel to the fracture.
- According to the USGS, when an earthquake occurs on one of these faults, the rock on one side of the fault slips with respect to the other.
- The fault surface can be vertical, horizontal, or at some angle to the surface of the earth.
 Types of Fault
Types of Fault
- Normal fault: It is a dip-slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below.
- Thrust fault: It is a dip-slip fault in which the upper block, above the fault plane, moves up and over the lower block.
- Strike-slip fault: It is a fault on which the two blocks slide past one another.
- The report has made a forecast of normal to above normal rainfall over most South Asian countries during the upcoming monsoon season.
- The report was prepared and released in consultation with global climate experts and meteorologists from South Asian countries.
- The report states that above normal rainfall is likely along the Himalayan foothills, central and western India.
- It also states that normal rain is expected along most parts of India, including the southern peninsula, north Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Bhutan and Pakistan.
- The report said that below normal rain is likely along southern Tamil Nadu, Jammu and Kashmir, Bihar, West Bengal, Jharkhand, northeast India, Afghanistan and its adjoining areas of Pakistan and south Myanmar.
- The international experts pointed out that the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) neutral conditions would prevail throughout the monsoon season.
- The South Asia could experience above normal minimum temperature whereas the maximum temperature here could range between normal to below normal during the four monsoon months.
- It is a forum of climate experts representing Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan
- It consists of expertise from members of the World Meteorological Organisation, Regional Integrated Multi-Hazard Early warning System, Japan Meteorological Agency and Korea Meteorological Administration.
- It is conducted by South Asian nations and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) since 2010.
- It prepares consensus seasonal climate information on a regional scale that provides a consistent basis for preparing national level outlooks.
- It serves to interface with user sectors to understand and enhance the use of climate information as orchestrated and supported by the Global Framework for Climate Services (GFCS).
- The North East Monsoon influences southern parts of South Asia, including peninsular India, Sri Lanka, Maldives and southern coastal areas of Myanmar.
- The Northern parts of the region including Afghanistan, Pakistan, north India, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh and Myanmar get influenced mainly during by extra-tropical activity dominated by Western disturbances.
- It is an approach that helps a country to ensure that it has diversified its supply risk across a clutch of supplying nations instead of being dependent on just one or a few.
- It is aimed at addressing the impact on economic activity due to disruption in supply chains caused by unanticipated events i.e. natural calamities such as volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, earthquakes or even a pandemic; or manmade, such as an armed conflict in a region.
- It is proposal of Japan as a trilateral approach to trade, with India and Australia as the other two partners.
- It is a direct response to the individual economies and companies who are concerned about the Chinese political behavior and disruption to the supply chain.
- The two-fold objectives of the SCRI are:
- Attract foreign direct investment to turn the Indo-Pacific into an ‘economic powerhouse’; and
- Build a mutually complementary relationship between the partner countries.
- Japan exported $135 billion worth of goods to China in 2019 while imported $169 billion worth from China but the COVID-19 pandemic has led China to shut down its market and disrupted the supply to Japan.
- According to Bloomberg report, the Japan's import from China fell by half in February 2020 when China was battling the peak of the virus impact.
- The growing trade tension between US and China has caused alarm in Japanese trade circles and if the world’s two largest economies do not resolve their differences; it could threaten globalisation as a whole and have a major impact on Japan.
- Japan is the fourth-largest investor in India with cumulative foreign direct investments touching $33.5 billion in the 2000-2020 period accounting for 7.2% of inflows.
- The imports from Japan into India have more than doubled over 12 years to $12.8 billion in FY19 and the exports from India to the world’s third-largest economy stood at $4.9 billion in 2019-20.
- India is home to atleast 1400 Japanese companies which are operating in India which gives a clear picture of long-standing and deepening trade relations.
- India also appears to be an attractive option for potential investors both as a market and as a manufacturing base.
- India and Japan have an Industrial Competitiveness Partnership (Indo-Japan) in existence which co-operates with Japanese businesses to set up their trade in Indian markets.
- It is significant that Japan has taken the initiative to include India and Australia, and potentially other Asian and Pacific Rim nations later, in a strategic dialogue.
- The recent border stand-off between India and China has led Japan to partner India through a dialogue on alternative supply chains and this move will certainly antagonise China.
- India should enhance its self-reliance or works with exporting nations other than China which could help in building resilience into the economy’s supply networks.
- India has been dependent on China on various products such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients for medicines such as paracetamol and an internal push to suddenly cut links with China would be impractical.
- China’s share of imports into India in 2018 (considering the top 20 items supplied by China) stood at 14.5%.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies