- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
April 24, 2024 Current Affairs
Recently, the Centre has issued few directions to the states with regard to NOTTO (National Organ and Tissue Transplantation Organisation)
Organ Transplant Violations Involving Foreign Nationals:
- Recently, two successive organ transplant cases involving foreign nationals came to the fore in which regulations were violated. In Rajasthan, fake NoCs were allegedly issued to Bangladeshi nationals, and in Delhi, poor Myanmar nationals were allegedly paid to donate kidneys.
- Earlier, after the case involving Myanmar nationals came to light, the Union health secretary had urged the foreign secretary to sensitize the embassies as they are required to issue a certificate to their respective citizens, stating that the donor and recipient are related to each other for undergoing transplant in India.
- The NOTTO registry data shows that there has been an increase in the number of transplants in foreign nationals.
Recently Issued Directions by the Centre:
- ID-Generation: The directions are given to ensure that a NOTTO ID is generated for the donor and recipient for living-donor as well as deceased-donor transplants.
- Mandatory Quick Identification: NOTTO-ID being mandatory for considering allocation of organs in case of deceased-donor transplant, this ID in case of a living-donor transplant shall also be generated at the earliest, maximum within 48 hours after the transplant surgery is done.
- Investigation & Inspection: The Union Health ministry has directed state authorities to investigate cases of commercial trading of organs and take appropriate action for violations, if any.
- State governments to devise a system for regular inspection of all transplant and retrieval centres.
- Combat Arising Commercial Trading Issue: Organs of the deceased donor are anonymously allocated to people waiting for a transplant, while an organ can be donated by a living person only if donor and recipient are close relatives or share a close bond and want to donate altruistically.
- Commercial trading of organs is not allowed under Indian laws.
- In Accordance with Law: To ensure that foreigners come to India to get a transplant by following the laws of the land.
- While it is encouraging to see an increasing number of foreign nationals choosing India as their destination for getting a transplant as India offers world class transplantation at a fraction of the cost as compared to several Western countries. It must be held in accordance with the law.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO):
- It is a national level organisation set up under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It functions as the apex centre for all India activities of coordination and networking for procurement and distribution of organs and tissues and registry of organs and tissues donation and transplantation in the country.
It has following two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network
- National Biomaterial Centre
Mandate:
- To establish a network for organ procurement and distribution.
- To maintain a national registry on organ donation and transplantation.
Amending nuclear law to spur ‘pink’ hydrogen generation.
- India is in talks with large domestic companies to invest in the regulated nuclear sector, including promoting clean power.
- The Atomic Energy Act, 1962, restricts private ownership of nuclear plants. The central government holds the power to produce, develop, use and dispose of ‘atomic energy’. After legislative amendments, such powers can be exercised through any authority/corporation established by the government in which the former holds at least 51 per cent of the paid-up share capital.
- The amended Atomic Energy Act also allows the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) to form joint ventures with other public sector units to secure funding for new projects. This does not extend to private or foreign companies. However, private companies may participate in certain related activities, including supply of components and reactors.
Pink Hydrogen:
- Pink hydrogen is generated through electrolysis powered by nuclear energy.
- It can also be referred to as purple hydrogen or red hydrogen.
- In addition, the very high temperatures from nuclear reactors could be used in other hydrogen productions by producing steam for more efficient electrolysis or fossil gas-based steam methane reforming.
- Nuclear power offers significant advantages for pink hydrogen production, including reducing production costs and emissions, making it a sustainable and more cost-effective alternative to conventional methods.
- Applications: Pink hydrogen is a promising replacement for fossil fuels in the cement industry, steel industry, aviation, and heavy transportation, as it can be used as a feedstock and energy source with no greenhouse gas emissions.
- It is a promising option for carbon-free hydrogen production from renewable and nuclear resources.
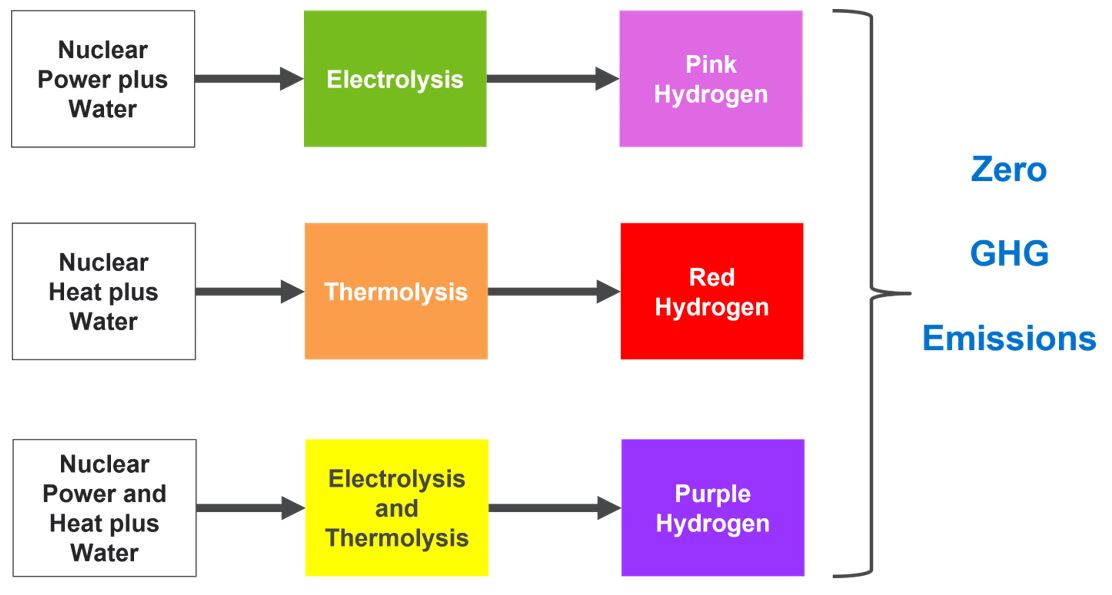
Electrolysis:
- Electrolysis is the process of using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This reaction takes place in a unit called an electrolyzer.
World Meteorological Organization’s (WMO) report -“State of the Climate in Asia 2023”.
- Asia is experiencing a warming trend that is almost twice as fast as the global average compared to the period from 1961 to 1990.
- State of the Climate in Asia
- Published by: World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Objective: To assess and present the current state of climate conditions and trends across Asia.
- Scope: It covers various aspects such as temperature patterns, precipitation levels, extreme weather events, and their impacts on ecosystems, agriculture, and human populations.
- Data Sources: The report relies on data collected from weather stations, satellite observations, climate models, and scientific research conducted by experts in the field.
WMO Report:
Global Climate
- Sea Level: In 2023, the global average sea level continued to rise at a sustained rate (3.43 ± 0.3 mm/year over the period from January 1993 to May 2023).
- However, the rise in sea level is not uniform in all regions.
Climate in Asia
- Most disaster-hit region: Asia was the region most affected by weather, climate, and water-related disasters in 2023.
- Heat wave intensification: The impact of heat waves in Asia worsened in 2023.
- Dominant disasters: Floods and storms were the most common disasters, leading to the highest number of casualties and economic losses.
- Disaster statistics: 79 hydro-meteorological disasters struck Asia in 2023, with floods and storms making up over 80% of these events.
- These disasters resulted in more than 2,000 deaths and affected over 9 million people.
- Climate change impact: The report highlights that climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events.
- Sea surface temperature rise: In 2023, area average Sea-surface temperatures in the northwest Pacific Ocean reached record highs, with a marine heat wave even affecting the Arctic Ocean.
- The upper layer of the ocean (0 m–700 m) is heating up significantly faster in specific areas like the North-Western Arabian Sea, the Philippine Sea, and the seas east of Japan.
- In these regions, the warming is over three times faster than the global average.
- Precipitation: In 2023, many regions experienced below-average rainfall:
- The Turan Lowland (Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan)
- The Hindu Kush (Afghanistan, Pakistan)
- The Himalayas
- Areas around the Ganges and lower course of the Brahmaputra Rivers (India and Bangladesh)
- The Arakan Mountains (Myanmar)
- The lower course of the Mekong River
- Drought in Southwest China: In 2023, southwestern China experienced a drought, with lower-than-usual rainfall throughout the year.
- Temperature anomaly: The annual average near-surface temperature across Asia in 2023 was the second-highest ever recorded.
- It exceeded the 1991-2020 baseline by 0.91 degrees Celsius and the 1961-1990 baseline by 1.87 degrees Celsius.
Severe Heat Waves:
Japan’s Record Summer Heat:
- Japan and Kazakhstan both experienced their hottest years ever in 2023.
- The temperatures reached incredibly high levels all over the country.
China’s High Temperature Events:
- China witnessed 14 extreme heat events during the summer.
- Approximately 70% of the country’s meteorological stations recorded temperatures exceeding 40℃.
- Sixteen stations broke their previous temperature records.
Indian Climate:
- Extreme event: In India, floods were the main reason due to which many people died.
- In the North Indian Ocean basin, Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Mocha made landfall along the Rakhine Coast in Myanmar.
- It caused widespread destruction.
- Severe Heat Waves: Severe heat waves in April and June caused around 110 reported deaths in India due to heatstroke.
- Widespread Heat in South-East Asia: A big and long-lasting heat wave affected many areas of South-East Asia during April and May.
- It reached from Bangladesh and Eastern India to southern China, with extremely high temperatures.
- During this time, record-breaking heat was recorded.
- Sea- level: In 2023, the sea level rise in the Bay of Bengal was the second-highest in the area, exceeding the global average by 30 percent.
- Precipitation: Rains in the summer-monsoon were below average in India.
Srinagar vies for global craft city tag as World Craft Council International team tours craft clusters.
Srinagar Seeks World Craft City Nomination:
- To nominate Srinagar as a World Craft City (WCC) from India this year.
- They checked out clusters where artisans were busy crafting local items.
- These items included Pashmina shawls, carpets, and papier mâché.
- The Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage-Kashmir (INTACH-K) is teaming up with the J&K Handicrafts department.
- They’re working together to map out the craft industry before the official nomination process.
- The city’s official inclusion announcement is expected within the next couple of months.
World Crafts Council International (WCCI):
- It is a non-profit organization dedicated to recognizing and preserving traditional crafts globally.
- It is based in Kuwait.
- The WCC was founded in 1964.
- Objective: The WCCI aims to promote, preserve, and evolve handicrafts globally.
The World Craft City (WCC):
- Establishment Date: 2014
- Organising Institution: The World Crafts Council International (WCCI)
- Country of Establishment: Kuwait
- Objective: It aims to recognize the efforts of local governments, artisans, and communities in enhancing culture, economy, and society.
- WCC wants to create a worldwide network of craft cities.
- It promotes the ideas of the creative economy and protects traditional crafts.
- Legal Status: WCC is registered in Belgium as an international association without lucrative purposes (AISBL).
- This registration status signifies its non-profit nature and international scope of operations.
- It is Affiliated to the UNESCO under Consultative Status
World Crafts Council (WCC) Regions:
- WCC is divided into five regions: Africa, Asia Pacific, Europe, Latin America, and North America.
- These regions help organize and manage WCC activities worldwide.
- Criteria to grant cities WCC Status:
- Cities are granted the prestigious WCC status based on their commitment to craftsmanship, cultural heritage, and sustainable practices.
Parameters:
- How well crafts have been preserved
- Initiatives for artisans
- Adherence to age-old practices.
Kashmir Craft:
- Kashmir’s rich tradition of handicrafts is significantly influenced by Central Asian countries.
- The handicrafts, including shawls and carpets, reflect centuries-old practices.
- Craftsman and Artisan Base:
- Srinagar is home to 20,822 registered craftsmen engaged in various crafts such as papier mâché, walnut wood carving, and hand-knotted carpets.
- These craftsmen contribute approximately 1.76% to the total workforce of the area.
Benefits of selecting Srinagar:
- Srinagar’s centuries-old practices of handicrafts would be highlighted on the global stage.
- The world would come to know about the flawless craft work done by Srinagar’s artisans.
- Handicrafts contribute about 2.64% to Jammu and Kashmir’s economy by 2016-17
- Local artisans from Kashmir would get an opportunity to interact with the best of artisans from across the world.
- Close linkage with other countries: Srinagar being included in the WCC would help in building linkages with those countries that influenced the crafts of Kashmir many centuries ago.
- It would be helpful in strengthening relations between India and other countries.
Bombay High Court in its verdict dismissed a suit challenging Syedna Mufaddal Saifuddin’s position as the 53rd religious leader of Dawoodi Bohra Community.
- Ruling Based on the Petition: In 2014, the 52nd al-Dai al-Mutlaq, Syedna Mohammad Burhanuddin, passed away, and his son, Mufaddal Saifuddin, succeeded him as Syedna. This was challenged by the late Syedna’s (Burhanuddin’s) half-brother, Khuzaima Qutbuddin, in the Bombay HC.
- Judgment pronounced Based on the issue of proof and not faith : High Court Considered the Maintainability of Suit, Can the Objective of Nass be changed with time ?, On the Validity of Nass to Saifudin, Requirement of Nass, is there any adequate evidence with claimants etc
- Therefore By Considering all the Fact HC observed that : Based on the more evidence with current Dai & nass could be changed with time etc. gave its judgment.
Dawoodi Bohra Community:
- The Dawoodi Bohra are a Shia Muslims, sect of followers of Islam who adhere to the Fatimi Ismaili Tayyibi school of thought.
- Their faith is based on the belief in one deity; Allah Taʿala, in the Holy Quran as the word of Allah and in the sacred mission of the Prophets and their successors.
- This sect is known to have originated from Egypt later shifting to Yemen.
- The Dawoodi Bohra Muslims settled in India in the 11th century.
- The seat of the sect was moved to Sidhpur (Patan district of Gujarat), India in the year 1539 from Yemen.
- The Bohra Muslim community considers Surat in Gujarat their base, despite their presence in Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh as well.
- Occupation : They have traditionally been a community of traders and entrepreneurs & qualified professionals in numerous fields.
- Presence around the World : More than 5 lakh members in India and more than 10 lakh members over the 40 countries across the world.
- Power to excommunicate:
- The leader of the community is recognised by the members as having the right to excommunicate its members.
- In practical terms, excommunication means not being allowed to access a mosque belonging to the community or a burial dedicated to the community.
- Among the members of the community who have faced excommunication in the past are those who contested the headship of the leaders.
- Al-Dai-Al-Mutlaq (Spiritual Head):
- Throughout the world they are guided by their spiritual leader known as the Al-Dai-Al-Mutlaq.
- The present leader is the 53rd al-Dai al-Mutlaq, ‘Dr Syedna Mufaddal Saifuddin’
- Their Principal seat in Mumbai.
How is the successor of the Dawoodi Bohra leader picked?
- Through Nass ( Conferment of Succession)
- As per faith and the Dawoodi Bohra doctrine, a successor to the Dai is appointed through “divine inspiration”.
- The “nass”, or conferment of succession, can be conferred upon any deserving member of the community.
- In practice though, the nass is often conferred upon a member of the family of the current Dai.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies