- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
7th July 2021
Govt launches mobile app 'Matsya Setu' for Indian aqua farmers
Recently, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying has launched an app called ‘Matsya Setu’.
Matsya Setu
 Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park
 Concerns expressed for Aatmanirbhar Bharat
Concerns expressed for Aatmanirbhar Bharat
 About Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
About Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
- It is Online Course Mobile App.
- It is developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA), Bhubaneswar, with the funding support of the National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB), Hyderabad.
- It aims to disseminate the latest freshwater aquaculture technologies to the aqua farmers of the country.
- It has species-wise/ subject-wise self-learning online course modules, where renowned aquaculture experts explain the basic concepts and practical demonstrations on breeding, seed production and grow-out culture of commercially important fishes.
- It will be helpful for the farmers to learn the advancements in the technologies and Better Management Practices at their convenience.
- It will be an important tool to disseminate the latest information on different schemes among the stakeholders, especially fishers, fish farmers, youth and entrepreneurs across the country, assist them and facilitate ease of doing business.
- It will conduct quizzes/tests for self-assessment in order to motivate the learners and provide a lively learning experience.
- The capacity building of fish farmers is a very vital part of spearheading the Technology-led Aquaculture Development in the country.
- The training for farmers should be provided on various activities including ornamental fisheries, seaweed culture, module on feed preparation, post-harvest value addition.
- The social infrastructure created out of the project sanctioned will be the State of the Art ‘Dental Hospital’ for major dental treatment.
- The Government of India had created the RIDF under NABARD in 1995-96, with an initial corpus of Rs.2000 crore.
- At present, there are 37 eligible activities under RIDF as approved by Government of India which are classified under three broad categories i.e.
- Agriculture and related sector
- Social sector
- Rural connectivity
- It is maintained by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD).
- The main objective of the Fund is to provide loans to State Governments and State-owned corporations to enable them to complete ongoing rural infrastructure projects.
- The scope of RIDF has been widened to include activities such as rural drinking water schemes, soil conservation, rural market yards, rural health centres and primary schools, mini hydel plants, shishu shiksha kendras, anganwadis etc.
- State Governments / Union Territories
- State Owned Corporations / State Govt. Undertakings
- State Govt. Sponsored / Supported Organisations
- Panchayat Raj Institutions/Self Help Groups (SHGs)/ NGOs
- Assist the government in identifying the important projects and in listing them according to their priority;
- Sanction of projects from the priority list, which is done by the sanctioning committee of NABARD;
- Provides the fund support that is needed and also in cost-effective ways;
- Monitors the entire process and evaluates them finally; and
- Associates, along with the Government for timely delivery
- It is previously known by its formal scientific name C.37.
- In June 2021, the World Health Organization has designated the Lambda variant, as the seventh and newest “variant of interest”.
- It has been the dominant variant in Peru and other countries of South America.
- The Lambda variant has not yet been found in the Indian population, but has been detected in the UK and other European countries.
- According to the WHO, the Lambda variant has at least seven significant mutations in the spike protein (the Delta variant has three).
- It could have a range of implications, including the possibility of increased transmissibility or enhanced resistance to antibodies, created either through natural infection or vaccination.
- It had greater infectivity than the Alpha and Gamma variants (known to have originated in the UK and Brazil respectively).
- The study by researchers at the Chile reported decreased effectiveness of the Chinese Sinovac vaccine (Coronavac) against the Lambda variant.
- It implies that the genetic changes involved are predicted or known to affect transmissibility, disease severity, or immune escape.
- It is an acknowledgement of the fact that the variant has caused significant community transmission in multiple countries and population groups.
- There are currently seven variants, including the Lambda that the WHO classifies as “variants of interest”.
- It aims to convey distress about the financial crunch the low-income families have had to deal with amid the lockdowns due to Covid-19.
- The families that are facing hunger or need any other kind of assistance are encouraged to wave a white flag or put a piece of white cloth outside their homes to signal that they need help.
- The idea is that by spotting the white flag, neighbours and good Samaritans can reach them.
- The Bendera Putih app or the Sambal SOS app provides the map of Malaysia where active food banks are marked and helps people easily track down food banks.
- The world over, white flags are used as a symbol of surrender or truce.
- The phrase ‘white flag’ has also found its way into the Cambridge dictionary, which defines it as “a flag that is waved to show that you accept defeat or do not intend to attack”.
- In some Central American countries such as El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras "white flags have appeared all over the social terrain".
- It depicted indictments of a failed political and economic system whose primary effect for common people has been enduring a life of dehumanization, precarity, and marginalization.
- It is project of Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- Its primary objective is to curb digital monopolies.
- Under the project, the onboarding of sellers, vendor discovery, price discovery and product cataloguing could be made open source on the lines of Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- It is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiency in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- The task of implementing DPIIT’s ONDC project has been assigned to the Quality Council of India (QCI).
- It aims at promoting open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols, independent on any specific platform.
- It is a step in the direction of making e-commerce processes open source, thus creating a platform that can be utilised by all online retailers.
- The open source of software and process implies that the code or the steps of that process is made available freely for others to use, redistribute and modify it.
- It would mean that all e-commerce companies will have to operate using the same processes which could give a huge booster shot to smaller online retailers and new entrants.
- It is expected to set standards for onboarding retailers on online market places as well as for the supply and delivery of products through online channels.
- It aims to bring some kind of standards and streamline the country’s e-commerce ecosystem.
- The National Health Authority CEO and former TRAI Chairman RS Sharma and Infosys non-executive chairman Nandan Nilekani are on this council.
- The other members are:
- Quality Control of India Chairman Adil Zainulbhai,
- Avaana Capital Founder Anjali Bansal,
- Digital India Foundation Co-Founder Arvind Gupta,
- National Payments Corporation India CEO Dilip Asbe,
- NSDL e-Governance MD & CEO Suresh Sethi,
- CAIT Secretary General Praveen Khandelwal, and
- Retailers Association of India CEO Kumar Rajagopalan
- It refers to a scenario wherein e-commerce giants or Big Tech companies tend to dominate and flout competition law pertaining to monopoly.
- The giants have built their own proprietary platforms for operations.
- India moved to shake up digital monopolies in the country's $ 1+ trillion retail market by making public a draft of a code of conduct i.e. Draft Ecommerce Policy.
- The three tiger reserves are Ranthambore National Park, Ramgarh Vishdhari Sanctuary and Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve.
- Tigers have always frequented the area demarked for the Ramgarh Vishdhari tiger sanctuary and even now, tigers regularly pass through this area from the direction of Ranthambore.
- It is adjoining the buffer area of the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
- The Ramgarh Vishdhari tiger sanctuary in Bundi district will connect the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in Sawai Madhopur district and with the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Kota district.
- The tiger corridor will be a functional corridor which will help in dealing with the issue of overpopulation of tigers which Ranthambore is facing currently.
 Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park
- It is located about 13.5 kilometers from the city of Sawai Madhopur in Rajasthan.
- It is located at the junction of the Aravali and Vindhya hill ranges.
- It was established initially as Sawai Madhopur Game Sanctuary in 1955 by the Government of India.
- In 1973, it was declared as one of the Project Tiger reserves in India.
- It was in 1980 that Ranthambore was declared a national park, while the forests located beside it were named Sawai Man Singh Sanctuary & Keladevi Sanctuary.
- It is the third tiger reserve of Rajasthan which is also known as Darrah wildlife sanctuary in the past.
- It is located in the southern eastern part of Kota town of Rajasthan.
- It is located on the eastern bank of Chambal River and its tributaries touch this area.
- The Darrah wildlife sanctuary was declared Mukundra Hills National Park in 2004.
- It consists of three wildlife sanctuaries namely Darrah wildlife sanctuary, Chambal wildlife sanctuary and Jaswant Sagar wildlife sanctuary.
- It got the approval of National Tiger Conservation authority NTCA in 2013 and then the Rajasthan gets its third tiger reserve in the form of the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve.
- It is well nestled in the Aravali Hills covering 800 sq km area divided into the grasslands, dry deciduous forests, sheer cliffs and rocky landscape.
- Nearly 90% of the area in the sanctuary is covered with dhok trees accommodating various wildlife species.
- It is home to India's largest population of peafowl, and harbours quail, sand grouse, golden- backed woodpeckers and crested serpent eagles, among other species.
- It was declared a sanctuary in 1955 and attained the status of a National Park in 1979.
- It is home to numerous carnivores including Leopard, Wild Dog, Jungle Cat, Hyena, Jackal, and Tiger.
- The report has been launched when the UK and Indian Governments have not only agreed an Enhanced Trade Partnership but have committed to start FTA negotiations by the end of 2021 with the goal of doubling trade by 2030.
- The report sets out how a comprehensive UK-India FTA should accelerate self-reliance and why international investors' perceptions of Aatmanirbhar Bharat should be wholly positive.
- 77% of UK companies surveyed by the UKIBC stated that Aatmanirbhar Bharat is an opportunity for them to do more business with India.
- The report includes five recommendations that the UKIBC believe would support the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign's success and deliver the objectives of the Enhanced Trade Partnership and FTA.
- They include a sharp focus on innovation and on digital and data sectors, and an assertion that India should remain open to free and fair trade.
- The report also stresses that India's State governments are critical so, in attracting investment, the states and the centre have important roles to play in enacting strategic policy reforms.
- The report highlighted that India is aiming to play a greater role in manufacturing supply chains through its self-reliant campaign.
- Build a Strategy for the Future, Taking a Long-Term View
- It is vital that the Government of India and State Governments adopt policies and approaches designed to win in the future.
- India should Become Increasingly Open to Free and Fair Trade
- India should attract investors due to its strengths rather than by using tariffs as a tool to push international businesses to invest and make in India.
- Focus on Developing and Supporting Innovators
- India should develop an innovator-friendly intellectual property policy and enforcement regime.
- Digital and Data
- India should continue to harness and actively invest in the opportunities that AI, digital technology and data present to achieve its growth potential.
- Put Sustainability at the Heart of India’s Trade and Investment Strategy
- The countries and trade blocs are cognizant of this fact and as such are increasingly integrating sustainability and human rights into their trade agreements and strategies.
- India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat mission should be viewed as an extension of PM Modi’s “Make in India” campaign.
- It was launched in 2014 with the aim of securing manufacturing investments from domestic and international business.
- The self-reliant movement seeks to make India a global supply chain hub by boosting exports and reducing the country’s dependence on imports.
- The Atmanirbhar Bharat campaign is about making India resilient to future supply chain disruptions and reducing its dependence, particularly at times of crisis, on other countries.
- The self-reliant campaign is based on five pillars:
 Concerns expressed for Aatmanirbhar Bharat
Concerns expressed for Aatmanirbhar Bharat
- It has been expressed by domestic and international businesspeople, politicians, and economists that being “self-reliant” could be regarded as protectionist and isolationist.
- It was also pointed out that some of the reforms are in continuation to earlier measures, which would have taken place even without the COVID-19 pandemic.
- It is a membership-based, non-profit organisation founded in 2007 to foster trade and business relations between the United Kingdom and India.
- It supports businesses with the insights, networks, policy advocacy, services, and facilities needed to succeed in the UK and India.
- Its headquarters are located in London (United Kingdom).
- It is a sister organisation to the UK-ASEAN Business Council.
- It is the sole accredited UK Government Overseas Business Network Initiative provider for India.
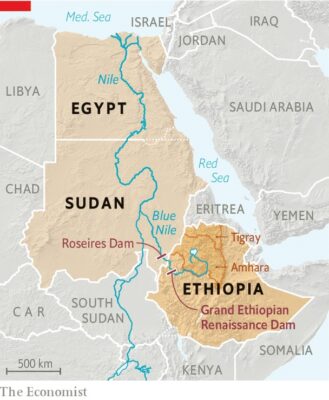
- The Nile, Africa’s longest river, has been at the center of a decade-long complex dispute involving several countries that are dependent on the river’s waters.
- At the forefront of this dispute are Ethiopia and Egypt, with Sudan having found itself dragged into the issue.
- The main waterways of the Nile run through Uganda, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt, and its drainage basin runs through several countries in East Africa, including Ethiopia.
- The construction of the dam was initiated in 2011 on the Blue Nile tributary of the river that runs across one part of Ethiopia.
- The Nile is a necessary water source in the region and Egypt has consistently objected to the dam’s construction, saying it will impact water flow.
- Given the dam’s location on the Blue Nile tributary, it would potentially allow Ethiopia to gain control of the flow of the river’s waters.
- Egypt lies further downstream and is concerned that Ethiopia’s control over the water could result in lower water levels within its own borders.
- Egypt proposed a longer timeline for the project over concerns that the water level of the Nile could dramatically drop as the reservoir fills with water in the initial stages.
- Sudan’s location between Egypt up north and Ethiopia down south has caused it to become an inadvertent party to this dispute.
 About Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
About Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
- It was formerly known as the Millennium Dam and sometimes referred to as Hidase Dam.
- It is a gravity dam which is situated on Blue Nile River in Benishangul-Gumuz region of Ethiopia.
- The reservoir and dam will offer major benefits to Ethiopia, Egypt and Sudan.
- After completion, it will be Africa’s biggest hydroelectric power plant.
- It is a bone of contention between Egypt and Ethiopia.
- It empties into Mediterranean Sea after traveling for over 6,600 kilometers (4,100 miles).
- It flows from south to north through eastern Africa.
- It begins in the rivers that flow into Lake Victoria (located in modern-day Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya).
- In addition to Egypt, the Nile runs through or along the border of 10 other African countries, namely, Burundi, Tanzania, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia and South Sudan.
- Its three main tributaries are the White Nile, the Blue Nile and the Atbara.
- It is a river originating in natural springs above Lake Tana in Ethiopia.
- Along its upper reaches in Ethiopia the river is called the Abbai.
- The Blue Nile joins the White Nile at Khartoum, Sudan, and, as the Nile, flows through Egypt to the Mediterranean Sea at Alexandria.
- Melanistic leopards are commonly called black panthers or black leopards.
- The black color variants of cats like leopards, jaguars and ocelots are known by experts as melanism.
- Melanism is a genetic condition in which an animal overproduces melanin, the dark colour pigment in skin or fur.
- The Black coat coloration is attributed to the expression of recessive alleles in leopards and dominant alleles in jaguars
- They are found in the forests of the Western Ghats and north-east India and are black in colour due to the presence of excess melanin in their bodies.
- The colour of their fur is a mixture of blue, black, grey and purple.
- It is listed as ‘Vulnerable’ under the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- It is protected in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It was notified as 46th tiger reserve of India in 2013 and the 5th tiger reserve of Maharashtra.
- It is situated in Gondia and Bhandara districts of Maharashtra.
- It is comprised of notified area of Nawegaon National Park, Nawegaon Wildlife Sanctuary, Nagzira Wildlife Sanctuary, New Nagzira Wildlife Sanctuary and Koka Wildlife Sanctuary.
- It has connectivity with major tiger reserves in central India like Kanha and Pench Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh and Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra and Indravati Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh.
- The major forest type found in NNTR is Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies