- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
Jan 05, 2023 Current Affairs
Cabinet approves BIND scheme to further modernise Public Service Broadcasting
- It is a Central Sector Scheme which provides financial support for the infrastructure development of Prasar Bharati i.e. All India Radio (AIR) and Doordarshan (DD).
- This scheme will enable the public broadcaster to undertake a major upgradation of its facilities with better infrastructure which will widen its reach, including in the LWE, border and strategic areas and provide high-quality content to the viewers.
- Another major priority area of the scheme is the development of high-quality content for both domestic and international audiences and ensuring the availability of diverse content to the viewers by upgradation of the capacity of the DTH platform to accommodate more channels.
- Purchase of OB vans and digital upgradation of DD and AIR Studios to make them HD-ready will also be done as part of the project.
- The Project for modernization and augmentation of broadcast infrastructure also has the potential to generate indirect employment by way of manufacturing and services related to the supply and installation of broadcast equipment.
- The Scheme will increase coverage of AIR FM transmitters in the country to 66% by geographical area and 80% by population up from 59% and 68% respectively.
- It also envisages free distribution of over 8 lakh DD Free Dish STBs to people living in remote, tribal, LWE and border areas.
Orange alert issued for Delhi over next two days
- In Delhi, the day temperature settled several notches below normal and the minimum temperature plunged to 4.4 degrees Celsius, the season’s lowest and making the national capital colder than Dharamshala, Nainital and Dehradun.
Colour-coded weather warning
- These are issued by the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) for explaining the severity of the weather phenomena which has the potential to cause damage, widespread disruption or danger to life.
- These alerts are also issued during floods, depending on the amount of water rising above land/in a river as a result of torrential rainfall. Warnings are updated daily.
- The IMD uses 4 colour codes:
- Green (All is well): No advisory is issued.
- Yellow (Be Aware): Yellow indicates severely bad weather spanning several days. It also suggests that the weather could change for the worse, disrupting day-to-day activities.
- Orange/Amber (Be prepared): The orange alert is issued as a warning of extremely bad weather with the potential of disruption in commute with road and rail closures, and interruption of power supply.
- Red (Take Action): When extremely bad weather conditions are certainly going to disrupt travel and power and have significant risks to life, the red alert is issued.
India Meteorological Department
- It is the main agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology in India.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica.
- Regional offices are in Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Nagpur, Guwahati and New Delhi.
- It is also one of the six Regional Specialised Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organisation.
- It has the responsibility for forecasting, naming and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Malacca Straits, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
Birders spot 17 newcomers in Silent Valley
- This year’s survey marked the 30th anniversary of the first bird survey in Silent Valley.
- Brown wood owl, Banded Bay cuckoo, Malabar woodshrike, White-throated kingfisher, Indian nightjar, Jungle nightjar, and Large cuckooshrike were among the 17 species newly identified in the Silent Valley.
Silent Valley National Park:
- It is a beautiful representation of the last remaining rainforest of Kerala. The forests of the Silent Valley National Park harbour some of the most pristine, unique and highly productive forests in the world.
- Silent Valley is located in the Southwestern corner of Nilgiris.
- A perennial river named Kunthipuzha is passing through the western side of the park, from north to south direction finally merging into Bharathapuzha.
- **Fauna:**Silent Valley Park is known for many highly endangered species such as lion-tailed macaque, tiger, gaur, leopard, wild boar, panther, Indian Civet and Sambhar.
- The indigenous tribal groups that live within park boundaries include Irulas, Kurumbas, Mudugas and Kattunaikkars.
An organism that eats viruses has been discovered. What is a ‘virovore’?
- The organisms which eat viruses are called virovore.
- It has been identified as an actual species of protist that feasts on viruses.
- These virus-eating species of protists which are their kingdom on the tree of life and are not an animal, plants, or fungi are now classified as Virovores.
- It is a species of Halteria; microscopic ciliates that populate freshwater worldwide.
- The microbe Halteria is a common genus of protists known to flit about as its hair-like cilia propel it through the water.
- They''re made up of nucleic acids, nitrogen, and phosphorus. It can eat huge numbers of infectious chloroviruses that share their aquatic habitat.
- These organisms can sustain themselves with viruses, consuming many and growing in size.
- The new findings may change our understanding of the role viruses play in the food chain at a microscopic level.
Cabinet approves National Green Hydrogen Mission
- The initial outlay for the Mission will be Rs.19,744 crore, including an outlay of Rs.17,490 crore for the SIGHT programme, Rs.1,466 crore for pilot projects, Rs.400 crore for R&D, and Rs. 388 crores towards other Mission components.
- Aim: To make India a Global Hub for the production, utilization and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy will formulate the scheme guidelines for implementation of the respective components.
Components
- The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition Programme (SIGHT): Under this two distinct financial incentive mechanisms will be provided
- Targeting domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and
- Production of Green Hydrogen
- The Mission will also support pilot projects in emerging end-use sectors and production pathways.
- Regions capable of supporting large-scale production and/or utilization of Hydrogen will be identified and developed as Green Hydrogen Hubs.
- A public-private partnership framework for R&D (Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership – SHIP) will be facilitated under the Mission.
- A coordinated skill development programme will also be undertaken under the Mission.
Green hydrogen
- It is the gas produced by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrolyzer that may be powered by electricity generated from renewable energy sources.
Centre approves Rs 2614 crore for 382 MW Sunni Dam Hydro Project in Himachal Pradesh
- It is a Run of River project.
- It was being executed on the Sutlej in Shimla and Mandi districts and it would have a 71-metre-high concrete gravity dam and six generating units in its surface power house.
- The project will generate 1,382 million units annually.
- On commissioning, 13 per cent of the electricity generated will be provided free of cost to government of Himachal Pradesh, including 1 per cent for Local Area Development Fund. For the project life cycle of 40 years, this free power translates into benefits of Rs 2,803 crore.
- The objective behind generating hydroelectric power resources is to produce as much energy as possible, with minimum cost and fewer negative impacts on the environment.
- The Projects are being envisioned to fulfil a steady increase in peak electricity demand and the growing energy deficit in the Northern Region.
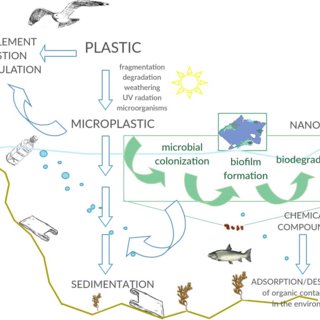
Novel water filter quickly removes 99.9 per cent of microplastics
- Microplastics are tiny bits of various types of plastic found in the environment.
- The name is used to differentiate them from “macroplastics” such as bottles and bags made of plastic.There is no universal agreement on the size that fits this bill — the U.S. NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) and the European Chemical Agency define microplastic as less than 5mm in length.
Types of microplastics
- There are two categories of microplastics: primary and secondary.
- Primary microplastics are tiny particles designed for commercial use, such as cosmetics, as well as microfibers shed from clothing and other textiles, such as fishing nets.
- Secondary microplastics are particles that result from the breakdown of larger plastic items, such as water bottles.
- This breakdown is caused by exposure to environmental factors, mainly the sun’s radiation and ocean waves.
How termite behaviour is linked to a warming world?
- It has found that termites decompose wood at a much higher rate in warmer conditions.
- For every 10 degrees Celsius increase in temperature, their decomposition activity goes up by almost seven times.
- According to the study, termites release carbon from dead wood in the form of carbon dioxide and methane, two of the most important greenhouse gases. So, an increase in termite population and their faster decomposing activity can cause more greenhouse emissions, resulting in a hotter planet.
- There are around 3,000 species of termites across the world, including the ones that consume plant material and even soil. However, the most famous are the wood-eating termites.
- Another research by scientists at the University of Florida found that two Floridian varieties of termites were able to interbreed during warmer winters and hybridise into new “highly destructive super-termites”.
Members of high-powered committee on Ladakh say MHA order is vague, avoids mention of Sixth Schedule
High-power Ladakh committee:
- The committee will discuss measures to:
- protect the region’s unique culture and language taking into consideration its geographical location and strategic importance;
- ensure protection of land and employment for the people of Ladakh;
- strategise inclusive development and discuss issues related to the empowerment of the Ladakh Autonomous Hill District Councils of Leh and Kargil.
- Why was the committee formed?
- After the unique status of the formerly-existing State of Jammu and Kashmir under Article 370 of the Constitution was read down by Parliament on August 5, 2019, civil society organisations in Ladakh have been calling for the protection of land, resources, and jobs for the previous three years.
- What is the sixth schedule?
- The sixth schedule under Article 244 of the Constitution protects the autonomy of tribal populations through creation of autonomous development councils which can frame laws on land, public health and agriculture.
- As of now ten autonomous councils exist in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- As per the 2011 Census, the total population of Ladakh was 2,74,289, and nearly 80% of them are tribals.
Meet on SYL remains inconclusive as Punjab, Haryana CMs stick to their stands
- The Sutlej Yamuna Link Canal (SYL), is an under-construction canal to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers.
- The decades-old dispute over the canal, which is supposed to carry water from Punjab to Haryana, has its origin in a disagreement over sharing of Ravi-Beas water.
- The river Beas joins river Sutlej in Punjab.
- The dispute regarding sharing of river water emerged after Punjab was reorganised in 1966, and the state of Haryana was created (out of Punjab).
- After this, Punjab refused to share waters of Ravi and Beas with Haryana.
Dispute on water sharing:
- Before the reorganisation in 1955, out of 15.85 million acre feet (MAF) water of Ravi and Beas, the Centre had allocated 8 MAF to Rajasthan, 7.20 MAF to undivided Punjab, 0.65MAF to Jammu and Kashmir.
- In March 1976, when Punjab Reorganisation Act was implemented, the Centre notified fresh allocations, providing 3.5 MAF To Haryana.
- Later, in 1981, the water flowing down Beas and Ravi was revised and estimated to be at 17.17 MAF. Out of this, 4.22 MAF was allocated to Punjab, 3.5 MAF to Haryana, and 8.6 MAF to Rajasthan.
- To enable Haryana to use its share of the waters of the Sutlej river and its tributary, Beas, a canal linking the Sutlej with the Western Yamuna Canal, was planned. The 212-km canal (SYL) was supposed to carry Haryana’s share of water to its southern parts.
- 122 km of the canal was to pass through Punjab and the remaining 90 km was to pass through Haryana. Haryana has completed its side of the canal, however, Punjab has continued to delay the construction for over three decades.
- In 2002 and 2004, the Supreme Court ordered the completion of the canal in Punjab.
- In 2004, the Punjab assembly passed a law, which declared all inter-state agreements related to the sharing of Ravi and Beas waters, as invalid.
- However, in 2016 the Supreme Court invalidated (cancelled) this law.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies