- Home
- Prelims
- Mains
- Current Affairs
- Study Materials
- Test Series
 EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
EDITORIALS & ARTICLES
May 10, 2024 Current Affairs
A new biocontrol agent to manage ‘foot rot’ disease in Basmati crop: Why this matters?
- Recently , The Punjab Agricultural University (PAU), Ludhiana, has developed biocontrol agent “Trichoderma Asperellum” to combat ‘foot rot’ disease in Basmati Varieties of Rice.
Foot Rot Disease:
- It is also known as Bakanae disease.
- Causative Agent: ‘Fusarium verticillioides’
- It is a soil-seed borne pathogen which spreads the infection through the root of the plant, and eventually leads to the colonization of the stem base.
- It affects Basmati rice crops particularly at the seedling stage, though it might also cause infection after transplantation in case infected seedlings are transplanted.
- Symptoms : Infected seedlings first turn pale yellow, then elongate and dry up, and eventually (usually) die.
Preventive Management Strategies to Control Foot Rot Disease:
- To prevent the disease from occurring and spreading, farmers resort to
- Early seedling treatment,
- Try to use disease-free seeds, and
- Destroy infected seedlings.
Timely seed nursery management :
- Seed sowing in the first fortnight of June, and transplantation in July.
- Sowing in May often leads to problems as the month’s high temperatures are favourable to the disease.
- Well Drained Fields : Fields where the nursery is being set up must also be well-drained, with proper irrigation, to avoid the spread of foot rot.
Current Practices :
- Seedlings are treated with ‘Trichoderma harzianum’ before sowing and transplantation.
- Seeds are also treated with fungicides such as Sprint 75 WS (carbendazim + mancozeb) before sowing.
- But these are the chemical treatments which are harmful for the soil, and can be toxic for consumers of the rice.
Importance of New Biocontrol Agent ‘Trichoderma Asperellum’:
- It is an important development in rice farming techniques, bringing in a more sustainable strategy that will offer a non-chemical alternative to traditional pesticides.
- This transition ensures safer rice production, aligning with global standards for food safety.
- It will help in aiding in disease management while minimizing environmental harm.
Basmati Rice:
- Basmati rice is a long-grain aromatic rice known for its extra-long slender grains, fluffy texture, delightful taste, superior aroma, and distinct flavor.
- Varieties of Basmati Rice: Around 34 varieties recognized under the Seeds Act, 1966.
- Cultivation Areas: Only Permitted to cultivate in J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttarakhand, and western Uttar Pradesh.
- It is a registered GI (geographical indication) product.
- Largest Producer & Export Leader: India is the top exporter, around 70% of global production.
India Contributes $5,00,000 to UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund
- India contributed $500,000 to the UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund (CTTF), underscoring its unwavering commitment to support multilateral efforts in the global fight against terrorism.
- Terrorism: UN defines terrorism as “Criminal acts intended or calculated to provoke a state of terror in the general public, whatever the considerations of a political, philosophical, ideological, racial, ethnic, religious or any other nature that may be invoked to justify them”
- India Contributes $500000 to UN Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund
- India’s Contribution to Fund: With its current contribution, India’s cumulative financial support to the trust fund now stands at $2.55 million.
- India announced its contribution to the trust fund during the special meeting of the counter-terrorism committee held in New Delhi in October 2022 under India’s presidency.
- Significance of Fund: India’s contribution would support global programmes of United Nations Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) — Countering Financing of Terrorism (CFT) and Countering Terrorist Travel Programme (CTTP).
- They are aimed at building capacities of the member states of eastern and southern Africa to combat the critical issues of financing of terrorism and prevent the movement and travel of terrorists.
Counter-Terrorism Committee:
- Background: In the aftermath of the 11 September attacks against the United States in 2001, the Security Council established a dedicated Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC) of the Council.
- Members: It consists of all 15 members of the Security Council, to monitor the implementation of the provisions of resolution 1373 (2001) and other resolutions.
- Mandate: It focuses on the following areas:
- Counter-terrorism strategies
- Countering the financing of terrorism
- Border security and arms trafficking
- Law enforcement
- Legal issues
- Human rights
- Integrating gender into counter-terrorism
- Countering violent extremism and terrorist narratives
- Information and communications technologies
- United Nations Countering Terrorist Travel Programme (CTTP): It is a global initiative of the United Nations Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT) which assists beneficiary Member States in building their capabilities to detect and counter-terrorists and serious crimes.
- Countering Financing of Terrorism (CFT): Under this, UNOCT-UNCCT assists Member States in a sequential, coordinated and results-oriented manner on a variety of CFT topics.
UN Security Council:
- UN Organ: The UN Security Council is one of the six main organs of the United Nations. It was established by the UN Charter in 1945.
- The other 5 organs of the United Nations are—the General Assembly (UNGA), the Trusteeship Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat.
- Headquarter: NewYork
- Primary Responsibility: Maintaining international peace and security.
- Council Composition:
- Membership: Consists of 15 Members (5 permanent, 10 non-permanent).
- Five permanent members: China, France, the Russian Federation, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Non-permanent member: Elected for two-year terms by the General Assembly.
- Veto: A “No” vote from one of the five permanent members blocks the passage of the resolution.
- Presidency: The Security Council has a rotating Presidency, changing every month. (alphabetical Order).
Recently, The Delhi High Court emphasized the need of teaching minors about the concept of “virtual touch” alongside traditional notions of “good touch” and “bad touch.”
- Objective: in today’s virtual world, this step will help them identify potential risks in cyberspace.
Virtual Touch:
- Virtual touch technology creates a way to interact with digital content using hand movements like touching, even though it’s not real touch.
Applications:
- Virtual reality: VR technology builds simulated environments using computers.
- It allows users to be fully immersed in a 3D experience
- Augmented Reality (AR): This technology lets you see and interact with virtual stuff that appears to be right there in your surroundings, making the real world more interactive.
- Gaming: Virtual Touch takes gaming to a new level. Players can control characters, objects, and menus with simple gestures, making gameplay smoother and more intuitive.
- Smartphones and Tablets: The touchscreens you use on your phone or tablet rely on virtual touch.
- Haptic Technology: This technology increases interaction with Digital products through simulation of senses by using forces, motions, and vibrations.
- It increases immersion in virtual reality or remote control applications.
- For example: Touching a virtual button on a scream makes us feel like clicking or a buzzing.
- It helps people to navigate, type, and interact with apps using simple touches on the screen.
- Haptic technology: This technology is sometimes called kinaesthetic communication or 3D touch.
- It creates a sense of touch for users by using forces, vibrations, or motions.
Technologies:
- Gesture Recognition: Gesture recognition is a computer skill that uses math algorithms to understand and respond to human gestures.
- Electrostatics: In some touchscreens, electromagnetic phenomena is used to detect the proximity of fingers without making direct contact.
Challenges:
- Fidelity Challenges: The replication touch in virtual experiences, like in video games or virtual reality, it’s hard to make it feel just like real touch.
- Things like texture, temperature, and how hard or soft something feels are tough to copy accurately.
- This can make virtual stuff feel fake and not as engaging.
Hardware Limitations:
- Existing haptic technology relies on bulky devices or gloves.
- These devices can hinder movement and user comfort.
- To encourage more people to use this technology, there is need
- More advanced interfaces.
- User-friendly designs.
- Equipment that is easier to use and more comfortable.
- Accuracy and Latency Concerns: There is a need of Precise hand tracking and real-time response for seamless virtual touch experience.
- Delays or jittery movements can disrupt the sense of immersion and lead to frustration.
- Privacy and Security Issues: Virtual touch technology may collect and analyze hand movement data, posing privacy risks.
- Therefore, there is a need to establish clear guidelines and provide users with control over data collection are crucial for addressing privacy and security concerns.
Components of “Virtual Touch” Education:
- Teaching appropriate online behavior.
- Recognizing warning signs of predatory behavior.
- Understanding privacy settings and online boundaries.
Significance of “Virtual Touch Education”:
- “Education on Virtual Touch’ holds significance as it provides users, particularly minors, with essential knowledge and abilities to safely and responsibly maneuver through the expanding digital realm. Here’s why it’s crucial:”
Ensuring Safe Online Navigation:
- Virtual touch education provides users, especially minors, with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate the digital landscape securely and responsibly.
- Users learn about setting online boundaries and appropriate behavior, helping them identify warning signs and steer clear of potentially risky online situations.
Safeguarding Privacy:
- Understanding the implications of virtual touch technology on data collection empowers users to make informed decisions regarding their privacy settings and the use of their personal information.
- Users gain insight into how their data may be collected and utilized, enabling them to protect their privacy effectively.
Preventing Cyberbullying:
Recognizing inappropriate virtual touch interactions enables users to shield themselves from cyberbullying and online harassment.
By understanding what constitutes inappropriate behavior, users can take proactive measures to safeguard their well-being and maintain a positive online experience.
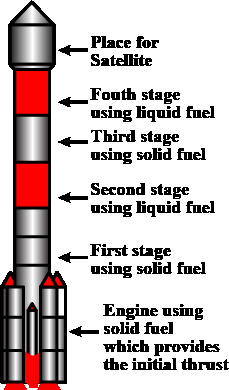
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved yet another milestone in design and manufacturing by successfully conducting a long duration test of the PS4 engine of the PSLV stage.
PS4 engine:
- It is the uppermost stage of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), comprising two Earth storable liquid engines.
- It uses a bipropellant combination of nitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer and monomethyl hydrazine as the fuel, developed by Isro''s Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
- The same engine is also used in the Reaction Control System (RCS) of the first stage (PS1) of PSLV.
- ISRO redesigned the conventionally manufactured PS4 engine to make it compatible with additive manufacturing techniques and this innovative approach, known as Design for Additive Manufacturing, has yielded remarkable advantages.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
- It is also known as 3D printing which is an emerging technology that is rapidly transforming manufacturing processes worldwide.
- It creates 3-dimensional objects by successively layering materials under computer control.
- It involves layering materials like plastics, composites, or bio-materials to create objects that range in shape, size, rigidity, and colour.
- Compared to traditional subtractive techniques, 3D printing offers immense design flexibility, reduced waste, and the ability to produce complex geometries.









 Latest News
Latest News General Studies
General Studies