- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
30th Aug 2021
"KARMAYOGI" DIGITAL LEARNING FACILITY AT ISTM, DELHI
Recently, the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions has inaugurated the "Karmayogi" Digital Learning Facility.
"Karmayogi" Digital Learning Facility







- It is launched for Civil Servants at the Institute of Secretariat Training & Management (ISTM), a premier Central Training Institution under the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT).
- It will help further extending the citizen centric reforms initiated by the Government under leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi.
- It is meant to upgrade the skills of Central Government officers and personnel.
- It is a new capacity-building scheme for civil servants aimed at upgrading the post-recruitment training mechanism of the officers and employees at all levels.
- It will be delivered by setting up a digital platform called iGOTKarmayogi.
- The iGOT platform will act as a launchpad for the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), which will enable a comprehensive reform of the capacity building apparatus at the individual, institutional and process levels.
- NPCSCB will be governed by the Prime Minister’s Human Resource Council, which will also include state Chief Ministers, Union Cabinet ministers and experts.
- A wholly-owned Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) will be set up under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013 to govern the iGOT-Karmayogi platform.
- The SPV will be a “not-for-profit” company and will own and manage iGOT-Karmayogi platform.
- A sum of Rs 510.86 crore will be spent over a period of 5 years from 2020-21 to 2024-25 in order to cover 46 lakh central employees.
- It will radically improve the Human Resource management practices in the Government.
- It will use scale & state of the art infrastructure to augment the capacity of Civil Servants.
- It aims to prepare Civil Servants for the future by making them more creative, constructive & innovative through transparency and technology.

- The climate crisis is a child rights crisis presents the Children’s Climate Risk Index (CCRI).
- It uses data to generate new global evidence on how many children are currently exposed to climate and environmental hazards, shocks and stresses.
- It is a composite index which brings together geographical data by analyzing the exposure to climate and environmental hazards, shocks and stresses and child vulnerability.
- It helps to understand and measure the likelihood of climate and environmental shocks or stresses leading to the:
- Erosion of development progress; and
- Deepening of deprivation and/or humanitarian situations affecting children or vulnerable households and groups
- It provides the first comprehensive view of children’s exposure and vulnerability to the impacts of climate change to help prioritize action for those most at risk and ultimately ensure today’s children inherit a livable planet.
- India is among four South Asian countries where children are most at risk of the impacts of climate change threatening their health, education, and protection.
- The index has placed India as one of the 33 extremely high-risk countries with flooding and air pollution being the repeated environmental shocks.
- It is estimated that more than 600 million Indians will face ‘acute water shortages’ in the coming years.
- It stated that twenty-one of the world’s 30 cities with the most polluted air in 2020 were in India.

- It stated that, approximately 1 billion children (nearly half of the world’s children) live in extremely high-risk countries.
- It found that:
- 1 billion children are “highly exposed” to exceedingly high levels of air pollution;
- 920 million to water scarcity;
- 820 million to heat waves;
- 815 million to lead pollution;
- 600 million to vector-borne diseases;
- 400 million to tropical storms;
- 330 million to riverine flooding; and
- 240 million to coastal flooding
- The 33 extremely high-risk countries for children such as the Central African Republic, Chad, Nigeria, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau, collectively are responsible for a mere nine percent of global carbon dioxide emissions.
- Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan and India are among four South Asian countries where children are at extremely high risk of the impacts of the climate crisis, with a ranking of 14th, 15th, 25th and 26th respectively.
- India’s neighbours Nepal is ranked 51st and Sri Lanka 61st whereas Bhutan is ranked 111th, with children at relatively lower risk.
- It calls on governments and businesses to protect children from the climate crisis not only by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also by:
- Increasing investments in health and hygiene services, education and clean water;
- Providing children with climate education and green skills;
- Including young people in climate negotiations and decision making; and
- Ensuring a “green, low-carbon and inclusive” COVID-19 recovery
- It stated that investments that reduce exposure to water scarcity can considerably reduce overall climate risk for 120 million children.
- It also provided that investments that reduce exposure to coastal flooding can considerably reduce overall climate risk for 525 million children.
- Improving access to social protection requires working towards universal coverage of child and family benefits as well as ensuring that social protection systems provide connections to other vital services in health, education and nutrition as well as the social welfare workforce.
- Improved education which builds knowledge and skills will contribute to improved sustainability practices and a reduction in emissions at the individual, institutional and communal levels.
- It s a first-of-its-kind toolkit to be indigenously developed and is intended to be a vital tool in learning and understanding the practical aspects of programming using Quantum Computers.
- It is an outcome of the project “Design and Development of Quantum Computer Toolkit (Simulator, Workbench) and Capacity Building”.
- It is being executed collaboratively by IISc Bangalore, IIT Roorkee and C-DAC with the support of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Intuitive UI: QSim offers a robust QC Simulator integrated with a GUI based Workbench allowing students / researchers to create Quantum programs, visualize the instant circuit generation and simulated outputs.
- Simulate noisy Quantum logic circuits: Helps simulate Quantum circuits with and without noise and test how well various algorithms work with imperfect quantum components. This is essential to simulate real-life conditions.
- Pre-loaded Quantum algorithms and Examples: QSim comes loaded with Quantum programs and algorithms providing a head start to the users. E.g. QFT, Deutsch Jozsa, Grovers and so on.
- Integrated with HPC: The quantum simulations are performed on powerful HPC resources allowing multiple users to submit jobs simultaneously with different QuBit configurations.
- PARAM SHAVAK QSim - Standalone system with Quantum Simulator in a box
- PARAM QSim Cloud - Available on cloud using HPC infrastructure PARAM SIDDHI AI (developed and deployed under NSM program)
- It aims to enable Researchers and Students to carryout research in Quantum Computing in a cost effective manner.
- It is one of the first initiatives in the country to address the common challenge of advancing the Quantum Computing research frontiers in India.
- It allows researchers and students to write and debug Quantum Code that is essential for developing Quantum Algorithms.
- It allows researchers to explore Quantum Algorithms under idealized conditions and help prepare experiments to run on actual Quantum Hardware.
- It can serve as an important educational / research tool providing an excellent way to attract students / researchers to the field of Quantum Technology.
- It provides a platform to acquire the skills of ‘programming’ as well as ‘designing’ real Quantum Hardware.
- The seeds of the project were planted during the External Affairs Minister’s visit to Malé in September 2019.
- In August 2020, New Delhi had decided to support the implementation of this project following a request from the Maldives government.

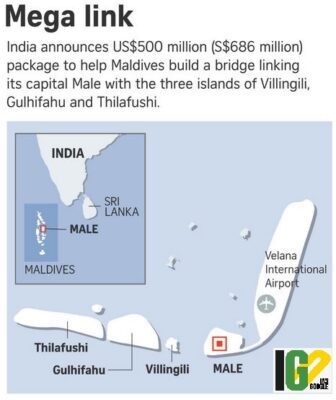
- It is a $500-million infrastructure project between the Maldives government and a Mumbai-based company AFCONS.
- It involves the construction of a 6.74-km-long bridge and causeway link that will connect the Maldives capital Male with the neighbouring islands of Villingli, Gulhifalhu and Thilafushi.
- It is funded by India in a grant of $100 million, with a line of credit of $400 million.
- Male is the most densely populated cities because close to 40% of the entire population of the Maldives lives in Malé, that has an area of approximately 8.30 square kilometers.
- It is very congested and land is a major issue and also there is very little scope for Malé city to expand.
- It prompted the current government in the Maldives to consider decentralisation and the development of other inhabited islands by equipping them with civic facilities like hospitals and other institutions.
- The transportation and connectivity to the capital city would improve and opening up an alternative route for transport, that has been a persistent issue for the country’s people.

- It supports the vision of Prime Minister Modi and President Solih (Maldives) for strong bilateral relations.
- It is a concrete proof that India is a robust development partner of the Maldives in addition to being the First Responder in times of any emergency in the Maldives.
- It is the biggest project India is doing in the Maldives and also the biggest infrastructure project in the Maldives overall.
- The Chinese-made 1.39 km-long Sinamalé Bridge connects Malé with the islands of Hulhulé and Hulhumalé and this project, four times longer, would link the other three islands.
- The Minister was addressing the 11th meeting of BRICS Agriculture Ministers under the theme BRICS Partnership for Strengthening Agro Biodiversity for Food Security and Nutrition.

- It is a global platform for science-led agriculture will help in addressing the issues of world hunger, undernutrition, poverty and inequality
- It is prepared and set up in India for strengthening the cooperation in the field of agricultural research & innovations amongst the BRICS member States.
- The Coordinating Centre of the BRICS-ARP is housed at NASC Complex, Pusa under the governance of Department of Agricultural Research & Education/ICAR.
- The BRICS Nations have also appointed their focal points for BRICS-ARP to interact virtually through the platform and identify the common problems and develop joint projects for finding the solutions.
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research is the focal organization from India.
- It is aimed at promoting sustainable agricultural development through strategic cooperation in agriculture and allied sector.
- It has been operationalized to intensify cooperation in the areas of agricultural research, technology, policy, innovations and capacity building to sustainably increase yields and farmers income in the BRICS member countries.
- The platform shall escalate the exchange of research findings and innovation and best practices for upscaling in the respective BRICS Nations.
- It is a joint training between the armies of India and Kazakhstan.
- The KAZIND-21 will be conducted at a Kazakh training node in Aisha Bibi in Kazakhstan.
- It will provide an opportunity to the Armed Forces of India & Kazakhstan to train for counter-insurgency/counter-terrorism operation in the mountainous, rural scenario under UN mandate.
- It will strengthen mutual confidence, interoperability and enable sharing of best practices between the armed forces of India and Kazakhstan.

- It is a scheme launched by the government of India to provide hassle free access to various financial services in 2014.
- It is a National Mission for Financial Inclusion to ensure access to financial services such as a basic savings & deposit accounts, remittance, credit, insurance, pension in an affordable manner.
- Under the scheme, a basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account can be opened in any bank branch or Business Correspondent (Bank Mitra) outlet, by persons not having any other account.
- One basic savings bank account is opened for unbanked person.
- There is no requirement to maintain any minimum balance in PMJDY accounts.
- Interest is earned on the deposit in PMJDY accounts.
- Rupay Debit card is provided to PMJDY account holder.
- Accident Insurance Cover of Rs.1 lakh (enhanced to Rs. 2 lakh to new PMJDY accounts opened after 28.8.2018) is available with RuPay card issued to the PMJDY account holders.
- An overdraft (OD) facility up to Rs. 10,000 to eligible account holders is available.
- PMJDY accounts are eligible for Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Atal Pension Yojana (APY), Micro Units Development & Refinance Agency Bank (MUDRA) scheme.
- In order for individuals to open a PMJDY account, the below given criteria must be met:
- The person must be citizen of India
- The person should be at least 10 years of age
- The person should not have a bank account
- It is aimed at ensuring access to various financial services to the excluded sections i.e. weaker sections & low income groups.
- It envisages universal access to banking facilities with at least one basic banking account for every household, financial literacy, access to credit, insurance and pension facility.
- It envisages channeling all Government benefits (from Centre / State / Local Body) to the beneficiary’s accounts and pushing the Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT) scheme of the Union Government.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies