|
Railway Panel Formed After CRS Flags ''Lapses'' in Pamban Bridge Construction
- The Commissioner of Railways Safety has identified serious flaws in the newly constructed vertical lift bridge at Pamban, which was built to replace the old bridge from 1914, which was closed in December 2022.
- It is India’s first vertical lift rail bridge. It is being built parallel to the existing 110-year-old Pamban Bridge at Rameshwaram in Tamil Nadu.
- The old bridge, which has served its lifespan and is facing structural issues like corrosion and damage to its lift spans, has had to impose a permanent speed restriction of 10 km/h.
- It was the sole connection between Mandapam and Rameswaram until a parallel road bridge was built in 1988.
- In recent years, there were intermittent closures for repairs, which prompted the need for a new bridge.
- The new Pamban Rail Bridge is designed to improve both rail traffic and facilitate the movement of ships, as it features a vertical lift span that can be raised to allow larger ships to pass underneath.
- This modern bridge will be 2,070 meters long, with the ability to accommodate future track doubling.
- It will connect Mandapam town in mainland India to Pamban Island and
- The bridge’s construction is expected to enhance the efficiency and safety of rail operations while also facilitating maritime activity, thereby benefiting both the transportation and shipping sectors in the region.
- The project is being executed by Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL), on behalf of Southern Railway.
- The Pamban Bridge is located in a cyclone-prone area with high wind velocitie
Key Points of Concern Raised by CRS:
- Lack of Technical Advisory Group (TAG): A typical procedure for such projects, but it was skipped due to the decision to dissociate RDSO.
- Flouting Railway Board''s Own Guidelines: The Railway Board failed to follow its own guidelines for the project.
- Issues with Fabrication and Testing: Inadequate inspection by the Fabrication Inspection Unit (FIU) led to testing failures and potential safety risks
Ministry of Railways’ Response:
- Defending the Design and Construction: The Ministry of Railways defended the bridge’s design and construction, stating that:
- The design was created by TYPSA, an international consultant, using both European and Indian standards.
- The design was proof-checked by IIT Chennai and further checked by IIT Mumbai to ensure technical reliability.
- The bridge has been constructed with state-of-the-art design and adheres to best construction practices.
- Corrosion Protection: The Ministry emphasized that special polysiloxane paint with a design life of 35 years has been used for corrosion protection in this highly corrosive environment.
CRS Approval and Conditions:
- Despite these concerns, the Commissioner of Railway Safety cleared the bridge for train operations, albeit with certain conditions.
- However, CRS''s report also called attention to substantial lapses in following safety standards throughout the bridge’s construction.
|
|
Scientists, industry demand passage of new Seeds Bill, changes in policy
- During the 13 th National Seed Congress (NSC), experts, scientists, and industry partners came together to highlight the need to revise and modernize the Seeds Bill of 2004 and the Seeds Policy of 2002. They called for these policies to reflect the current challenges and advances in the seed industry, as well as to address farmers'' concerns more effectively.
India’s Seed Industry
- Seed is the most important and vital input for agricultural production.
- In fact, it is the most cost efficient means of increasing agricultural production and productivity.
- Seeds Efficacy of other agricultural inputs in enhancing productivity and production, such as fertilizers, pesticides and irrigation is largely determined by the quality of seed.
- The Indian seed industry’s foundation was established in the 1960s and subsequent policies in the late 1980s, including the New Seed Development Policy (1988-1989), transformed the industry and provided Indian farmers access to superior seed and planting materials.
- In 2022, the Indian seed market was valued at $6.3 billion, projected to reach $12.7 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 12.43 per cent.
- Focus area for the sector: Pest and disease-resistant seeds, drought and heat-tolerant varieties, and more nutritious options to address the challenges of climate change and enhance nutritional value.
Technological Advancement made in Seed Industry:
- Genetic advancement - Seed technology used today combines genetic advancement with applied technologies to provide quality-enhanced seeds with the ability to withstand a range of biotic and abiotic stressors.
- Priming and enhancement technologies- Priming and enhancement technologies are emerging as an essential package of practices to ensure that seeds perform well under a wide range of growing conditions.
- Film coating technology- Film coating technology is applied to organic and inorganic cultivation to improve seed handling, precision planting and use as carriers of pesticides and nutrients.
Issues in the Seed sector
- There are several roadblocks to the growth of India’s seed sector:
- Outdated laws and conflict between Central and State regulations make it difficult to implement policies effectively.
- Poor availability of quality seeds, especially for smallholder farmers, and high dependency on informal seed systems are major challenges.
- Conflicts over proprietary technologies (like genetically modified seeds) and farmers’ rights were also mentioned, as well as disagreements over royalties and technology-sharing agreements between private companies and farmers.
- The sector’s reliance on imported germplasm (genetic material for creating hybrid seeds) is also a concern, as it prevents self-sufficiency.
- There is a lack of investment in seed research and development to develop better varieties suited for local conditions.
- Climate Change: Heatwaves caused a 4.5 per cent decrease in wheat yield across India, with some areas experiencing up to a 15 per cent drop in April 2022 due to an unprecedented rise in temperatures in the month.
- The combination of water scarcity, heatwaves, frequent droughts, and unpredictable monsoons presents a significant challenge to India’s agricultural productivity.
- These challenges underscore the urgent need to prioritise the development of drought-resistant crop varieties.
Suggestions for Reform:
- The government should focus on improving farmer education on the importance of good quality seeds.
- There is need for strengthening seed cooperatives to help empower smallholder farmers and make high-quality seeds more accessible.
- The seed certification system should be made more transparent and in line with global standards to ensure better seed quality.
|
Key Schemes/Acts
- Central Sector Scheme “Development and Strengthening of Infrastructure Facilities for Production and Distribution of Quality Seeds”:
- The restructured Central Sector Scheme “Development and Strengthening of Infrastructure Facilities for Production and Distribution of Quality Seeds” is under implementation from the year 2005-06.
- The objective of the scheme is to develop and strengthen the existing infrastructure for the production and distribution of certified /quality seeds to farmers.
Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmer’s Rights Act, 2001
- It provides for the establishment of an effective system for protection of plant varieties, the rights of farmers and plant breeders and to encourage the development of new varieties of plants.
- The scheme is implemented by Protection of Plant Varieties and farmers’ Rights (PPV&FR) Authority and autonomous statutory body corporate established under PPV & FR Act, 2001 in November, 2005.
|
|
|
Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) released its “Half-Yearly Complaints Report
- The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI) released its “Half-Yearly Complaints Report 2024-25”.
- ASCI is registered as a non-profit organization under Section 25 of the Companies Act 1956.
- It was founded in 1985 as a voluntary self-regulatory organization for the advertising industry to self-regulate advertising practices, to ensure that advertisements follow its Code of Self-Regulation and protect consumers'' interests.
- It monitors advertisements in all media, including print, television, radio, hoardings, SMS, emailers, internet/websites, product packaging, brochures, promotional materials, and point-of-sale materials.
- In 2006, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting mandated that all TV advertisements in India follow to ASCI codes.
Highlights of the Half-Yearly Complaints Report 2024-25
- The real estate sector had the most advertising violations, accounting for 34% of the ads examined by ASCI.
- In 59% of cases, advertisers responded quickly by modifying their ads to include the missing information or withdrawing them completely.
- It reviewed 890 ads promoting illegal betting and forwarded them to the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting for further action.
- It discovered 50 websites and social media pages promoting illegal betting apps and platforms.
- The Home Care sector had the most violations related to green claims, with many products falsely claiming to be eco-friendly without proper supporting documentation.
|
|
BSF celebrates its 60th Raising Day
- The Border Security Force (BSF) celebrated its 60th Raising Day on December 1. Prime Minister Narendra Modi lauded the BSF on its raising day, saying it stands as a critical line of defence, embodying courage, dedication and exceptional service.
- The BSF, with about 2.65-lakh personnel, guards over 6,300 km of Indian fronts with Pakistan and Bangladesh.
Border Security Force
- International borders of India with Pakistan, both east and west, were being manned by the respective state police forces till Indo-Pak war in September 1965.
- Certain inherent shortcomings of this arrangement came to light during the war and it was decided to have one single force under the Union of India for guarding the international borders with Pakistan.
- The Border Security Force was raised in 1965 with 25 battalions. Over the years, the Force has grown in size and has 186 battalions including three NDRF battalions, five major training institutions, 11 subsidiary training centres and three minor training institutions.
- The headquarters of BSF is in New Delhi.
- Its field formations include two Special Directorates General — Spl DG (Eastern Command) and Spl DG (Western Command), 13 Frontiers and 46 sector headquarters, water wing, air wing and other ancillary units.
BSF’s role during peacetime:
- i) To promote a sense of security among the people living in the border areas.
- ii) To prevent trans-border crimes, unauthorised entry into or exit from the territory of India.
- iii) To prevent smuggling and any other illegal activities on the border.
- iv) Anti-infiltration duties.
- v) To collect trans-border intelligence.
Its role during wartime:
- i) Holding ground in assigned sectors.
- ii) Limited aggressive action against paramilitary or irregular forces of the enemy.
- iii) Maintenance of law and order in enemy territory administered under the Army’s control.
- iv) Guarding prisoners of war camps.
- v) Acting as guides to the Army in border areas.
- vi) Assistance in control of refugees.
- vii) Provision of sectors.
- viii) Performing special tasks connected with Intelligence including raids.
|
|
Gaganyaatri’s completed Initial Phase of Training.
· The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully completed the Initial Phase of Training for the Gaganyatris (astronauts) in collaboration with NASA as part of the joint ISRO-NASA mission to the International Space Station (ISS). This marks a significant step toward India''s maiden crewed space mission, the Gaganyaan mission.
· The Gaganyaan mission, meaning ''celestial vehicle'', will send astronauts into Low Earth Orbit (LEO) about 400 km above Earth. The mission will last three days, with the spacecraft returning safely to Earth and landing in the Indian Ocean.
· The primary goal is to demonstrate India’s ability to launch and bring back astronauts safely to Earth.
· Astronauts: The first batch of astronauts (referred to as Gaganyatris) are four Indian Air Force (IAF) pilots: Group Captains Prashanth Balakrishnan Nair, Ajit Krishnan, Angad Pratap, and Wing Commander Subhanshu Shukla.
· Launch Vehicle: The mission will use the Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3), India’s heaviest and most powerful rocket, to carry the crew into space.
· Mission Phases: The mission will include four test flights, including two uncrewed flights and one with a humanoid robot to test systems before the final crewed flight.
· TV-D1 (October 2023): The first test successfully demonstrated the crew escape system in case of a malfunction.
· TV-D2 (2024): The second test will focus on testing orbital modules and re-entry technologies.
Significance of the Gaganyaan Mission:
· Advancing Scientific and Technological Expertise: The mission will provide data on microgravity, radiation, and human physiology, advancing India’s knowledge in these areas, which can have broader scientific and health applications.
· Inspiring the Next Generation: It will inspire young Indians to pursue careers in STEM fields (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), contributing to long-term educational growth and innovation.
· Global Space Cooperation and Prestige: The mission showcases India’s capability to participate in international space projects, including collaborations with the International Space Station (ISS), Artemis Program, and Lunar Gateway. It also raises India’s global prestige as a space-faring nation.
· Social and Economic Impact: The mission is expected to generate economic benefits through job creation and innovations in sectors like education, healthcare, agriculture, disaster management, and environmental protection.
|
India’s Growing Space Power
· The Gaganyaan Mission places India in an elite group of nations—the United States, Russia, and China—that have sent astronauts into space using their own indigenous rockets.
· Success in the Gaganyaan mission would further solidify ISRO’s status after recent triumphs like the Chandrayaan Mission to the Moon and the Aditya L-1 mission to study the Sun.
|
|
|
Global Matchmaking Platform
· The Global Matchmaking Platform (GMP) aims to accelerate the decarbonization of heavy-emitting industries in emerging and developing economies by connecting country-specific needs with global technical and financial assistance.
· Initiated at COP28 in December 2023 under the Climate Club, the GMP focuses on reducing emissions in energy-intensive industrial sectors. It offers tailored support through a network of delivery partners, assisting nations with policy development, technology transfer, and investments to achieve zero and low-emission industrial practices while enhancing emissions goals.
· As a support mechanism of the Climate Club, the GMP''s secretariat is hosted by UNIDO, with additional backing from the interim Climate Club Secretariat, jointly managed by the OECD and IEA. The platform streamlines access to resources and guidance, enabling countries to customize their decarbonization strategies and achieve deep emissions reductions with comprehensive technical and financial support from partner organizations.
Climate Club Work Programme 2025-26
· The Climate Club was launched at COP28 in Dubai last year — It is an initiative that aimed at cooperation between countries in decarbonizing the industrial sector. It is led by Germany and Chile, the Club has garnered support from 38 member countries including Kenya, the European Union, Switzerland, and others. They have each committed to efforts in developing strategies and standards for decarbonisation.
· The Climate Club members’ statement to COP29 underlined the new work programme for 2025-26. The work programme progresses the work on three pillars —
· Pillar 1: Advancing ambitious and transparent climate change mitigation policies
· Pillar 2: Transforming industries
· Pillar 3: Boosting international climate cooperation and partnerships.
|
|
India re-elected to UN Peacebuilding Commission for 2025-2026
· India was re-elected to the UN Peacebuilding Commission for 2025-2026. India’s current term on the Commission was expiring on December 31.
UN Peacebuilding Commission
· The Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) is an intergovernmental advisory body that supports peace efforts in conflict-affected countries and is a key addition to the capacity of the International Community in the broad peace agenda.
· In 2005, the General Assembly and Security Council established the PBC, mandating it to provide political accompaniment and advocacy to conflict-affected countries, with their consent.
· It supports national and regional peacebuilding priorities, at the request of concerned governments.
· The PBC is composed of 31 Member States, elected from the General Assembly, the Security Council, and the Economic and Social Council.
· The top financial contributing countries and the top troop-contributing countries to the United Nations system are also members.
· Since its inception, the Commission has engaged with a total of 31 countries and regions. The Commission’s activities include holding meetings, joint events, giving briefings and providing advice to the main bodies of the United Nations (such as the General Assembly, the Security Council and the Economic and Social Council) and other fora, as well as undertaking field visits and informal interactions with relevant stakeholders.
· The Peacebuilding Commission Support Branch (PBCSB) within the Peacebuilding Support Office (PBSO), Department of Political and Peacebuilding Affairs (DPPA), provides substantive and technical support to the Peacebuilding Commission.
Mandate of PBC:
· To bring together all relevant actors to marshal resources and to advise on and propose integrated strategies for post-conflict peacebuilding and recovery.
· To focus attention on the reconstruction and institution-building efforts necessary for recovery from conflict and to support the development of integrated strategies in order to lay the foundation for sustainable development.
· To provide recommendations and information to improve the coordination of all relevant actors within and outside the United Nations, to develop best practices, to help to ensure predictable financing for early recovery activities and to extend the period of attention given by the international community to post-conflict recovery.
Its functions include:
· • To bring sustained international attention to sustaining peace, and to provide political accompaniment and advocacy to countries affected by conflict, with their consent.
· To promote an integrated, strategic and coherent approach to peacebuilding, noting that security, development and human rights are closely interlinked and mutually reinforcing.
· To serve a bridging role among the principal organs and relevant entities of the United Nations by sharing advice on peacebuilding needs and priorities, in line with the respective competencies and responsibilities of these bodies.
· To serve as a platform to convene all relevant actors within and outside the United Nations, including from Member States, national authorities, United Nations missions and country teams, international, regional and sub-regional organisations, international financial institutions, civil society, women’s groups, youth organisations and, where relevant, the private sector and national human rights institutions, in order to provide recommendations and information to improve their coordination, to develop and share good practices in peacebuilding, including on institution-building, and to ensure predictable financing to peacebuilding.
|
|
INDIAN ARMY AND SINGAPORE ARMED FORCES CONCLUDE JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE “AGNI WARRIOR - 2024
• The 13th edition of joint military exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024) between the Indian Army and Singapore Armed Forces concluded at Field Firing Ranges, Devlali (Maharashtra) on November 30.
• The three-day exercise witnessed participation by the Singapore Armed Forces contingent comprising 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery and the Indian Army contingent comprising 114 personnel from the Regiment of Artillery.
• It is conducted under the ambit of the Army Bilateral Agreement, and highlights the warm and long-standing defence relationship between Singapore and India.
• The Singapore Armed Forces and the Indian Armed Forces share a long history of military cooperation, with regular interaction through exercises, military exchanges, visits, courses and other professional exchanges.
• The aim of XAW-2024 was to maximise mutual understanding of drills and procedures to achieve jointness as a multinational force under the United Nations Charter. The exercise showcased joint firepower planning, execution and use of new generation equipment by the Artillery of both Armies.
• The exercise involved extensive joint preparation, coordination, understanding of each other’s capabilities, procedures and evolution of common interface between Indian and Singapore Artillery procedures.
• It marked the culmination of successful training by Singapore Armed Forces troops exposing them to intricacies of fire power planning.
|
|
NGT on SUO MOTO issues notice to GSI over Varkala cliff
· The National Green Tribunal has sought a reply from the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and others in a matter over the deteriorating conditions of Kerala’s Varkala cliff, a designated national geo-heritage site.
· The NGT was hearing the issue after taking suo motu cognisance of a media report regarding the site facing threats due to environmental violations and administrative oversight.
Key facts about Varkala cliff:
· Varkala Cliff is a stunning natural formation located in Varkala, a coastal town in Thiruvananthapuram district of Kerala.
· It is famous for its high cliffs that overlook the Arabian Sea, offering breathtaking views and a serene atmosphere.
· Varkala is also known for its Papanasam Beach, which is believed to have religious significance.
· The stretch of cliff is lined with several restaurants, cafes, and accommodations, making it a popular spot for both tourists and locals.
· Additionally, the town is home to the Janardhana Swamy Temple, an ancient temple dedicated to Lord Vishnu, adding a spiritual dimension to the destination.
Unique features of the cliff:
· Size and Height: Stretching over 6 kilometers in length and rising to a height of 30 meters, the cliff offers dramatic views of the Arabian Sea, providing a spectacular coastal landscape.
Ancient Formation: The cliff is believed to be 23 million years old, making it an ancient geological feature, adding a layer of historical significance to its beauty.
· Geological Composition: The cliff is primarily made up of laterite on the top, a type of reddish soil rich in iron and aluminum, while its base comprises softer layers of sandstone and clay, which influence the cliff’s appearance and erosion patterns over time.
· National Geological Monument: In recognition of its unique geological characteristics, Varkala Cliff was designated as the 27th National Geological Monument of India by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) in 2014.
|
|
Rai Mona National Park in Kokrajhar
- Personnel of the Assam Forest department and Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) arrested three poachers from the Rai Mona National Park in Kokrajhar.
|
Location
|
- Located along the Indo-Bhutan border in Kokrajhar district, Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR), Assam.
|
|
National Park Status
|
- Declared a national park on June 5, 2021.
|
|
Trans-boundary Links
|
- Shares contiguous forest patches with Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary and Jigme Singye Wangchuck National Park in Bhutan, forming a conservation landscape of over 2,400 sq km.
|
|
Rivers
|
- Sonkosh River (west) and Saralbhanga River (east).
|
|
Vegetation
|
- Features 12 forest types, including very moist sal forests, sub-Himalayan high alluvial semi-evergreen forests, savannah forests, moist-mixed deciduous forests, and khoir-sisoo forests.
|
|
Flora
|
- Rich in orchid species, tropical rainforest vegetation, and riverine grasslands.
|
|
Fauna
|
- Known for the endemic golden langur (mascot of Bodoland), elephants, Bengal tigers, wild bison, white-spotted deer, clouded leopards, and wild buffalo.
|
|
|
SC seeks report on dispute between Tamil Nadu, Karnataka over sharing of Pennaiyar river water
- Bench grants two weeks’ time to the Union, which facilitated the mediation, to produce the Negotiation Committee’s report
- The Supreme Court asked the Union government to place on record the report prepared by a committee negotiating a dispute between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka over the sharing of the Pennaiyar River water
Background of the dispute:
- The State had told the Supreme Court that Karnataka had no right to utilise the waters of the Pennaiyar river to the detriment of the people of Tamil Nadu. The flowing water of an Inter-State River is a national asset and no single State can claim exclusive ownership of its water, Tamil Nadu had argued.
|
SC Deadline
|
A two-week deadline was granted to the Union government to produce the report.
|
|
Tamil Nadu’s Concerns
|
Tamil Nadu approached the Supreme Court in 2018 to oppose Karnataka’s construction of check dams and diversion structures on the Pennaiyar River.
|
|
Argument on National Asset
|
Tamil Nadu argued that the river’s flowing water is a national asset and that Karnataka cannot unilaterally claim its waters to the detriment of Tamil Nadu residents.
|
|
Validity of the 1892 Agreement
|
Tamil Nadu asserted that the 1892 agreement remains valid and binding on both States, emphasizing that it includes the main river, its tributaries, and contributing streams.
|
|
Markandeya River Contention
|
Tamil Nadu contended that the Markandeya River, a major tributary with a catchment area spanning both States, falls under the 1892 agreement''s purview.
Tamil Nadu opposed Karnataka’s construction of diversion structures and large dams on the river.
|
 Pennaiyar River Pennaiyar River
|
Other Names
|
- Dakshina Pinakini (Kannada), Thenpennai, Ponnaiyar, Pennaiyar (Tamil)
|
|
Origin
|
- Eastern slope of the Nandidurg Mountain, Chennakesava Hills, Karnataka
|
|
Course
|
- Flows through Karnataka, enters Tamil Nadu, and empties into the Bay of Bengal
|
|
Basin Distribution
|
- Approximately 77% of the drainage basin lies in Tamil Nadu
|
|
Length
|
- 497 km (second-longest river in Tamil Nadu after the Kaveri River)
|
|
Tributaries
|
- Markandeyanadhi, Kambainallur, Pambar rivers
|
|
Important Cities
|
- Bangalore, Hosur, Tiruvannamalai, Cuddalore
|
What is Inter-State River Water dispute (IRWD):
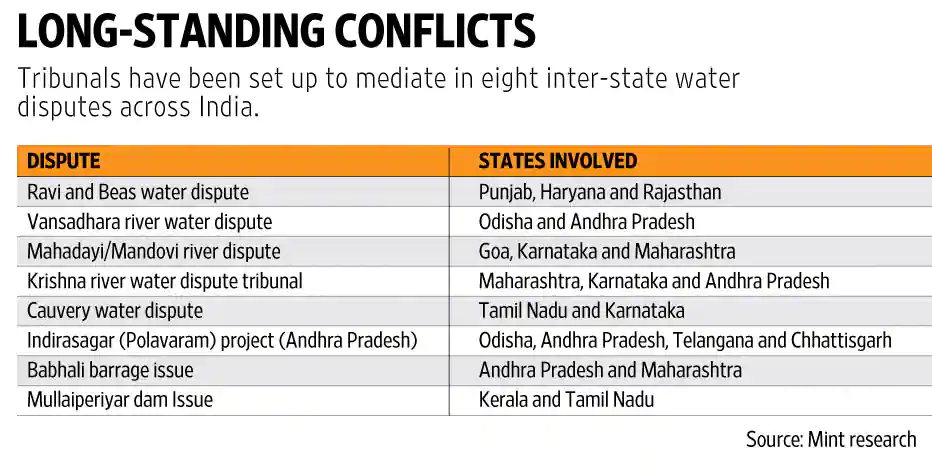
- It is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted under Article 262 of the Constitution of India on the eve of the reorganization of states on the linguistic basis to resolve the water disputes that would arise in the use, control, and distribution of an interstate river or river valley.
- Article 262 of the Indian Constitution provides a role for the union government in adjudicating conflicts surrounding interstate rivers that arise among the state/regional governments. This Act has been amended subsequently, with the most recent amendment in 2002.
- IRWD Act applies only to interstate rivers/river valleys. An action of one state should affect the interests of one or more other states. Then only water dispute is deemed to have arisen under the IRWD Act (section 3). It can be divided into two independent parts for clarity purposes in understanding the techno-legal application of the IRWD Act.
Amendment to the 1956 Act
- The 2002 amendment to the Inter-State Water Disputes Act, of 1956, mandated constituting a tribunal within one year of a request and delivering its award within 3 years (extendable to 5 years in exceptional cases). The award, equivalent to a Supreme Court decree, is final but allows clarifications within three months if not implemented. States can still approach the SC under Article 136, and private individuals may seek recourse under Article 21 for rights violations.
|
The story behind cyclone names
- Cyclonic storm ‘Fengal’ over Bay of Bengal is likely to make a landfall on November 30, close to Puducherry, with wind speed up to 90 kmph, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said.
- The name ‘Fengal’ (pronounced as Feinjal) was proposed by Saudi Arabia and is a word rooted in Arabic.
- Under its influence, heavy to very heavy rainfall at a few places and extremely heavy rainfall at isolated places is expected in north Tamil Nadu and Puducherry. Earlier in the day, the IMD said the deep depression intensified into cyclonic storm.
Naming of tropical cyclones
- Tropical cyclones are named to provide easy communication between forecasters and the public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. Since the storms can often last a week or longer and that more than one can be occurring in the same basin at the same time, names can reduce the confusion about what storm is being described.
- In general, tropical cyclones are named according to the rules at regional level. In the Atlantic and in the Southern hemisphere (Indian ocean and South Pacific), tropical cyclones receive names in alphabetical order, and women and men’s names are alternated.
- In the beginning, storms were named arbitrarily. An Atlantic storm that ripped off the mast of a boat named Antje became known as Antje’s hurricane. Then the mid-1900s saw the start of the practice of using feminine names for storms.
- In the pursuit of a more organised and efficient naming system, meteorologists later decided to identify storms using names from a list arranged alphabetically. Thus, a storm with a name which begins with A, like Anne, would be the first storm to occur in the year. Before the end of the 1900s, forecasters started using male names for those forming in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Since 1953, Atlantic tropical storms have been named from lists originated by the National Hurricane Center. They are now maintained and updated by an international committee of the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO). The original name lists featured only women’s names. In 1979, men’s names were introduced and they alternate with the women’s names. Six lists are used in rotation. Thus, the 2019 list will be used again in 2025.
- Short and easy-to-pronounce names are helpful in rapidly and effectively disseminating detailed storm information between hundreds of scattered stations, coastal bases and ships at sea.
- It is less subject to error than the older and more cumbersome latitude-longitude identification methods.
- There are six Regional Specialised Meteorological Centres (RSMCs) worldwide and five regional Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres, which are mandated for issuing advisories and naming of cyclonic storms.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is one of the RSMCs and is tasked with giving a title to a cyclone that forms over the northern Indian Ocean when they have reached a maximum sustained surface wind speed of 62 kmph or more.
- The IMD provides cyclone and storm surge advisories to 13 countries across the north Indian Ocean.
- For cyclones in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea, a naming system was agreed by countries of a group called World Meteorological Organisation/Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (WMO/ESCAP) and took effect in 2004.
- The eight countries along the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea — Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Thailand — suggested names that were sequentially listed.
The list is arranged according to the names, given by alphabetically-arranged counties, that are neutral to gender, politics, religious beliefs and cultures. It is used sequentially, column wise.
- The designation should not be present in the existing list of the six RSMCs. The name of a storm from the South China Sea that crosses Thailand and emerges into the Bay of Bengal will not be changed
- Once a name is used, it will not be repeated again. The word, which can have a maximum of eight letters, should not be offensive to any member country or hurt the sentiments of any group of population.
- In 2020, a new list was released with 169 names, including 13 names each from 13 countries. Earlier, eight countries had given 64 designations.
|
|
Tourism 2.0: Government Approves ₹3,295 Crore to Develop 40 Lesser-Known Destinations
The Centre has approved interest-free loans worth Rs 3,295 crore to States for the development of tourism sites and infrastructure. As part of this initiative, 40 new projects have been identified across 23 States.
Details of the Scheme:
- This initiative, called Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI), aims to support the comprehensive development of iconic tourist centres in India.
- The scheme offers interest-free loans for a period of 50 years to the States, helping them enhance tourism infrastructure, promote tourism in lesser-known locations, and market these destinations globally.
- The initiative is part of a broader strategy to enhance the tourism sector, promote lesser-known destinations, and boost local economies by improving infrastructure and facilities for tourists.
- The objectives of the scheme include:
- Development of Tourism Infrastructure: The funds will be used for the development of infrastructure such as roads, hotels, transport facilities, and other amenities to make these sites more attractive and accessible to tourists.
- Promotion of Lesser-Known Destinations: The Tourism Ministry is encouraging States to develop new and lesser-known tourism destinations, like Bateshwar in Uttar Pradesh, Ponda in Goa, Gandikota in Andhra Pradesh, and Porbandar in Gujarat, in order to reduce the pressure on already overcrowded popular destinations.
- Sustainable Growth and Employment: By funding these projects, the scheme aims to generate sustainable growth in local economies and create employment opportunities in tourism-related sectors.
- Global Branding and Marketing: The scheme also envisions branding and marketing of these tourist centres at a global scale to attract international visitors, thereby boosting the tourism sector in India.
- Collaboration with Hospitality Chains: The Tourism Ministry is collaborating with global hospitality chains to train Indian youth in the tourism sector. Upon completion of training, they will be absorbed by these hotel chains, improving employment prospects for young Indians in the hospitality industry.
|
India’s Tourism Sector
- India has been ranked 39th among 119 countries in the latest TTDI 2024 report published by the World Economic Forum.
- In 2023, India recorded 9.24 million foreign tourist arrivals (FTAs), a growth of 43.5% compared to 6.44 million in 2022. FTAs contributed Foreign Exchange Earnings (FEEs) of Rs 2.3 lakh crores (Provisional estimates), a growth of around 65% in the same period compared to Rs. 1.39 lakh crores in 2022.
- Over the last few years, India has built extensive tourism infrastructure worth approximately $1 billion (Rs. 7,000 Crores) to improve the tourist experience.
- In 2022-23, 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs were created due to tourism in India, compared to 70.04 million direct and indirect jobs created in 2021-22.
- Initiatives Implemented to Enhance Tourism Promotion
- Swadesh Darshan
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD)
- Assistance to Central Agencies for Tourism Infrastructure Development Scheme
- Dekho Apna Desh initiative
- Vibrant Village Programme
- SWADESH 2.0
- Regional Connectivity Scheme – Udaan
|
A Comprehensive Approach to Development
The SASCI scheme represents a significant investment in India’s tourism sector, focusing on creating long-term economic benefits through sustainable practices. Selected projects include enhancing infrastructure at locations like Matsyagandha Lake in Bihar and developing an underwater museum in Sindhudurg, Maharashtra. The funding will be provided as interest-free loans with a repayment period of 50 years, allowing states to improve their tourism offerings without impacting their debt levels. The Ministry of Tourism has already released 66% of the allocated funds to facilitate immediate project commencement.
Promoting Sustainable Tourism
This initiative is part of a broader strategy to address the challenges faced by India’s tourism industry, particularly overcrowding at popular destinations. By investing in lesser-known locations, the government aims to diversify tourist experiences and promote regional development. Minister noted that this approach not only enhances local economies but also encourages private investment in tourism infrastructure.
|
|
Who are the rebels who have seized control of Aleppo, Syria?
- The civil war in Syria, which had faded from global attention, has escalated once again. Syrian rebel forces launched a major offensive on Aleppo, a key city in northern Syria. This surge in violence threatens to destabilize the region even more.
Why is there crisis in Syria?
- The conflict in Syria dates back to 2011. Many people were unhappy about the high levels of unemployment, widespread corruption and lack of political freedom.
- Inspired by the ‘Arab spring’ uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt, peaceful protests started in March.
- However, the peaceful demonstrations were met by swift government opposition.
- When the government used deadly force to crush the dissent, protests erupted nationwide. The violence rapidly escalated, eventually giving way to a brutal war.
- Now, the crisis is extending into its fourteenth year – with more people than ever sliding into deeper poverty and 16.7 million people in need of humanitarian assistance and protection.
- The Syria situation remains one of the largest displacement crises in the world, with a 2025 projection of 7.2 million internally displaced people(IDPs), and 6.2 million refugees, primarily hosted in the neighbouring countries of Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon and Türkiye.
Importance of Aleppo:
- Aleppo, roughly 350 km north of the capital Damascus, has been a critical battleground in the Syrian civil war. Before the conflict, it was one of Syria''s largest cities, home to 2.3 million people.
- In 2012, rebel forces seized the eastern half of Aleppo, making it a stronghold of the rebellion against President Assad.
- However, the balance shifted in 2016 when Syrian government forces, backed by a brutal Russian aerial campaign, recaptured the city.
- Currently, the roughly 30% of Syria that is not under Assad''s control is governed by a mix of opposition factions and foreign troops.
- The United States has about 900 military personnel stationed in northeastern Syria.
- The siege of Aleppo became symbolic, marked by indiscriminate bombings, starvation tactics, and massive displacement.
Regional Implications:
- The significance of the fighting in Aleppo cannot be understated as it can turn around the power structure in conflict-hit Syria where President Bashar Assad has managed to steer away the opposition forces seeking his ouster for more than a decade.
- The timing of this offensive is crucial as Iran, Hezbollah, and Hamas are already involved in other conflicts, including in Lebanon and Gaza. These ongoing wars are draining their resources.
- Russia, which supports Assad in Syria, is distracted by its war in Ukraine, limiting its ability to provide full support to the Syrian regime.
- This offensive marks a significant shift in the Syrian civil war, with the potential to reignite conflict and further destabilize the region.

|
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES









 Latest News
Latest News Pennaiyar River
Pennaiyar River
 General Studies
General Studies