- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Dec 29, 2021
KISAN DIWAS 2021: CELEBRATING THE BIRTHDAY OF CHAUDHARY CHARAN SINGH
23 December is celebrated as the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh Ji is as 'Farmer's Day' all over India.
 Chaudhary Charan Singh (1902 - 1987)
Chaudhary Charan Singh (1902 - 1987)
 History of Tai Khamti/ Tai Khamti Mutiny of 1839
History of Tai Khamti/ Tai Khamti Mutiny of 1839
 What is 5-G Technology?
What is 5-G Technology?


 Reorganization of States:
Timeline:
1947:
Reorganization of States:
Timeline:
1947:

 Features
Features
 Chaudhary Charan Singh (1902 - 1987)
Chaudhary Charan Singh (1902 - 1987)
- Chaudhary Charan Singh served as the 5th Prime Minister of India.
- He was born in 1902 at Noorpur in Meerut district of Uttar Pradesh.
- He shifted to Meerut in 1929 and later joined the Congress.
- He was first elected to the U.P. Legislative Assembly in 1937 from Chhaprauli, and represented the constituency in 1946, 1952, 1962, and 1967.
- He became Parliamentary Secretary in Pandit Govind Ballabh Pant’s Government in 1946.
- Charan Singh's ancestor was a prominent leader of the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
- He followed Mahatma Gandhi in a non-violent struggle for independence from the British Government.
- He opposed Jawaharlal Nehru on his Soviet-style economic reforms.
- As Chief Minister, he was instrumental in bringing about the Land Holding Act 1960.
- The act was aimed at lowering the ceiling on land holdings to make it uniform throughout the State.
- He was the chief architect of land reforms in U.P.
- He took a leading part in formulation and finalisation of the Redemption Bill 1939, which brought great relief to rural debtors.
- He was given the sobriquet ‘Champion of India’s Peasants’ for his work towards the upliftment of farmers and the development of agriculture throughout the country.
- He was the author of several books and pamphlets that includes:
- Abolition of Zamindari
- Co-operative Farming X-rayed
- India’s Poverty and its Solution
- Peasant Proprietorship or Land to the Workers
- Prevention of Division of Holdings Below a Certain Minimum
 History of Tai Khamti/ Tai Khamti Mutiny of 1839
History of Tai Khamti/ Tai Khamti Mutiny of 1839
- The Khamti migrated to Assam in the second half of the 18th century.
- They belong to the Shans (Tai) race, with their original home to the west of China.
- Their first settlement was on the Tengapani river south of Sadiya with the sanction of the ruling Ahom authorities.
- Their chief, Khamti Gohain soon arrogated to himself the title and office in 1794.
- The Khamti were so sturdy and powerful that the Ahoms and the British acknowledged the Khamti Gohain.
- The Khamtis rebelled in 1839 against the British as the Sadiya-khowa Gohain was deprived of his office:
- Tai Khamtis resisted colonization by the British, by suppressing the British garrison at Sadiya.
- Col. Adam White and 80 other soldiers were killed in the resultant conflict.
- The word ‘Khampti’ means ‘a land full of gold’.
- The Tai Khamti people live in areas straddling Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- They inhabit the district of
- They are followers of Theravada Buddhism.
- The community, as a matter of fact, is greatly orthodox and all its socio-cultural activities are religious.
- The Tai-Khamti have their own script for their language, known as 'Lik Tai',which originated from the Shan (Tai) script of Myanmar.
- Their mother tongue is known as Khamti language.
- It is a Tai language, closely related to Thai and Lao.
- The Tai Khampti people are settled agriculturists.
- They use the plough (Thai) drawn by a single animal, either an ox or a buffalo.
- They practice both jhum and settled agriculture and produce food grains, vegetables and cash crops.
- The Khampti have a very rich culture, equipped with magnificent arts and craft.
- Armoury is a part of the life, representing the aura of their skill as warriors.
- Their weapons include poisoned bamboo spikes (panjis), bow and arrows, spear, sword and shields.
- The Khampti also have firearms, resembling ancient flint muskets and horse pistols.
- It marks the celebration of Buddhist festivals such as Khamsang, Sangken, Potwah, Poi Lu kyong, Poi Lu Kyong kammathan etc.
- Sangken is the main festival of the Khamti.
- In Arunachal Pradesh, Khampti dance is also known as ka pung
- The Khamptis are famous for their cockfight dance called Ka-Fi fai.
- Anglo-Abor wars from 1858 to 1911: The Abors or Adis, inhabit central Arunachal Pradesh.
- Wancho-British war in Tirap district’s Ninu in 1875: Wanchos live in the southern part of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The cities are: Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Kolkata, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, and Pune
 What is 5-G Technology?
What is 5-G Technology?
- 5-G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long-term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks.
- It mainly works in 3 bands; low, mid and high frequency spectrum, which have their own uses as well as limitations.
- It has great coverage and high speed of Internet and data exchange.
- The maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- Telcos can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for high-speed Internet.
- The low band spectrum may not be optimal for specialized needs of the industry.
- It offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- This band can be used by industries and specialized factory units for building captive networks that can be molded into the needs of that particular industry.
- It offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
- Internet speed has been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (giga bits per second), while the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps.
- India had planned to start 5G services in 2018.
- Aim: To capitalize on the better network speeds and strength that the technology promised.
- 1980s: 1G delivered analog voice.
- Early 1990s: 2G introduced digital voice (CDMA- Code Division Multiple Access).
- Early 2000: 3G brought mobile data (CDMA-2000).
- 2010: 4G LTE ushered in the era of mobile broadband.
- It is a 210 MW project.
- It will be constructed on the River Sutlej.
- It will lead to the generation of over 750 million units of electricity per year.
- It will be the first hydropower project of Hamirpur district.
- It will be constructed on River Beas.
- The 66 MW project will lead to the generation of over 300 million units of electricity per year.
- Nadaswaram is a South Indian wind instrument, and is said to be one of the loudest non-brass acoustic instruments in the world.
- The nadaswaram is a wind instrument.
- It is also known as Nayana.
- It is made of wood and metal.
- Used in religious ceremonies, this instrument is found in Tamil Nadu.
- It has a unique place in the annals of the history of Carnatic music.
- All double-reed aerophones like nadaswaram, shahanai, mukhveena, nafiri, sundari, etc, have the same mechanism for producing the sound.
- All of them have the same basic structure and technique of playing. The differences among them lie mostly in their sizes and certain minor details.

- It is a form of painting on the inner and outer walls of the sacred spaces.
- It covers the ancient history of India in itself.
- Actually, ‘Kaava’ means red soil. In ancient times, red clay was used in this art.
- During the Portuguese rule in Goa, people who migrated from there introduced the people of other states to this wonderful painting form.
- It is a form of murals found in Konkan region especially in temples of Goa, parts of coastal Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- It can also be seen in old houses, small shrines.
- Only Indian red pigment color is used in this painting.
- Technique: On the wet walls.
- Themes: Kavi artist selects sequences from the Ramayana, the Mahabharata, and the Bhagavata Purana.

- Hydrogen wall is the place where bubbles of solar wind cease to exist.
- Here, the mass of matter is very small but strong enough to not let the solar winds to pass through. It presses the solar winds inward.
- Due to fusion activities at core, the sun keeps throwing out jets of matter and energy in the form of solar winds. They have potential to travel far beyond the orbit of dwarf Pluto.
- NASA’s report is based on data sent by its New Horizons spacecraft.
- New Horizons is an interplanetary space probe that was launched in 2006 by NASA.
- Earlier, the space was believed to be a continuous expanse of an imaginary sheet called ether.
- The Indian National Congress was founded at Bombay in December 1885.
- The early leadership – Dadabhai Naoroji, Pherozeshah Mehta, Badruddin Tyabji, W.C. Bonnerji, Surendranath Banerji, Romesh Chandra Dutt, S. Subramania Iyer, among others – was largely from Bombay and Calcutta.
- A retired British official, O. Hume, also played a part in bringing Indians from the various regions together.
- Formation of Indian National Congress was an effort in the direction of promoting the process of nation building.
- In an effort to reach all regions, it was decided to rotate the Congress session among different parts of the country.
- The President belonged to a region other than where the Congress session was being held.
- First Session: held at Bombay in 1885. President: C. Bannerjee
- Formation of Indian National Congress.
- Second Session: held at Calcutta in 1886. President: Dadabhai Naoroji
- Third Session: held at Madras in 1887. President: Syed Badruddin Tyabji, first Muslim President.
- Fourth Session: held at Allahabad in 1888. President: George Yule, first English President.
- 1896: President: Rahimtullah Sayani
- National Song ‘Vande Mataram’ sung for the first time by Rabindranath Tagore.
- 1899: President: Romesh Chandra Dutt.
- Demand for permanent fixation of Land revenue
- 1901: President: Dinshaw E.Wacha
- First time Gandhiji appeared on the Congress platform
- 1905: President: Gopal Krishan Gokhale
- Formal proclamation of Swadeshi movement against government
- 1906: President: Dadabhai Naoroji
- Adopted four resolutions on: Swaraj (Self Government), Boycott Movement, Swadeshi & National Education
- 1907: President: Rash Bihari Ghosh
- Split in Congress- Moderates & Extremist
- Adjournment of Session
- 1910: President: Sir William Wedderburn
- A Jinnah decried the separate electorate system introduced by act of 1909
- 1911: President: B.N. Dhar
- First time recital of Jan-Gan-Man in Congress session
- 1915: President: Sir S.P. Sinha
- Constitution of the Congress was altered to admit the delegates from the extremist section
- 1916: President: A.C. Majumdar
- Unity between two factions-Moderates and Extremists of Congress
- Lucknow Pact signed between Congress and Muslim League to build political consensus
- 1917: President: Annie Besant, First Woman President of Congress
- 1918 (Special session): President: Syed Hasan Imam
- The session was convened to deliberate the contentious Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms Scheme
- 1919: President: Motilal Nehru
- Congress extended support to Khilafat Movement
- 1920 (Special Session): President: Lala Lajpat Rai
- Mahatma Gandhi moved the Non-cooperation resolution
- 1920: President: C. Vijayaraghavachariar
- Reconstitution of Working committees of Congress on Linguistic basis
- MA Jinnah left the Indian National Congress
- 1922: President: C.R. Das
- CR Das and other leaders broke away from INC
- Formation of Swaraj Party
- 1924: President: M.K. Gandhi
- Only Session presided over by Mahatma Gandhi
- 1925: President: Sarojini Naidu, First Indian Woman President
- 1927: President: Dr. M.A. Ansari
- Passed a resolution against the use of Indian troops in China, Iran and Mesopotamia.
- Passed a resolution against boycott of Simon Commission
- Adoption of resolution on Purna Swaraj
- 1928: President: Motilal Nehru
- Formation of All India Youth Congress
- 1929: President: Jawahar Lal Nehru
- Passed the resolution on ‘Poorna Swaraj.’
- Civil Disobedience movement for complete independence to be launched
- 26 January to be observed as ‘Independence Day’.
- 1931: President: Vallabhbhai Patel
- Resolutions on Fundamental Rights and National Economic Programme
- Endorsement of Gandhi-Irwin pact
- Gandhi nominated to represent INC in the Second Round Table Conference to be held in London
- 1934: President: Rajendra Prasad
- Amendment in the Constitution of Congress
- 1936: President: Jawahar Lal Nehru
- Push towards socialist ideas by Jawahar Lal Nehru
- 1937: President: Jawahar Lal Nehru
- First Session to be held in a village
- 1938: President: Subhas Chandra Bose
- National Planning Committee set up under Jawahar Lal Nehru.
- 1939: President: Rajendra Prasad
- Subhas Chandra Bose was re-elected but had to resign
- Rajendra Prasad was appointed in his place
- Subhash Chandra Bose formed Forward Bloc
- 1940: President: Abul Kalam Azad
- Civil Disobedience movement to be launched at appropriate time and circumstances.
- 1941–45: This Period is marked by events i.e. Quit India movement, RIN Mutiny & INA trials.
- Phase of constitutional negotiations such as Cripps Mission, Wavell Plan and Cabinet Mission.
- On account of these events during this phase no congress session was held.
- 1946: President: J.B Kripalani
- Last session before independence
- B Kriplani was the president of INC at independence.
- President: Bishan Narayan Dar
- National anthem ‘Jana Gana Mana’ was sung for the first on December 27, 1911.
- The national anthem is also titled "the morning song of India".

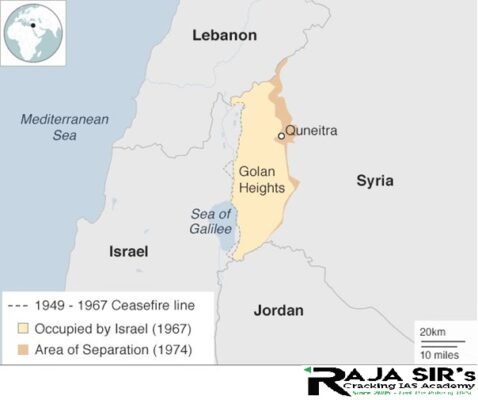
- The Golan Heights refers to the border region captured from Syria by Israel during the Six Day War of 1967.
- It includes the western two-thirds of the geological Golan Heights and the Israeli occupied part of Mount Hermon.
- Internationally recognized as Syrian territory occupied by Israel.
 Reorganization of States:
Timeline:
1947:
Reorganization of States:
Timeline:
1947:
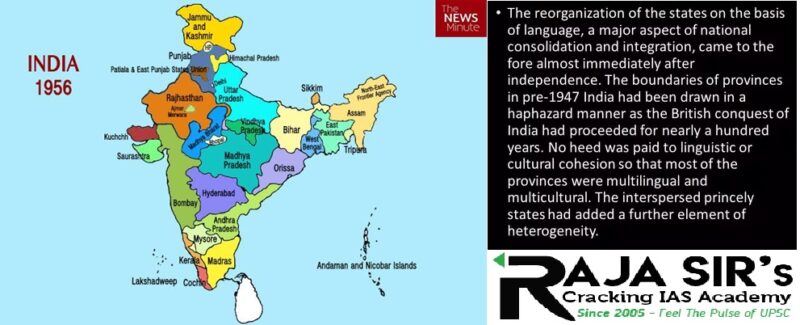
- India consisted of 571 disjointed princely states that were merged together to form 27 states.
- The grouping of states at the time was done on the basis of political and historical considerations rather than on linguistic or cultural divisions
- This was a temporary arrangement.
- The Commission preferred reorganization of states on the basis of administrative convenience including historical and geographical considerations instead of on linguistic lines.
- The JVP Committee comprising Jawaharlal Nehru, Vallabh bhai Patel and Pattabhi Sitaramayya was formed to study the issue.
- The Committee rejected the idea of reorganization of states on a linguistic basis but said that the issue could be looked at afresh in the light of public demand.
- The committee recommended that the whole country be divided into 16 states and three centrally administered areas.
- The government, while not agreeing with the recommendations entirely, divided the country into 14 states and 6 union territories under the State Reorganization Act that was passed in November 1956.
- The state of Haryana got the Punjabi-speaking areas.
- The hilly areas went to Himachal Pradesh.
- Chandigarh, which was made a Union Territory, would serve as the common capital of Punjab and Haryana.
- At the time of Independence, the region of Belagavi (the Belgaum) was part of the Bombay presidency.
- The region was, however, integrated with the state of Mysore (now Karnataka) during reorganisation of states on linguistic lines.
- Pro-Marathi groups claim that Belagavi is a largely Marathi-speaking region with many parts being exclusively Marathi speaking and that the region should be a part of Maharashtra instead of Karnataka.
- They claim that nearly 45 percent of the district is Marathi speaking.
- While pro-Kannada groups argue that the Marathi population is only around 35 per cent which is on par with the Kannada-speaking population of the region.


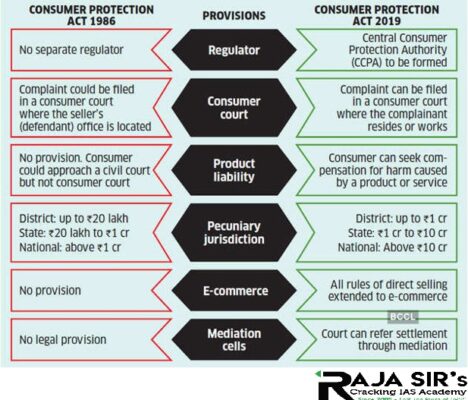
- The rules are complied for both direct selling entities and direct sellers using e-commerce platforms for sale.
- The entities have to ensure that these new rules are compiled by within 90 days.
- Every direct selling entity has to establish a grievance redressal mechanism and display the relevant information on its website.
- The grievance redressal officer must acknowledge the receipt of any consumer complaint within 48 working hours and redresses the complaint within a period of one month from the date of receipt of the complaint.
- In case of delay of more than a month, reasons for the delay and actions taken on the complaint are to be informed in writing.
- The entity shall appoint a nodal officer who will be responsible for ensuring compliance with the provisions of the Act and the rules made there under.
- The entity shall establish a mechanism for filing of complaints by consumers through its offices or branches or direct sellers.
- It shall maintain a record of all its direct sellers, including their identity proof and such other contact information.
- The entities shall, on the request in writing made by a consumer after purchase of any goods or services, provide him with the information regarding any direct seller from whom such consumer has made a purchase.
- It will ensure that advertisements for marketing of goods or services are consistent with the actual characteristics, access and usage conditions.
- No entity shall directly or indirectly, falsely represent itself as a consumer and post reviews about its goods or services.
- The entity which explicitly or implicitly vouches for the authenticity of the goods or services sold, shall bear the liability in any action related to the authenticity of such goods or services.
- A direct selling entity will monitor the practices adopted by its sellers and ensure compliance with these rules by legally binding contract with such sellers.
- State governments will set up a mechanism to monitor or supervise the activities of the entities.
 Features
Features
- The Bill introduces death penalty for certain offences against women and children such as rape.
- Punishment for certain offences such as providing false information and throwing acid has been enhanced.
- Punishment for acid attack causing grievous hurt:
- Under Section 326A, the punishment has been enhanced to a minimum of 15 years which can be extended to the remainder of the natural life of the perpetrator along with fine.
- Under section 326B, voluntarily throwing acid or attempting to throw it, punishment has been enhanced to a minimum of seven years and a maximum of ten years.
- Punishment between 1-3 years and a fine of up to Rs 1 lakh for any person for filing false complaint or providing false information in cases of rape, sexual harassment and acid attacks.
- The Bill proposes a shorter timeline for the investigation, trial, and disposal of appeal of certain offences.
- Investigation to be completed within a month of the FIR which can be extended by another month by the concerned Special Inspector General of Police or Commissioner of Police only for specific reasons given in writing.
- Trial to be conducted on a day-to-day basis and completed within 30 working days from the date of filing of the charge sheet.
- A separate provision under the law for sexual harassment.
- Section 354Ehas been inserted to the IPC for intimidation of women by any mode of communication, in addition to insulting modesty.
- It will be punishable for a maximum of two years and a fine up to Rs one lakh.
- The Bill extends Disclosure of identity provision to other offences committed against women such as sexual harassment, voyeurism, and stalking.
- Laws for social media platforms and mobile data companies:
- Now these companies have to share data sought for the purposes of investigation in cases of rape, sexual harassment, acid attacks and relevant provisions under the POCSO Act within three working days.
- Failing to comply with the rules, there is imprisonment for a maximum of three months and/or a fine of Rs 25 lakh.
- The Bill provides for mandatory death penalty, which has been held to be unconstitutional.
- The Supreme Court has ruled in Mithu vs. State of Punjab that mandatory death penalty for an offence violates Article 14 (right to equality) and Article 21 (right to life) of the Constitution.
- Shorter timeline for investigation and trial may not be sufficient to complete the relevant procedures.
- The Bill proposes that the investigation for offences such as rape, gang rape be completed within 15 working days after an FIR is filed.
- Obligations have been placed on data intermediaries and custodians to share data for investigation, without any safeguards.
- The timeline for investigation of sexual intercourse offences by a husband during separation, or by a person in authority has not been reduced.
- Bill propose to introduce some strict punishment for some offences. However, for all these offences, punishment under the IT Act is more stringent than the punishment envisaged by the Bill.
- The Indian liquor industry is divided into two broad segments: Indian Made Foreign Liquor (IMFL) and country-made liquor.
- IMFL comprises alcoholic beverages that were developed abroad but are being made in India.
- A country made liquor comprises alcoholic beverages made by local breweries.
- Illegal liquor also called hooch.
- Ingredients: Battery acid and methyl alcohol a chemical solvent used as furniture polish.
- India is the second biggest consumer for alcohol in the world after China.
- India consumes more whiskey than any other country in the world
- It is about three times more than the US.
- Nearly one in every two bottles of whiskey brought around the world is now sold in India.
- Indian states are highly dependent on alcohol taxes, which can account for as much as a quarter of their revenues.
- Five southern states Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala account for more than 45%of all liquor sold in India.
- Combination of price controls and awareness campaigns would be most effective in tackling the adverse effects of harmful drinking.
- The governments should reduce dependence on liquor revenues.
- There should be continued monitoring of illicit trade and robust evidence on illicit alcohol trade.
- It is essential to continue building awareness among policy makers of the intersection of alcohol regulation, illicit trade and public welfare.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies