- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Finding True Peace in Yemen
In April this year, just as the Saudi-led war in Yemen completed eight years, a diplomatic delegation from the kingdom reached Sanaa airport for talks with its Houthi enemies.
Genesis
- Saudi Arabia initiated military operations in Yemen in 2015 to prevent the Houthi rebels, aligned with Iran, from taking control of Yemen.
- The war has resulted in a stalemate, with the Houthis controlling the capital, Sanaa, and the port city of Hodeidah, while the coalition controls the sea and large parts of the south.
- The conflict has led to a severe humanitarian crisis, with a high death toll, displaced population, and widespread food and medical shortages.
Peace Process Initiatives:
- In April 2023, a Saudi delegation held talks with the Houthi rebels, leading to agreements such as a six-month truce, prisoner exchange, and easing of the blockade on Sanaa and Hodeidah.
- The peace process aims to negotiate a two-year transition period to finalize the future state of Yemen.
Challenges to the Peace Process
- Houthi Demands: The Houthis insist on the kingdom paying salaries from Yemen’s oil revenues and seeking compensation for war damage, which Saudi Arabia is reluctant to accept.
- Negotiation Dynamics: The Houthis prefer direct negotiations with the Saudis, while the Saudis want to mediate between Yemeni factions through the Presidential Leadership Council (PLC), supported by Saudi Arabia.
- Houthi Dominance: The Houthis, who have gained the upper hand militarily, have more leverage in the negotiations, potentially undermining the standing and credibility of the PLC.
Key Actors and Dynamics in the Yemen Conflict:
- Houthis: The Houthi rebels, also known as Ansar Allah, are a Zaidi Shia group from northern Yemen. They’ve been in conflict with the Yemeni government since 2004. They took control of the Yemeni capital, Sanaa, in 2014.
- Yemeni Government: The Yemeni government, led by President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, has been in power since 2012. Hadi came to power after President Ali Abdullah Saleh was ousted following protests during the Arab Spring.
- Former President Ali Abdullah Saleh and his loyalists: Saleh ruled Yemen for 33 years until he was ousted in 2012. Initially, Saleh allied with the Houthis against the Hadi government but was killed by Houthi fighters in 2017 after he switched sides.
- Southern Transitional Council (STC): The STC is a secessionist organization seeking independence for South Yemen. While they are technically part of the anti-Houthi coalition, they have occasionally clashed with forces loyal to President Hadi.
- Saudi-led Coalition: In 2015, Saudi Arabia formed a coalition of Arab states to defeat the Houthi rebels and restore the Hadi government. The coalition, which includes countries like the UAE, has been conducting airstrikes in Yemen.
- Iran: Iran is alleged to support the Houthi rebels, though it denies providing military support. The conflict is often seen as part of the broader regional power struggle between Sunni Saudi Arabia and Shia Iran.
- AL-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and ISIS: These extremist groups have taken advantage of the chaos and power vacuum in Yemen to expand their influence.
- The United States and Other Western Nations: The US, UK, and other western nations have been criticized for supplying arms and logistical support to the Saudi-led coalition.
- United Nations: The UN has been trying to mediate the conflict and organize peace talks. It also provides humanitarian aid and works to document human rights abuses.
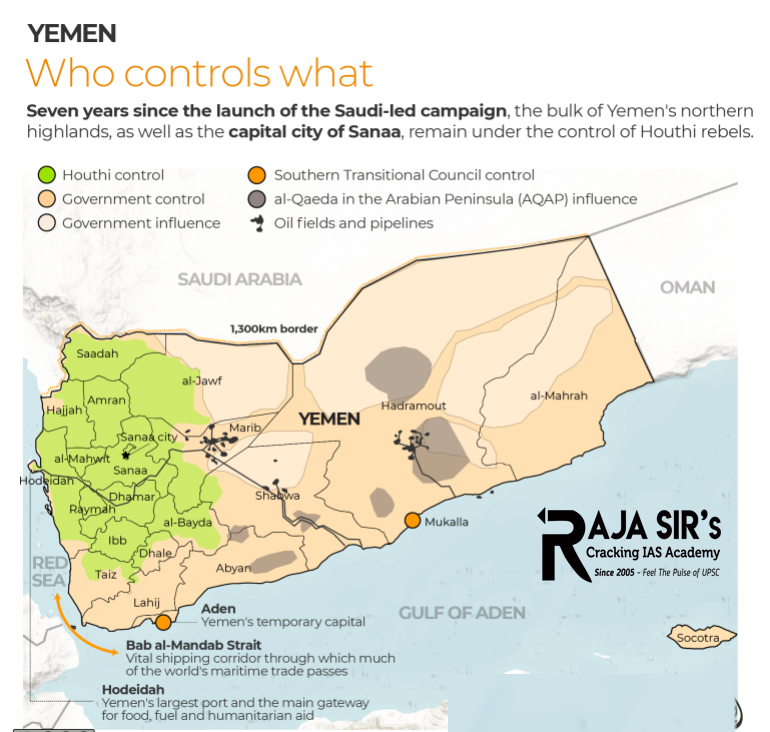
Importance of Yemen:
- Strategic Location: Yemen’s location at the strait linking the Red Sea with the Gulf of Aden is critical for global oil shipments.
- Oil & Energy: Yemen is a major source of crude oil.
- Expats: A huge Indian population is living there contributing significantly to the remittances and exhibiting soft power.
India’s Initiatives:
- Operation Rahat: It was launched by India for a massive air and sea operation to evacuate over 4000 Indian nationals from Yemen in April 2015.
- Humanitarian Assistance: India has contributed her assistance in the form of food providing, medical aid, to facilitate education in various Indian institutions.
Despite a temporary halt in fighting, the complex dynamics and conflicting interests of various Yemeni factions, as well as the involvement of regional powers, suggest that achieving lasting peace and stability in the war-ravaged country will be a challenging and lengthy process.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies